含例鄰域邏輯的薩奎斯特對(duì)應(yīng)理論
趙之光
1 Introduction
The notion ofcontingencygoes back to Aristotle,who develops a logic of statements about contingency.([1]) From modal logic point of view,[5] firstly defines the contingent statement aspossibly trueandpossibly false.The contingency logic,in which“contingency”is considered as a modal operator,has been well studied in[3,4],etc.In this paper,we focus oncontingencyin classical propositional logic.Here,a statementφiscontingent,if there is an assignmentvand an assignmentu,s.t.v(φ)tandu(φ)f.In other words,a statement iscontingentif it is neither a tautology nor a contradiction.The logic of truth-functional contingency,is to capture all these contingent statements.
There are many works on the complementary sentential logics,such as [2,7,9],etc.,all of which introduce different systems to capture non-tautologies in classical propositional logic.The first proper system for truth-functional contingency was introduced in [6].Using this system,in order to obtain a contingent formula,we can translate a formula into its perfect disjunctive normal form by transformation rules,and then remove all redundant variables occurring in it.T.Tiomkin introduced a sound,complete and cut-free calculus for contingent sequent in classical propositional logic.([8]) However,the cut rules and extension rules in [8] mix classical sequents with contingent sequents together.The standard Hilbert style calculus for this logic is still missing.In this paper,we are going to introduce a Hilbert calculus for the logic of truth-functional contingency,where every formula introduced in a deduction is a contingent formula,and it is introduced only if it is a contingent axiom,or it follows by one of the contingent rules of inference from contingent formulas introduced earlier in the deduction.
The paper is organized as follows.In the next section,we present syntax and semantics of truth-functional contingency.In Section 3,we introduce a Hilbert calculus for the logic of truth-functional contingency.In Section 4,we prove the soundness and completeness of the calculus.Finally,we present some directions for future research.
2 Preliminaries
In this section,we present syntax and semantics of truth-functional contingency which will be used in the following sections.
Fix a denumerable setVof atomic propositions.The language is defined recursively as follows:
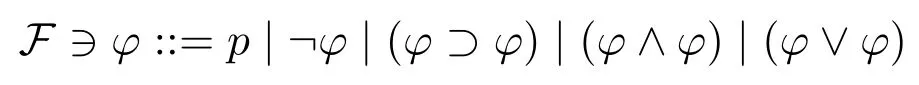
wherep ∈V.In what follows,we will usep,q,r,...(with or without subscripts)to denote any atomic proposition,andφ,ψ,χ,...(with or without subscripts)to denote any formula inF.The outmost parenthesis of formulas will be omitted.
An assignmentv:V →{t,f}is defined as the same as in classical logic,and it can be uniquely extended to:F →{t,f}.
Definition 1(Truth-functionally contingent formula) For any formulaφ ∈F,we sayφis atruth-functionally contingent formula,abbreviated as contingent formula,if there is an assignmentvand an assignmentu,s.t.(φ)tand(φ)f.
In what follows,we use|c φifφis a contingent formula.The logicLCof truth-functional contingency is the set of all contingent formulas.
3 A Hilbert Calculus for LC
In this section,we will introduce a sound and complete Hilbert calculus HLC forLC,which is inspired by[2].
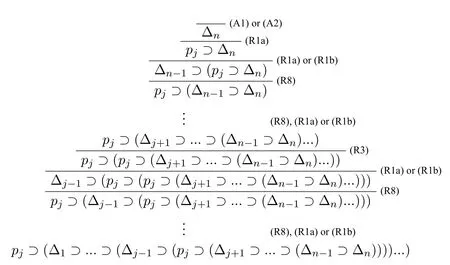
Before giving the calculus,we first introduce some notations which will be used in this section.For any formulaφ,we let Var(φ){p | poccurs inφ}.Let the formula be the form of ΔΔ1or ΔΔ1?(Δ2?...(Δn?1?Δn)...),where Δipior Δi?pi,andpipjforij.
