Anti-parity-time symmetric phase transition in diffusive systems?
Pei-Chao Cao(曹培超) and Xue-Feng Zhu(祝雪豐)
School of Physics and Innovation Institute,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,China
Keywords: anti-parity-time symmetry,phase transition,exceptional point,heat transfer
1. Introduction
In quantum mechanics, Hermitian Hamiltonians are widely used in describing the closed systems with orthogonal eigenstates and real eigenvalues. While in open systems,such as wave systems with gain or loss,the corresponding Hamiltonians are typically non-Hermitian with non-orthogonal eigenstates and complex eigenvalues, which brings challenges to evaluate the systems experimentally.[1]Until 1998, Bender and Boettcher discovered that systems exhibiting parity-time(PT) symmetry, subjected to [PT,H]=0, could display entirely real spectra below some threshold.[2]The threshold is later termed as an exceptional point (EP), where the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of H are degenerated, corresponding to mode generation or annihilation in parameter space.[3,4]Starting with the similarity between the quantum Schr¨odinger equation and paraxial wave equation, PT symmetry can be constructed in analogy by incorporating balanced gain and loss materials.[5]Various counterintuitive phenomena or nontrivial effects are theoretically and experimentally proposed in this new platform,such as one-way mode conversion,[6-10]coherent lasing and absorption,[11-13]EP-based sensing,[14-16]mode switches,[17,18]and topological bound states.[19-21]
As a counterpart, anti-PT symmetry, subjected to{PT,H} =0, was first proposed by replacing the balanced gain and loss with positive and negative refractions.[22]Subsequent theoretical and experimental realizations were conducted in different fields, ranging from cold-atom systems,nonlinear wave systems to the effective dissipative coupling systems.[23-28]In a mathematical view,the equivalent dissipative coupling always induces the APT symmetric Hamiltonian HAPT, which just is the result of PT symmetric Hamiltonian HPTby multiplied with an imaginary number i.[24,26]Since the APT symmetry is the complex conjugate of the PT symmetry,the corresponding phase transitions in those systems display two polar-opposite evolution paths in physics.
The APT symmetry was firstly introduced into diffusive systems by the analogy of wave equation and convectiondiffusion equation in the past year.[29]In fact, there exist precedents for the wave-diffusion mapping, which has advanced successes. A classical example is the functional heat manipulation via metamaterials designed by coordinate transformation theory,[30,31]such as thermal cloaks,[32-34]thermal camouflages and illusion,[35,36]and other thermal managements,[37,38]which also has a counterpart in electromagnetic and acoustic fields. Back to the APT symmetry in diffusive systems,it should be noticed that the heat transfer is a natural diffusion process. Thus the coupling between different channels or materials is spontaneously imaginary. Compared with the wave systems, through mimicking the pulse transport with convection flows,we can generate a similar wavelike transmission in diffusive systems.[29,39]Details can be found in the following.
2. The realization of APT symmetry in diffusive systems
2.1. Theoretical background: PT/APT symmetry and EP in wave systems
As there exists energy exchange with environment,Hamiltonian in non-Hermitian systems displays the relation H /=H?(transposition plus complex conjugation). Thus, the conservativeness of measuring a particle’s property with unitary time evolution is broken, or the complex energy eigenvalues principally make the systems unstable and unobservable. However, Bender and Boettcher showed that a non-Hermitian system satisfying[PT,H]=PTH ?HPT =0 can obtain purely real eigenvalues,[2]where P is the parity symmetry operator (a system at P symmetry is equivalent to its mirror image)and T is the time symmetry operator(a system at T symmetry returns to the original state,when the time goes backward). Intuitively,a second-order Hamiltonian satisfying PT symmetry[40,41]

describes a double-channel non-Hermitian system with complex frequencies ω0±ig, where g is a positive number with the sign ‘±’ being a gain/loss coefficient, and κ is the coupling strength,as shown in Fig.1(a).[40]The eigenvalues and eigenvectors can be obtained as

