視線驅動的云臺跟蹤技術
王建中 王洪楓 劉弘揚 張晟


摘 ?要: 人在回路的遙操作是未來相當長時期內無人武器云臺的主要操控方式。針對無人武器云臺手動遙操作控制方法存在的負擔重、效率低等問題,提出一種視線驅動跟蹤方法,通過檢測眼球運動來追蹤人眼視線,捕獲操控人員對特定目標的注視信息,建立操控人員眼動與無人武器云臺目標跟蹤的隨動關系,實現“看哪打哪”。給出了眼動檢測、視線估計、無人武器云臺運動映射模型及隨動跟蹤瞄準等的實現方法和流程,并進行了相關試驗驗證。結果表明,該方法可使無人武器云臺的目標跟蹤瞄準操控擺脫對肢體的需求,用視線操作代替傳統的手動操作,可有效減輕手動操控負擔,提高操控及時性、準確性和人機交互效率,將成為無人武器的重要操控方式。
關鍵詞: 無人武器; 云臺跟蹤; 視線驅動; 眼動檢測; 隨動跟蹤; 實驗驗證
中圖分類號: TN820.4?34; TP23 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼: A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文章編號: 1004?373X(2020)24?0166?04
Sight driven pan?tilt tracking technology
WANG Jianzhong, WANG Hongfeng, LIU Hongyang, ZHANG Sheng
(School of Mechatronical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China)
Abstract: The teleoperation of man in the loop is the main operation mode of unmanned weapon platform for a long time in the future. In allusion to the problems of heavy burden and low efficiency existing in the manual remote operation control method of unmanned weapon cradle head, a sight driven pan?tilt tacking method is proposed. In this method, the sight of the human eyes is tracked by detecting the eye movement to capture the information of the operator′s gaze at a specific target, and the follow?up relationship between the operator′s eye movement and the target tracking of the unmanned weapon is established, so as to realize the “hit where you see it”. The realization methods and processes such as eye movement detection, gaze estimation, motion mapping model of unmanned weapon pan?tilt, and follow?up tracking and sighting are given, and the relevant experimental verification are carried out. The results show that the method can make the target tracking and sighting of the unmanned weapon platform get rid of the remand of body, and replace traditional manual operation with sight operation, which can effectively reduce the burden of manual control, improve the timeliness and accuracy of the operation and the efficiency of the human?computer interaction. It will be an important means of control for unmanned weapons.
Keywords: unmanned weapon; pan?tilt tracking; sight driven; eye movement detection; follow?up tracking; experimental verification
0 ?引 ?言
人機分離而形成的無人武器是未來武器裝備發展的重要方向,目標跟蹤瞄準是其關鍵技術之一。由于相關技術發展階段的限制,實現目標跟蹤瞄準的無人武器云臺的操控在未來相當長時期內仍將是人在回路的遙操作模式。戰場環境和敵方目標復雜多變且十分危險,無人武器操控人員承受巨大的心理和生理壓力,導致武器云臺手動遙操作控制方法操控負擔重、效率低,目標跟蹤瞄準的及時性和準確性大打折扣[1]。
