Ultrafast carrier dynamics of Cu2O thin film induced by two-photon excitation*
Jian Liu(劉建), Jing Li(李敬), Kai-Jun Mu(牧凱軍), Xin-Wei Shi(史新偉),Jun-Qiao Wang(王俊俏), Miao Mao(毛淼), Shu Chen(陳述), and Er-Jun Liang(梁二軍)
School of Physics and Microelectronics,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450001,China
Keywords: carrier dynamics,cuprous oxide,transient absorption,two-photon absorption
1. Introduction
Cuprous oxide, as a p-type semiconductor, has been regarded as a promising material for applications in the fields of solar cells, photocatalysis, photoelectrode, photovoltaics and sensors,[1-7]owing to its high optical absorbance, nontoxicity and low cost. Recently, the optical nonlinearity of Cu2O has attracted much interest, and indicated potential nonlinear photonic applications.[8-10]Since the valence bands and conduction bands of Cu2O have the same parity, direct optical transition is parity forbidden but the two-photon transition is allowed. This initiates studies that focused on the two-photon absorption properties of Cu2O, demonstrating considerable applications in optical limiting, ultrafast all-optical modulation,and so on.[11-13]
As is known, understanding the carrier dynamics is essential for semiconductor optoelectronic devices. It has been proved that the carrier distribution generated by two-photon excitation is more uniform than that by one-photon excitation, due to the former has relatively weaker absorption coefficient.[14]As a result,carrier diffusion and surface recombination effects could be effectively avoided in the two-photon excitation scheme. However, the two-photon absorption generated carrier dynamics of Cu2O has not been investigated to the best of our knowledge. Therefore,it deserves deep insight into the carrier dynamics induced by two-photon excitation for future applications in the nonlinear photonics.
In this work, we prepared a Cu2O thin film using the radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. X-ray diffraction(XRD),scanning electron microscopy(SEM)and linear transmission spectra were applied to define the crystal structure,morphology and particle size. Using typical non-collinear ultrafast transient absorption experiments, carrier dynamics induced by the two-photon excitation were investigated,revealing an ultrafast carrier scattering process in hundreds femtoseconds and a slow carrier recombination in more than tens of picoseconds. Meanwhile, the carrier dynamics induced by the corresponding one-photon excitation were also studied for contrast. The time constant of carrier scattering process is found larger for two-photon excitation,since two-photon excitation generates carriers with less concentration for analogous laser peak power density.
2. Experimental details
Generally, several techniques such as electrochemical deposition,[7]molecular beam epitaxy,[15]thermal evaporation[16]and magnetron sputtering[17]have been employed to prepare the Cu2O film. Among these methods,radio-frequency magnetron sputtering is the best adopted one due to its high deposition rate, low resistivity and effective control of the chemical composition. Here, we prepared the Cu2O thin film deposited on a glass slide by a radio-frequency magnetron sputtering system(CS-300,Yuhua),using a Cu2O target with a purity of 99.99%,diameter of 60 mm and thickness of 5 mm. Before deposition, the glass slide was ultrasonically cleaned in deionized water,acetone and ethanol successively. Presputtering was performed for 10 min to remove the impurities on the surface of the target. During deposition,high-purity argon was used as the sputtering gas for 2 hours at 200°C,with a 46 sccm flow rate, 1.3 Pa vacuum chamber pressure and 70 W power.
XRD (PANalytical Empyrean) was carried out to determine the crystal structure of the Cu2O thin film. The surface morphology was characterized by a FIB field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Carl Zeiss Auriga-BU).The linear transmission spectrum was measured using a UVVis-NIR spectrophotometer (Hitachi UH-4150) to obtain the optical bandgap.

Fig. 1. (a) Non-collinear ultrafast pump-probe setup. M1-M4 are reflection mirrors. PD 1 and PD 2 are photodiodes. For one-photon excitation, a BBO crystal in inserted in the pump beam(not shown). (b)Schematic energy-level diagram of the processes during two- or onephoton excitation on Cu2O thin film.
