Generation of domain-wall solitons in an anomalous dispersion fiber ring laser*
Wen-Yan Zhang(張文艷) Kun Yang(楊坤) Li-Jie Geng(耿利杰) Nan-Nan Liu(劉楠楠)Yun-Qi Hao(郝蘊琦) Tian-Hao Xian(賢天浩) and Li Zhan(詹黎)
1Henan Key Laboratory of Magnetoelectronic Information Functional Materials,School of Physics and Electronic Engineering,Zhengzhou University of Light Industry,Zhengzhou 450002,China
2State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks,School of Physics and Astronomy,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
Keywords: optical solitons,fiber lasers,domain wall soliton,pulse laser
1. Introduction
Soliton fiber lasers, typically emitting bright pulses and/or dark pulses,have been studied extensively due to their versatile applications in laser optical frequency metrology,[1]optical sensing,[2]material processing and so on.[3-5]According to the energy distribution pattern, the bright pulse refers to a bulge increment of ultrashort pulse laser intensity beyond a continuous laser background; while the dark pulse,as the so-called dark soliton, conventionally means a dip of the ultrashort pulse laser intensity below a continuous laser background.[6,7]To date,various schemes on the formation of the bright-pulse trains and dark-pulse trains have been proposed and demonstrated in mode-locked lasers. Compared with bright pulses, dark pulses have many attractive advantages, such as better stability in the presence of noise, and are less influenced by intrapulse stimulated Raman scattering(ISRS).[8]Owing to their distinctive peculiarity,dark solitons are of great importance in scientific research and have attracted considerable attention from many research groups.
The conventional dark solitons, as the steady-state solutions of the nonlinear Schr¨odinger equation(NLSE),and usually generated in anomalous dispersion cases,have been fully investigated in optical fiber systems in previous studies.[9-12]However,in terms of the novel dark solitons,such as domainwall(DW)solitons,[13,14]whose operation dynamics are governed by the coupled Ginzburg-Landau equation(CGLE),not the traditional NLSEs,are still a hot topic in the ultrafast laser field.
Particularly, since Sylvestreet al.demonstrated a domain-wall dark soliton train using self-induced modulation instability,[15]over the past twelve years,the formation of the dark-pulse trains has been widely reported theoretically and experimentally in ultrafast fiber lasers using diverse modelocking techniques under different dispersion conditions. Recently, Zhanget al.experimentally observed dark solitons in fiber ring lasers with anomalous or abnormal dispersion fiber cavities.[16,17]Yinet al.also reported this type of DW pulses in a dispersion-managed fiber ring laser based on the nonlinear polarization rotation(NPR)technique.[18]Then, Liuet al.demonstrated the polarization domain wall pulses generated in an Er-doped mode-locked vector fiber laser that used a microfiber-based topological insulator as the saturable absorber for mode-locking.[19]In these soliton lasers,the formation dynamics of the induced dark solitons were all based on the CGLEs, indicating that due to the cross polarization coupling,different types of dark solitons,such as polarization domain walls(PDWs)and other types of vector dark PDW solitons, which refers to a localized structure that separates the two stable polarization eigenstates of a birefringent laser cavity,could be achieved.[20,21]Furthermore,considering that the all-fiber laser has the advantages of high reliability,easy operation and maintenance,and good compatibility,[22-24]it could be anticipated that the domain-wall soliton trains in the allfiber structure laser could greatly enhance applications in optical sensing,optical communication,and soliton multiplexed systems.[25,26]
In this paper, we report the experimental observation of DW dark solitons in a ring laser with an all-fiber structure. To be more compact and compatible,the laser is mode-locked by a segment of thulium-doped fiber. By slightly adjusting the pump power and polarization controller, the DW bright and dark solitons have been successfully observed. And the generation mechanism of the induced dark solitary pulse is based on the incoherent polarization coupling. These experimental results are not only greatly important to the improvement of the performance of ultrafast lasers, they also provide a direction for better understanding of the formation dynamics and operation regimes of domain-wall solitons.