本文提出一種穿戴式人機融合的視線驅動跟蹤方法,將頭戴顯示及眼動追蹤裝置、操控人員和無人武器云臺緊密耦合,通過檢測眼球運動來追蹤人眼視線,捕獲無人武器操控人員對頭戴顯示場景中敵方目標的注視信息,建立操控人員眼動與無人武器云臺目標跟蹤瞄準的隨動關系,在此基礎上控制無人武器云臺追隨操控人員的視線進行目標搜索、跟蹤及瞄準,實現“看哪打哪”[2?4]。該方法可使無人武器云臺的目標跟蹤瞄準操控擺脫對肢體的需求,用視線操作代替傳統的手動操作,可有效減輕手動操控負擔,提高操控及時性、準確性和人機交互效率,將成為無人武器的重要操控方式。該技術在社會安防和監控等領域也有重要的應用價值。
[βe=γx2-arctanlscreen-2xssin γxlscreen1+cos γx+2xs1-cos γx] ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?(12)
同理可得注視點與無人武器云臺俯仰角關系:
[?e=γy2-arctanwscreen-2yssin γywscreen1+cos γy+2ys1-cos γy] ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? (13)
式中:[γy]為武器瞄準攝像機俯仰方向視場角;[ys]為注視點在俯仰方向上的坐標;[wscreen]為武器瞄準攝像機圖像在顯示屏俯仰方向實際顯示所占用的像素長度。
3 ?無人武器云臺隨動跟蹤試驗
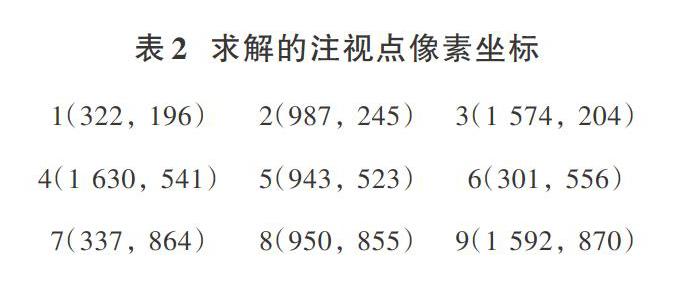
在頭戴顯示中設定圖5所示9個黑色十字目標點,眼睛攝像機采集依次注視目標點時的實時眼部圖像,檢測定位出對應的9個瞳孔中心,如表1和圖6所示,由式(3)求解出對應的9個注視點,如圖5藍色十字和表2所示。
無人武器云臺的隨動跟蹤瞄準由方位和俯仰運動實現,按照式(12)、式(13)獲得無人武器云臺隨注視點的跟蹤瞄準如圖5中的紅色十字和圖7所示。
視線操控無人武器云臺跟蹤瞄準人員目標的試驗場景如圖8所示,云臺上的激光筆投射在人員目標身上的紅點驗證了良好的跟蹤瞄準效果。
4 ?結 ?語
本文提出一種視線驅動的云臺跟蹤操控方法,給出瞳孔中心檢測與定位、視線估計、無人武器云臺方位和俯仰運動與注視點和瞳孔中心的映射模型以及無人武器云臺隨動跟蹤等實現方法和流程,建立操控人員眼動與無人武器云臺目標跟蹤的隨動映射控制關系,并進行設定目標點和實際人員目標的視線操控跟蹤瞄準試驗驗證。結果表明,該方法用視線操作代替傳統的手動操作,可有效減輕手動操控負擔,提高操控及時性、準確性和人機交互效率,對無人武器裝備的發展具有重要意義,在安防監控等領域也有重要的應用價值。
參考文獻
[1] CHASE M S, GUNNESS K A, MORRIS L J, et al. Emerging Trends in China's Development of Unmanned Systems [R]. Santa Monica: RAND Cooperation, 2015: 5?14.
[2] 張達磊.基于視線跟蹤的人機交互系統設計[D].杭州:浙江工業大學,2016.
[3] 馬衛華.人機交互系統的實時人眼跟蹤技術研究[J].現代電子技術,2019,42(13):65?68.
[4] BISWAS Langdon. Multimodal intelligent eye?gaze tracking system [J]. International journal of human?computer interaction, 2015, 31(4): 277?294.
[5] WANG Jianzhong, ZHANG Guangyue, SHI Jiadong, et al. 2D gaze estimation based on pupil?glint vector using an artificial neural network [J]. Applied sciences, 2016, 6(6): 174.
[6] 胡艷紅,魏江.紅外圖像中瞳孔定位算法[J].電子設計工程,2019,27(1):189?193.
[7] 張慧敏,羅珮允,隋建峰.基于圖像處理的瞳孔大小檢測算法研究[J].半導體光電,2017,38(1):136?141.
[8] 顧可可,付威威,董月芳,等.基于改進輪廓跟蹤的瞳孔快速檢測[J].紅外技術,2017,39(6):574?578.
[9] WANG Jianzhong, ZHANG Guangyue, SHI Jiadong. Pupil and glint detection using wearable camera sensor and near?infrared led array [J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(12): 30126?30141.
[10] 王建中,張廣月,王虹.人眼檢測的混合加權特征方法[J].北京理工大學學報,2019,39(8):819?824.
[11] CHENG Hong, LIU Yaqi, FU Wenhao, et al. Gazing point dependent eye gaze estimation [J]. Pattern recognition, 2017, 71: 36?44.
作者簡介:王建中(1963—),男,湖北人,博士,教授,研究方向為智能無人技術。
王洪楓(1994—),男,山東人,博士研究生,研究方向為智能無人技術。
劉弘揚(1994—),男,黑龍江人,碩士研究生,研究方向為智能無人技術。
張 ?晟(1995—),男,吉林人,碩士研究生,研究方向為智能無人技術。

