High-order rational solutions and resonance solutions for a(3+1)-dimensional Kudryashov–Sinelshchikov equation*
Yun-Fei Yue(岳云飛), Jin Lin(林機(jī)), and Yong Chen(陳勇),,3,?
1School of Mathematical Sciences,Shanghai Key Laboratory of PMMP,Shanghai Key Laboratory of Trustworthy Computing,East China Normal University,Shanghai 200062,China
2Department of Physics,Zhejiang Normal University,Jinhua 321004,China
3College of Mathematics and Systems Science,Shandong University of Science and Technology,Qingdao 266590,China
Keywords: rational solution,N-wave resonance solution,Hirota bilinear method,Kudryashov–Sinelshchikov equation
1. Introduction
It is well known that the research on wave propagation is one of the important problems in bubble liquid. The dynamics of pressure waves in the gas–liquid mixtures are characterized by the Burgers–Korteweg–de Vries(BKdV)equation and the Korteweg–de Vries(KdV)equation.[1]The(3+1)-dimensional Kudryashov–Sinelshchikov (KS) equation with the effects of liquid viscosity and heat transfer on the phase interface is
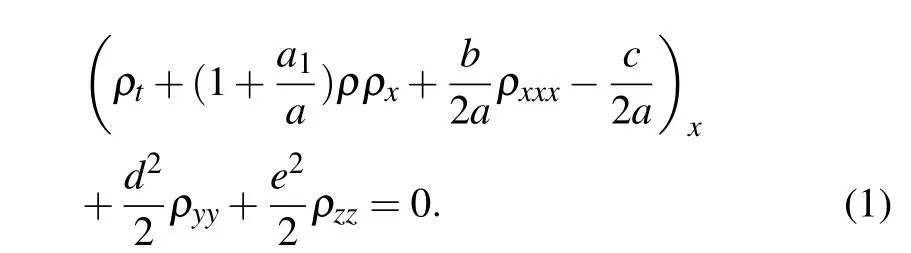
Here the long waves propagate along the x axis and allow for horizontal development in the y and z directions. The solution ρ=ρ(t,x,y,z)represents the density in the bubble–liquid mixture, the parameters a, a1, b, and c are constants relying on the radius of bubbles and the pressure of the gas in the unperturbed state,the kinematic viscosity and the surface tension of the liquid,the polytrophic exponent,and the volume of gas in the per unit mass of the bubble–liquid mixture, etc. The parameters d and e denote the perturbations in the y and z directions.
With the scaling transformation
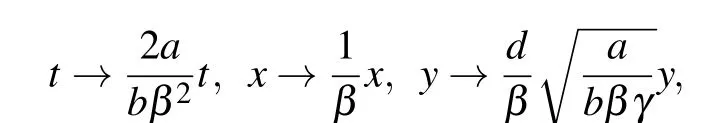
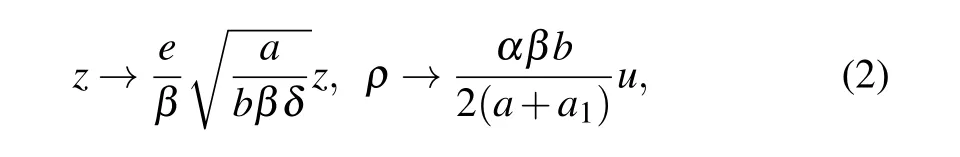
the three-dimensional KS equation (1) can be converted into the following form:
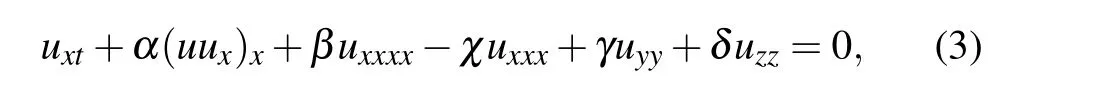
where χ =c/b. It is noted that this equation has very important physical implications, and can be reduced to some classical physical models by choosing suitable parameters in the following cases:
(i)The two-dimensional BKdV equation[2](δ =0);
(ii)The KdV equation[3](α =6,β =1,χ =γ =δ =0);
(iii) The KP equation[4](α = 6, β = 1, χ = δ = 0,γ =±1);
(iv) The one-dimensional KS[5]or BKdV equation[6](β =1,γ =δ =0);
(v) The two-dimensional Burgers-KP (BKP) equation[6](α =1,β =δ =0);
(vi)The three-dimensional KP equation[7](α=6,β =1,χ =0,δ =γ =±3).
In recent years,several attempts have been made to construct explicit solutions for some nonlinear systems.[9–15]It is a difficult and complicate but very important and meaningful work to find the nonlinear wave solutions and interaction solutions for nonlinear systems. By solving the nonlinear mathematical physics model,many kinds of nonlinear physical phenomena can be effectively described in nature. With the deepening of the nonlinear system research, a series of effective methods have formed for solving nonlinear partial differential equations,such as Hirota method,[16]Darboux transformation method,[17]KP reduction method,[18]nonlocal symmetry method,[19]and so on.
Consideration here is the issue of rational solutions for the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation only with the highest derivative terms of each variables,namely

where α, β, γ, and δ are real constants. It can be used to describe the liquid containing gas bubbles without considering its viscosity. To our knowledge, localized wave solutions, periodic wave solutions and interaction solutions of the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation (4) have been obtained in Refs. [20,21] Moreover, bright soliton, resonant multiple wave, lump-stripe, breather and rogue wave solutions have been derived for the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation with the scaling u(t,x,y,z)=u(t-hx,x,y,z).[22–25]Motivated from the work by Clarkson and Dowie in a study of rational solutions to the Boussinesq equation,[26]the aim of the present paper is to construct rogue wave-type rational solution, W-shaped rational solution,multiple basic rogue wave solution,and N-wave resonance solution of the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation(4),which have not been reported before.