Definition 2(Hilbert calculus HLC) The Hilbert calculus HLC is defined as follows:
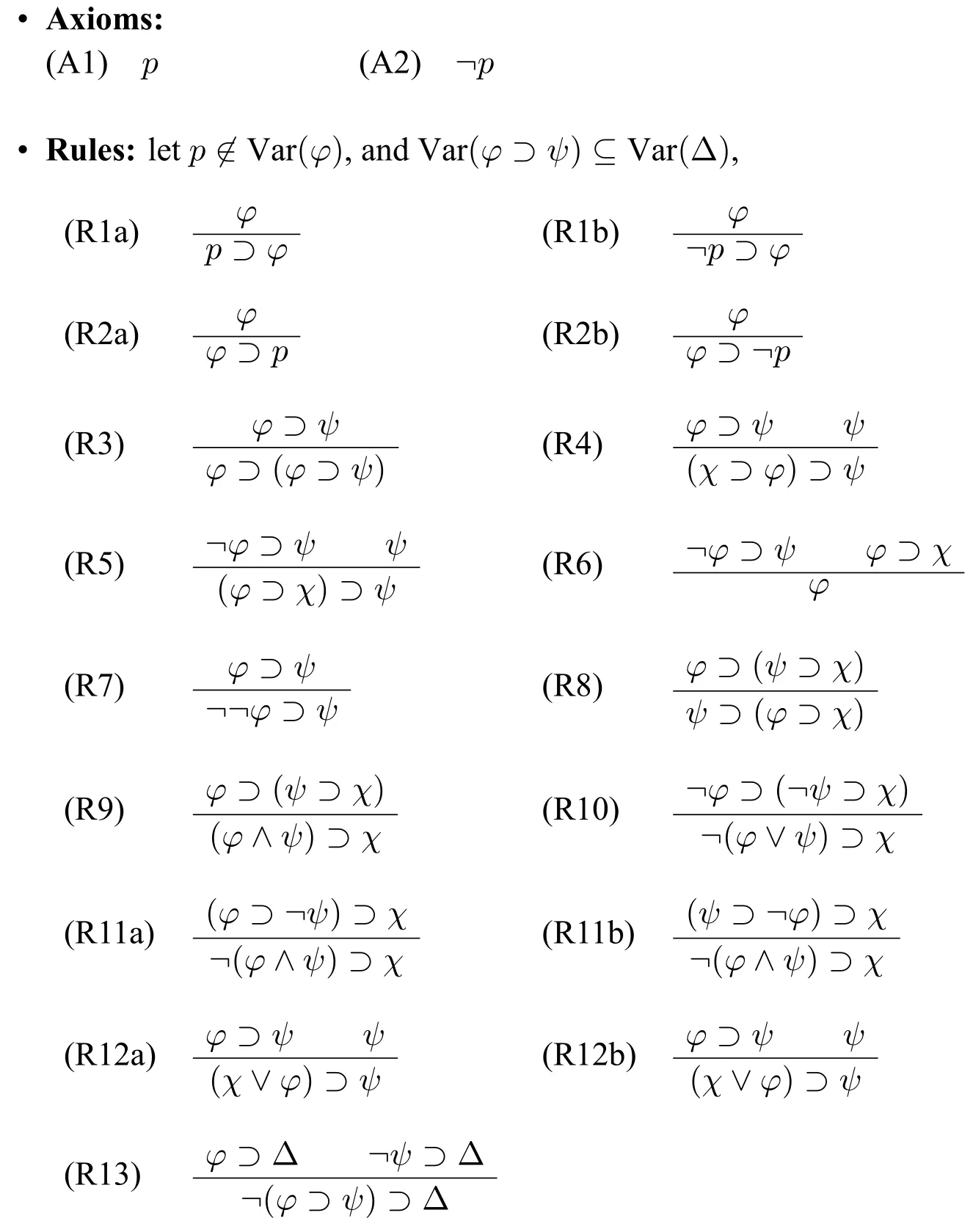
Adeductionin HLC is a finite sequenceφ1,...,φn,s.t.φi(i ∈{1,...,n})is either an axiom or a formula which is derived by applying rule(s) to its previous formula(s) occuring in the sequence.A formulaφis atheoremin HLC if there is a dedutionφ1,...,φn,s.t.φφn.In what follows,we use?c φto meanφis a theorem in HLC.
We first show some theorems in HLC,which will be used in the subsequent sections.
