Magnetic properties and promising cryogenic magneto-caloric performances of Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 amorphous ribbons*
Yikun Zhang(張義坤), Bingbing Wu(吳兵兵), Dan Guo(郭丹),Jiang Wang(王江), and Zhongming Ren(任忠鳴)
1State Key Laboratory of Advanced Special Steels,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200072,China
2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced Ferrometallurgy,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200072,China
3School of Materials Science and Engineering,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200072,China
Keywords: microstructure,magneto-caloric effect(MCE),amorphous ribbons,magnetic properties
Nowadays, the interest in research on magnetic solids with promising magneto-caloric performances has considerably grown due to the potential applications in the field for future magnetic cooling (MC).[1–4]Magneto-caloric effect(MCE) is a magneto-thermodynamic property of magnetic solids, which depends on the interaction between external field and magnetic sub-lattices. Generally,MCE is characterized by two important factors, i.e., magnetic entropy change ΔSMand refrigerant capacity (RC), when the external field changes. Due to special characterizations of promising highefficiency and environmental friendliness, the MCE-based cooling technology would be able to replace the presently available gas compression/expansion cooling technology.[1–4]The Ericsson cycles consisting of two isomagnetic fields and two isothermal processes have been recognized as the best choice for cryogenic MC.For the most ideal Ericsson MC cycles,the magneto-caloric materials should have constant ΔSMin the whole cooling temperature range, i.e., a table-shaped MCE.[5,6]This performance can be indirectly identified with the help of magnitude of RC. Thus, searching for magnetic solids that exhibit promising magneto-caloric materials, especially the ones with a table-shaped performance, is one of the most important issues for MC.For this purpose,magnetic alloys and compounds have been fabricated or designed and systematically checked with their MCE performances.[7–10]
Moreover, researchers have focused on magneto-caloric performances in some selected heavy rare-earth (RE) rich magnetic alloys in amorphous states due to their promising applications.[11–13]Compared with the crystallized HRE-rich alloys or compounds, the magnetic-entropy-change maxima,i.e., |ΔSM|, for the alloys in amorphous states are usually smaller. However,magnetic transitions for the alloys in amorphous states are somehow broader,since there is no long-range ordering which will widen the peak of|ΔSM(T)|curves. Previous investigations have demonstrated that most of the heavy rare-earth based alloys could be synthesized as amorphous formulae with a similar wide composition region.[14]Moreover,according to the de Gennes factor,i.e.,(gJ-1)2J(J+1),the magnetic phase transition temperature decreases gradually with increasing atomic number from Gd to Tm,which means that Tm-based compounds should possess the lowest phasetransition temperature.[4,5]Therefore, the temperature range of the magnetic phase transition would be further widened by alloying different RE elements with proper ratios, which may induce a table-shaped MCE.On this purpose, the multiple heavy RE-based Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons were selected and successfully fabricated,and the tableshaped MCE with large RC values were realized.
The Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20alloy ingot was fabricated by arc-melting the bulk metals of Ho, Tm, Gd, Cu, and Ni(purity ≥99.9 wt.%) with Ti-getter under high-purity Argas. The ingots were flipped and re-melted 4 times; and the weight loss was ~0.4 wt.% during this process. Then, the amorphous ribbons with width of 2.0–3.2 mm and thickness of 30–40 μm were obtained from the ingot by the melt-spun method under high-purity Ar-gas using Cu-wheel(33 m/s surface speed). The structures were checked by x-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker-D8). The microstructure and elemental distribution was determined by a high resolution (HR) transmission electron microscope(TEM)with an attached energydispersive x-ray (EDX) diffractometer (JEOL JEM-2010).The magnetization data was collected using a commercial superconducting quantum interference device(SQUID,QD)and the ribbon is paralleled to the magnetic field to minimize the shape anisotropy effect.