In the present paper, a total of nine district solutions of Eq.(4)will be obtained by the Hirota bilinear method,[16]including bright rogue wave-type rational solution, dark rogue wave-type rational solution,bright W-shaped rational solution,dark W-shaped rational solution,generalized rational solution,bright-fusion resonance solution,dark-fusion resonance solution, bright-fission resonance solution, and dark-fission resonance solution. By introducing two polynomials, the generalized rational solutions splitting from two peaks into three peaks are constructed. The dynamical behavior of these phenomena are demonstrated in detail. With the analysis of the first- to third-order rational solution, it is extremely interesting to find that s-order rational solution has 2s+1 points for rogue wave-type solution or parallel lines for W-shaped solution.More importantly,the bright rational solution must have s peaks above the zero background plane and s+1 valleys below the background plane,while the dark one is just the opposite.
The remainder of our article is organized as follows. In Section 2, bright and dark cases of rogue-type rational solution, W-type rational solution, high-order rational solutions and generalized rational solutions for the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation are constructed by virtue of the Hirota bilinear method. Section 3 is devoted to deriving four types of bright-fusion,dark-fusion,bright-fission,and dark-fission resonance solutions for the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation. Finally,some conclusions are given in Section 4.
2. Bright and dark high-order rational solutions
In this section, rogue wave-type rational solutions, Wshaped rational solutions, high-order rational solutions, and generalized rational solutions are investigated for the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation(4). Let ξ =x+my+nt in Eq.(4).It follows that
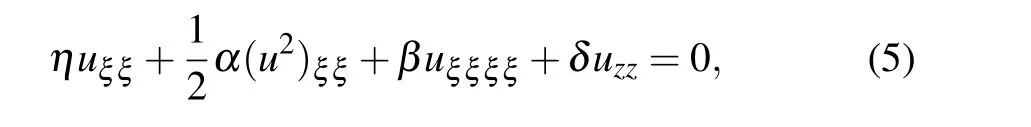
here η =γm2+n. It is then deduced that
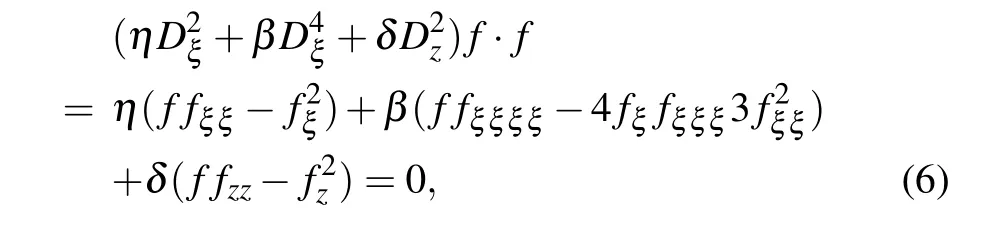
with the transformation
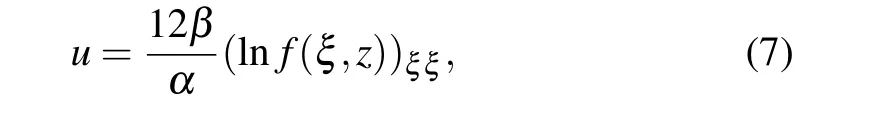
where Dξand Dzare Hirota operators.[16]
In order to construct the rational solution(7)of the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation(4),we first introduce a polynomial function Fs= f with the following form:

Substituting Fsinto Eq.(6)and collecting the coefficients of ξ and z, we can get a set of equations that determine the value of ai,jby setting the coefficients equal to 0. According to the transformation (7), the specific rational solution of Eq. (4) is obtained. Obviously,the power of the denominator for the solution u with respect to the independent variables, is always higher than that of the numerator,which gives rise to u →0 as x2+y2+z2+t2→∞.
Remark 1 The proposed form of Eq. (8) has some limitations on constructing the nontrivial rational solutions of the nonlinear models in the bilinear form, which means it is not applicable to all the bilinear equations. Only all the bilinear operator in these models are linear combinations of D2pv(p ∈Z+, v denotes independent variable)or they can be transformed into this form could be suitable for this method, otherwise the coefficients ai,jobtained are all trivial. If ai,jis trivial, then the first-order rational solution u = 0, let alone the high-order ones. Many examples can be calculated to verify the above conclusion, such as (2+1)-dimensional Benjamin–Ono equation,[27](2+1)-dimensional Camassa–Holm–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation,[28](3+1)-dimensional Hirota equation,[29](3+1)-dimensional KP equation,[30]and so on.
For s=1,a set of non-trivial coefficients of function F1is obtained,i.e.,a0,2=-η2a0,0/3βδ,a2,0=-ηa0,0/3β. Plugging them into Eq. (7), there appears the expression for the first-order rational solution in the form
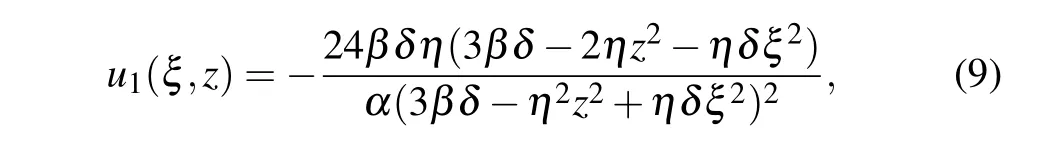
where ξ =x+my+nt and α, β, δ are all non-zero real numbers. Then we can get the following rogue wave-type and Wshaped rational solutions in case 1 and case 2.
