Clinical study of treating somatoform pain disorder with the combination of electroacupuncture and duloxetine
DONG Yongsheng (董永生), SUN Shuhong (孫淑紅), XU Shuang (徐爽), YU Dongbo (于東波), LI Wei (李偉)Tangshan Fifth Hospital, Hebei Province, Tangshan 063000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Points, Governor Vessel; Points, Conception Vessel; Acupuncture Medication Combined; Pain; Somatoform Disorders
Somatoform pain disorder (SPD) is characterized by persistent pain that cannot be fully explained by a physiological process or somatic disease[1].It is very difficult to diagnose SPD in the early stage.Patients usually visit a general hospital first and are finally diagnosed in psychiatry.Medications such as non-steroidal non-inflammatory drugs and anesthetics are often used before diagnosis.However, apart from adverse reactions, these drugs are unsatisfactory regarding the treatment result, which brings about grave economic and mental stress to the patients and their families.Duloxetine is a classic Western
medication for treating SPD.Modern research shows that oral duloxetine can effectively reduce pain ratings and improve SPD patients’quality of life and sleep quality[2].Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) holds that SPD is associated with disorders of the “five spirits”and the “five Zang organs”[3].Based on the knowledge above, this study adopted electroacupuncture (EA) at the points of the Governor Vessel and Conception Vessel plus duloxetine to treat SPD, with duloxetine as the control.The report is given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria developed in this study referred to the diagnostic criteria for SPD under the scope of somatoform disorders in theChinese Classification and Diagnosis of Mental Diseases:CCMD-3[4]: met the diagnostic criteria for somatoform disorder; persistent severe pain; pain directly caused by psychosocial and emotional issues; examinations found no corresponding somatic diseases accounting for the main complaint; the condition lasted for 6 months or longer.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Conformed to the diagnostic criteria for SPD mentioned above; aged between 30 and 50 years; not on any medications or TCM treatments in the last 2 weeks; signed informed consent from the patient or the authorized family member.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Other neurotic disorders, depression, schizophrenia,and paranoid disorders; co-morbid organic diseases; the patient refused acupuncture treatments; serious deafness or cognitive impairment.
1.4 Dropout and elimination criteria
Those who showed angina pectoris or a continuous significant increase in blood pressure during the treatment process; topical skin infection or severe adverse drug reactions occurred during the treatment process; those who failed to complete the whole treatment process and lost to visit; those who took other psychotropic substances during the treatment process on their own; incomplete medical data.
1.5 Statistical processing
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS version 23.0 software.Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation,analyzed by the pairedt-test in intra-group comparisons and the independent samplest-test in between-group comparisons.Counting data were expressed as rates and examined by the Chi-square test.Statistical significance was accepted whenP<0.05.
1.6 Subjects
This trial achieved approval from the Ethics Committee of Tangshan Fifth Hospital, Hebei Province(Approval No.2019-02-06).
The sample size calculation formula is:n= 2 ×[(uα+ uβ)2σ2]/δ2[5].We took the short-form McGill pain questionnaire (SF-MPQ) score as the primary outcome measure.Based on literature[6]and our preliminary study, we assumed an SF-MPQ score of (25.87±1.78)points in the control group, hypothesized a decrease of 8 points after treatment in the score, and obtained a sample size of 30 cases in each group.Then we assumed a dropout rate of 10% and finally determined the sample size to be 43 cases in each group.Of which,the control group had 1 case of dropout (failed to complete the whole intervention) and 1 case of elimination (voluntarily took other psychotropic substances); the treatment group had 2 cases of dropout (failed to complete the whole intervention).Therefore, each group contributed 41 cases for clinical efficacy assessment.Figure 1 details the trial procedure.
The patients in the two groups were aged between 30 and 50 years with a disease duration ranging from 1 to 7 years.The baseline data had no significant differences between the two groups (P>0.05),suggesting comparability.The details are shown in Table 1.
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
Patients in the control group orally took duloxetine hydrochloride enteric capsules (State Food and Drug Administration Approval No.H20203192, Chengdu Brilliant Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China) at a dose of 60 mg per time in the morning, once a day for 8 consecutive weeks.
2.2 Observation group
Patients in the observation group received the same medication as in the control group but with additional EA at points of the Governor and Conception Vessels.
