Northern pig-tailed macaques (Macaca leonina)infected with SARS-CoV-2 show rapid viral clearance and persistent immune response
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), has become an unprecedented global health emergency.At present, SARS-CoV-2-infected nonhuman primates are considered the gold standard animal model for COVID-19 research. Here, we showed that northern pig-tailed macaques(Macaca leonina, NPMs) supported SARS-CoV-2 replication.Furthermore, compared with rhesus macaques, NPMs showed rapid viral clearance in lung tissues, nose swabs,throat swabs, and rectal swabs, which may be due to higher expression of interferon (IFN)-α in lung tissue. However, the rapid viral clearance was not associated with good outcome.In the second week post infection, NPMs developed persistent or even more severe inflammation and body injury compared with rhesus macaques. These results suggest that viral clearance may have no relationship with COVID-19 progression and SARS-CoV-2-infected NPMs could be considered as a critically ill animal model in COVID-19 research.
Animal models are essential for studies on the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the evaluation and development of potential antiviral treatments or vaccines. SARS-CoV-2-infected nonhuman primates (NHPs) are considered good models for COVID-19 research. SARS-CoV-2 infection has been successfully established in various NHPs, including rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta, RMs), crab-eating macaques (Macacafascicularis), common marmosets(Callithrixjacchus), and green monkeys (Chlorocebus sabaeus). At present, RMs (3-5 years old) are regarded as the most suitable animal model for COVID-19 research(Munster et al., 2020; Shan et al., 2020; Song et al., 2021;Zheng et al., 2020) due to their similarities with SARS-CoV-2-infected patients in regard to clinical features, virus replication,and pathological changes (Lu et al., 2020). However, only mild clinical manifestations and temporary cytokine increases have been observed in RMs (Munster et al., 2020; Song et al.,2020). Previously, we confirmed that northern pig-tailed macaques (Macaca leonina, NPMs) are a suitable animal model for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)research (Pang et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018). Different from RMs, NPMs can be infected with HIV-1 and viral reservoirs can formin vivo(Pang et al., 2017). Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate whether NPMs could be infected by SARS-CoV-2 and used as an animal model for COVID-19 research.
Four healthy NPMs (male, 6-8 kg, 5 years old), named 15 207,15 209, 15 213, and 15 223, were sourced from the Kunming Primate Research Center, Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ),Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Animal feeding and experiments were performed at the Kunming National High-Level Biosafety Research Center for Non-Human Primates,Center for Biosafety Mega-Science, KIZ, CAS. All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of KIZ, CAS (Approval No.: IACUC20005). All macaques were intratracheally inoculated with 1×107TCID50SARS-CoV-2 in 2 mL volume via bronchoscope. Nose, throat,and rectal swabs were collected at 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15 days post infection (dpi) for viral RNA detection. Venous blood was drawn into vacuum tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and vacuum blood collection tubes (serum) for routine blood tests and serum biochemistry, respectively. Two NPMs (15 207 and 15 223)were euthanized by Zoletil 50 at 7 dpi and the other two were euthanized at 15 dpi. Lung samples (100-150 mg) from the middle and lower sections of all seven lung lobes were collected after left heart perfusion with precooled phosphatebuffered saline (PBS). The methods used for viral RNA detection, immunofluorescence, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are described in our previous study (Song et al., 2020). In addition, the characteristics of four RMs (15 011, 15 335, 15 333, and 15 341), used to compare the differences between NPMs and RMs during SARS-CoV-2 infection, were reported in our previous study(Song et al., 2020).
Viral RNA in the swabs remained positive from 1 to 15 dpi in RMs, whereas SARS-CoV-2 infection in the NPMs was negative in all nose and throat swabs from 3 to 15 dpi(Figure 1A). In addition, the viral loads in lung tissue and the counts of SARS-CoV-2+ lung lobes in RMs were greater than that in NPMs at 15 dpi (Figure 1B). Therefore, compared with RMs, NPMs showed rapid clearance of SARS-CoV-2 in the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
Type I interferons (IFNs) show broad spectrum antiviral activities by inducing several IFN-stimulated genes that encode a variety of antiviral effectors (Schoggins & Rice,2011). Clinically, type I IFNs have been approved in the treatment of certain cancers, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections. Furthermore, type I IFNs show potent anti-SARSCoV-2 activities in cultured cellsin vitro(Mantlo et al., 2020),and severe SARS-CoV-2-infected patients show impaired type I IFN activity and inflammatory responses (Hadjadj et al.,2020). In this study, the levels of IFN-α+, IL-1β+, and IL-6+cells in the lungs were analyzed by immunofluorescence(Figure 1C). Results showed no significant differences in the levels of IL-1β+ and IL-6+ cells in the lungs of NPMs and RMs.However, compared with RMs, NPMs showed a higher percentage of IFN-α+ cells in lung tissue at 7 dpi (P=0.006 7).Therefore, the rapid clearance of SARS-CoV-2 in NPMs may be due to the rapid and active expression of IFN-α in lung tissue during infection.