The carrier dynamic measurements of the Cu2O thin film were carried out via typical non-collinear ultrafast pumpprobe setup, as shown in Fig. 1(a). An amplified Ti:sapphire laser source (Solstice ACE, Spectra-Physics) with 800 nm wavelength, 120 fs pulse width, 1 kHz repetition rate passes through an optical parametric amplifier system(OPA,TOPASPrime, Light Conversion) and generates wavelength tunable femtosecond pulses(240 nm-2600 nm). The residual 800 nm pulse served as the pump beam for the two-photon excitation,while the output pulse from OPA served as the probe. The differential transmission of the probe beam was recorded by a couple of synchronized photodiodes(918D-UV-OD3R,Newport). The delay time between the pump and probe pulses was controlled through a retroreflector mounted on a linear motor stage(M-ILS200CC,Newport)in the pump arm. Two neutral density filters(ND filter)were placed in the two arms to adjust the laser powers.In addition,a BBO crystal was inserted in the 800 nm arm to generate the 400 nm pulses to implement onephoton excitation for comparison. Both the pump and probe laser in our experiments were horizontal polarized.
3. Results and discussion
The XRD pattern of the obtained Cu2O thin film is shown in Fig.2(a),showing obvious diffraction peaks. Each diffraction peak matches with that in JCPDS file No. 01-078-2076,indicating that the pure polycrystalline Cu2O film is obtained.The average particle size is evaluated to be about 25 nm according to the Scherrer’s equation.[18]
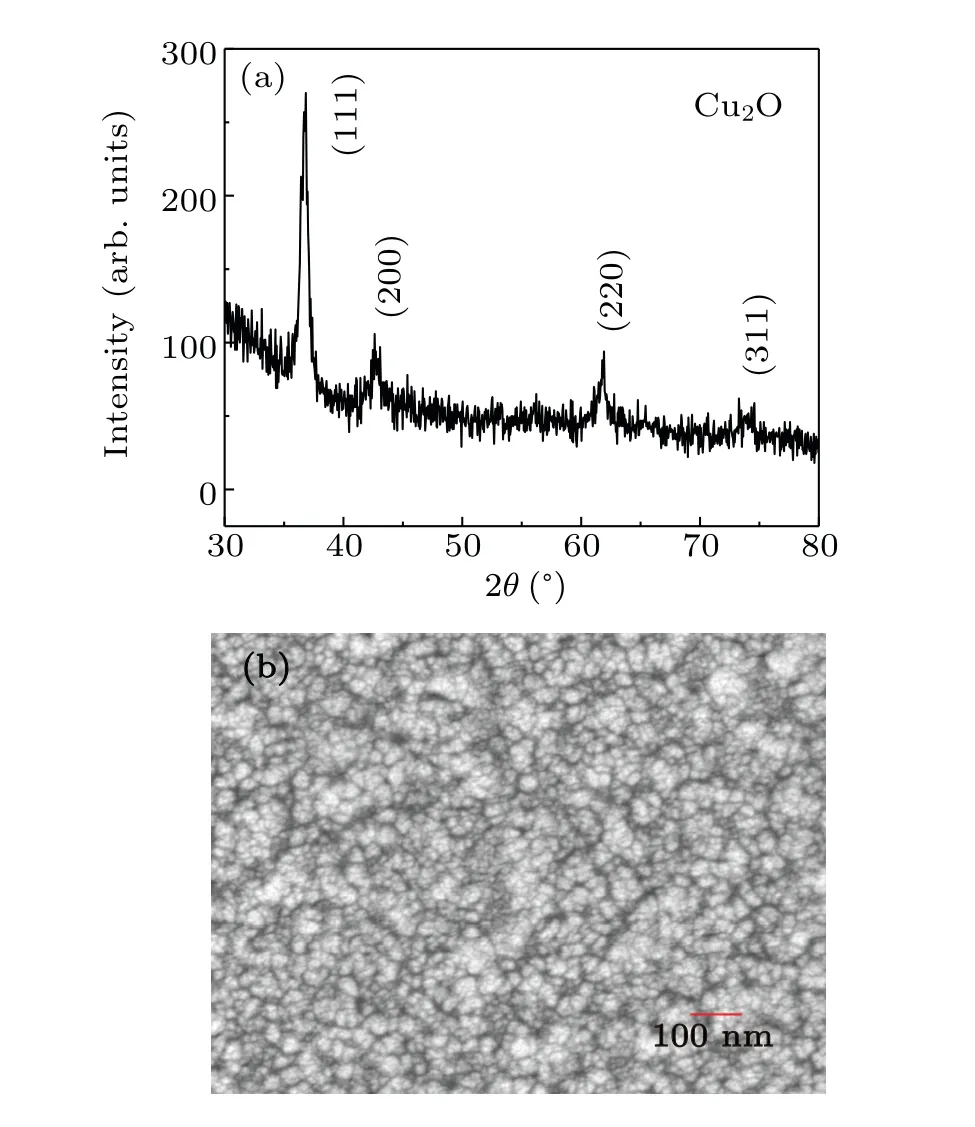
Fig.2. (a)XRD pattern and(b)SEM image of the Cu2O thin film.