Points: Shenting (GV24), Baihui (GV20), Shendao(GV11), Jinsuo (GV8), Jiuwei (CV15), Juque (CV14),Zhongwan (CV12), and Shimen (CV5).
Method: The patient first took a prone position to receive EA at Shenting (GV24), Baihui (GV20), Shendao(GV11), and Jinsuo (GV8), followed by EA at Jiuwei(CV15), Juque (CV14), Zhongwan (CV12), and Shimen(CV5) in a supine position.After routine sterilization for the selected points with 75% alcohol, the physician took disposable sterile acupuncture needles of 0.25 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length for acupuncture.The needle was inserted subcutaneously upward into Shenting (GV24) for 10 mm, and subcutaneously backward into Baihui (GV20) for 10 mm; obliquely upward into Shendao (GV11) and Jinsuo (GV8) for 10 mm; obliquely downward into Jiuwei (CV15) for 10 mm; perpendicularly into Juque (CV14), Zhongwan(CV12), and Shimen (CV5) for 10 mm.After insertion of the needles, the doctor performed balanced liftingthrusting and twirling or rotating needling methods and connected them with G6805-2A low-frequency electronic pulse therapeutic device after the arrival of Qi.The needle handle at Shenting (GV24) was attached to the positive pole, and the one at Baihui (GV20) to the negative pole; Shendao (GV11) to the positive pole, and Jinsuo (GV8) to the negative pole; Jiuwei (CV15) to the positive pole, and Juque (CV14) to the negative pole;Zhongwan (CV12) to the positive pole, and Shimen (CV5)to the negative pole.A sparse-dense waveform was selected with a frequency of 14-26 times per minute.The intensity increased gradually based on the patient’s tolerance.The stimulation lasted for 15 min in the prone and supine positions each, and the intervention was offered once a day, 6 times a week from Monday to Saturday for 8 weeks.
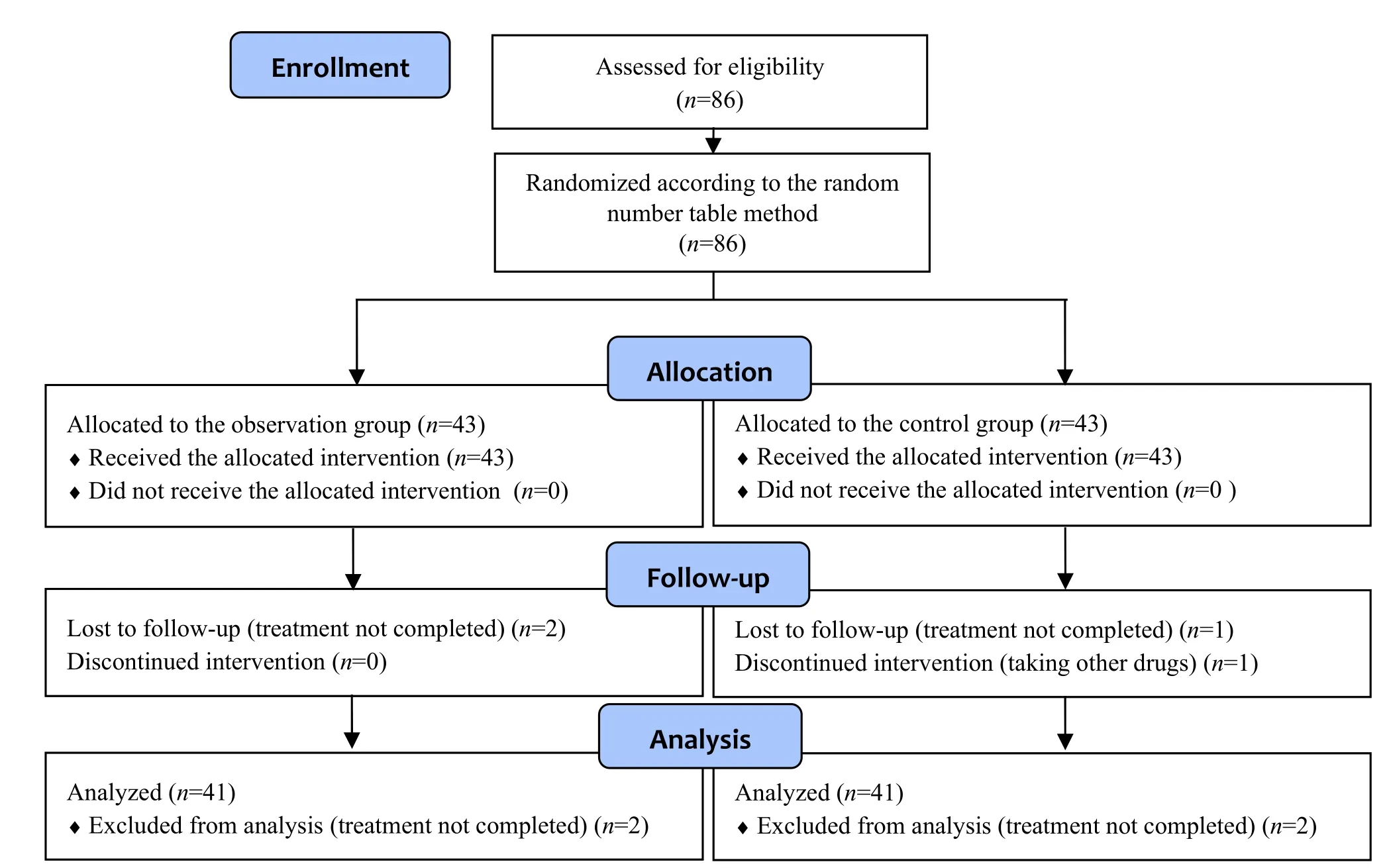
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study

Table 1 Comparison of the baseline data between the two groups
3 Results
3.1 Observation indicators
3.1.1 Primary outcome measures
SF-MPQ[7]: Consists of pain rating index (PRI), visual analog scale (VAS), and present pain intensity (PPI); the sum of the three is taken as the general score.PRI includes 11 sensory and 4 affective items, rated 0-3 points each.The VAS score ranges from 0 to 10 points, and the PPI from 0 to 5 points.For the three scales, a higher score indicates a worse condition.The general score ranges from 0 to 60 points.
