High-precision three-dimensional Rydberg atom localization in a four-level atomic system*
Hengfei Zhang(張恒飛), Jinpeng Yuan(元晉鵬),?, Lirong Wang(汪麗蓉),?,Liantuan Xiao(肖連團(tuán)), and Suo-tang Jia(賈鎖堂)
1State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices,Institute of Laser Spectroscopy,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China
2Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China
Keywords: Rydberg atom,three-dimensional localization,standing-wave field
1. Introduction
Rydberg atoms are high-excited atoms with large principal quantum numbers, which have attracted considerable focus recently for the demonstrated remarkable properties.[1]The large size and long radiative lifetime make the Rydberg quantum system have a long coherence time.[2]The Rydberg atom is sensitive to external electric field since the huge polarizability.[3]In addition, the strong long-range dipole–dipole interactions lead to the investigation of dipole blockade effects.[4]Based on these peculiar properties, Rydberg atoms are greatly applied in ultra-cold plasmas,[5]many-body physics,[6]quantum information,[7]quantum computing,[8]and microwave field measurements.[9]
In the applications based on Rydberg atoms,the research of localization provides the position information of the Rydberg atom in spatial coordinates. Over the past few decades,the high-precision atom localization has been used in trapping and cooling of atoms,[10]atom nanolithography,[11,12]coherent patterning of matter waves[13]and Bose–Einstein condensation.[14]The proposal to use quantum interference and atomic coherence effect has already been applied for atom localization in one-dimensional (1D)[15,16]and twodimensional(2D)space.[17,18]Until recent years,research interest transfers to three-dimensional(3D)space. Several highprecision 3D atom localization schemes have been proposed by measuring the probe absorption,spontaneous emission,and Kerr nonlinearity.[19–24]
Even though there are many efficient schemes for atom localization, until now only a few Rydberg atom localization have been reported.[25]The large size of the Rydberg atom makes it a good candidate for studying the quantum coherence phenomena. For achieving the high-precision localization of a Rydberg atom,an effective scheme is needed.Recently,an experiment realization of the Rydberg atom based on a four-level atomic system in Ref.[26]attracts our attention. This system utilizes Rydberg level as the uppermost level and composed of two V- and Ξ-type electromagnetically induced transparency(EIT)systems,provides a novel configuration for studying the localization of Rydberg atom. Compared with the V- and Ξtype atomic system of atom localization schemes, this fourlevel configuration increases the controllability of the experiment and produces more fantastic results.
In this work, a four-level atomic system is employed for realizing the high-precision 3D Rydberg atom localization.Three pairs of orthogonal standing-wave fields aligned respectively in the x,y,and z directions couple the same energy level transition of the Rydberg atom. Due to the interaction between the atom and fields, the 3D localization of a Rydberg atom is achieved by measuring the absorption of probe field,which is much more convenient to realize in experiment.In result,the maximum probability of finding the Rydberg atom is achieved as 100%in the sub-wavelength region. This scheme provides an effective way to realize the high-precision 3D Rydberg atom localization in the experiment.
2. Theoretical model
Taking cold85Rb atoms for the experimental implementation,a four-level atomic system involving a Rydberg state is considered as shown in Fig. 1, where level |g〉 is the ground state of 5S1/2, levels |e〉 and |s〉 denote the excited states of 5P3/2and 5P1/2and the level |r〉 is the 44D5/2Rydberg state. The decay rates of these states are Γg=0 MHz, Γe=2π×6.1 MHz, Γs=2π×5.9 MHz and Γr=2π×0.3 MHz,respectively.[27]A weak probe field with Rabi-frequency ?pdrives the|g〉→|e〉transition. The strong switching and control fields with Rabi frequencies ?sand ?cact on the transitions of |g〉→|s〉 and |e〉→|r〉, respectively. All three laser fields move along the z direction. Here, we employ three orthogonal standing-wave fields to couple the same transition of|g〉→|s〉,i.e.,
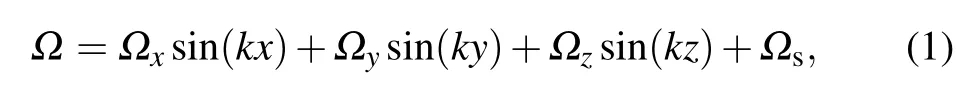
where k is the corresponding laser field wave vector, ?x, ?yand ?zare the Rabi frequencies of standing-wave fields propagating along x, y and z directions, respectively. We assume that the atom moves along the z direction,and passes through the intersecting region of the three orthogonal standing-wave fields in 3D space. As a consequence,the interaction between the atom and standing-wave fields is spatially dependent in the 3D space.
