Bidirectional highly-efficient quantum routing in a T-bulge-shaped waveguide?
Jia-Hao Zhang(張家豪), Da-Yong He(何大永), Gang-Yin Luo(羅剛銀) ,Bi-Dou Wang(王弼陡), and Jin-Song Huang(黃勁松)
1Engineering Industrialization Research Center,Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Suzhou 215011,China
2School of Information Engineering,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,China
Keywords: scattering theory,optical waveguide,quantum routing
1. Introduction
In a quantum network, photons are usually utilized as perfect information carriers to transmit quantum information over long distances,[1]and thus, it is of great importance to tailor and enhance the light-matter interactions to route efficiently these photons in different quantum channels. In the past decades, the strong field-matter interactions have be achieved by waveguide quantum electrodynamics (QED)systems,[2-7]and many interesting transport properties such as optical nonreciprocity and directional light amplification have still been exploited experimentally.[8-12]With the ideal platform, quantum routing of single photons is also investigated, where waveguide is utilized as the quantum channel,and the photon signal transport is controlled effectively via the strong light-matter interactions. Accordingly, numerous theoretical[13-26]and experimental[27-30]investigations on the quantum routing of single photons have been demonstrated in many waveguide-QED systems. For example,Zhou et al. examined the single-photon quantum routing properties in an Xshaped coupled-resonator waveguide(CRW),and showed that efficient routing can be implemented between two quantum channels with the help of a classical field.[13,14]By using the interferences of photons with the phase differences, a router with multi-output ports has also been investigated by Yan et al.[15]
However, in a multichannel quantum network, there exists a confine of low routing rate (no excess of 0.5) of single photons transmitted between different channels in many proposed routers,owing to extended assignments for the increasing ports. This could limit their potential applications, since the desired high routing capability of redirecting the incident photons into another channel is very essential for the efficient distributions of transmission signals. To enhance the interchannel transfer rate of routed photons, a T-shaped or an extended T-bulge-shaped waveguide[16,17]is proposed to achieve it via the radiation field modification from the boundary effect of the semi-infinite CRW,and an unidirectional high probability transfer only from the semi-infinite channel to the infinite one is realized. Thus, it is of considerable interest to design a high-efficiency router with bidirectional high transfer-rate routing.
Motivated by these considerations, we extend the previous single-atom coupled scheme and propose a two-atom coupled one to effectively perform bidirectional high-efficiency quantum routing of single photons in a T-bulge-shaped waveguide system, in which a three-level atom and an additional two-level atom are coupled. By applying the discretecoordinate scattering approach, the single-photon scattering amplitudes into three ports of the waveguide network are obtained analytically. Then,we examine how to efficiently control the quantum routing of the single photons by tuning the atom-resonator coupling strengths and the driving field. In contrast to the previous schemes[11,12]with a unidirectional high transfer-rate routing from the semi-infinite channel to the infinite channel,bidirectional highly-efficient routing between two channels can be achieved via the effective potential from the additional atom. In addition, compared to the T-shaped waveguide system with the bare boundary,multiple band zerotransmission with filtering function is exhibited in the scattering spectra,due to the multiple quantum interferences of these photons located in the boundary and the bulged resonators in the T-bulge-shaped waveguide system. Therefore, the proposed system can be utilized as a multi-function router.
2. Theoretical method
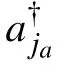

Fig.1. Schematic view of routing single photons in two channels formed by one infinite CRW and another semi-infinite CRW with N ?1 bulged resonators below the cross resonator. A three-level system,located at the crosspoint(ja =0, jb =N),is resonantly driven by a classical field Ω.Another two-level atom is located at ja = p. A single photon incoming from the left side of CRW-a is reflected, transmitted, or transferred to CRW-b.
When a photon is incident from one cavity of the CRWa, it propagates with the transmission probability Taor is reflected by the atoms along the channel-a with the reflection probability Ra,and it is also routed into CRW-b with the transfer rate Tb, with the help of a driving. The total Hamiltonian of the composite system consists of three parts