Self-report symptom inventory, symptom check list-90 (SCL-90)[8]: Somatization subscale, 12 items, each graded 0-4 and scored 0-4 points from mild to severe,making the total score in the range of 0-48 points.A higher score stands for worse symptoms.
3.1.2 Secondary outcome measures
Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI)[9]: Consists of 18 items, which can be divided into 7 dimensions, with each dimension rated at a 4-grade scale, scored 0, 1, 2,and 3 points accordingly.The PSQI general score ranges from 0 to 21 points; the higher the score, the worse the sleep quality.
Generic quality of life inventory-74 (GQOLI-74)[10]:Contains a total of 74 items, which can be classified into 4 categories, including psychological function, physical function, material life status, and social function.Its total score ranges from 0 to 74 points; a higher score suggests a better quality of life.
3.2 Efficacy criteria
We referred to the Nimodipine method for efficacy index calculation in theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[11].We defined the total score as the sum of the SF-MPQ score and the somatization subscale score in the SCL-90.Efficacy index = (Total score before treatment - Total score after treatment) ÷ Total score before treatment × 100%.
Clinical control: Efficacy index ≥90%.
Markedly effective: Efficacy index ≥60% but <90%.
Effective: Efficacy index ≥30% but <60%.
Ineffective: Efficacy index <30%.
3.3 Result observation
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
After 8-week treatments, the total effective rate was 90.2% in the observation group, notably higher than 75.6% in the control group; the between-group difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).The details are shown in Table 2.
3.3.2 Comparison of the SF-MPQ score
The SF-MPQ score decreased significantly after treatment in both groups (P<0.05) and was markedly lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05).See Table 3 for details.
3.3.3 Comparison of the somatization score in the SCL-90
After treatment, the SCL-90 somatization score dropped significantly in the two groups (P<0.05) and was significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05).See Table 4 for details.

Table 2 Comparison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups Unit: case
GroupnBefore treatment After treatmentt-valueP-value
Table 3 Comparison of the SF-MPQ score Unit: point

Table 3 Comparison of the SF-MPQ score Unit: point
Note: SF-MPQ=Short-form McGill pain questionnaire.
