Raman investigation of hydration structure of iodide and iodate?
Zhe Liu(劉喆), Hong-Liang Zhao(趙洪亮), Hong-Zhi Lang(郎鴻志), Ying Wang(王瑩), Zhan-Long Li(李占龍),Zhi-Wei Men(門志偉), Sheng-Han Wang(汪勝晗),?, and Cheng-Lin Sun(孫成林),?
Keywords: Raman spectroscopy,hydrogen bond,hydration structure
1. Introduction

In the liquid state, water molecules are connected with each other through complex hydrogen bonds(H bonds),forming clusters of varying sizes. These H bonds usually have a lifetime of only picoseconds and undergo dynamic breaking and re-bonding. At the same time, water molecules also rotate rapidly at a picosecond time scale, and hydrogen atoms also exhibit quantum effects, where the liquid water presents a dynamic equilibrium state. When ions are dissolved in water,they disturb the water environment and hydration by forming a hydration layer outside the ions with surrounding water molecules. Then, both anions and cations will affect the structure of the hydration layer with the increase of ion concentration. Cations may lead to the aggregation of ions, and the increase of anions affects the number of water molecules in the hydration layer. It is generally believed that the influence of anions on the H bond structure in the hydration layer is more obvious than that of cations, and anions mainly affect the water molecules in the first hydration layer.[10–13]The number of water molecules in the hydration layer varies from 5 to 50 due to the difference in ionic electronegativity, size,polarity,etc. The signal-to-noise ratio and accuracy of experimental methods are stringent due to the complex structure of the H bond network in liquid water and the uncertainties of the interaction between anions and water molecules. The theoretical and experimental methods that can be used to investigate the structure of water molecules in liquid water mainly include ab initio molecular dynamics simulations,[14]neutron scattering,[15,16]vibration spectroscopy,[17]etc. The Raman spectroscopy of water has high accuracy, making it suitable for studying the interactions between halogen ions and water molecules. Moreover, there are also notable differences between infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy in the field of local structure research of water,[18,19]From the mechanism, the infrared spectroscopy shows dipole moment transition of the molecule, while Raman spectroscopy shows the change of molecular polarizability. From the experimental perspective, as the Raman spectroscopy is more sensitive to the movement of free OH groups,[20]it can be used to study the local H bond structure of water directly. However, the infrared absorption coefficient[21]should be introduced when using infrared spectroscopy, which not only makes the relevant research complicated,but it also introduces errors. Moreover,Raman spectroscopy has the characteristics of low cost,convenient operation, and high signal-to-noise ratio. Therefore, Raman spectroscopy measurement has great advantages in studying the local H bond structure of water compared with other research methods.


2. Experimental setup
The Raman spectra of the aqueous solution of potassium iodate and potassium iodide were measured using a Renishaw InVia micro-confocal Raman spectrometer at room temperature(20?C)and ambient pressure(1.0×105Pa). The 514.5 nm Ar+laser source with an output power of 4 mW was focused on the sample. The 1200 lines/mm grating was used in the experiment, which produced a spectral resolution of 4 cm?1. Then the spectrum was obtained using a 20×magnification objective lens(LEICA DMLM 0.12 NA).
The samples of potassium iodate and potassium iodide,analytically pure(>99.5%v/v%),provided by Beijing Chemical Works,were used without further purification. The potassium iodide-water and potassium iodate-water binary solution were prepared with different concentrations 0.05, 0.5, 1, 1.5,2 mol/L and 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 mol/L respectively by adding certain amount (0.415, 4.15, 8.3, 12.45, 16.6 g potassium iodide and 0.107, 0.535, 1.07, 3.21, 5.35 g potassium iodate) of solute into 50 mL water. The binary solution was pipetted into a glass capillary(inner diameter is 0.9–1.1 mm,wall thickness is 0.10–0.15 mm),which was tested by placing it on the stage.
3. Results and discussion
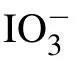
Table 1. The FWHM and Raman shift after deconvolution of I?and at the concentration of 0.05 mol/L(unit:cm?1).
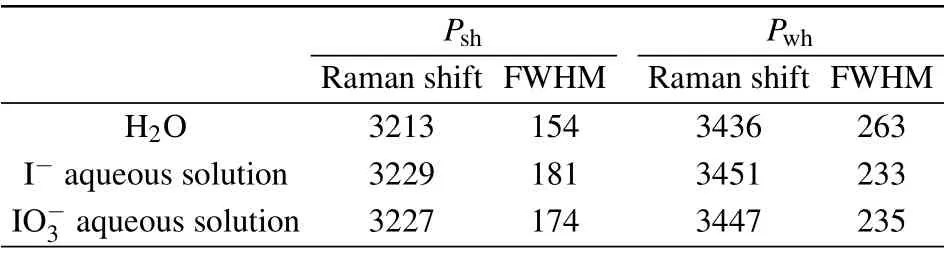
Table 1. The FWHM and Raman shift after deconvolution of I?and at the concentration of 0.05 mol/L(unit:cm?1).