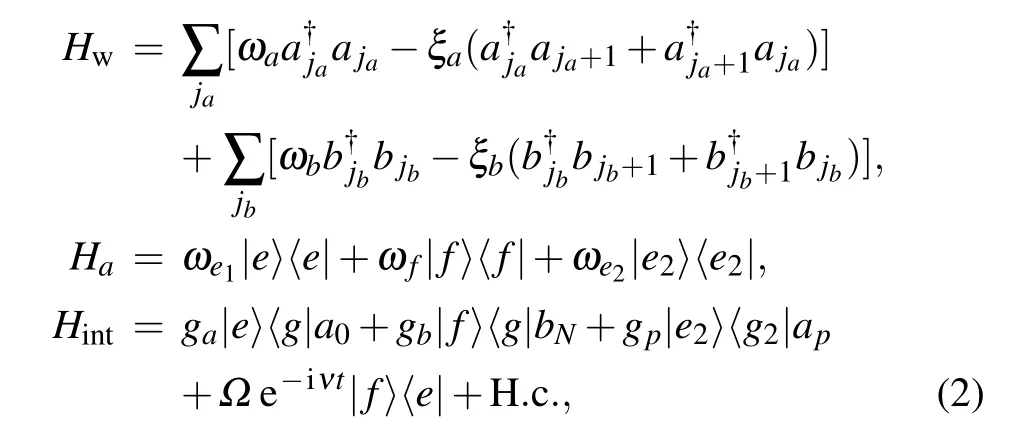

By performing a time-dependent unitary transformation Heff=U?HU ?iU??U/?t with the operator U = e?iνt|e〉〈e|,one gets the effective Hamiltonian under the rotating framework


Since the total number of excitations is conserved in this hybrid system,the eigenstate of Hamiltonian(1)is given by

where|/0a,/0b〉describes the waveguide vacuum state. α(ja)and β(jb)denote the probability amplitudes of photons in the ja-th cavity of CRW-a and jb-th cavity of CRW-b,respectively. ce(cf,c2)is the excitation amplitude of the atomic state|e〉(|f〉,|e2〉).
From the eigen-equation H|ψ〉=Ek|ψ〉,we get


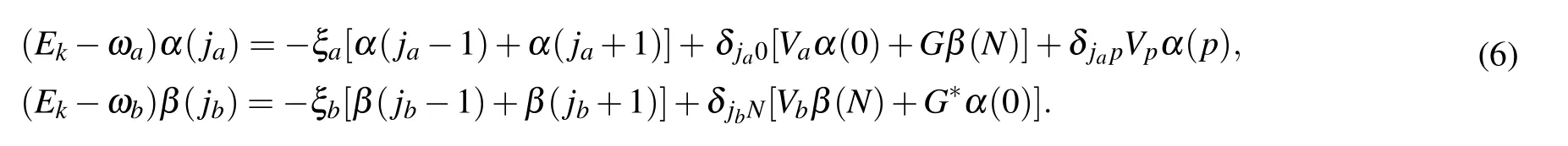
The coupling between the three-level atom and CRWs yields the energy-dependent effective potentials with strengths

and the dispersive coupling strength between two CRWs


3. Quantum routing properties of single photons
Considering the coupled T-bulge-shaped waveguide system as a two-channel quantum router, we thus focus on routing rate of single photons from one CRW to the other. As the structural symmetry is break by the boundary of the CRW-b,we examine two cases of incident waves incoming from both CRWs,respectively.
3.1. Single photons incident from the left side of CRW-a
We consider the first case of a single photon incoming from the left of CRW-a. There are two possible locations for the two-level atom,e.g.,in the right of CRW-a or in the above of CRW-b.We first discuss the former,as shown in Fig.1.The corresponding wave functions have the solutions
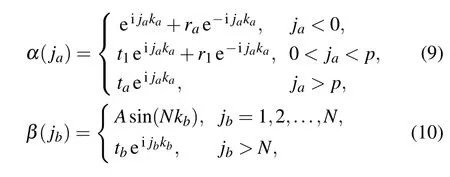
where r1and t1represent reflection and transmission amplitudes between the 0-th and p-th resonators in CRW-a,respectively. ra,ta,and tbare reflection,transmission in CRW-a,and transfer in CRW-b,respectively. A is an amplitude constant at the boundary cavity jb≤N.
Substituting Eqs.(9)and(10)into Eq.(6),after some algebra,we obtain the scattering amplitudes