Observation 41 40.93±5.68 19.88±3.04 21.245 <0.001 Control 41 39.59±4.59 29.78±3.87 10.084 <0.001t-value 1.162 -12.736P-value 0.249 <0.001
GroupnBefore treatment After treatmentt-valueP-value
Table 4 Comparison of the SCL-90 somatization score Unit: point

Table 4 Comparison of the SCL-90 somatization score Unit: point
Note: SCL-90=Self-report symptom inventory, symptom check list-90.
Observation 41 38.95±4.27 18.95±2.85 24.398 <0.001 Control 41 39.17±4.41 28.44±3.68 13.127 <0.001t-value -0.226 -12.894P-value 0.822 <0.001
3.3.4 Comparison of the PSQI score
After the intervention, the PSQI score decreased notably in both groups (P<0.05) and was markedly lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05).See Table 5 for details.
3.3.5 Comparison of the GQOLI-74 score
After treatment, the GQOLI-74 score increased significantly in each dimension in both groups (P<0.05)and was notably higher in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05).See Table 6 and Table 7 for more details.
Table 5 Comparison of the PSQI score Unit: point
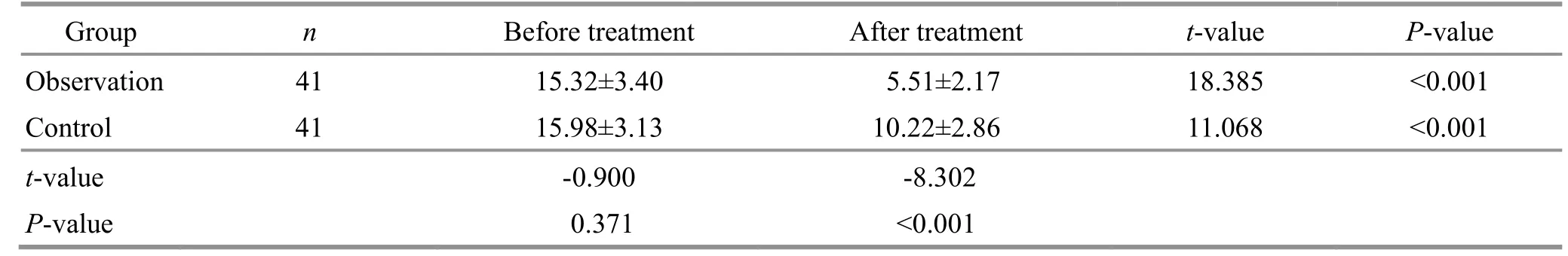
Table 5 Comparison of the PSQI score Unit: point
Note: PSQI=Pittsburgh sleep quality index.
Group n Before treatment After treatmentt-valueP-value Observation 41 15.32±3.40 5.51±2.17 18.385 <0.001 Control 41 15.98±3.13 10.22±2.86 11.068 <0.001t-value -0.900 -8.302P-value 0.371 <0.001
Table 6 Comparison of the physical function and psychological function scores in the GQOLI-74 Unit: point
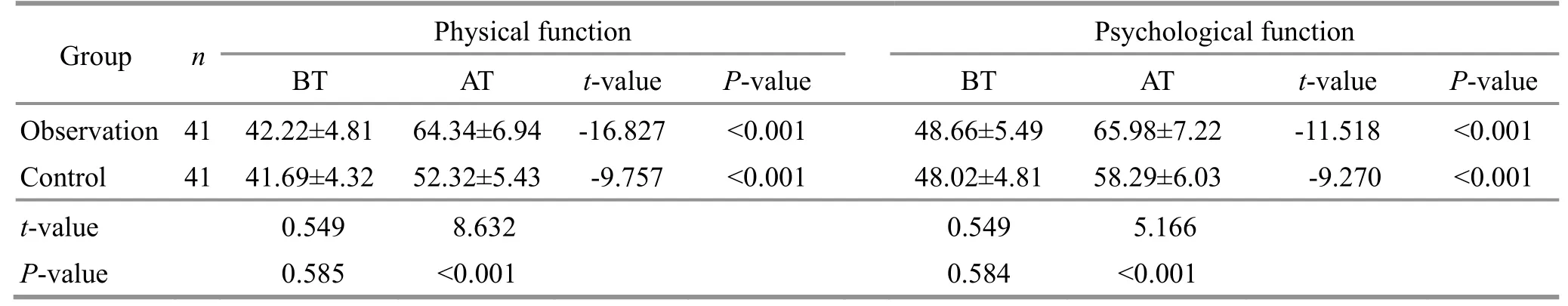
Table 6 Comparison of the physical function and psychological function scores in the GQOLI-74 Unit: point
Note: GQOLI-74=Generic quality of life inventory-74; BT=Before treatment; AT=After treatment.