Psh Pwh Raman shift FWHM Raman shift FWHM H2O 3213 154 3436 263 I?aqueous solution 3229 181 3451 233 IO?3 aqueous solution 3227 174 3447 235
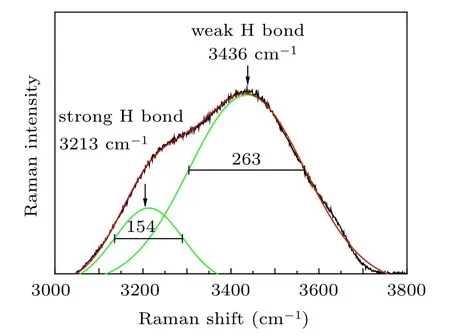
Fig.1. Raman spectrum of pure water with the deconvolution results being curved in the green line.
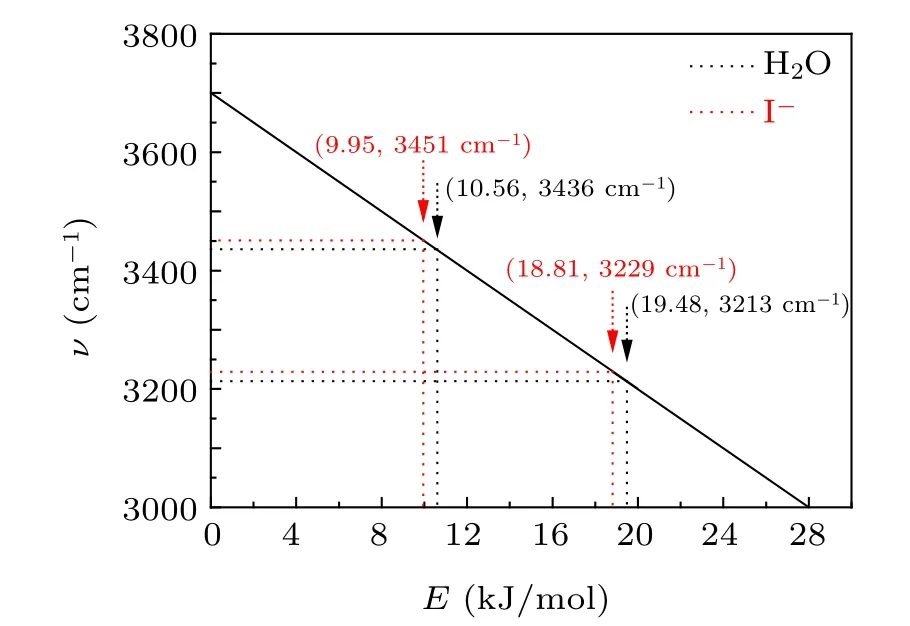
Fig.2. The relationship between hydrogen bond energy and OH stretching vibration frequency in liquid water.
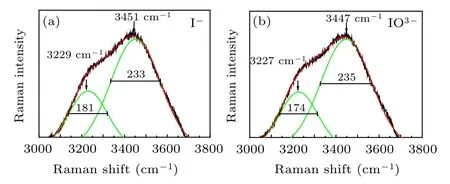
Fig.3. Deconvoluted Raman spectra of 0.05 mol/L I?(a)and (b)aqueous solution.
To gain insights into the relationship between solution concentration and H bond structure, the frequency shift of the Pwhand Pshof I?aqueous solution was analyzed. Compared with pure water, both Pwhand Pshmove towards high wavenumber,indicating that the OH stretching vibration under the strong H bond is enhanced,corresponding to the weakening of the H bond. The change of H bond strength is mainly caused by the addition of I?ions,which destroys the original H bond structure by forming a new interaction between anionic water molecules,namely the hydration layer. Therefore,the interaction force between anions and water molecules is smaller than the original interaction between water molecules,thus weakening the H bond.[30,31]According to the previous theoretical calculation, at this concentration, the number of water molecules in iodide’s first hydration layer is 5–6,[13,32]as shown in Fig.4. Using the corresponding relationship between OH vibration frequency and H bond strength as shown in Fig.2, it can be concluded that the H bond strengths corresponding to the two peaks in I?aqueous solution at 0.05 are 18.81 kJ/mol and 9.95 kJ/mol,respectively,which are weaker than that of pure water.
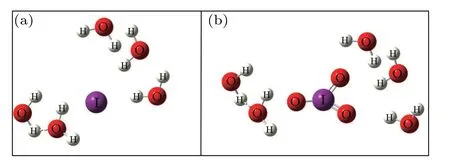
Fig.4. Schematic first hydration layer of I?at 0.05 mol/L.