Fig.2. (a)Transmission Ta (cyan solid line)and reflection Ra (pink dashed line)as a function of the momentum k for Ω =0 and gn=0. (b)Transmission Ta (cyan solid line),reflection Ra (pink dashed line),transfer Tb (black dash dotted line)for Ω =1 and gn =0. Transfer Tb for different gp: black dash dotted line for gp=0,red solid line for gp=0.4,and blue dashed line for gp=0.8,in(c)Ω =1.0,and(d)Ω =2.0,respectively. (e)Maximum transfer as a function of gp (red dashed line for Ω =1 and blue solid line for Ω =2). (f)Maximum transferas a function of Ω (red dashed line for gp =0.4, and blue solid line for gp =0.8). The other parameters are taken as ga =gb =1.0,ω0 ?ωe=2,ω0 ?ωf =1.6,ω0 ?ωe2=2,ξa=ξb=ξ0=1, p=4,and N=4,respectively.
In the system with three ports, scattering properties are engineered by the transmission Ta=|ta|2,reflection Ra=|ra|2,and transfer Tb=|tb|2. For simplicity,we assume ωa=ωb=ω0, ωe=ωe2, ξa=ξb=ξ0, and ka=kb=k in our discussion.In our numerical calculations,these parameters are taken as ω0?ωf=1.6, ω0?ωe=2, ω0?ωe2=2, ga=gb=1,and ξ0=1,and all the parameters are in units of the hopping coefficient ξ0. It is a reasonable selection, since the adopted parameters are close to the same order of magnitude in a circuit QED experimental system,[33,34]and the waveguide can be constructed by the superconducting transmission-line resonators.
As a contrast,we first research the single-atom case with gp=0,in which the scattering coefficients in Eq.(11)are reduced to the forms in Ref. [17], where only a driven threelevel atom is used to scatter the single photon. If the classical drive is turned off,it is easy to see from Eq.(11)that CRW-b is not coupled to CRW-a,and the incoming photon cannot be routed into another channel completely.In this case,the cyclic three-level atom degenerate to a two-level atom with a single excitation path, and serves as a perfect mirror to completely reflect the input photon at the resonance point, as shown in Fig.2(a). When the classical field is open, another output channel (CRW-b) is connected, and the conservation relation of the photon flow becomes|ta|2+|ra|2+|tb|2=1. With the help of the classical drive, the single photons are redirected from CRW-a into CRW-b,and the transfer Tbof no more than 0.5 is presented in Fig.2(b).

What is more interesting, we find that there exists 2N zero-value transmission in the scattering spectra for the N bulged resonators,except the point of k=0(υg=2ξasink=0) for no incident wave, which may result from the multiple quantum interferences among the standing waves scattered by the boundary and the bulged resonators. This may provide a potential application as a multi-wavelength filter. With such a device,the desired wavelengths in the output port are selected to drop,which can be used in designing multi-wavelength selectors,multiplexers,and other optical devices.
As a contrast, we also examine another case in which the two-level atom is placed at jb=m of the CRW-b. In the case,the atom interacts with m-th cavity mode in CRW-b,with the interaction Hamiltonian Hint=ga|e〉〈g|a0+gb|f〉〈g|bN+gm|e2〉〈g2|bm+Ω|e〉〈f|+H.c. Similar to the above process,after some algebra,we get the scattering amplitudes

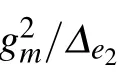

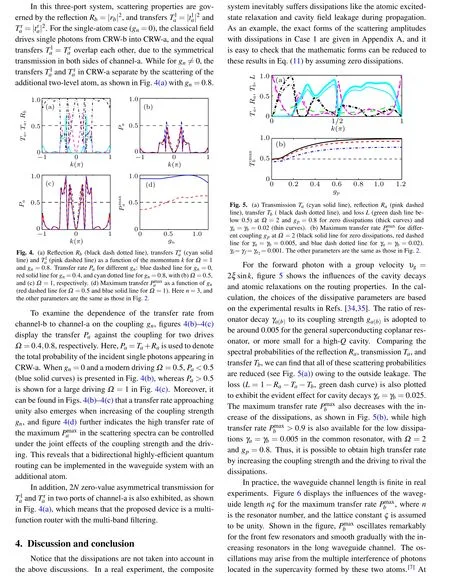
Fig.3. (a) Transmission Ta (cyan solid line), reflection Ra (pink dashed line), and transfer Tb (black dash dotted line) as a function of the momentum k.(b)Transfer Tb for different gm:blue dashed line for gm=0,red solid line for gm=0.4,and cyan dotted line for gm=0.8,with(b)Ω =1,and(c)Ω =2, respectively. (d) Maximum transfer as a function of gm (red dashed line for Ω =1 and blue solid line for Ω =2). Here m=4,and the other parameters are the same as those in Fig.2.
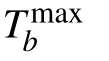
3.2. Single photons incident from the upward side of the CRW-b
We then discuss the case of a single photon incoming from the CRW-b, in which the two-level atom is located in ja=n of the CRW-a.
Using the similar process of the calculation in case 1,we get the scattering amplitudes




- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Nonlocal advantage of quantum coherence in a dephasing channel with memory?
- New DDSCR structure with high holding voltage for robust ESD applications?
- Nonlinear photoncurrent in transition metal dichalcogenide with warping term under illuminating of light?
- Modeling and analysis of car-following behavior considering backward-looking effect?
- DFT study of solvation of Li+/Na+in fluoroethylene carbonate/vinylene carbonate/ethylene sulfite solvents for lithium/sodium-based battery?
- Multi-layer structures including zigzag sculptured thin films for corrosion protection of AISI 304 stainless steel?