2. Experimental setup
Our experiment was conducted on an erbium-doped fiber laser,schematically shown in Fig 1. A fiber-pigtailed 976 nm laser diode with a maximum pumping power of 600 mW was used to pump the Er-doped fiber(EDF)through a 980/1550 nm wavelength-division multiplexer (WDM). A 2.1 m long EDF with group velocity dispersion (GVD) of?16 ps/km/nm and a peak core absorption of 80 dB/m at 1530 nm band was adopted as the gain medium. A 0.8 mm long, highconcentration thulium-doped fiber (TDF) with 340 dB/m absorption at 1550 nm was applied as the saturable absorber(SA) for mode-locking and to realize the self-starting operation of the laser. Here, the SA is the non-equilibrium SA, in which the upper-level population return to the ground state incompletely between two adjacent pulses,but a quantity of the population remains in the upper-level.[27,28]Meanwhile, the population inversion level of the Tm ion can be easily optimized by simply varying the length of TDF while,simultaneously, the loss of the cavity is accordingly adjusted. A 40 m long highly nonlinear fiber(HNLF)with nearly zero GVD at 1550 nm was deliberately inserted in the cavity to increase the nonlinearity. A polarization controller (PC1) was employed to control the polarization state of light in the resonant cavity,and a polarization-independent isolator (PI-ISO) was utilized to force unidirectional operation of the laser. The tails of all the optical components are standard single-mode fibers(SMF)with GVD of 17 ps/km/nm at 1550 nm connected by splicing.The laser signal was extracted using one port of a 50:50 optical coupler(OC2)spliced at the 10%output port of the 10:90 optical coupler(OC1). A second polarization controller(PC2)and a polarization beam splitter(PBS)at the output end were used to separate the two orthogonal polarizations of the laser emission.And the PC2 was inserted to balance the phase delay caused by the pigtailed fibers of the two OCs used outside the cavity. The unresolved output of the laser and the polarization resolved beams could be simultaneously detected. The output spectrum was measured using a Yokogawa AQ6370 optical spectrum analyzer,and the pulse beams from the fiber laser were monitored using a photodiode (20 GHz) and visualized on an oscilloscope(RTO 1002,2 GHz).
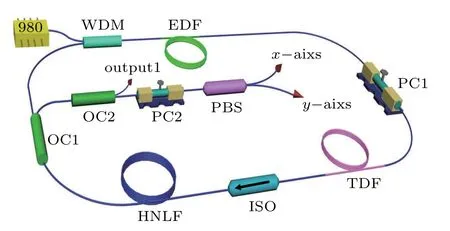
Fig.1. The schematic setup of the DW soliton fiber laser. WDM:wavelength division multiplexer,EDF:Er-doped fiber,TDF:thulium-doped fiber,HNLF:highly nonlinear fiber, PC: polarization controller, PI-ISO: polarizationindependent isolator, OC: output coupler, PBS: fiber pigtailed polarization beam splitter.

Fig.2. The saturable absorption response of the TDF-SA.
The total cavity length was 53.65 m, and the total group velocity dispersion(GVD)in the cavity was negative.Notably,no polarization-dependent components are inserted in the cavity;consequently,the laser emits simultaneously along its two principal polarization directions,and the domain wall solitons can be produced under the appropriate conditions.
3. Nonlinear absorption of the TDF-SA
It is worth mentioning that,in addition to mode-locking,another motivation for choosing the TDF with the length of 0.8 mm as the SA is to achieve the all-fiber structure. Here,the nonlinear response of the TDF-SA employed in the cavity was characterized by utilizing the typical balanced twodetector measurement system,which was the same as that used in Ref.[27]. The experimental data of the measured transmission ratio and the homologous fitting curve as a function of the pump power are sketched in Fig.2. The typical saturable absorption is obviously observed,and the experimental data is well fitted with the saturable-absorption formula of the transmission rate. Based on the fitting curve,the modulation depth of the TDF-SA is~11.5%,which is fully sufficient for modelocking.
In addition,the modulation depth can be easily optimized by simply varying the length of the TDF,which means that the population inversion level of the doped Tm ion can be expediently enhanced or weakened;this is indeed another advantage of using the TDF as the SA.