The SEM image in Fig.2(b)indicates that the surface is compact and uniform. The linear transmission spectrum and the corresponding relationship betweenαhν2andhνwere plotted in Fig. 3. According to the Tauc’s equation,[19]the optical bandgapEgis obtained to be 2.54 eV by using linear extrapolation method

whereαis the linear absorption coefficient and can be calculated from the linear transmission spectrum,hνis the photon energy of the incident light,andCis a constant. The obtainedEgof the present Cu2O thin film is larger than the calculated value of bulk Cu2O, which is due to the nanoscale particle size.[20,21]
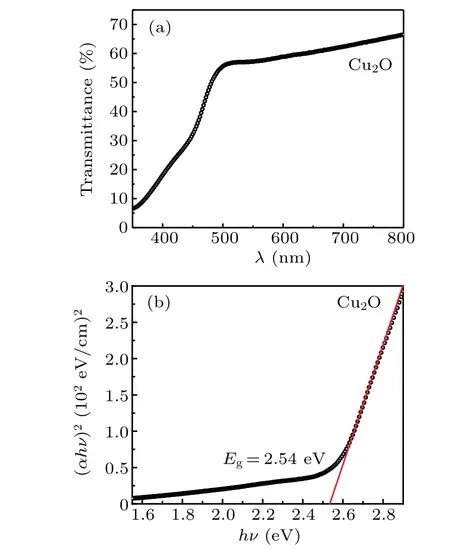
Fig. 3. (a) Linear transmission spectrum of the Cu2O thin film. (b)Tauc’s plot of(αhν)2 versus hν and the obtained bandgap.
Biexponential functionA1e?t/τ1+A2e?t/τ2was applied to fit the normalized (??T/T) as plotted in Fig. 4(b), whereτ1andτ2are time constants for the fast and slow processes,respectively,andA1andA2are weights. The extractedτ1andτ2for differentI800are listed in Table 1. AsI800increases,τ1exhibits a decreasing trend, which denotes that the generated carriers undergo an ultrafast carrier scattering process and then relax to the bottom of the conduction band, as illustrated in Fig.1(b). The time constantτ2is more than 30 ps,indicating a carrier recombination process.

Fig.4. (a)Time resolved differential transmission ?T/T under different I800 for two-photon excitation. The inset shows the dependence of the maxima ?T/T at t =0 on I800 and linear fitting. (b)Biexponential fitting for time resolved normalized(??T/T)under different I800.
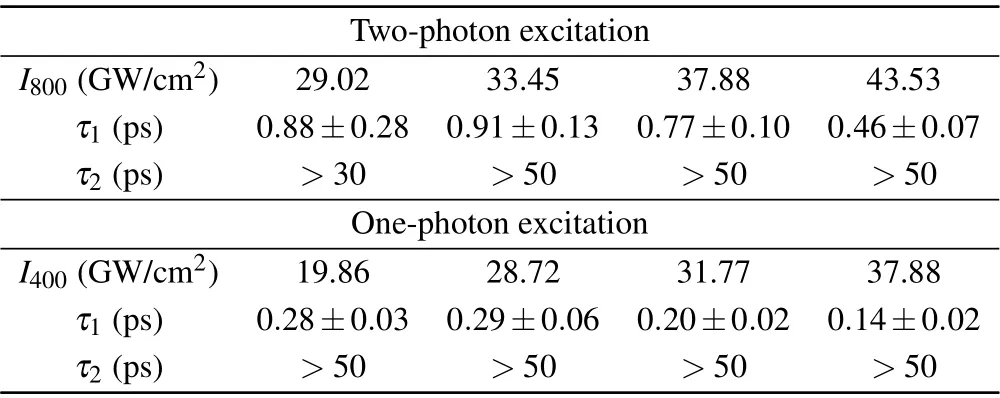
Table 1. Time constants of carrier scattering and recombination under different pump intensities for two-and one-photon excitation.