Figure 1(a) illustrates the XRD pattern of Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20spun ribbons. A broad diffraction halo in the angle range of 25?–40?is observed without obvious crystalline diffraction peaks,i.e.,Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons are with amorphous state and without crystalline phases. The microstructure of Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons was examined by HRTEM, as shown in Fig. 1(b).The inset of Fig. 1(b) illustrates the selected area electrondiffraction (SAED) pattern for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons. The HRTEM image and SAED pattern can further confirm that the present Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons are with full amorphous structures. The EDX mapping results for all the consistent elements (Gd, Ho, Tm, Cu, and Ni) are given in Figs. 1(c)–1(g), respectively, which clearly indicate that all the consistent elements are uniformly distributed in Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons, and the atom percentages of Gd, Ho, Tm, Cu, and Ni are 19.92 at.%,18.64 at.%, 17.85 at.%, 22.36 at.%, and 21.23 at.%, respectively.
Figure 2(a) illustrates the M(T) curves for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons. One can note that no obvious differences in M(T)curves for H=0.2 T can be found between the zero-field-cooled curve and the field cooled ones. Moreover, the external fields have significant effects on the magnetic transition for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons,a pronounced sharp transition from paramagnetic (PM) to ferromagnetic (FM) state happens at Curie temperature TCof 32 K under low H (0.2 T), and the transition is continuously becoming wider with increasing H.Especially, for the 5 and 7 T from 10 to 80 K, an almost linear relationship between the magnetization and temperature is observed, i.e., the magnetic transition is flat and continuous under high magnetic fields. Such a character could be easily identified in the dM/dT versus T data of the Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons, as represented in Fig.2(b). dM/dT has a significant change from a sharp to a flat and then to a table-like feature with increasing H.
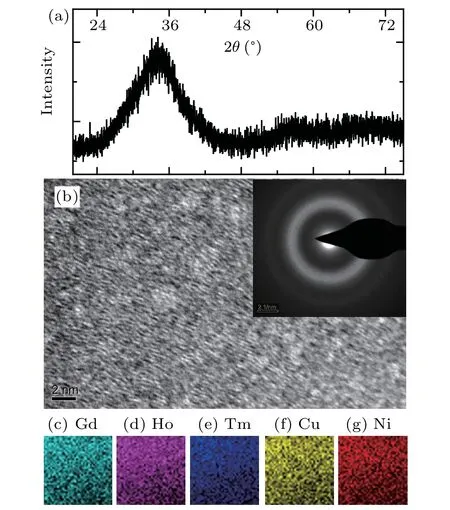
Fig.1.(a)XRD pattern,(b)HRTEM images,and(c)–(g)EDX mapping for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 amorphous ribbons. Inset of(b)shows the SAED pattern for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 amorphous ribbons.
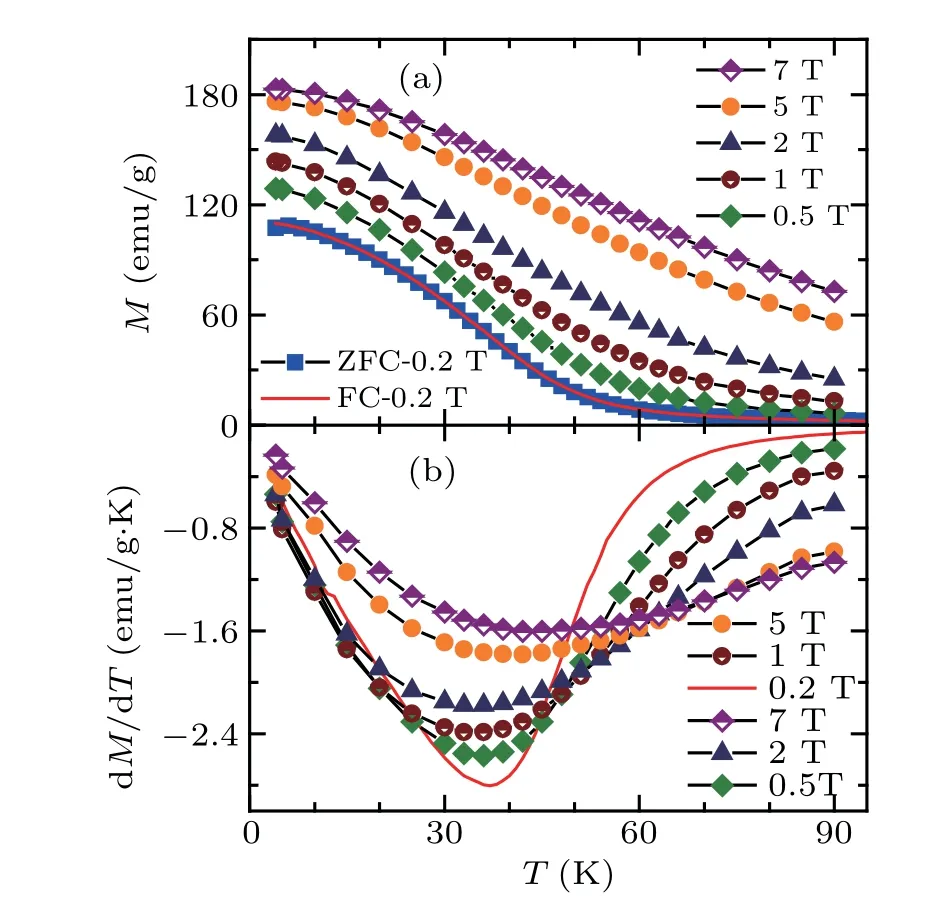
Fig. 2. (a) The M(T) curves for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 amorphous ribbons with H up to 7 T. (b) The dMFC/dT versus T for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 amorphous ribbons.