Case 1 Rogue wave-type rational solutions

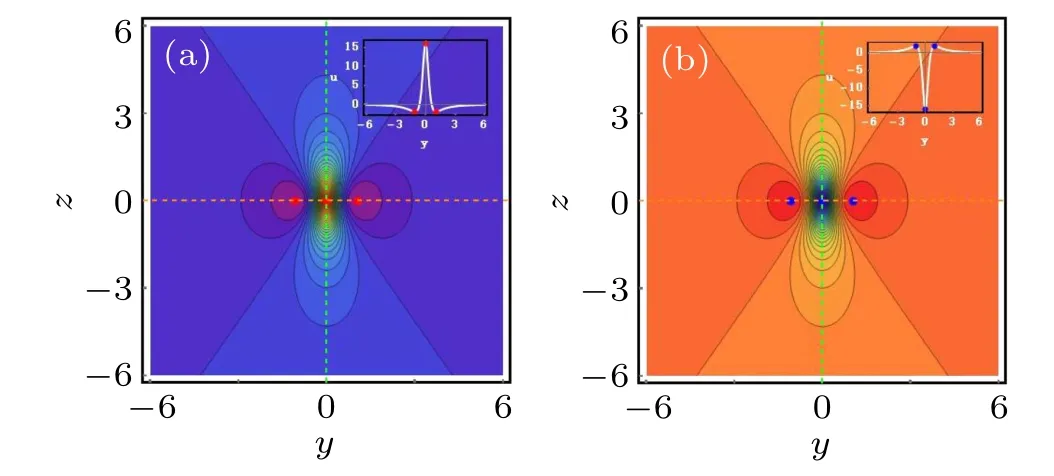
Fig. 1. The first-order rational solution of the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation (4) at the plane (y,z) with the parameters (β,γ,δ,m,n) =(1,-1,-1,2,2). (a) Bright rogue wave-type rational solution with α =1,(b)dark rogue wave-type rational solution with α =-1.


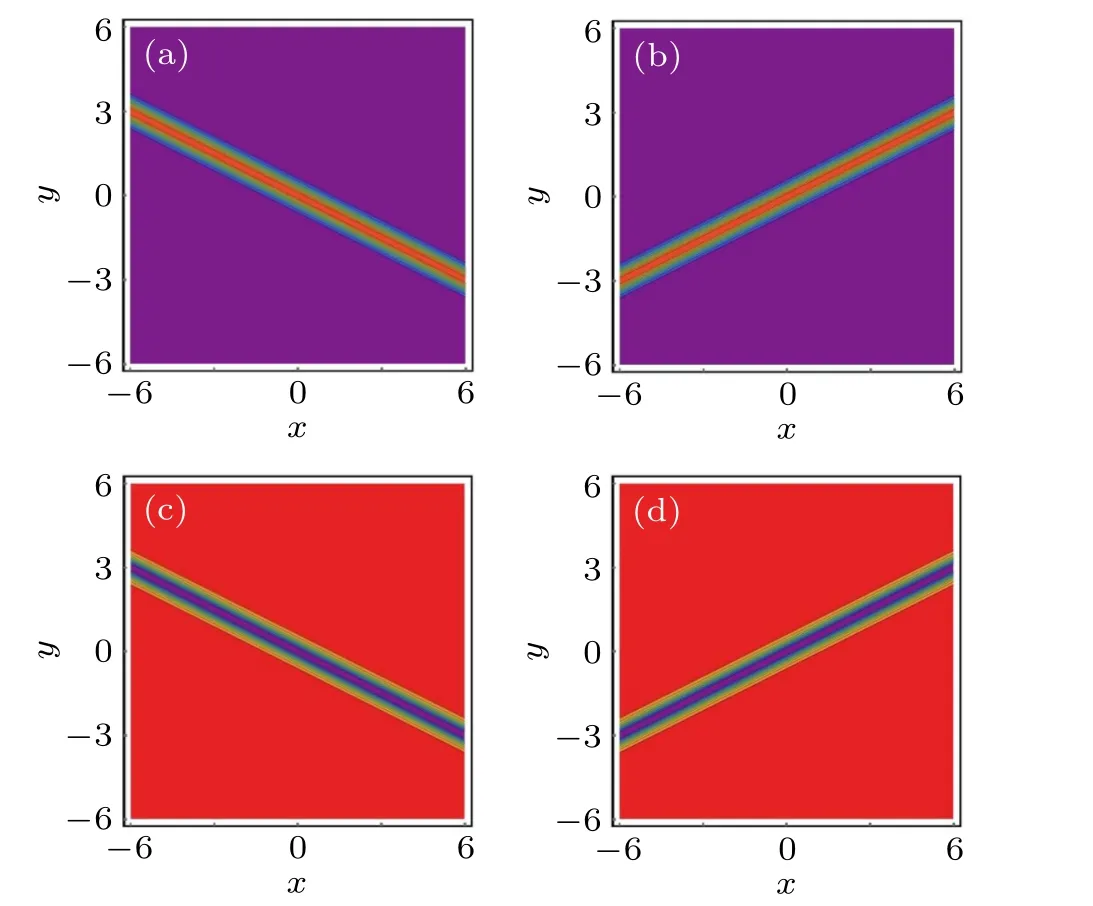
Fig.2. The first-order W-shaped rational solution of the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation (1) at (y,z) plane with the parameters (α,β,γ,δ,m,n) are:(a) (1,1,-1,1,2,2); (b) (1,1,-1,1,-2,2); (c) (-1,1,-1,1,2,2); (d)(-1,1,-1,1,-2,2). (a)and(b)bright W-shaped rational solution; (c)and(d)dark W-shaped rational solution.