4. Results and discussion of the DW soliton
In the experiment, when the pump power is beyond the mode-locking threshold of 100 mW,by carefully adjusting the orientation of the intra-cavity PC1, stable soliton pulses are efficiently obtained,and the self-starting mode-locking operation can be achieved. The most attractive characteristic of the generated pulses is that,associated with each of the appearing narrow dark solitons, there was always a subtle bright pulse that concurrently formed on the bottom of each of the dark pulses,similar to the so called bright-dark soliton pairs,[29,30]to some extent. Figure 3(a) shows the temporal trace of the total laser emission at the pumping power of 250 mW. The bright and the dark pulses have the same repeat frequency of 3.83 MHz, corresponding to the cavity length of 53.65 m.As depicted in the zoom-in of one bright-dark pulse pair in Fig. 3(b), the pulse durations of the narrow dark pulse and the bright pulse are about 12.8 ns and 19.1 ns, respectively.Note that due to the response time of our photodetector and the bandwidth limitation of our oscilloscope,the real pulse width should be smaller.
Moreover, the generated pulse will be influenced by the polarization state and/or the pump power.[31,32]Meanwhile,when the pump power is increased to 500 mW,the dark pulse emerges with some fluctuations of the tip depths, and then higher pump strength will tend to generate erratic multiple dark pulses that coexist with unstable bright pulses, similar to that demonstrated in Ref.[20]. However,the spitted pulses can be collapsed into one single pulse again by varying the orientation of the PC1. Nevertheless, once the operating condition is fixed,the fundamental dark-pulse emission state can be maintained for decadal hours,certifying the excellent stability of the laser. And the TDF-SA could have played an important role in the pulse stabilization.
In this laser, the maximum output power at the available pump power of 600 mW is 35 mW,and the single-pulse energy reaches 9.14 nJ.
As the above experimental results show, the generated laser pulses exhibit typical characteristics,such as lower onset threshold and broader pulse width (nanosecond scale), fully conforming to the morphological features of the DWSs. Besides,we note that our cavity design possesses a polarizationindependent nature; the two orthogonal polarization components exist and couple to each other,leading to the formation of dark pulses, which might be the polarization domain wall solitons.