Several selected M(H)curves for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons are illustrated in Fig. 3(a). At low H,M increases rapidly for lower temperature ones and demonstrates a saturation-like behavior with further increasing magnetic field, i.e., the Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons exhibit a typical behavior as FM ordering amorphous materials.Furthermore, the magnetic phase transition for amorphous Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons is detailedly analyzed by Arrott plots (M2versus H/M) and Banerjee criterion, as illustrated in Fig.3(b).[16]No negative slope or inflection could be found as a character for the first-order magnetic transition,suggesting that the phase transition in the present amorphous Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons is of a second-order type.
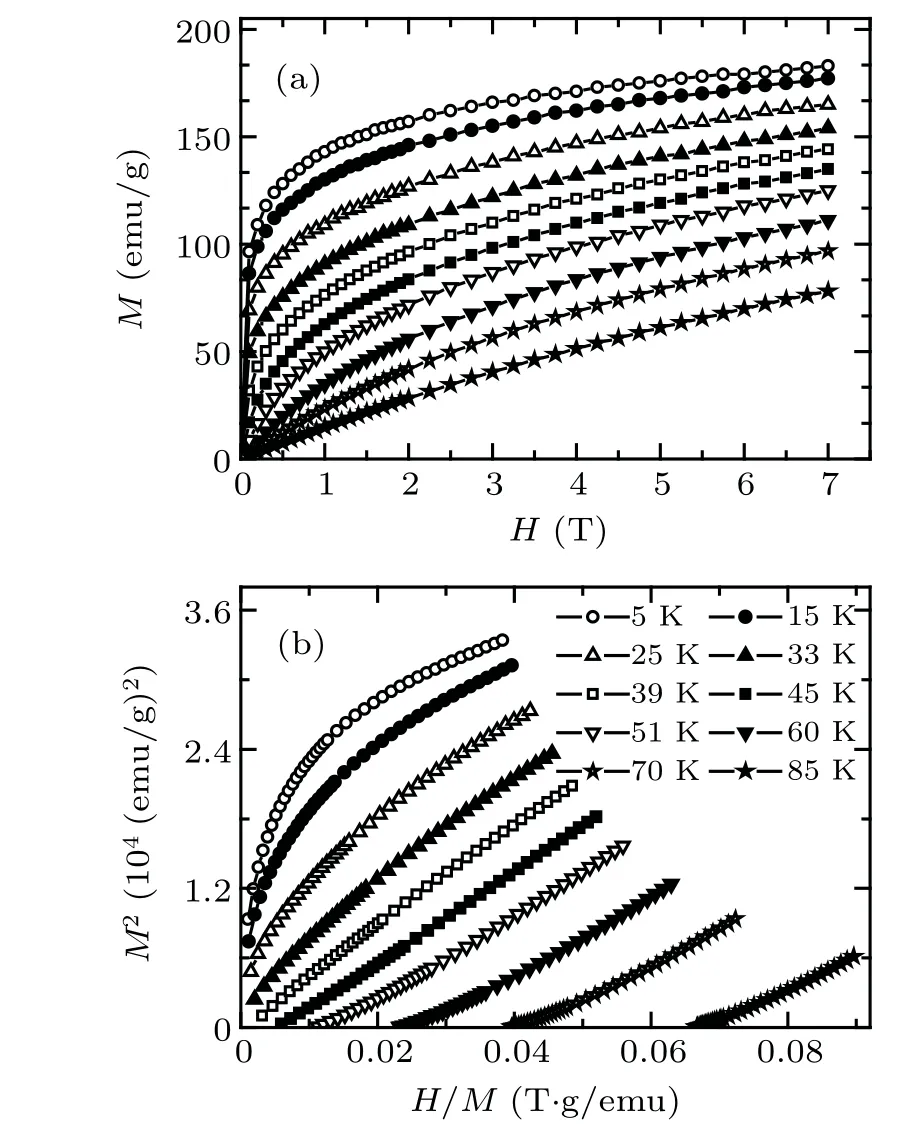
Fig. 3. (a) Selected M(H) data for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 ribbons.(b)The corresponding plots of H/M vs M2.