Group nPhysical function Psychological function BT AT t-valueP-valueBTATt-valueP-value Observation 41 42.22±4.81 64.34±6.94 -16.827 <0.001 48.66±5.49 65.98±7.22 -11.518 <0.001 Control 41 41.69±4.32 52.32±5.43 -9.757 <0.001 48.02±4.81 58.29±6.03 -9.270 <0.001t-value 0.549 8.632 0.549 5.166P-value 0.585 <0.001 0.584 <0.001
Table 7 Comparison of the social function and material life status scores in the GQOLI-74 Unit: point
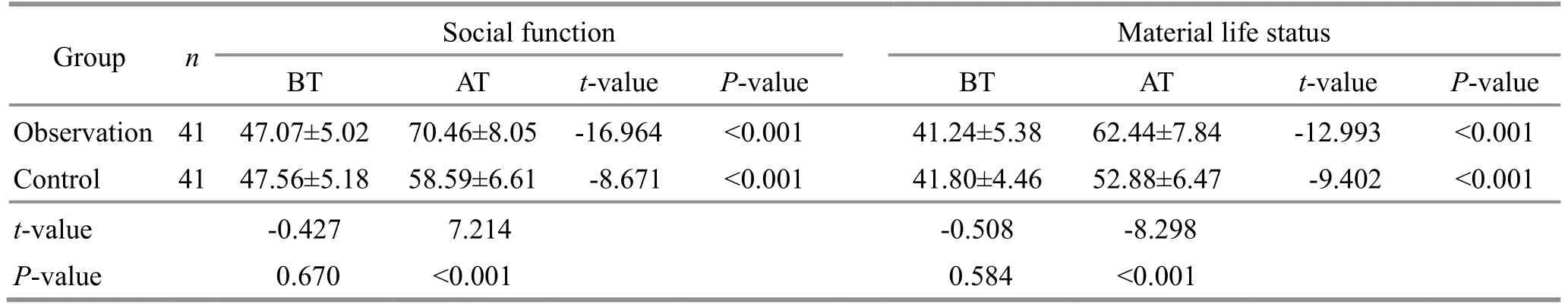
Table 7 Comparison of the social function and material life status scores in the GQOLI-74 Unit: point
Note: GQOLI-74=Generic quality of life inventory-74; BT=Before treatment; AT=After treatment.
Group nSocial function Material life status BT AT t-valueP-valueBTATt-valueP-value Observation 41 47.07±5.02 70.46±8.05 -16.964 <0.001 41.24±5.38 62.44±7.84 -12.993 <0.001 Control 41 47.56±5.18 58.59±6.61 -8.671 <0.001 41.80±4.46 52.88±6.47 -9.402 <0.001t-value -0.427 7.214 -0.508 -8.298P-value 0.670 <0.001 0.584 <0.001
4 Discussion
SPD is a mental illness closely associated with psychosocial function, genetic susceptibility, functional deficits in bilateral frontal lobes, and functional decline in the non-dominant brain hemisphere[12].Antidepressants are currently used as the principal treatment in Western medicine but require long-term administration and may cause various adverse reactions.TCM classifies SPD into the scope of “pain symptoms”.According to the TCM theory, there are two major causes of pain: blocked or undernourished.There is a close tie between SPD and the uncoordinated “five spirits”in TCM, which are known as the five types of spiritual activities, i.e., mind, corporeal soul, ethereal soul, intent, and will.In TCM’s five-element theory, the five spirits correlate with the five Zang organs, which can be summarized as the storage of the five Zang organs: the heart governs the mind, the lung governs the corporeal soul, the liver governs the ethereal soul,the spleen governs the intent, and the kidney governs the will.The five spirits are interdependent and inseparable and are comprehensive spiritual activities of human beings.Uncoordinated functions of Zang-Fu organs and meridians may significantly affect people’s mental activities, leading to pain due to blockages or malnourishment.