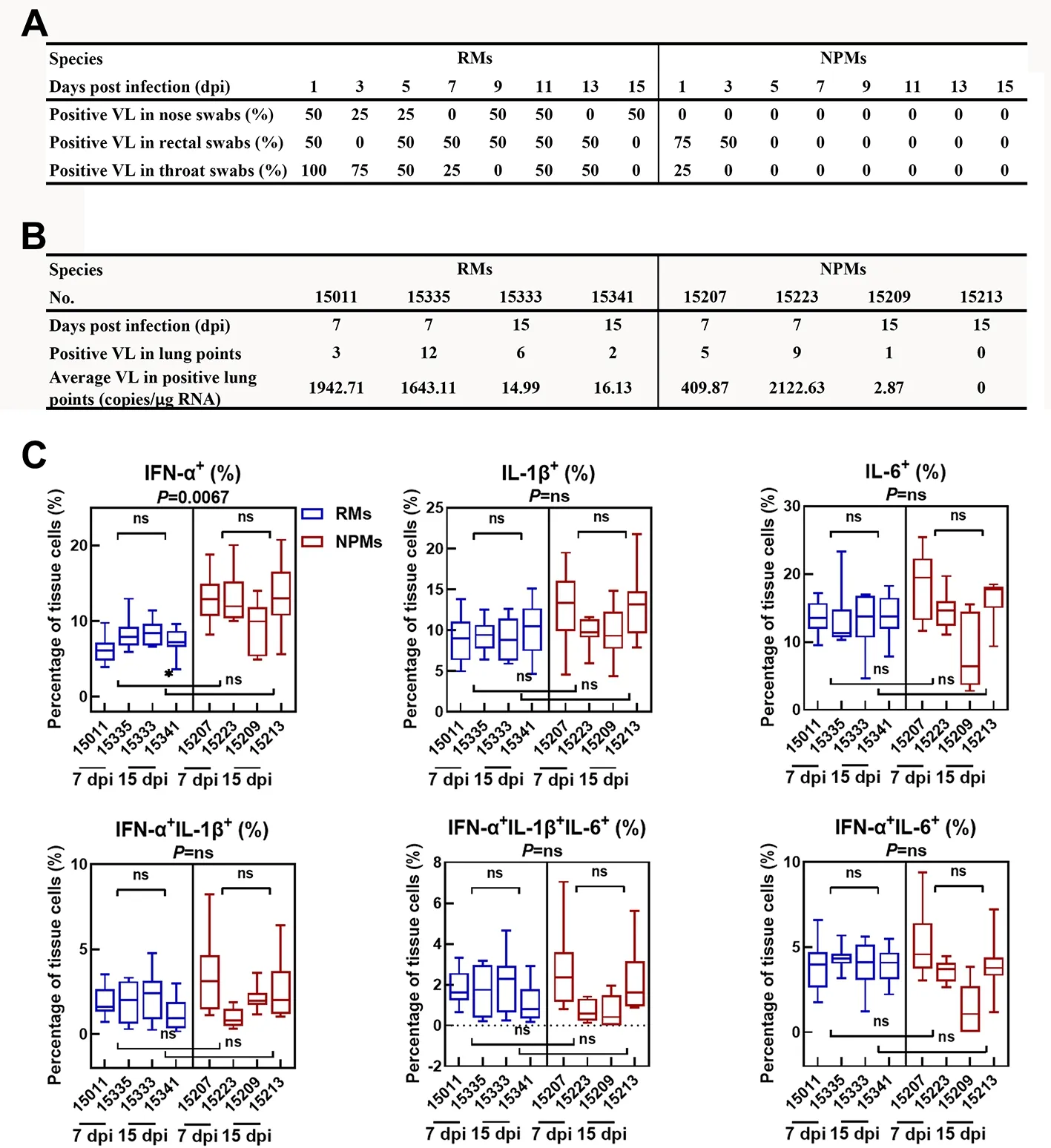
Figure 1 Clearance of SARS-CoV-2 in NPMs
The clinical manifestations in macaques (15 209 and 15 213)were monitored until 15 dpi. The temperatures of 15 209 and 15 213 remained normal during the first week post infection(1 wpi) but increased markedly at 2 wpi (Figure 2A). The concentrations of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) increased significantly in all four NPMs at 7 dpi and in two animals (15 209 and 15 213) at 15 dpi. In addition, the level of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased substantially until 11 dpi in 15 209 and 15 213 (Figure 2B). Furthermore, an obvious increase in immune cells in peripheral blood, including white blood cells, monocytes, and neutrophils, was also observed at 2 wpi (Figure 2C). Compared with RMs (Song et al., 2020),NPMs showed an increase in body temperature, abnormal hepatic and renal function, and enhanced neutrophil and monocyte counts at 2 wpi. These results strongly imply that total body injury and systematic immune responses remained persistent or even more serious in NPMs at 2 wpi. Afterwards,the immune states of lung tissues were analyzed by detecting the levels of cytokines and immune cells in lung tissues. In our previous study, we confirmed that cytokine concentrations and neutrophil counts decreased significantly in young RMs at 15 dpi compared with that at 7 dpi (Song et al., 2020). However,in the lung tissues of NPMs, the concentrations of IL-6, IL-1β,IL-23, and TNF-α increased markedly at 15 dpi compared with that at 7 dpi (Figure 1D). In addition, the percentages of CD11b+ cells increased significantly in NPMs at 15 dpi compared with that at 7 dpi (P=0.024 4) (Figure 1E).Therefore, despite the viral loads in lung tissues and swabs predominantly remaining