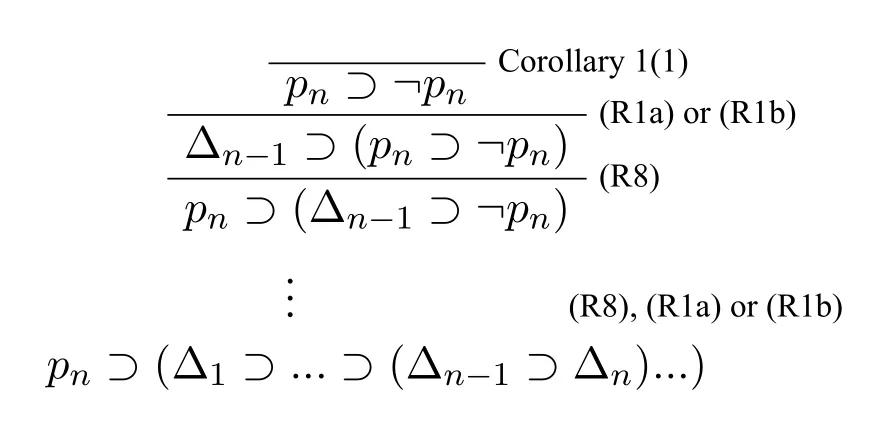
Corollary 1The following formulas are theorems in HLC.For any Δ defined as above:
(1)?c p ??p;
(2)?c ?p ?p;
(3)?cΔ;
(4)?cΔi ?Δ fori (5)?c ?Δn ?Δ; (6)?c ?Δ?Δ. ProofWe use proof tree to show above formulas are theorems in HLC.(1)can be shown as follows: (4)can be shown by the following proof tree: (5) can be proven as follows:If Δnpn,then ΔΔ1?(...?(Δi?1?(Δi ?(Δi+1?...?(Δn?1?pn)))...)). In this section,we are going to show that HLC is sound and complete,that is,?c φiff|c φf(shuō)or anyφ ∈F.We call HLC issound,if every axiom in HLC is a contingent formula,and every rule is contingency-preserving,that is,if the premise(s)of a rule is(are) (a) contingent formula(s) then the conclusion of the rule is also a contingent formula.We call HLC iscompleteif every contingent formula is deducible in HLC. Lemma 1|cΔ. ProofIt suffices to show that there exist assignmentsvandu,s.t.(Δ)tand Ifn1,then ΔΔ1por?p.It is obvious that there exist assignmentsvandu,s.t.(Δ)tand(Δ)f.Ifn>1,then ΔΔ1?(...?(Δn?1?Δn)...).For any 1≤i ≤n,there always existvianduis.t.(Δi)tand(Δi)fby the construction of Δ(Definition 2).Since Var(Δi)Var(Δj)whenij,we can defineandas follows: Theorem 1(Soundness).HLCis sound. ProofThat is to show that every theorem in HLC is a contingent formula.It is clear that the two axioms are contingent formulas,we only need to prove that all rules are contingency-preserving. As to (R1a),suppose that|c φ,then there existv′andu′,s.t.