Case 3 High-order rational solutions
The above discussed are the cases of the first-order rational solutions,high-order rational solution can be derived with the increase of s. Here we take s=2 and s=3 as examples to analyze the dynamic characteristic of the high-order rational solution at (y,z) and (x,y) planes. For s=2, a set of coefficients ai,jof the function F2can be derived,that is

Taking the coefficients into Eq.(8),It then follows Eq.(7)that the expression of second-order rational solution u2(ξ,z) can be adduced,namely,

where
When the parameters selected in u2are the same as those in u1of case 1,it will give rise to the second-order rogue wavetype rational solution, namely, bright and dark rational solution,as shown in Fig.3. According to the analysis process of the first-order rational solution, we can also calculate the coordinates of the red and blue points in the(y,z)plane and their corresponding values of the second-order rational solutions.The y and z coordinates of the red points are approximately localized at (±1.768,0), (0,0), and (±0.821,0). Their corresponding values of u2are approximately -3.2 for the first three points and 19.385 for the last two points. After further calculation,it is not difficult to find that the blue points and the red points have the same coordinates,while the corresponding values of u2are just opposite with each other. Figure 3(a)displays the dynamics of the second-order bright rogue wave-type rational solutions,while figure 3(b)shows the dark one.
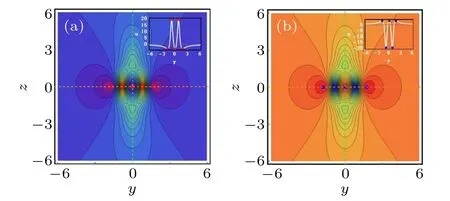
Fig.3. The second-order rogue wave-type rational solution in Eq.(4)at the(y,z)plane with the similar parameters as those given in Fig. 1. (a)Bright rogue wave-type rational solution; (b) dark rogue wave-type rational solution.
Similarly,when the parameters selected in u2are the same as those in u1of case 2, the second-order bright and dark W-shaped rational solutions can be constructed, as shown in Fig. 4. It is obvious that the tilt angles of the corresponding W-shaped rational solutions in Figs.2 and 4 are the same and the slopes are ±1/2, which are determined by the parameter m.
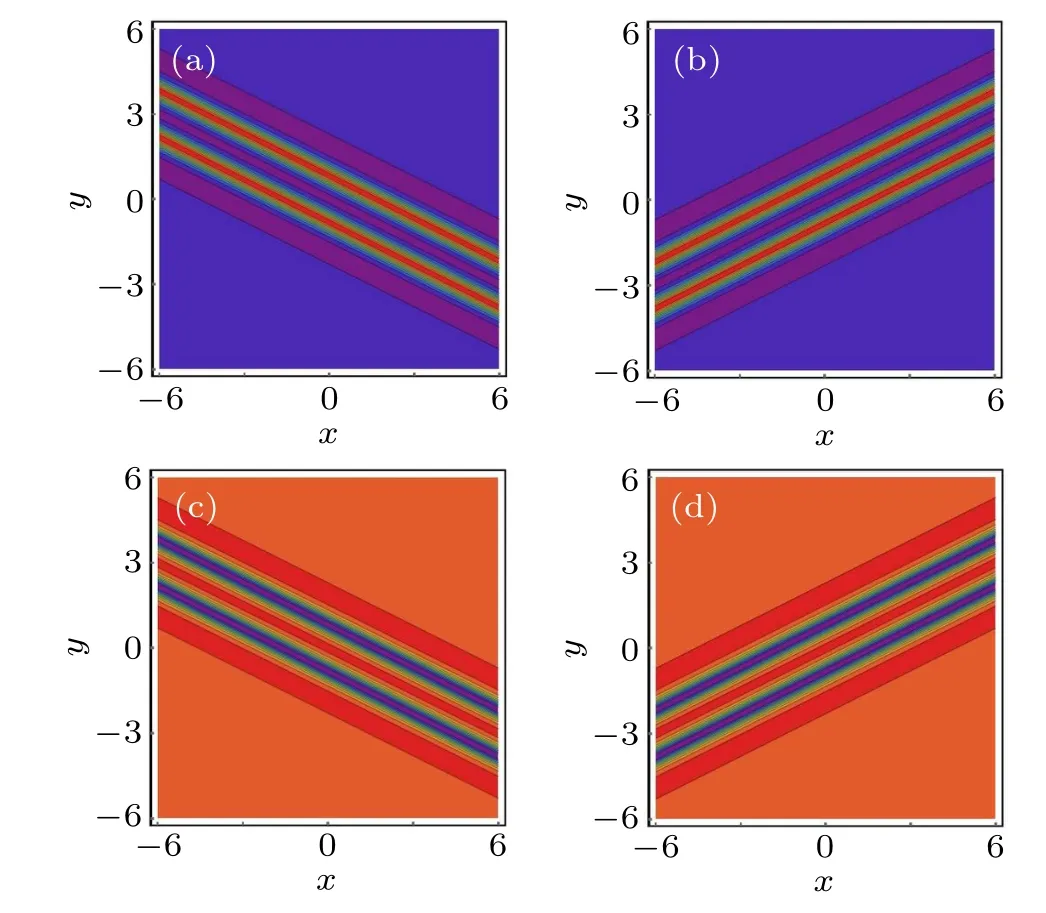
Fig.4. The second-order W-shaped rational solution in Eq.(4)at the(x,y)plane with the similar parameters as those given in Fig. 2. (a) Bright Wshaped rational solution;(b)dark W-shaped rational solution.