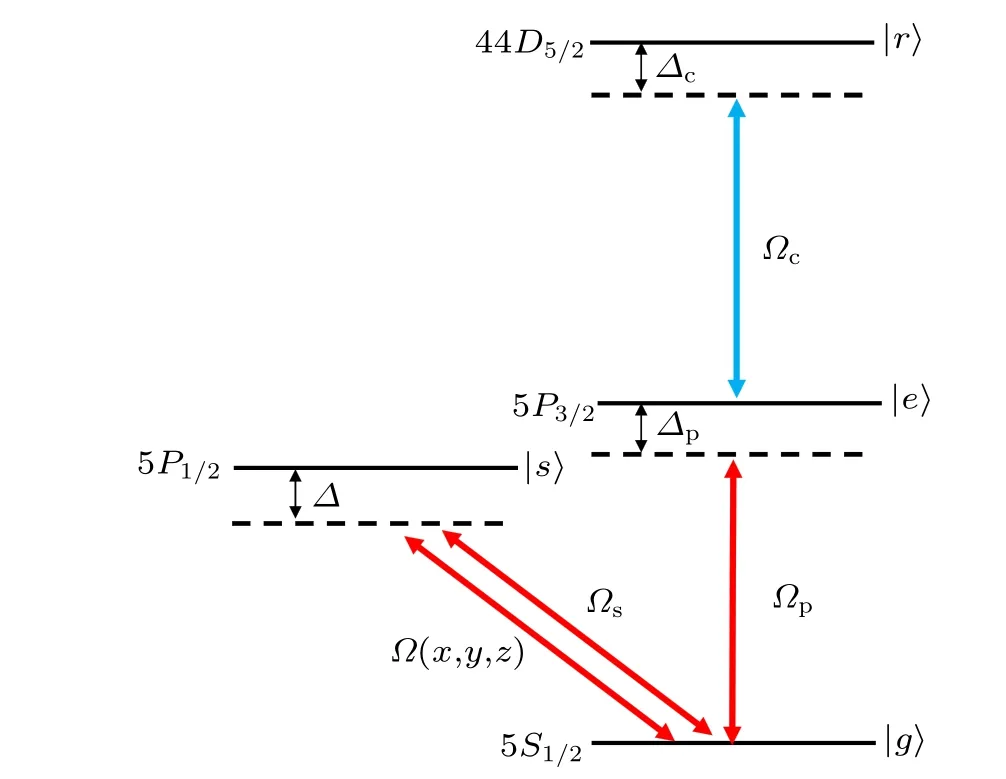
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of a four-level 85Rb atomic system. This system composes of two EIT configurations of V- and Ξ-type, which share the same probe field. The level|g〉is the 5S1/2 ground state,levels|e〉and|s〉are the 5P3/2 and 5P1/2 excited states and the level|r〉is the 44D5/2 Rydberg state.
Applying the rotating-wave and electric dipole approximation, the interaction picture Hamiltonian for this system is given by(ˉh=1)
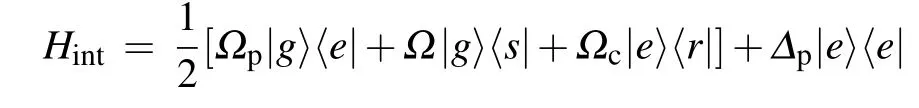
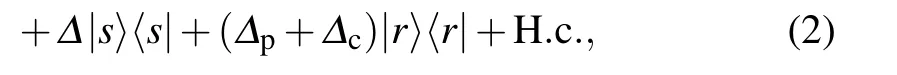
where H.c. represents the Hermitian conjugation, and ?p, ?,?cdenote the corresponding laser frequency detunings.