The Governor Vessel is the sea of Yang meridians and is in charge of Qi and blood running in Yang meridians;the Conception Vessel is the sea of Yin meridians and is in charge of Qi and blood running in Yin meridians.In addition, the Governor Vessel travels into the brain, the house of the original spirit.Therefore, it can be an approach to adjust spirit, unblock collaterals, and cease pain by regulating the Governor and Conception Vessels,which inspires this study to select points from these two meridians to treat SPD.The results here demonstrated that EA applied to Shenting (GV24), Baihui (GV20),Shendao (GV11), Jinsuo (GV8), Jiuwei (CV15), Juque(CV14), Zhongwan (CV12), and Shimen (CV5)significantly improved the SF-MPQ, SCL-90 somatization,PSQI, and GQOLI-74 scores.Shenting (GV24) can dispel head wind and calm the mind and is the crossing point of the Governor Vessel and Foot Taiyang and Yangming Meridians.Modern research also reveals that Shenting(GV24) can modulate the nervous system and treat mental disorders and pains[13].Baihui (GV20) gathers Qi from Yang meridians and can harmonize the meridian Qi of the Governor and Conception Vessels to balance Yin and Yang.It shows that acupuncture at Baihui (GV20)can treat acute pain, emotional and mood disorders,and diseases of the head and five sense organs[14].Shendao (GV11) works to strengthen Yang, supplement Qi, and calm the mind.It can release back pain,hypochondriac pain, and joint pain.Research suggests that needling Shendao (GV11) can produce significant efficacy in treating arrhythmia, insomnia, angina pectoris, depression, and anxiety[15].Jinsuo (GV8)soothes the liver and extinguishes wind, calms the mind,and relieves convulsions.This point can treat rigid spine and back, back pain, stomachache, epilepsy, convulsions,low back neuralgia, gastric spasms, gastritis, and hysteria.Research has proven its effects of relieving convulsions, ceasing pain, unblocking collaterals, and extinguishing wind; furthermore, needling this point can notably mitigate abdominal pain and improve quality of life[16].As the Luo-Connecting Point of the Conception Vessel, Jiuwei (CV15) has the effects of harmonizing the middle Jiao (energizer), downregulating Qi, clearing heat, and transforming phlegm.Modern research demonstrates that acupuncture at Jiuwei (CV15) can treat mental diseases, pains, and various internal medical diseases caused by disordered Qi movements[17].Juque (CV14) is the Front-Mu Point of the heart.When combined with Jiuwei (CV15), it serves as the pivot of the human body to coordinate the Qi movements in the upper, middle, and lower Jiao.As the Front-Mu Point of the stomach and the Influential Point of Fu organs in the Eight Influential Points, Zhongwan(CV12) can harmonize the stomach, strengthen the spleen, down-regulate Qi, and drain water retention.It is reported that stimulating Zhongwan (CV12) with an elongated needle can treat types of pain with significant efficacy[18].Finally, Shimen (CV5) is the Front-Mu Point of the three Jiao.This point can gather Qi and blood of the three Jiao and harmonize the meridian Qi of the twelve regular and eight extraordinary meridians.Furthermore, EA was used in this trial as it can combine the two kinds of stimulation, electrical and acupuncture,and precisely control stimulation parameters to enhance clinical efficacy.
In brief, it is worth promoting to treat SPD with EA at the Governor and Conception Vessel points plus duloxetine as this combined treatment can significantly improve somatization symptoms, reduce pain, and heighten the quality of life and sleep quality.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Program of Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (河北省中醫藥管理局中醫藥類科研計劃課題, No.2020262).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 19 September 2022/Accepted: 28 February 2023
——中醫藥科研創新成果豐碩(一)
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2023年3期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2023年3期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina ScienceInstructions for Authors
- Editorial Members of Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science
- Acupuncture intervening depressive disorder:research progress in its neurobiological mechanism
- Efficacy and safety of acupuncture-moxibustion for cerebral palsy-induced speech impairment:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Clinical observation of acupuncture treatment for children with accommodative myopia
- Clinical observation of Tuina combined with Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang in the treatment of rectocele