(φ)tand(φ)f.It is clear that|c p,that is,there existv′′andu′′s.t.(p)tand(p)f.Sincep/∈Var(φ),we can defineand ˉuas follows: As to (R9),it suffices to show that if|c φ ?(ψ ?χ),then there exist assignmentsvandu,s.t.((φ ∧ψ)?χ)tand((φ ∧ψ)?χ)f.Hence|c φ ?(ψ ? χ),then there existands.t.(φ ?(ψ ? χ))tand(φ ?(ψ ?χ))f.We can defineandas follows: Lemma 2Let Var(φ)?Var(Δ)and ΔΔ1?(Δ2?...?(Δn?1?Δn)...)withpipjforij,and Δipior Δi?pi.Then,|c φ ?Δ implies?c φ ?Δ. ProofBy induction on the complexity of the formulaφ.Ifφpj,there are two subcases. Subcase 1:whenj Subcase 2:whenjn.If Δnpn,thenpn ?Δ is a tautology,so that Δnmust be?pn,by Corollary 1(1),we have the proof as follows: Ifφ?ψ.By subinduction on the complexity ofψ: Ifψpj,the proof of it is omitted since it is quite analogous to the proof above. Ifψ?χ,i.e.|c ??χ ?Δ,it is clear that|c χ ?Δ,then by induction hypothesis,?c χ ?Δ,then by(R6),we have?c ??χ ?Δ. Ifψχ ∧δ,i.e.|c ?(χ ∧δ)?Δ,then by Lemma 1,there existsvsuch that(Δ)t,which makes(?χ ?Δ)(?δ ?Δ)t.And there existsusuch that(?(χ ∧δ)?Δ)f,hence(Δ)f,and(χ)or(δ)is false,which makes(?χ ?Δ)for(?δ ?Δ)f.Now it is clear in this case we have|c ?χ ?Δ or|c ?δ ?Δ.By induction hypothesis,?c ?χ ?Δ or?c ?δ ?Δ.Corollary 1(3) and?c ?χ ?Δ imply that?c ?(χ ∧δ)?Δ by (R5) and (R11a),Corollary 1(3)and?c ?δ ?Δ imply that?c ?(χ ∧δ)?