We further investigated the transient absorption pumped by 400 nm pulse(photon energy 3.1 eV)through one-photon excitation and probed by 600 nm pulse. The focal peak power density of the probe pulse is 1.14 GW/cm2. At the first glance of Fig.5(a),the differential transmission ?T/Tappears similar evolution trend with the two-photon excitation case,that is a fast drop followed by a slow recovery. The maxima ?T/Tis also linearly dependent on the focal peak power density of the pump pulseI400without saturation.
Figure 5(b) illustrates the fitting curves with the biexponential function. The extracted time constantτ1for carrier scattering also shows a decreasing trend with the increase ofI400,and the time constantτ2for carrier recombination is more than 50 ps. It is noticed thatτ1is smaller than that in the twophoton excitation case. We attribute it to the different transition selection rules as well as the much smaller absorption coefficient of two-photon absorption than one-photon absorption. Consequently,the carrier concentration generated by the two-photon excitation is less than that by the one-photon excitation for analogousI800andI400, leading to slower carrier scattering timeτ1under the two-photon excitation.This would make the Cu2O great potential in the nonlinear optical applications.
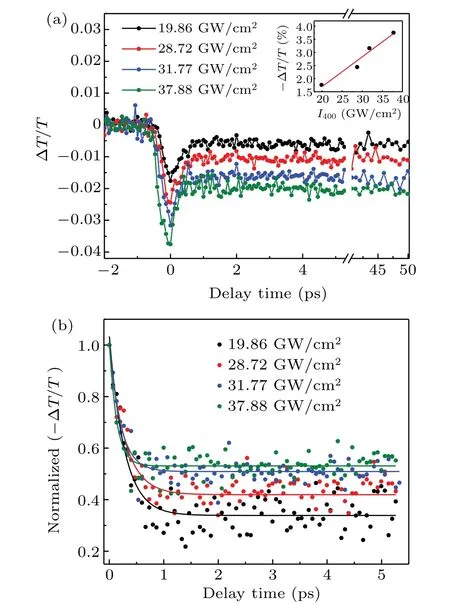
Fig.5. (a)Time resolved differential transmission ?T/T under different I400 for one-photon excitation. The inset shows the dependence of the maxima ?T/T at t =0 on I400 and linear fitting. (b)Biexponential fitting for time resolved normalized(??T/T)under different I400.
4. Conclusion
In summary, pure Cu2O thin film has been prepared by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. Using transient absorption experiments,the carrier dynamics have been investigated under the two-and one-photon excitation. It revealed an ultrafast carrier scattering in hundreds femtoseconds and carrier recombination in more than tens of picoseconds.Owing to the smaller absorption coefficient for the two-photon absorption, the carrier scattering time constant for the two-photon excitation is slower than that for the one-photon excitation.This study has provided essentical understanding of the carrier dynamic processes following the two-photon excitation,thus paves the way for further nonlinear optical applications of Cu2O based on the two-photon absorption, such as optical limiting,ultrafast all-optical switching and femtosecond laser reductive sintering.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Erratum to“Floquet bands and photon-induced topological edge states of graphene nanoribbons”
- Viewing the noise propagation mechanism in a unidirectional transition cascade from the perspective of stability*
- Nonlinear signal transduction network with multistate*
- Optical strong coupling in hybrid metal-graphene metamaterial for terahertz sensing*
- Any-polar resistive switching behavior in Ti-intercalated Pt/Ti/HfO2/Ti/Pt device*
- Magnetic two-dimensional van der Waals materials for spintronic devices*