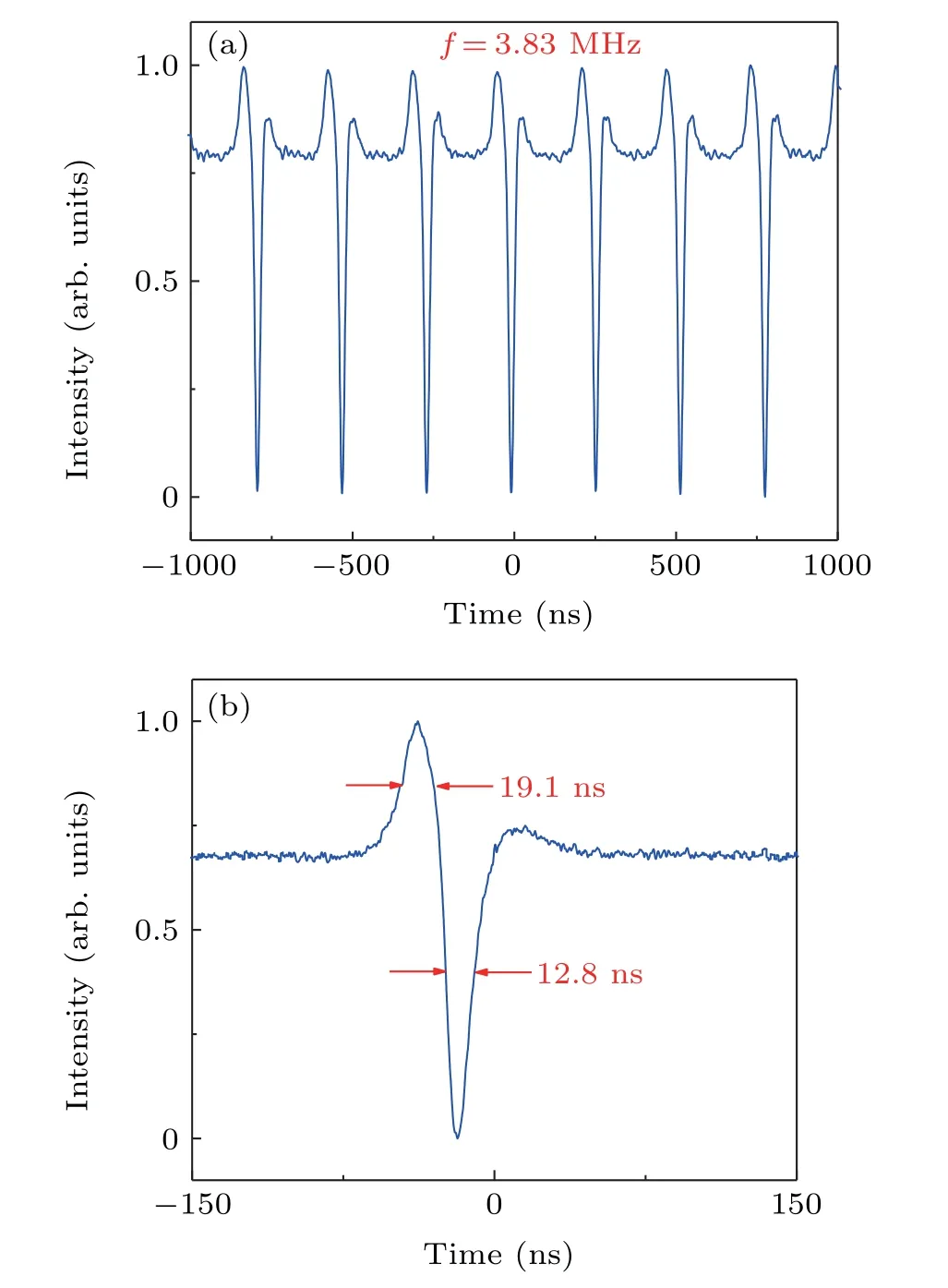
Fig. 3. Output characteristics of the laser emission. (a) Oscilloscope traces of the total laser emission. (b)Pulse duration of the dark and bright solitons.
To confirm the conjecture, experimental verification to separate the two orthogonal polarizations of the laser emission was carried out via the PBS and PC2. Figure 4 depicts the oscilloscope traces of the horizontal and the vertical axis polarization components,severally. As shown in Fig.4,in the case of weak net cavity birefringence,the oscilloscope traces of the two orthogonal polarization-resolved pulses are uniform,to a certain extent. The profile of the intensity dip is stable with the cavity roundtrips, and each dip separates the two stable linear polarization states of the laser emission. Likewise, the width and depth of the dip could be varied with both the cavity birefringence and/or the pumping strength. The stronger the pumping,the narrower and deeper the dip.
We also measured the total and polarization-resolved spectra of the laser,as shown in Fig.5. The spectra of the two orthogonally polarized components both have a main-peak wavelength of about 1562.16 nm and a 3-dB spectral width of about 0.15 nm,the same as that of the total laser emission,which indicates that the coupling between the two polarization components is extremely coherent.[33,34]Moreover,their spectral distributions are identical,and two peak-dip spectral structures located on both sides of the peak can be clearly observed,which indicates that the bright pulses have fully evolved into solitons. Therefore,the generation of the bright soliton is due to the intrinsic balance between the negative cavity dispersion and the fiber nonlinear optical Kerr effect. On the other hand,the energy exchange between the two polarization components means the coherent coupling induces the formation of the narrow dark solitary pulse. Thus, the bright and dark solitons could co-exist in an anomalous dispersion regime.
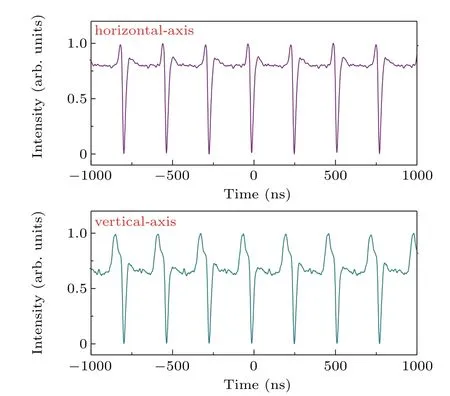
Fig. 4. An oscilloscope trace of the two polarization resolved components:horizontal axis(x-axis,upper trace)and vertical axis(y-axis,lower trace).