Δ by(R4)and(R11a). Theorem 2(Completeness).HLCis complete. ProofThat is to show that every contingent formula is a theorem in HLC.The proof strategy is as follows:we first show that|c φ ?Δ and|c ?φ ?Δ′by the assumption|c φ,and then use Lemma 2 to show that?c φ.Since|c φ,there existuandw,such that(φ)tand(φ)f.Assume that Var(φ){p1,...,pn},defineqi: Defineri: Corollary 2?c φiff?c ?φ. ProofFrom left to right direction,assume that?c φ,then by Theorem 1,we have|c φ,which means there existsvsuch that(φ)t,i.e.(?φ)f,and there existsusuch that(φ)f,i.e.(?φ)t,therefore,|c ?φ.By Theorem 2,we have?c ?φ.If?c ?φ,by Theorem 1,we have|c ?φ,which means there existsvsuch that(?φ)t,i.e.(φ)fand there existsusuch that(?φ)f,i.e.(φ)t,therefore|c φ.By Theorem 2,we have?c φ. □ In this paper,we introduced a complete and sound Hilbert calculus for the logic of truth-functional contingency,which captures all contingent formulas in classical logic.The quantificational extension of the logicLCwill be our next work.Inspired by[8],to develop a pure sequent calculus for contingent sequent without using classical sequent will be a challenge work in future.Another interesting topic is to study the relation between contingency logic([4]),as we introduced in Section 1,andLCin this paper.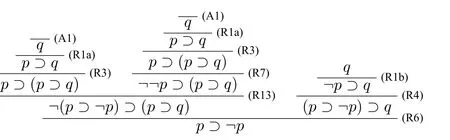
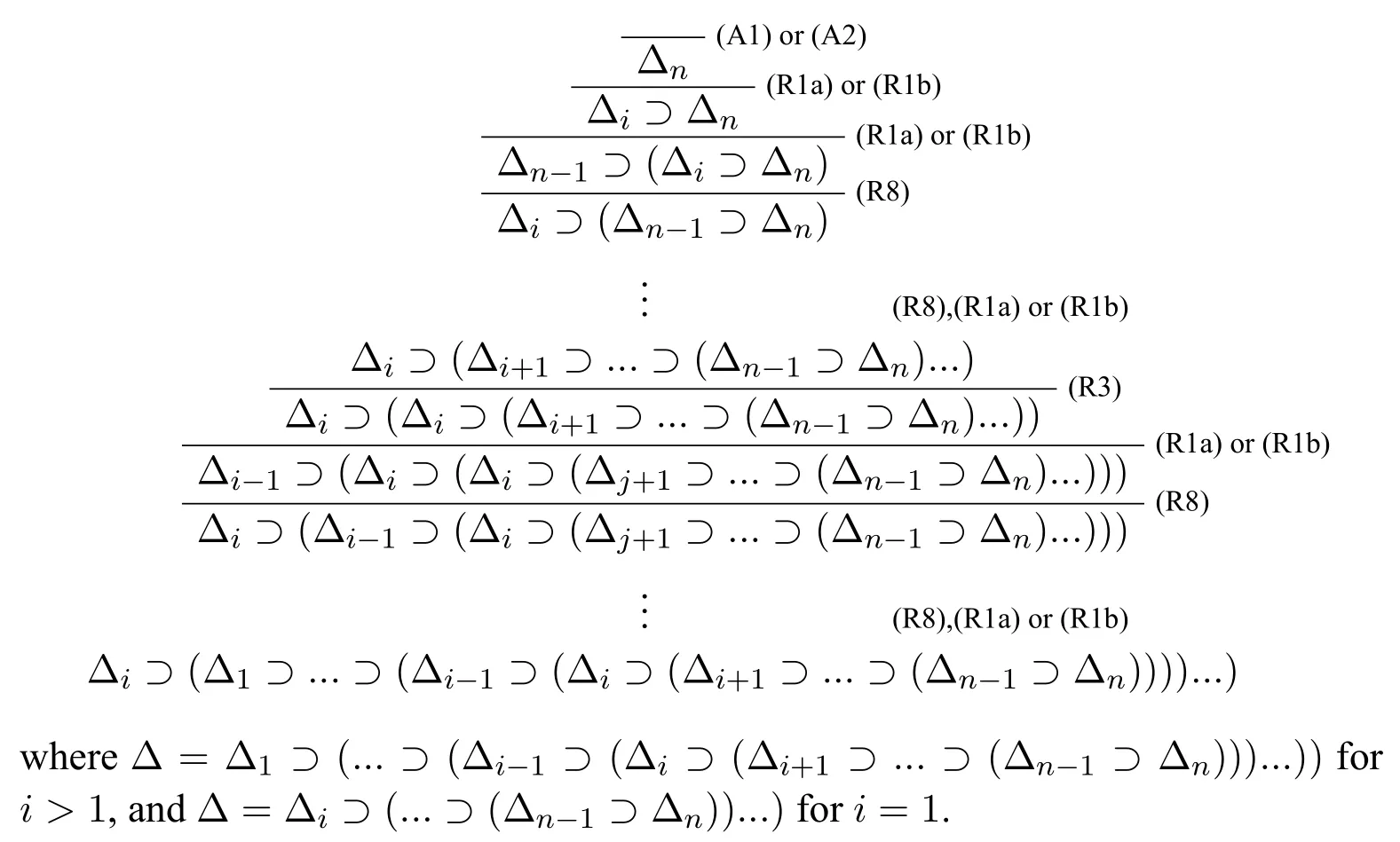

4 The Soundness and Completeness of HLC





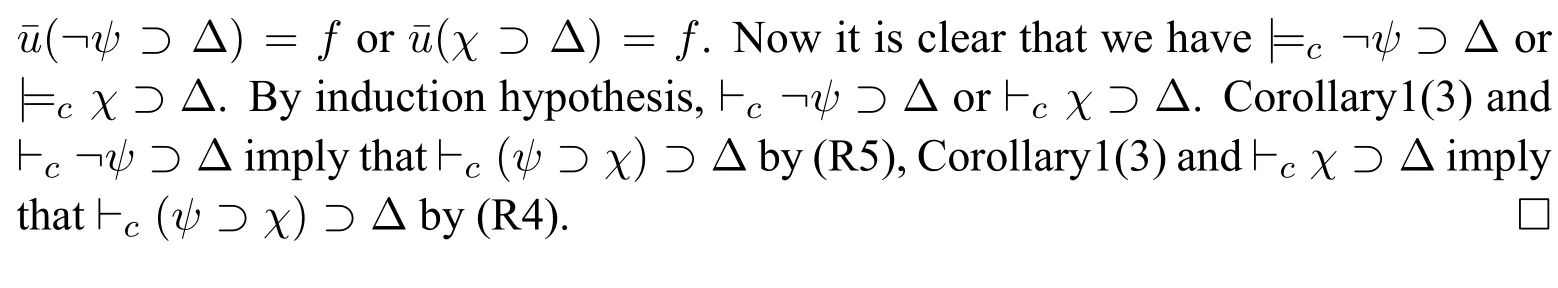

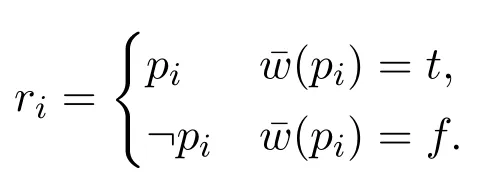
5 Future work