However,a Hamiltonian satisfying APT symmetry{PT,H}=PTH+HPT =0 has a different form[22,24,26]

with the real part of the complex frequencies in opposite sign and the imaginary part being the same. The coupling coefficient between different components is purely imaginary, as shown in Fig.1(b),which however is not easy to realize in experiments.Then the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of HAPTcan be obtained as follows:

Figures 1(a)and 1(b)show the schematic of how to construct PT symmetry and APT symmetry in wave systems. PT symmetry can be usually realized in a structure with balanced gain and loss distribution. Due to the difficulty of doping gain materials,the weak form of passive PT,with complex frequencies of the systems produced by different loss rates, has attracted lots of attention. In general,dissipation is regarded as a major negative factor especially in long-distance wave transport and processing. However, with the aid of PT symmetry theory, a structure with some losses can still produce highquality single mode lasing.[40]Compared with PT symmetry system,the APT symmetry system cannot go back to its original state after an odd number of PT symmetry operations,and phase transition in the APT symmetry system shows an opposite state evolution.
As shown in Eqs.(2)and(4),there exists a critical point(EP), where both real and imaginary parts of eigenvalues are degenerate,as marked by the green stars in Fig.2. It is shown that the eigenvalues of the PT symmetry system change from real (complex) to complex (real) after crossing the EP, while the eigenvalues of the APT symmetry system change from imaginary (complex) to complex (imaginary) after crossing the EP.In the symmetric phase,PT symmetry system and APT symmetry system are featured with uniformly distributed amplitudes and steady phase differences in the coupling channels,respectively.In the symmetry broken phase,PT symmetry system and APT symmetry system are featured with unequally distributed amplitudes and transient evolving phases, respectively.

Fig.1. The realization of PT symmetry and APT symmetry in wave systems. The parity operator (P) exchanges the spatial coordinates and the time operator(T)takes the conjugation of complex parameters(gain,loss,or coupling strength). (a)PT symmetry can be constructed by a system of two coupled structures with balanced gain(+ig)and loss(?ig),and the coupling strength(κ)is always real.(b)APT symmetry can be constructed by a system of two coupled structures with opposite real frequencies(positive and negative refractive indices),and the coupling strength is imaginary(iκ).

Fig.2. The eigenvalues of(a)PT symmetry systems and(b)APT symmetry systems versus the coupling strength κ. EPs are marked by the green stars.
2.2. The realization of APT symmetry in diffusive systems
In the above analyses, the key point in the realization of APT symmetry is to construct an imaginary coupling between two systems.However,the coupling in non-dissipative waveguide systems is real due to the invariant essence of PT symmetry operator. Researchers have made great efforts to overcome these difficulties. In 2016, the first experimental demonstration of optical APT symmetry was realized by setting rapidly flying atoms between two long-lived atom spin waves,which can produce an effective dissipative coupling.[24]As a result,unidirectional reflectionless light transport was observed. In 2017, this method was introduced into waveguide coupling systems.[26]In 2018, dissipative coupling was implemented in a resistively coupled amplifying-LRC-resonator circuit.[27]In 2019, C.T.Chan et al. found that APT symmetric system can be employed for asymmetric mode switching,with an EP dynamically encircled.[28]
Different with wave systems, thermal system is an inherent dissipative one with energy exchange in an open environment. Thus, the coupling coefficient is imaginary spontaneously. Compared with the complicated post-processing in wave systems,APT symmetry can be realized in diffusive systems in a much easier way. In analogy with the positive and negative refraction indices in optics by introducing opposite convection flows in coupling diffusive systems,APT symmetry can be directly implemented(Fig.3(a)).[29]Figure 3 shows the two paths to construct PT/APT symmetry in wave systems and diffusive systems. With the aid of convection-diffusion physical process, heat can be dynamically stopped, or even flows against the moving background. The simplest way is to bridge the two opposite rotating rings through a thermal coupling layer. As shown in Figs.3(c)and 3(d),the parameters b and d are the thicknesses of the channels and the interlayer.R1and R2are the inner and outer radii(R1≈R2). v and Ω are the linear velocity and rotating angular velocity of the channels,respectively(Ω=v/R1).
3. Phase transition
According to the Fourier law, the temperature field of a convection-diffusion system is expressed as[42]