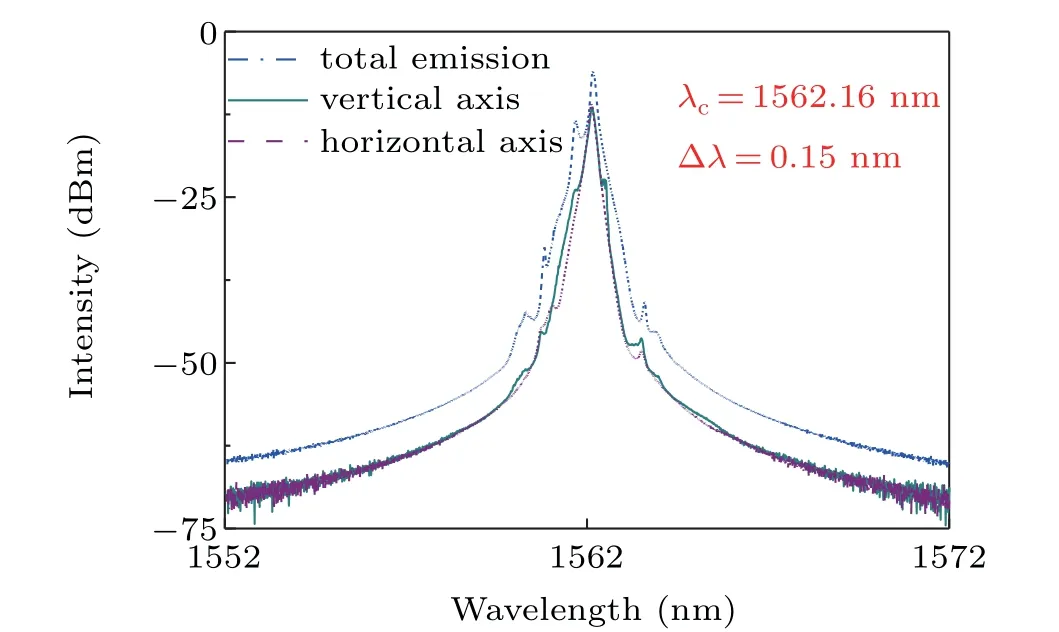
Fig.5. The corresponding optical spectra.
Besides, by appropriately altering the net linear cavity birefringence, the wavelength separation between the two orthogonal linear polarization components could be effectively controlled. Here, we made the separation zero; within this regime, the solitons maintain both their temporal and polarization profiles during propagation within the birefringent environment.
Unambiguously, the rendered nanosecond-pulse fiber laser operates with good stability, an all-fiber structure, and controllable pulse duration, and can withstand the environmental perturbation. Hence, we believe this new nanosecond pulse laser will have widespread applications in optical communication,sensing technology,and ultrafast optics.
5. Conclusion and perspectives
In conclusion,we have demonstrated an Er-doped modelocked fiber laser that used one segment of Tm-doped fiber as a saturable absorber. DW solitons were successfully induced and stably existed in the laser cavity. The experimental results showed that the DW pulse generation was attributed to the coherent polarization coupling, under the assistance of gain,loss of the TDF-SA,and the high nonlinearity provided by the HNLF and the intra-cavity dispersion in the ring laser.In addition to operating at the fiber optical communication band,the proposed fiber laser has advantages such as easy fabrication,low cost, an all-fiber adjustable device, and efficient implementation of the generation of dark or bright pulses. Hence,we believe it will have widespread applications in optical communication,optical sensing,and soliton multiplexed systems.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Erratum to“Floquet bands and photon-induced topological edge states of graphene nanoribbons”
- Viewing the noise propagation mechanism in a unidirectional transition cascade from the perspective of stability*
- Nonlinear signal transduction network with multistate*
- Optical strong coupling in hybrid metal-graphene metamaterial for terahertz sensing*
- Any-polar resistive switching behavior in Ti-intercalated Pt/Ti/HfO2/Ti/Pt device*
- Magnetic two-dimensional van der Waals materials for spintronic devices*