Generally,the ΔSMwith external field change of 0–Hmaxwas evaluated by Maxwell’s thermo-dynamic relation with integrating over the isothermal magnetization curves:[1–3]
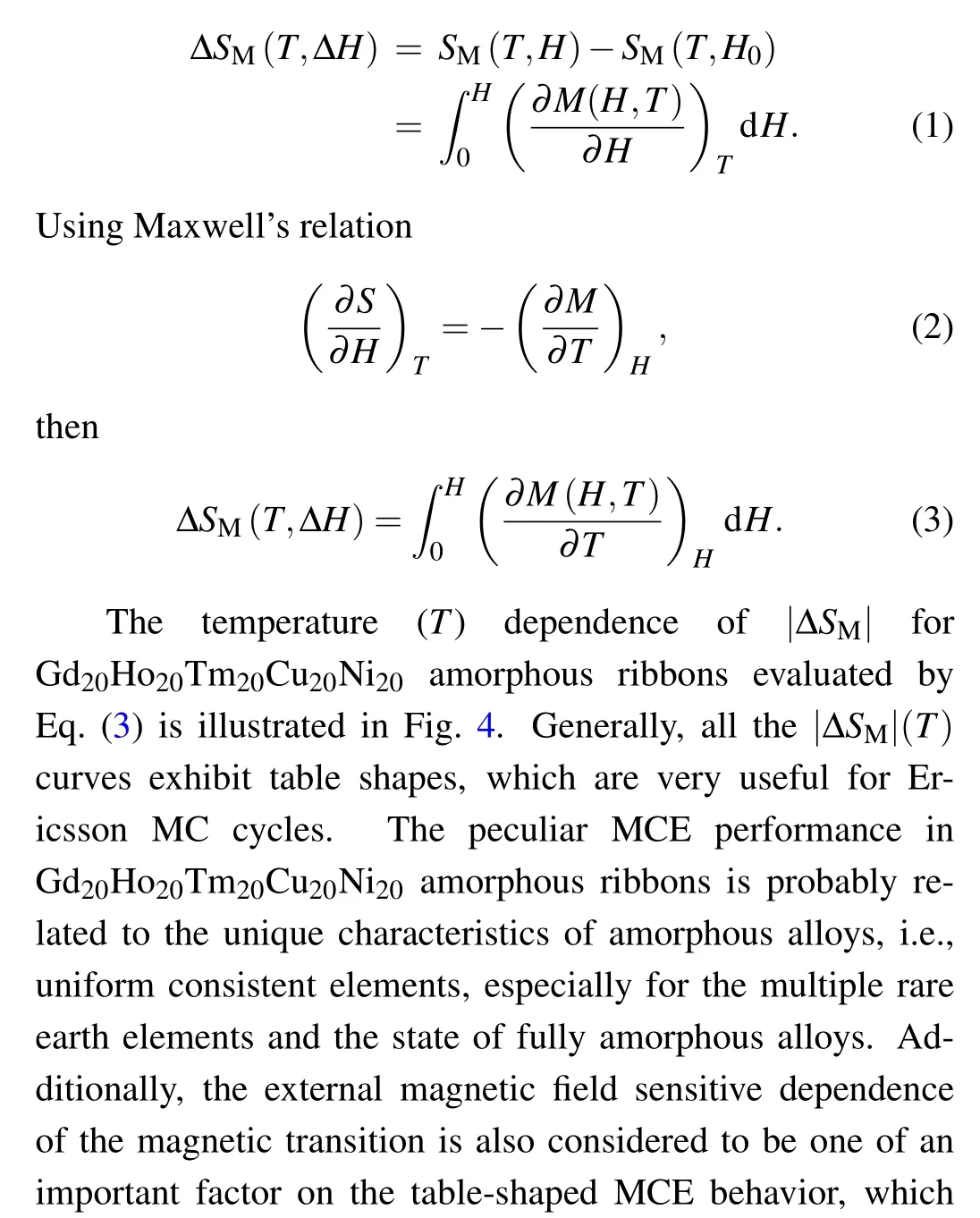

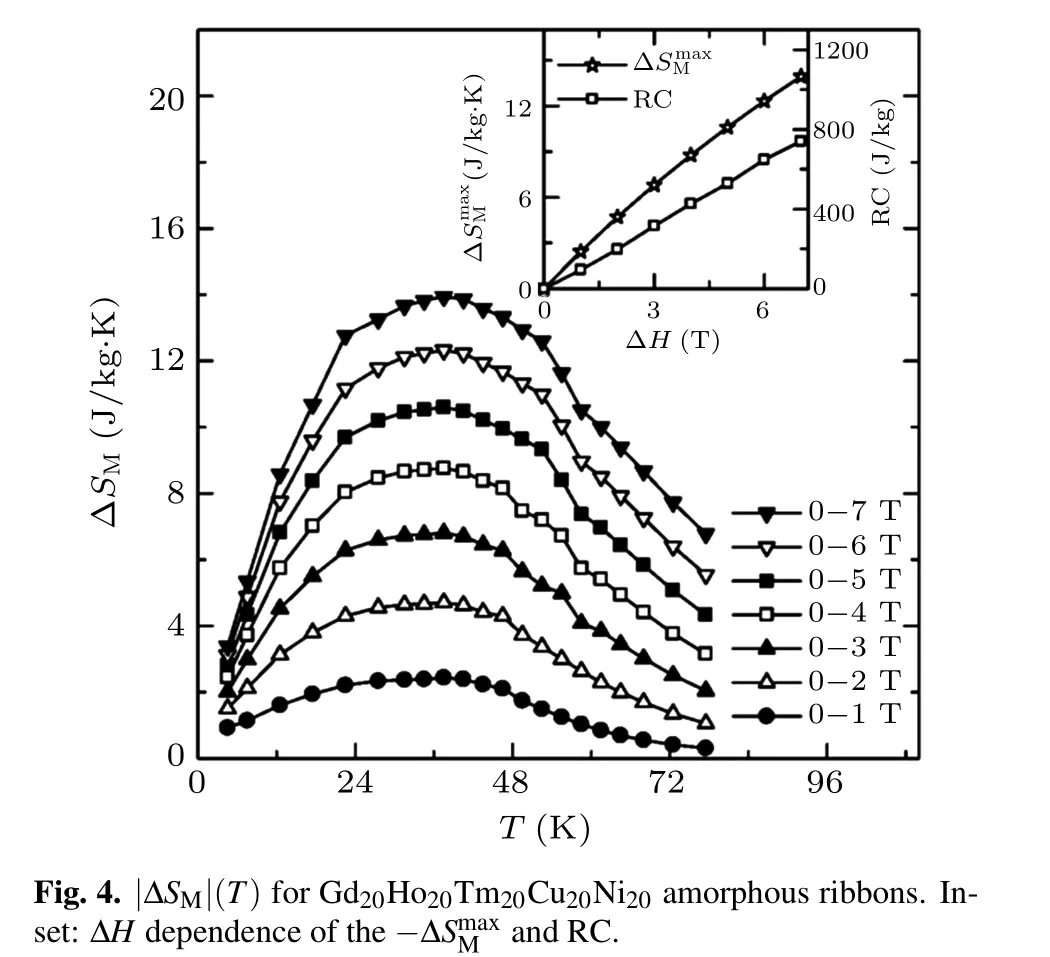
Additionally,Griffith et al. have applied the temperatureaveraged gΔSM(i.e.,TEC)to characterize the magneto-caloric performances.[17]It is described that the MCE materials can reasonably response to the temperature lift (ΔTlift), and it is defined as

where Tmiddenotes the value of the average temperature.The TEC is calculated at 10 K temperature lift [TEC(10),and the values are 2.39, 4.67, 10.52, and 13.84 J/kg·K for ΔH =0–1, 0–2, 0–5, and 0–7 T,respectively. Obviously, the|ΔSM|maxand TEC(10) values are close to each other with the same ΔH, which is the consequence of the table-shaped MCE and the ΔTliftvalue of 10 K is much lower than the full width at half maximum (δTFWHM) in the ΔSM–T curves for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20ribbons.