Setting s=3 in Eq.(8),the expression for the coefficients ai,jin the function F3is as follows:
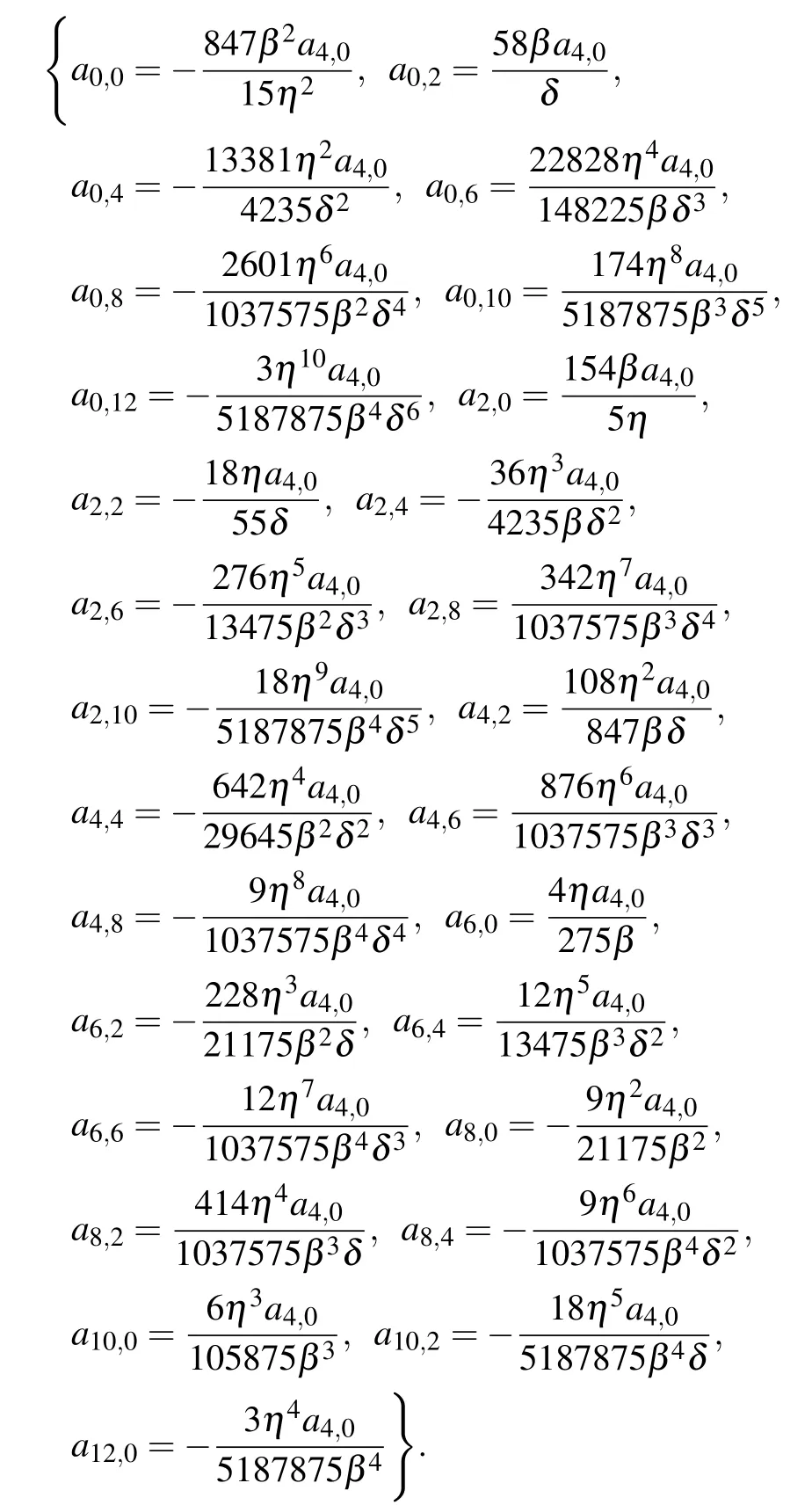
By taking them into Eq.(7)with Eq.(8),it yields the expression of the third-order rational solution u3(ξ,z). Since the expression of u3(ξ,z) is too cumbersome, we only shows its dynamic behavior,as illustrated in Figs.5 and 6.
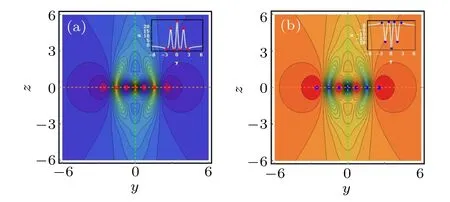
Fig. 5. The third-order rational solution at the (y,z) plane with the similar parameters as those given in Fig.1. (a)Bright rogue wave-type rational solution;(b)dark rogue wave-type rational solution.
