Tool wear monitoring based on wavelet packet coefficient and hidden Markov model*
Ying QIU, Feng-yun XIE
School of Mechanical and Electronical Engineering, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, China
Tool wear monitoring based on wavelet packet coefficient and hidden Markov model*
Ying QIU, Feng-yun XIE?
SchoolofMechanicalandElectronicalEngineering,EastChinaJiaotongUniversity,Nanchang330013,China
In order to prevent tool failures during the automation machining process, the tool wear monitoring becomes very important. However, the state recognition of the tool wear is not an easy task. In this paper, an approach based on wavelet packet coefficient and hidden Markov model (HMM) for tool wear monitoring is proposed. The root mean square (RMS) of the wavelet packet coefficients at different scales are taken as the feature observations vector. The approach of HMM pattern recognition is used to recognize the states of tool wear. The experimental results have shown that the proposed method has a good recognition performance.
Tool wear, Wavelet packet coefficient, Hidden Markov model, Root mean square
Tool wear monitoring is crucial in order to prevent tool failures during the automation machining process. However, the on-line tool wear monitoring is not an easy task due to the complexity of the process. For many years, lots of scholars have studied tool wear monitoring by various methods. There are important contributions presented for condition monitoring, for instance, on-line tool monitoring by using Artificial intelligence was presented by Vallejo[1], a method of state recognitions based on wavelet and hidden Markov model (HMM) was presented by Xie[2]. On-line condition monitoring based on empirical mode decomposition and neural network was proposed by Xie[3]. A prediction tool wear in machining processes based on ANN was proposed by Haber et al[4]. A new hybrid technique for cutting tool wear monitoring, which fuses a physical process model with an artificial neural networks (ANN) model, is proposed for turning by Sick[5]. However, ANN in tool wear monitoring requires a lot of empirical data for the learning algorithm. Otherwise, it will reduce the recognition rate of the tool wear.
In this paper, an approach based on wavelet packet coefficient and HMM for tool wear monitoring is proposed. In order to monitor the tool wear states in machining process, the dynamometer is used for data acquisition. The wavelet packet decomposition is adopted for data processing. The root mean square (RMS) of the wavelet packet coefficients at different scales are taken as the feature observations vector. The HMM is used to recognize the states of tool wear. The results show that the proposed method has a relatively high recognition rate.
1.Introduction
1.1.Wavelet packet analysis
Wavelet packet decomposes the lower as well as the higher frequency bands and leads to a balanced binary tree structure. Wavelet Packet could be defined as:
(1)
Where,hl-2kandgl-2kare called as orthogonal mirror filter, the function seriesW(2-jt-k) is called as orthogonal wavelet packet.
Wavelet packet function is defined as
(2)
Where,Nis the set of positive integers andZis the set of integers;nis the oscillation parameter;jandkare the frequency localization parameters and the time localization parameter, respectively.
The first two wavelet packet functions are defined as:
(3)
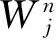
The basic wavelet functionΨ(t) is defined as:
(4)
Where,a,b∈L2(R) (square-integrable space),a≠0. Parameterais called as scale parameter, which is related to the frequency. Parameterbis called as position parameter, which determines the time-domain or space-domain information in the transformed results.
The diagram of this algorithm is shown in Figure 1, where,AandDare the wavelet packet coefficients[6].
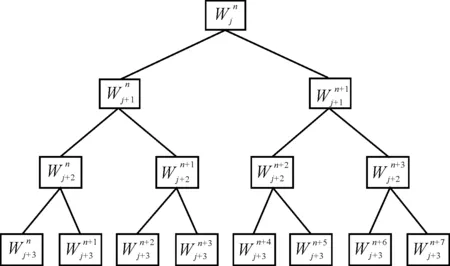
Figure 1. Wavelet packet decomposition tree at level 3
When sampling frequency 2fsis adopted, the different frequency bands range by three layers of wavelet packet decomposition could be shown in Table 1.