In addition, RC is another crucial parameter which can justify the MCE performances.Detailed description of the calculation method of RC is given in our review articles.[1]The obtained values of δTFWHMare 65.1 and 60.8 K for ΔH =0–7 and 0–5 T, respectively. Correspondingly, the RC values for the present Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons are evaluated to be 528 and 740 J/kg. The transition temperature (TC), the δTFWHM, |ΔSM|maxand RC values for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons and several reported promising magneto-caloric materials with close working temperature span under ΔH = 0–5 T are listed in Table 1. Obviously, these δFWHM, |ΔSM|max, and RC values for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons are quite competitive. In other words,the obtained promising MCE parameters for the present Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20amorphous ribbons, especially for large values of δFWHMand RC, together with the observed table-shaped MCE,make them considerable for cryogenic MC.
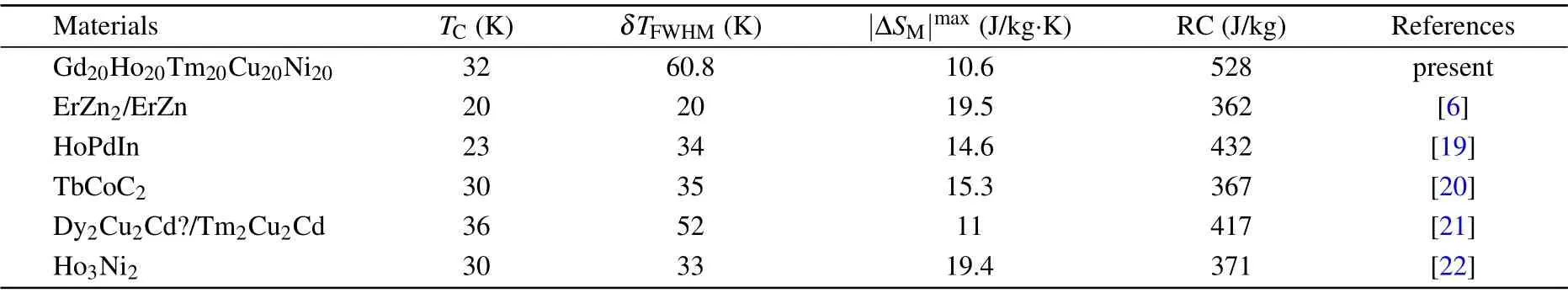
Table 1. The MCE parameters (TC, gδTFWHM, -ΔSmaxM , RC) for ΔH =0–5 T for Gd20Ho20Tm20Cu20Ni20 and several reported promising magneto-caloric solids with similar TC.

Acknowledgement
The authors thank Analysis and Test Center of Shanghai University for providing the instrument.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Numerical simulation on ionic wind in circular channels*
- Interaction properties of solitons for a couple of nonlinear evolution equations
- Enhancement of multiatom non-classical correlations and quantum state transfer in atom–cavity–fiber system*
- Protein–protein docking with interface residue restraints*
- Effect of interaction between loop bases and ions on stability of G-quadruplex DNA*
- Retrieval of multiple scattering contrast from x-ray analyzer-based imaging*