negative at 15 dpi, the NPMs showed uncontrolled enhanced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neutrophils in their lung tissues. This strongly implies the occurrence of cytokine storm syndrome (CCS) in NPMs during SARS-CoV-2 infection. CSS is an uncontrolled and dysfunctional immune response involving the continual activation and expansion of immune cells, which secrete large amounts of cytokines, thus causing a cytokine storm (Shimizu,2019). Approximately 40% of patients with CCS show pulmonary manifestations, including cough, dyspnea, and respiratory failure (Karras et al., 2004), especially in cases triggered by respiratory viruses. In addition, pulmonary infiltrates are found in ~30% of the patients with CCS (Ohta et al., 1994). CSS has also been reported in several viral infections, including influenza H5N1 (Kalaiyarasu et al., 2016),influenza H1N1 (Woo et al., 2010), SARS, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) (Lau et al., 2013). By analyzing the concentrations of cytokines during SARS-CoV-2 infection,several studies have confirmed that CCS is directly correlated with lung injury, multiorgan failure, and unfavorable prognosis of severe COVID-19 (Chen et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2020).Therefore, the appearance of CCS during SARS-CoV-2 infection is indicative of poor prognosis in NPMs.
In summary, we confirmed that NPMs infected with SARSCoV-2 are a suitable animal model for COVID-19 research due to their sensitivity to viral infection and typical immune changes during infection. Although the NPMs showed rapid viral clearance in lung tissues and swabs, an uncontrolled and dysfunctional immune response appeared at 2 wpi. Therefore,compared with RMs, NPMs could be regarded as a severe disease animal model for COVID-19 research.