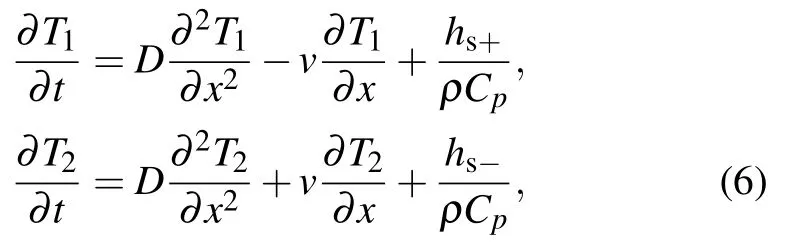


Fig.3. The realization of APT symmetry in diffusive systems.[29] (a) PT symmetry can be constructed by balancing gain and loss in wave systems. APT symmetry can be constructed by opposite convection flows in diffusive systems. (b)Temperature profiles can follow, hold, or even move against the background motion with the convection flow modulation. (c) and (d) 2D and 3D models of APT symmetry systems.(e)Eigenvalues in the case of uncoupling.
3.1. APT symmetric phase
Based on Eq.(6),the Hamiltonian of this APT symmetric system is established[29]


where S0=k2D+h. To generate the temperature profile exactly,we can combine the forward and backward solutions together as

It is clearly shown that the EP in parameter space is at the threshold as v increases to vEP=h/k.When v ≤vEP,the eigenfrequencies are pure imaginary and the eigenvectors in different channels have uniform modulus (A=B=1). Moreover,the eigenvectors satisfy the symmetry relation PTu±=?u±,and the system is under the exact APT symmetric regime with a static phase difference of θ =sin?1(v/vEP) and equal amplitudes in all channels. The temperature fields in different channels are
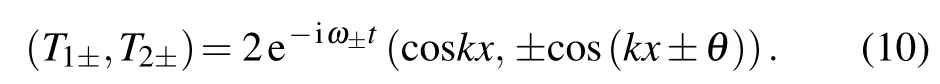
3.2. APT symmetry broken phase
If the flow velocity is continually increased and surpasses the EP,v >vEP,the eigenfrequencies become complex and the moduli of different channels are unequal. APT symmetry is broken with a time-varying phase difference and nonuniform distribution amplitudes. To facilitate the calculation process,we take a parameter ψ =cosh?1(v/vEP)and extract the real part of the eigenfrequencies out. The temperature field can be expressed as[29]

where j = 1,2,A1= AA2= Ae?ψB1= BB2= Beψ, and ?2??1=π/2. According to Eq. (11), the trajectory of the maximum points in the channels can be calculated as

with a phase difference

where

We take the material parameters as ρ = 103 kg/m3, Cp=103 J/(kg·K), κ = 100 W/(m·K), κi= 1 W/(m·K) and the structure parameters as b = 5 mm, d = 1 mm, R1=0.1 m, R2= 0.11 m in the finite element solver COMSOL Multiphysics? 5.3. Then the coupling coefficient can be deduced as h = 0.2 s?1, wave number k = 10 m?1, and diffusion coefficient D=10?4m2/s. Figure 4 shows the transient phase transition with the convection flow velocity increasing from below vEPto above vEP, the initial conditions are T =293.15+0.5y and T =293.15+0.5x,respectively.