Then,the variation of FWHM of I?ions aqueous is studied. The narrowing of the Pwhis mainly caused by the weakening of the H bond, which agrees well with the inference above.[33,34]The frequency shift of Psh, shifting to the right,is consistent with the trend of the Pwh, indicating that the H bond is weakened. However,the widening of the Pshindicates that the H bond is strengthened,which does not conform to the inference of the H bond weakening above. The main reason could be the existence of the H-down structure of the H bond in the hydration layer,[35]as shown in Fig.5. The H-down structure comes from the bilayer structure of water, which is composed of an H-up structure and an H-down structure.[36]The orientation of the H-up structure is upwards,while the orientation of the H-down structure is towards bulk water.Generally speaking,the OH stretching band depends not only on the influence of the H bond on OH stretching vibration, but also on the molecular coupling, which is mainly the intramolecular, intermolecular vibration coupling, and Fermi resonance.Both intramolecular and intermolecular coupling can enhance OH stretching vibration on water molecule surface,and intermolecular coupling is stronger than intramolecular coupling.The intramolecular coupling results in a bimodal structure of water, while the intermolecular coupling causes a red shift in OH stretching.[37–39]After the formation of the hydration bilayer, the central ion acts on the orientation of H bonds, resulting in the enhancement of vibration coupling and the formation of H-down structure, which widens the Psh.[40]This unique structure causes anions to tend to stay in the interfacial region. According to the actual situation of the ocean,the H-down structure makes the I?tend to stay in the boundary layer of the ocean. Since the H-down structure in the water corresponds to the H-down structure formed at the interface,the result is helpful to analyze the iodine transfer process in the marine interfacial layer.
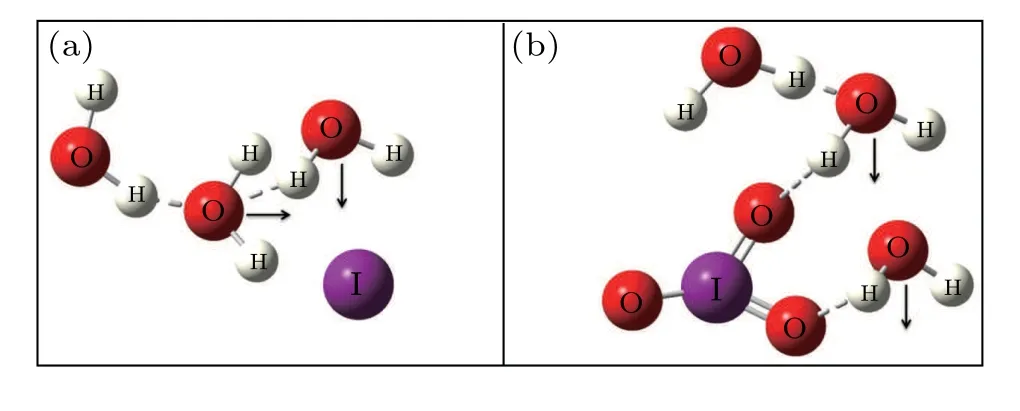
Fig.5. The H-down structure of(a)I?and(b).
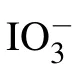
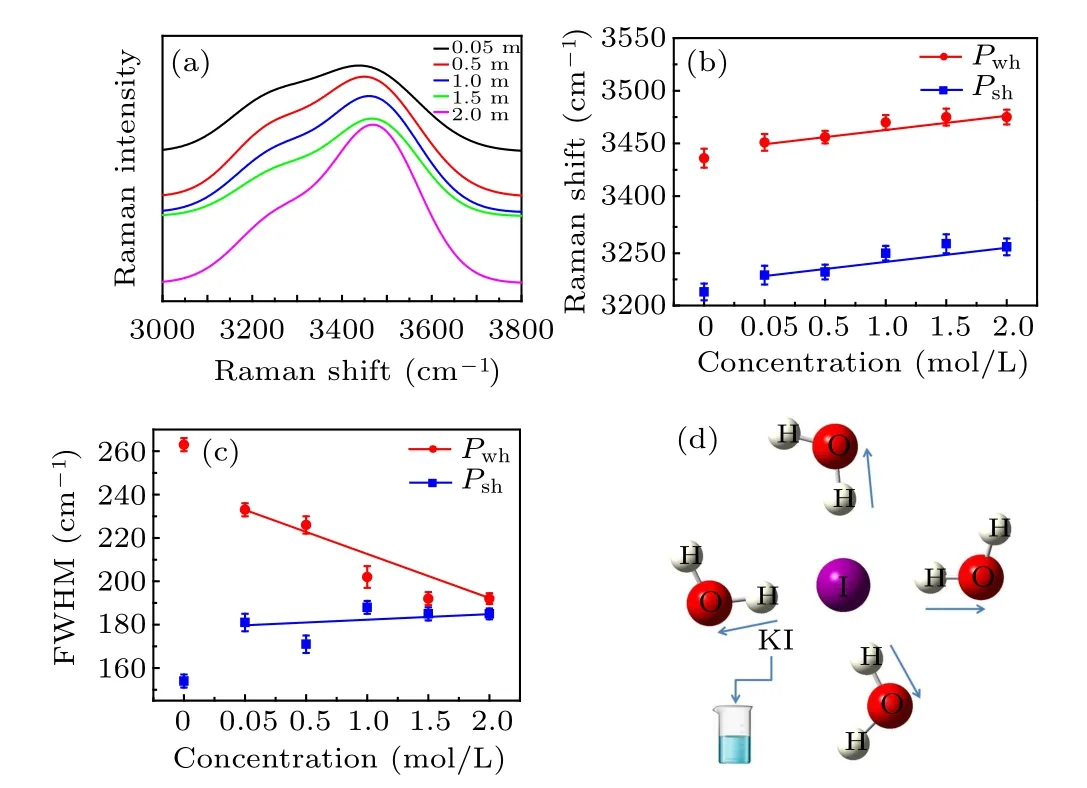
Fig.6. (a)The spectrum of I?aqueous solution at different concentrations and (b) the corresponding frequency shift trend, (c) the change trend of FWHM,(d)schematic molecular interaction.