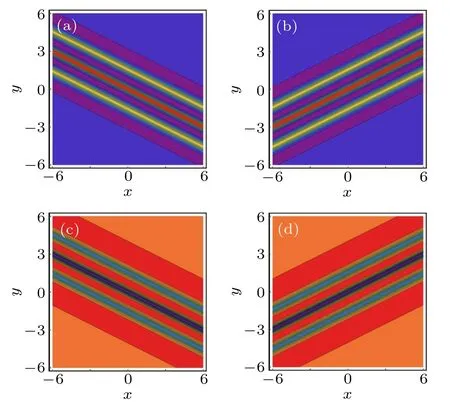
Fig. 6. The third-order W-shaped rational solution in Eq. (4) at the (x,y)plane with similar parameters as those given in Fig. 2. (a) and (b) Bright W-shaped rational solution;(c)and(d)dark W-shaped rational solution.
There are seven critical points for the third-order rational solution on the z=0 axis at the(y,z)plane,and they also have the above symmetry results, see Fig.5. The y and z coordinates of the critical points for the bright and dark thirdorder rogue wave-type rational solution are approximately localized at(±2.54,0),(±1.565,0),(±0.718,0),(0,0),and the corresponding values of u3are ?3.534, ±18.556, ?4.516,±26.182, respectively. Simultaneously, the third-order Wshaped rational solution has the same characteristics as the lower one,and seven critical lines can be seen in Fig.6.
As s increases,high-order rational solution(rogue wavetype or W-shaped)of the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation can be generated. It is noticeable that the solution meets a rule:s-order rational solution has 2s+1 points or parallel lines on different planes,and the two situations show different dynamic behavior characteristics.
Case 4 Generalized rational solutions
Attention is now turned to investigate generalized rational solutions for the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation. To achieve this purpose,we introduce two polynomials

in the same form as Fs(ξ,z) in Eq. (8), where the two coefficients bs(s+1)-2j,2iand cs(s+1)-2j,2iwill be determined later.Applied the method used in Ref.[26],it is natural to have the following result.
Theorem 1 The(3+1)-dimensional KS equation(4)has generalized rational solutions in the form
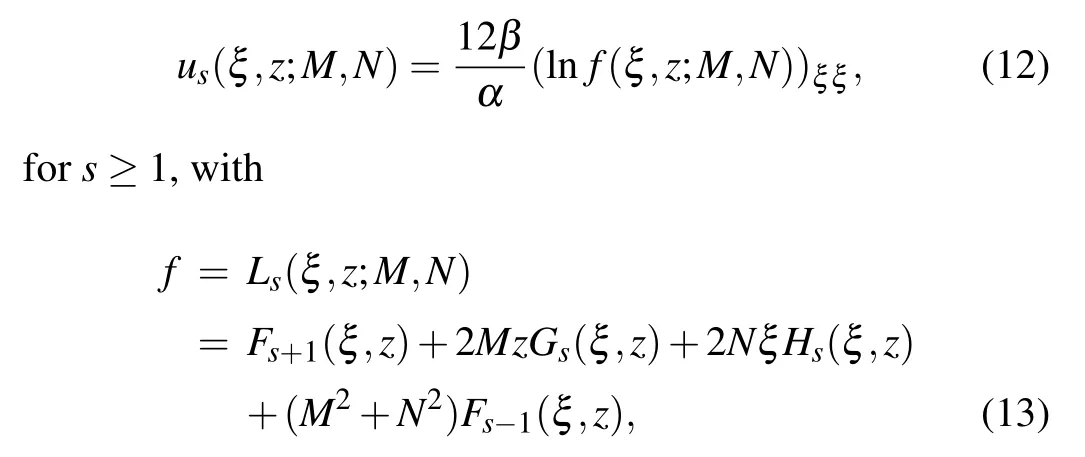
where M and N are arbitrary constants.
Obviously,let M,N,and s in Eq.(13)be equal to zero,the one-order rational solution can be obtained, which is consistent with the results obtained at the beginning of this section.Without loss of generality,when s=1,a set of non-trivial coefficients of function L1can be obtained as
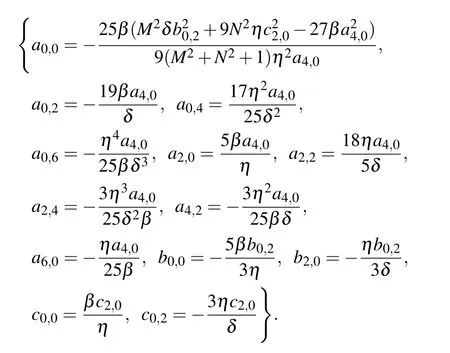
Plugging them into Eq.(7),it gives rise to the first generalized rational solution u2(ξ,z;M,N). Here we only analyze their dynamic behavior.
When M =N =0, it becomes the obtained rational solution and can bring in similar results as shown in Fig. 3 by selecting appropriate values for the remaining parameters. As|M|and|N|increase, the solution can be split from two peak into three peaks rogue wave solution,which is also known as‘rogue wave triplet’solution.Figure 7 shows its evolution process of the bright case. Let α =-1, the dark case can be obtained. Using Theorem 1, high-order generalized rational solutions can be derived for the case of s ≥2.