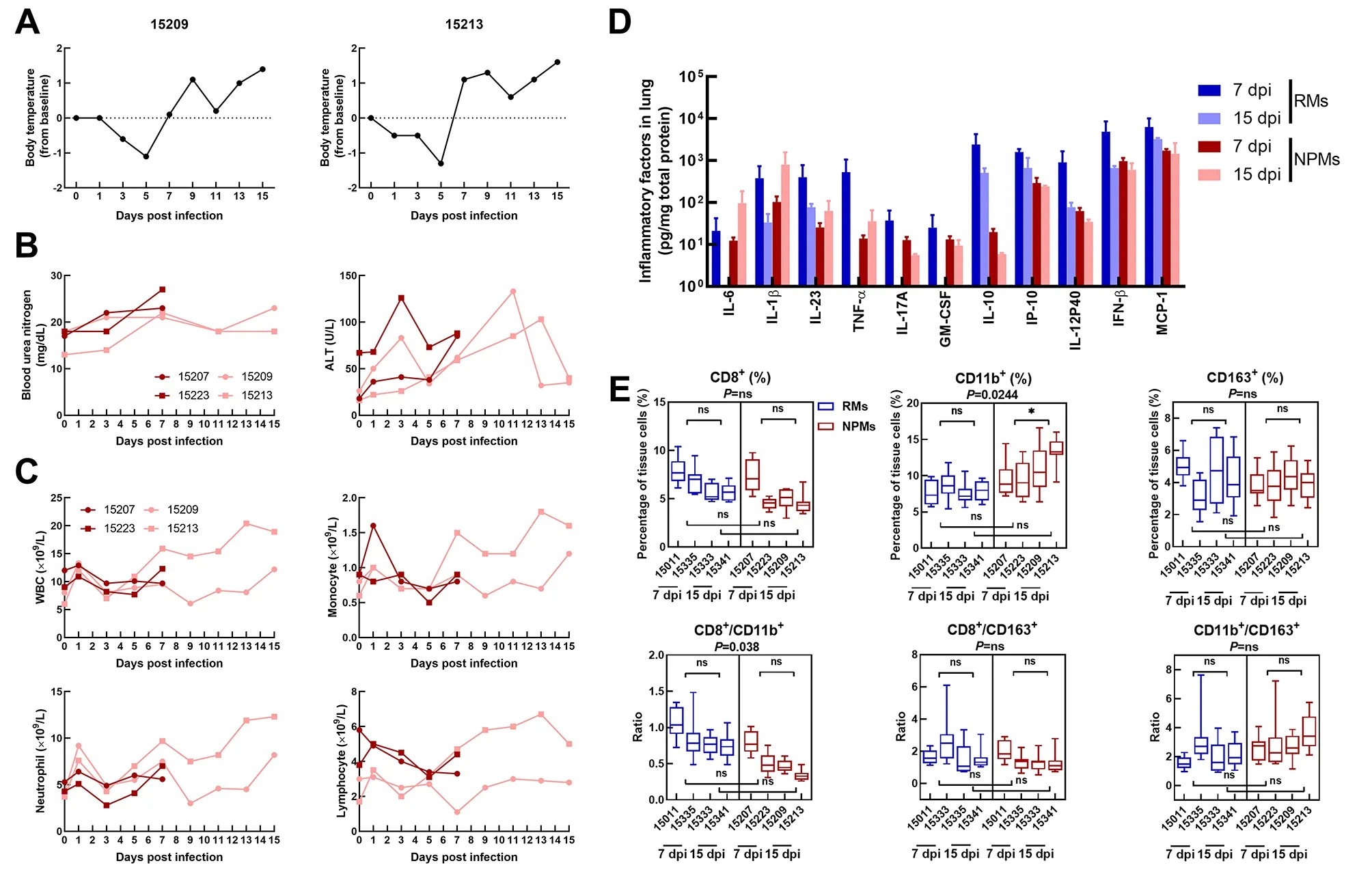
Figure 2 Body injuries and immune response in NPMs
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
Y.T.Z., T.Z.S., and H.Y.Z. conceived and designed the experiments. T.Z.S., H.Y.Z., J.B.H., X.L.F., F.L.L, X.Y., L.J.R.H.L, R.R.T., C.L., and M.H.L. performed the experiments.T.Z.S. and H.Y.Z. analyzed the data. T.Z.S. and H.Y.Z. wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Dr. Chang-Wen Ke (Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention) for providing the SARSCoV-2 strain.

- Zoological Research的其它文章
- LIN28A inhibits DUSP family phosphatases and activates MAPK signaling pathway to maintain pluripotency in porcine induced pluripotent stem cells
- Molecular mechanisms of intermuscular bone development in fish: a review
- Species bias and spillover effects in scientific research on Carnivora in China
- Potential aquatic environmental risks of trifloxystrobin:Enhancement of virus susceptibility in zebrafish through initiation of autophagy
- Particulate matter exposure exacerbates susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection in humanized ACE2 mice
- A review of the Cypriniform tribe Yunnanilini Prokofiev,2010 from China, with an emphasis on five genera based on morphologies and complete mitochondrial genomes of some species