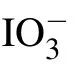
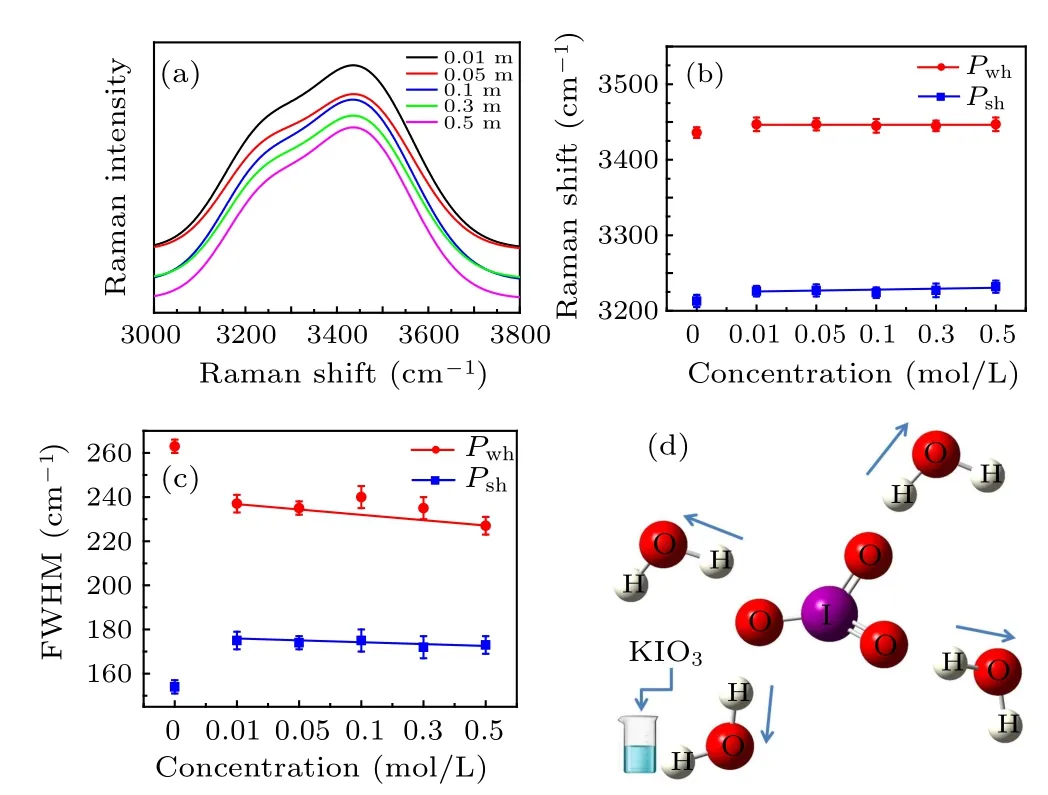
Fig.7. (a) The spectrum of aqueous solution at different concentrations and (b) the corresponding frequency shift trend, (c) the change trend of FWHM,(d)schematic molecular interaction.
4. Conclusion

- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Quantum annealing for semi-supervised learning
- Taking tomographic measurements for photonic qubits 88 ns before they are created*
- First principles study of behavior of helium at Fe(110)–graphene interface?
- Instability of single-walled carbon nanotubes conveying Jeffrey fluid?
- Relationship between manifold smoothness and adversarial vulnerability in deep learning with local errors?
- Weak-focused acoustic vortex generated by a focused ring array of planar transducers and its application in large-scale rotational object manipulation?