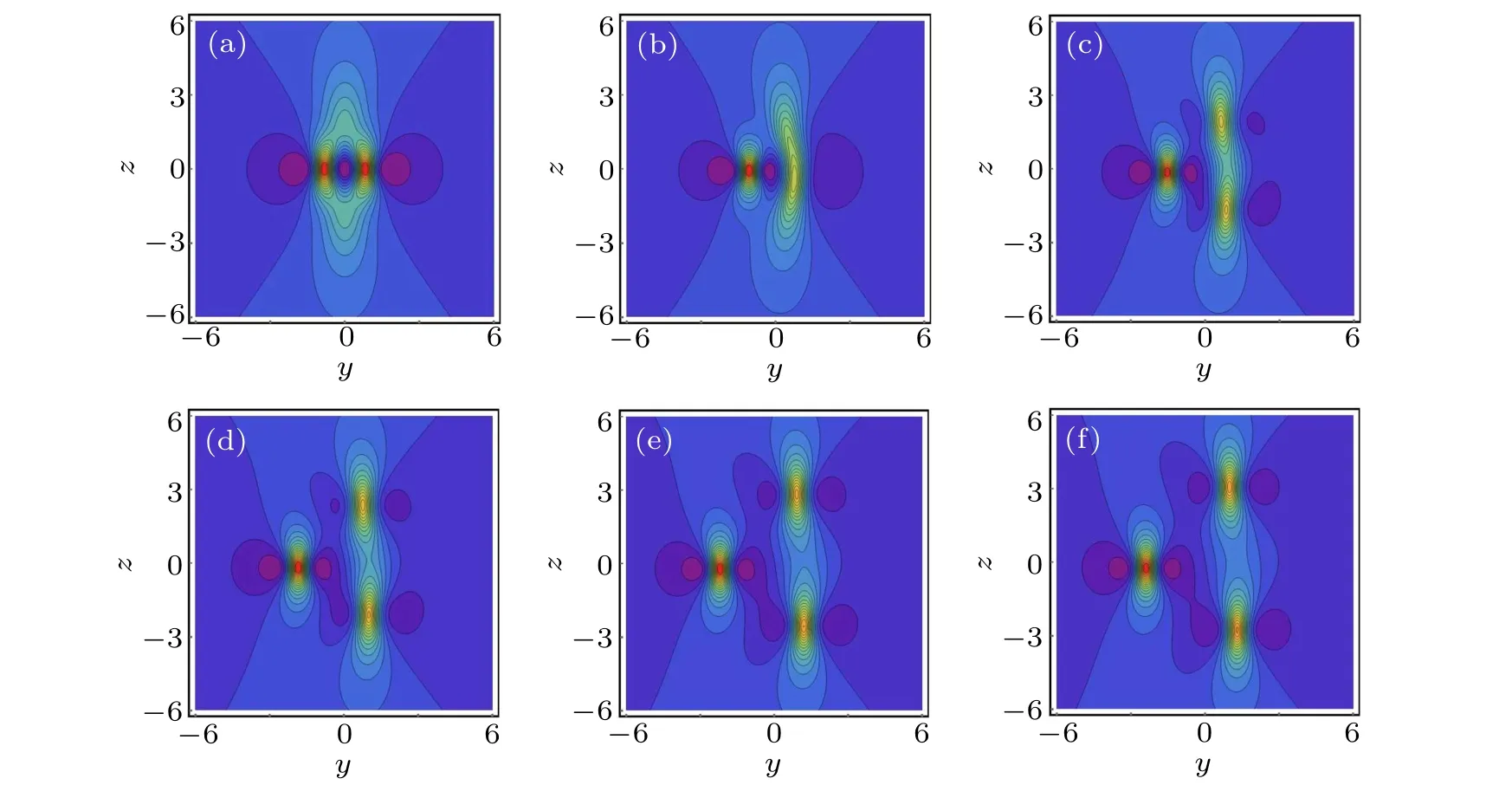
Fig.7. Decomposition process of the generalized rational solution u2(ξ,z;M,N)for the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation with distinct values of the parameters M,N and(α, β, γ, δ, m, n, a4,0, b0,2, c2,0)=(1,1,-1,-1,2,2,2,2,2). (a): M=N=0;(b): M=N=1;(c): M=N=3;(d): M=N=5;(e): M=N=8;(f): M=N=10.
3. The N-wave resonance solution
The purpose of this section is to construct N-wave resonance solutions of the (3+1)-dimensional KS equation (4) by reverting it into the following bilinear form:
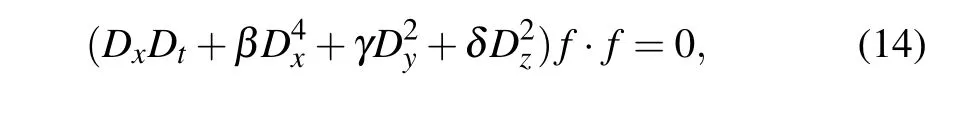
where D is the Hirota operator,[16]here use has been made of the transformation

By choosing appropriate parameters, four different resonance solutions are discussed, including bright-fission, darkfission,bright-fusion,and dark-fusion solutions. Figure 8 displays different dynamical phenomena of the two-wave resonance solution. Fission waves can be split from one wave to multiple waves, while fusion waves are just the opposite.In order to understand the fusion and fission processes of the soliton solutions clearly,the three-wave resonance solution is taken as an example, and the evolution processes of fusion and fission over time are given respectively. Figure 9 shows the bright type of the three-wave resonance solution,dark type of the three-wave resonance solution also has the same phenomena. In the same way,N-wave resonance solution can be constructed.