Fig.4. Numerical calculation of transient phase evolution in the APT symmetric system.[29] (a)v <vEP. (b)v=vEP. (c)v >vEP.
3.3. Experiments
From above, we can predict the counterintuitive phenomenon of heat “stopping” with a static phase difference in the APT symmetry phase. When we increase the velocity of moving background at v >vEP, the temperature profile evolves in time. Going one step further, can we make the temperature profile move against the motion of background,or so-called negative thermal transport? In fact, if the channels are given different initial phases and temperature gradients, we can achieve a counter-flow of heat in the reverse direction.[29,43]
As shown in Fig.3(d), we can use two oppositely rotating motors to drive the two rings in contact,where the grease is painted evenly between them. Initial temperature gradients can be imposed through a copper plate with one side in hot water bath and the other side in cold water bath.
4. High-order EP in diffusive systems
4.1. Phase transition at high-order EP
Compared with the double-channel toy model with one EP, previous works in wave systems inspire us that multiple channels can have higher-order EPs, which will be illustrated in the following. Figure 5(a) shows a four-channel convection-diffusion-coupling structure with adjacent channels at the same but opposite velocities. From Eqs. (5)-(7),we can deduce the Hamiltonian of this system as[39]

The eigenvalues are solved, in Fig.5(b), from which we find that there are two EPs, denoted by A and B, as marked by green stars;

The eigenvectors are also derived as follows:[39]

Different from the double-channel toy model with only one second-order EP,we can obtain a third-order EP at A and the other second-order EP at B.

Fig.5. (a)A schematic of the 2D model with high-order EP in diffusive systems.[39] (b)Eigenvalues evolve with convection flow velocity,the EPs are marked with green stars. (c)Transient phase differences of adjacent channels in APT symmetric phase.


where ? =sin?1(v/vEP1). When v>vEP1, the APT symmetry is broken (PTu±/=?u±). In the APT symmetry broken phase,substituting ψ =cosh?1(v/vEP)into Eq.(15),we can obtain[39]Obviously,the temperature fields in the four channels are uneven with divergently evolving phase differences between adjacent channels.

4.2. Perturbation at high-order EP
A four-channel structure with high-order EP provides us more degrees of freedom to manipulate the temperature field.We have investigated how the perturbation impacts the APT system on the basis of high-order EP.Firstly,we assign all adjacent channels with opposite velocities at the high-order EP.Then,a perturbation Δv is added to the channels with different directions. The velocities of background motion in different channels are vEP1?Δv, ?vEP1?Δv, vEP1+Δv, and ?vEP1+Δv,respectively. The Hamiltonian containing this perturbation is[39]

By increasing the perturbation strength from zero, the initial high-order EP(Δv=0)splits into two second-order EPs.Simulation results show that when the perturbation strength is between the two EPs at the lowest branch, the whole system is still in APT symmetric phase, which displays a strong antiperturbation ability. After crossing this region, the phase differences of adjacent channels show periodic oscillations.
5. Conclusion and perspectives
In this paper,we give a short review on the APT symmetry and the phase transition at EP in diffusive systems(or thermal systems).First,we discuss the realization of APT symmetry in a double-channel diffusive system.Then,we analyze the phase transition of temperature profiles around the EP.Finally,we extend the double-channel toy model to a four-channel one for the exploration of high-order EP and various wavelike motion of heat flow. In a general conclusion,the phase difference of adjacent channels is always static,when the introduced flow velocity is below vEPor in the APT symmetry phase. Above vEPor in the APT symmetry broken phase, the phase begins to dynamically evolve in time. The APT symmetry in non-Hermitian diffusive systems provides us a unique platform to investigate the heat flow manipulation in a different way,such as thermal stealing,heat rotation and concentration,[44]or even topological non-Hermitian bulk-boundary state.[45-47]
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Nonlocal advantage of quantum coherence in a dephasing channel with memory?
- New DDSCR structure with high holding voltage for robust ESD applications?
- Nonlinear photoncurrent in transition metal dichalcogenide with warping term under illuminating of light?
- Modeling and analysis of car-following behavior considering backward-looking effect?
- DFT study of solvation of Li+/Na+in fluoroethylene carbonate/vinylene carbonate/ethylene sulfite solvents for lithium/sodium-based battery?
- Multi-layer structures including zigzag sculptured thin films for corrosion protection of AISI 304 stainless steel?