The observable in this scheme is the response of the atoms to applied laser fields,which is described by susceptibility of the weak probe field. The susceptibility is determined by the coherence between levels|g〉and|e〉and can be written as
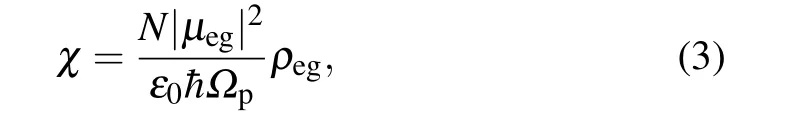
where N is the atomic density, ε0is the permittivity of free space, μegand ρegare the dipole momentum and density matrix element, respectively. According to Eq. (3), the density matrix element ρegneeds to be calculated for tracing the atomic response of the system to external fields. The dynamics of the system by the density matrix formalism are described as[28]
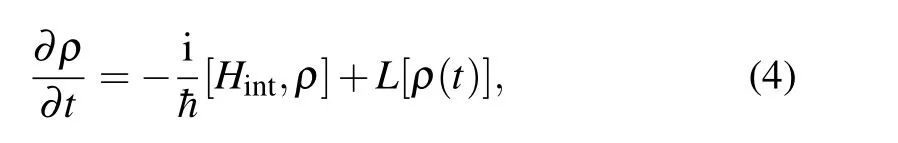
where the Lindblad form of Liouvillian matrix L[ρ(t)]describing the relaxation by spontaneous decay is expressed as

Thus, the motion equations for the density-matrix elements are given by


The imaginary part of the susceptibility can be used to express the absorption of the probe laser field, which reflects the atomic position distribution probability in 3D space when the atom interacts with the three standing-wave fields. Probe absorption can localize the atom at a particular position in subwavelength space under the proper parameters. Therefore,the 3D atom position information can be obtained with the measurement of probe absorption Im(χ).
3. Results and discussion



Fig.3. Isosurfaces of the probe absorption Im(χ)=0.1 versus positions(kx,ky,kz)for different traveling-wave fields Rabi frequencies ?s. (a)?s=1Γe;(b)?s=1.5Γe;(c)?s=2Γe. The other parameters are the same as Fig.2(d).

Fig.4. Isosurfaces of the probe absorption Im(χ)=0.1 versus positions(kx,ky,kz)for different combinations of the two frequency detunings(?,?c). (a)(?,?c)=(3Γe,1Γe);(b)(?,?c)=(1Γe,2Γe);(c)(?,?c)=(0.25Γe,2.5Γe). (d)–(f)The views of x–y,y–z,and z–x of the minimum localization pattern in Fig.4(c),respectively. The other parameters are the same as Fig.3(c).
To locate the Rydberg atom with a higher probability, a traveling-wave field ?sis coupled to the transition of |g〉→|s〉. Figure 3 investigates the influence of the switching field Rabi frequency ?son the 3D Rydberg atom localization.Here, we choose ?p=8Γefor showing clearly the variation trend of the localization patterns. As shown in Fig.3(a)with?s=1Γe,the probe absorption displays a sphere pattern with small diameter in the subspace(?x,?y,?z)and a sphere pattern with large diameter in the subspace (x,y,z). This result indicates that the switching field ?smakes the Rydberg atom localization precision different in the two subspaces. In Fig.3(b),the sphere volume becomes smaller in the subspace(?x,?y,?z) while becomes larger in the subspace (x,y,z)when ?s=1.5Γe. More interestingly,with further increasing the switching field to ?s=2Γe, the sphere disappears in the subspace(?x,?y,?z)and there only exists one large sphere in the subspace(x,y,z). This result suggests that we can achieve a 100% probability localization of the Rydberg atom in subwavelength region,but the localization precision is low owed to the large volume of the sphere.
In order to improve the precision of the Rydberg atom localization, the influence of two laser frequency detunings(?,?c) is studied. Figure 4 illustrates the effect of two frequency detunings (?,?c) on the 3D Rydberg atom localization. As we can see from Fig. 4(a), the sphere in the subspace (?x,?y,?z) appears again when (?,?c)=(3Γe,1Γe).In Fig. 4(b), the sphere in the subspace (?x,?y,?z) disappears and the other in the subspace (x,y,z) becomes smaller than that in Fig.3(c)when(?,?c)=(1Γe,2Γe). We find that in the subspace (x,y,z), the sphere becomes smaller with decrease in ?and increase in ?c. The smallest sphere volume is achieved in Fig.4(c)with(?,?c)=(0.25Γe,2.5Γe),which indicates that the 3D Rydberg atom localization precision is improved significantly. To further evaluate the precision in determination of the atom position by this scheme,Figs.4(d)–4(f)show the views of x–y, y–z, and z–x of the localization pattern in Fig. 4(c), respectively. The spatial precision is about 0.031λ×0.031λ×0.031λ under the condition of probe absorption Im(χ)=0.1.