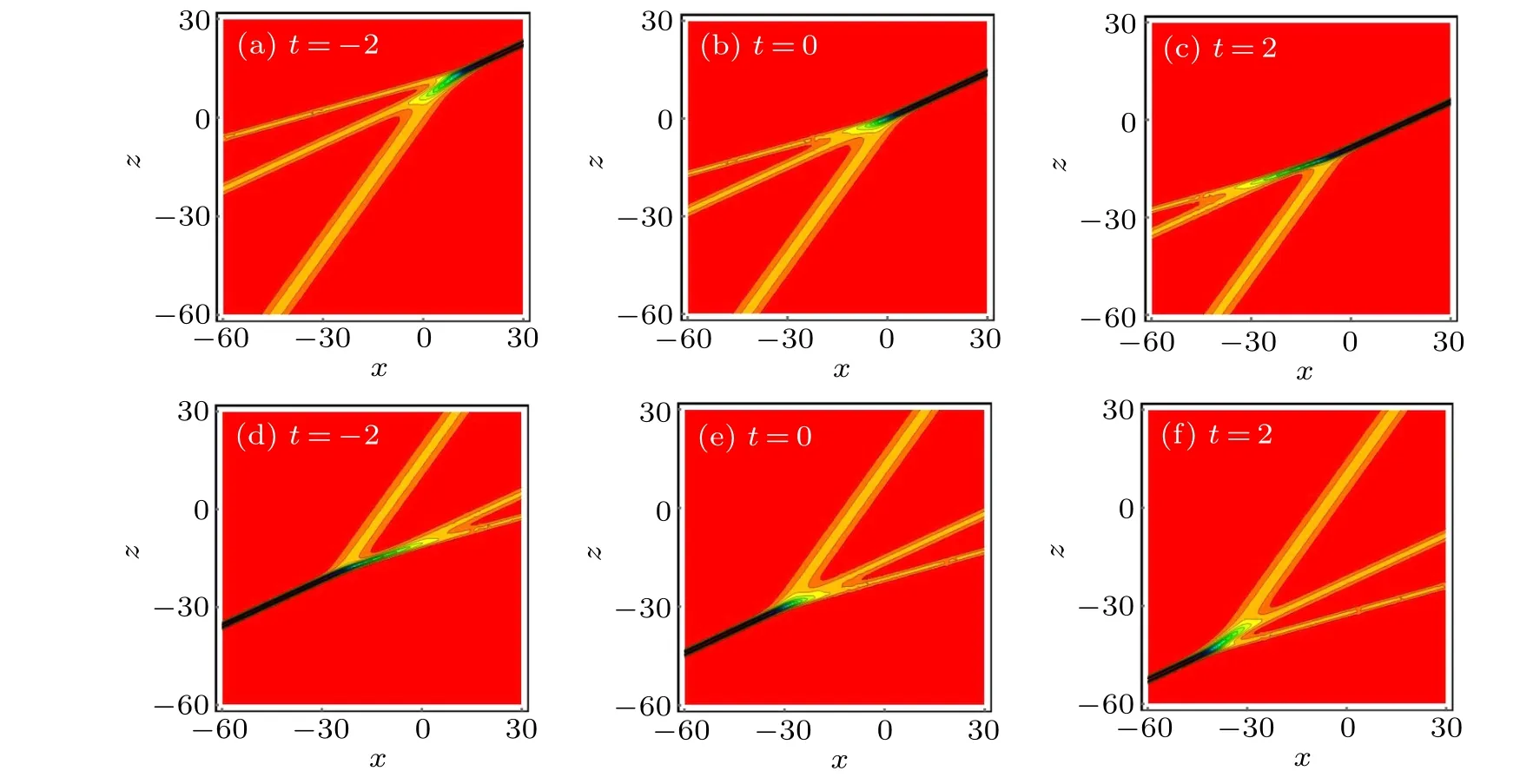
Fig.9. The evolution of three-wave resonance solution over time with similar parameters as those given Figs.8(a)and 8(c). Top row: brightfusion solution(k3=-3/2). (d)–(f)bright-fission solution(k3=3/2).
4. Summary and discussion
A (3+1)-dimensional Kudryashov–Sinelshchikov equation modelling the liquid containing gas bubbles has been studied in this paper.Rogue wave-type rational solution,W-shaped rational solution, Multiple basic rogue wave solution, and Nwave resonance solution are provided explicitly for this equation based on two kinds of bilinear equations.
By introducing the polynomial function (8), we obtain bright rogue wave-type rational solution, dark rogue wavetype rational solution, bright W-shaped rational solution, and dark W-shaped rational solution,see Figs.1–6. From the analysis of the first-to third-order rational solutions,it is not difficult to find that s-order rational solution has 2s+1 points for rogue wave-type solution or parallel lines for W-shaped solution. As long as it is a bright rational solution, there must be s peaks above the background plane (zero plane), s+1 valleys below the background plane,and the dark one is just the opposite. Their corresponding properties, such as amplitude,wave width,and tilt angle,are all parametrically controllable.Moreover, generalized rational solutions splitting from two peaks to three peaks are derived by introducing two polynomials (11). The dynamical behavior of the splitting process has been demonstrated in Fig.7.
In addition,the N-wave resonance solution of the(3+1)-dimensional KS equation is constructed under the dispersion relation and specific constraints. Bright-fission, dark-fission,bright-fusion, and dark-fusion two-wave resonance solutions are constructed, see Fig. 8. Fission waves can be split from one wave to multiple waves, while fusion waves are just the opposite. Figure 9 shows the evolution processes of fusion and fission three-wave resonance solutions, which reveal diverse dynamic behavior.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Numerical simulation on ionic wind in circular channels*
- Interaction properties of solitons for a couple of nonlinear evolution equations
- Enhancement of multiatom non-classical correlations and quantum state transfer in atom–cavity–fiber system*
- Protein–protein docking with interface residue restraints*
- Effect of interaction between loop bases and ions on stability of G-quadruplex DNA*
- Retrieval of multiple scattering contrast from x-ray analyzer-based imaging*