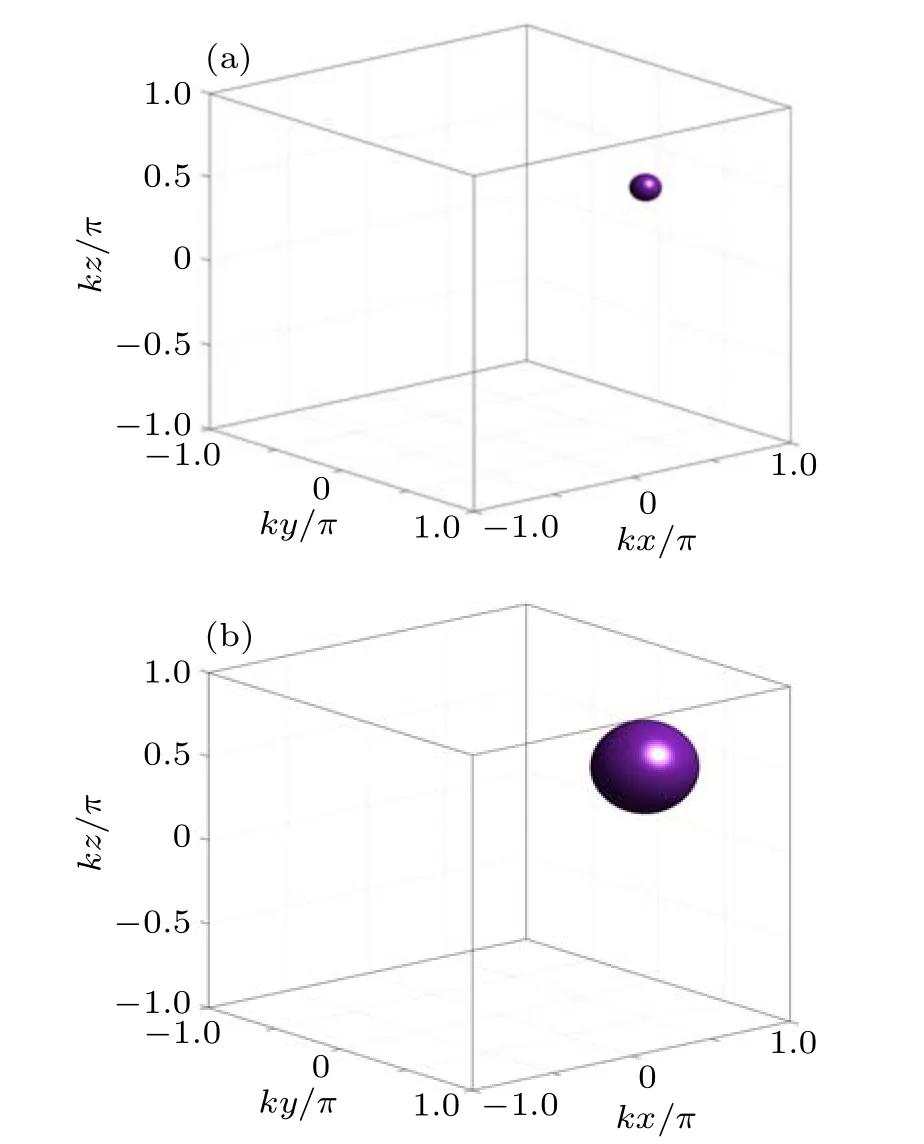
Fig. 5. Isosurfaces of the probe absorption Im(χ)=0.1 versus positions (kx,ky,kz) for different Rabi frequencies ?c. (a) ?c =4Γe; (b)?c=2Γe. The other parameters are the same as Fig.4(c).
4. Conclusion
In summary, we have realized a high-precision 3D Rydberg atom localization with the measurement of a weak probe field spatial absorption in a four-level atomic system. The numerical simulation results indicate that the 3D Rydberg atom localization precision can be improved significantly by adjusting the Rabi frequency and detuning of laser fields. More importantly,we realize a 100%localization probability of the Rydberg atom in a specific position, and the spatial precision is about 0.031λ×0.031λ×0.031λ with optimal parameters.By taking cold85Rb atoms as the candidate to implement,this work demonstrates the possibility for 3D atom localization of the Rydberg atom,which further promotes the applications of Rydberg atoms in the areas of quantum information and manybody physics.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Process modeling gas atomization of close-coupled ring-hole nozzle for 316L stainless steel powder production*
- A 532 nm molecular iodine optical frequency standard based on modulation transfer spectroscopy*
- High-throughput identification of one-dimensional atomic wires and first principles calculations of their electronic states*
- Effect of tellurium(Te4+)irradiation on microstructure and associated irradiation-induced hardening*
- Effect of helium concentration on irradiation damage of Fe-ion irradiated SIMP steel at 300 °C and 450 °C*
- Optical spectroscopy study of damage evolution in 6H-SiC by H+2 implantation*