The decomposition coefficients of a signalf(t) into Wavelet Packet are computed by applying the low-pass and high-pass filters iteratively. The decomposition coefficients are defined as:
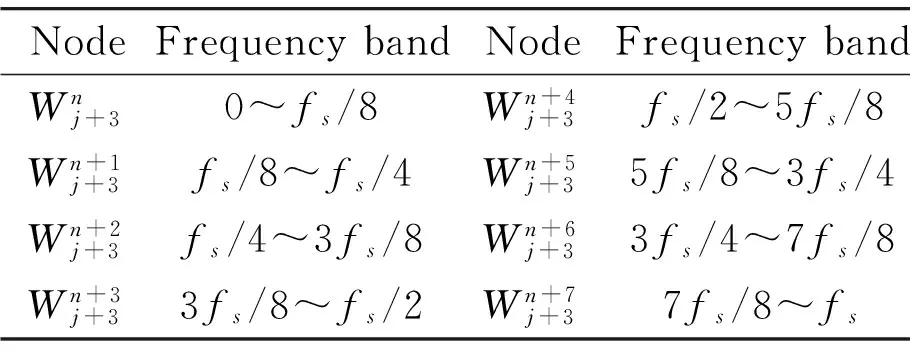
(5) Table 1. Different frequency bands range
1.2.Hidden Markov model
HMM is an extension of Markov chains. Unlike Markov chains, HMM is doubly stochastic process, i.e., not only is the transition from one state to another state stochastic, but the output symbol generated at each state is also stochastic. Thus the model can only be observed through another set of stochastic processes. The actual sequences of states are not directly observable but are “hidden” from observer. A HMM are illustrated in Figure 2.
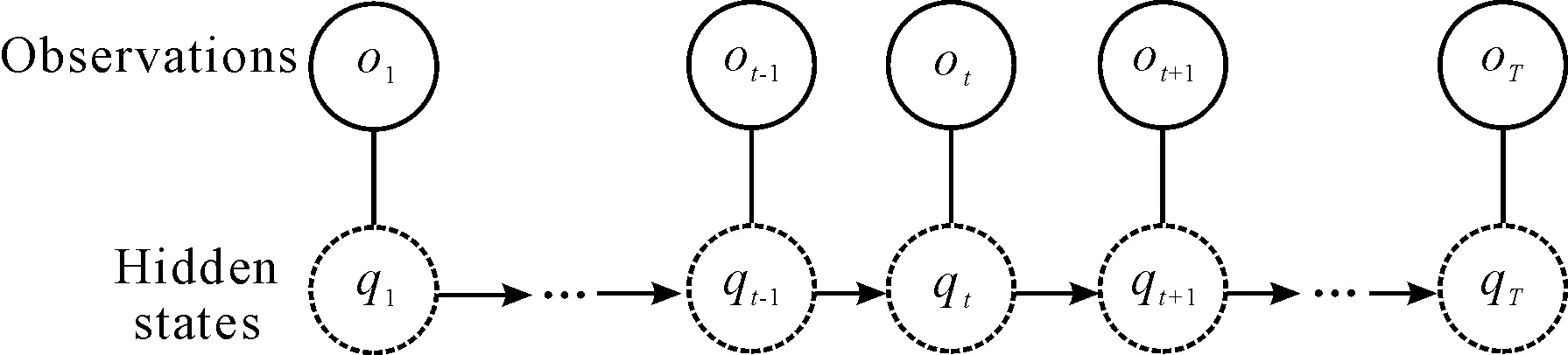
Figure 2. Hidden Markov model
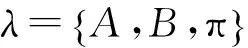
2.Experiment and feature extraction
TheexperimentalsetupusedinthisstudyisillustratedinFigure3.Thecuttingtestsareconductedonfive-axismachiningcenterMikronUCP800Duro.ThethrustforceismeasuredbyaKistler9253823dynamometer.TheforcesignalsareamplifiedbyKistlermultichannelchargeamplifier5070andsimultaneouslyrecordedbyNIPXIe-1802datarecorderwith5kHzsamplingfrequency.ThecollectedsignalsaredisplayedbyCathoderaytubeCRT.Theworkpieceiscontinuouslyprocessedunderdifferentprocessingconditionsuntiltheobviouscuttingtoolwearisobserved.
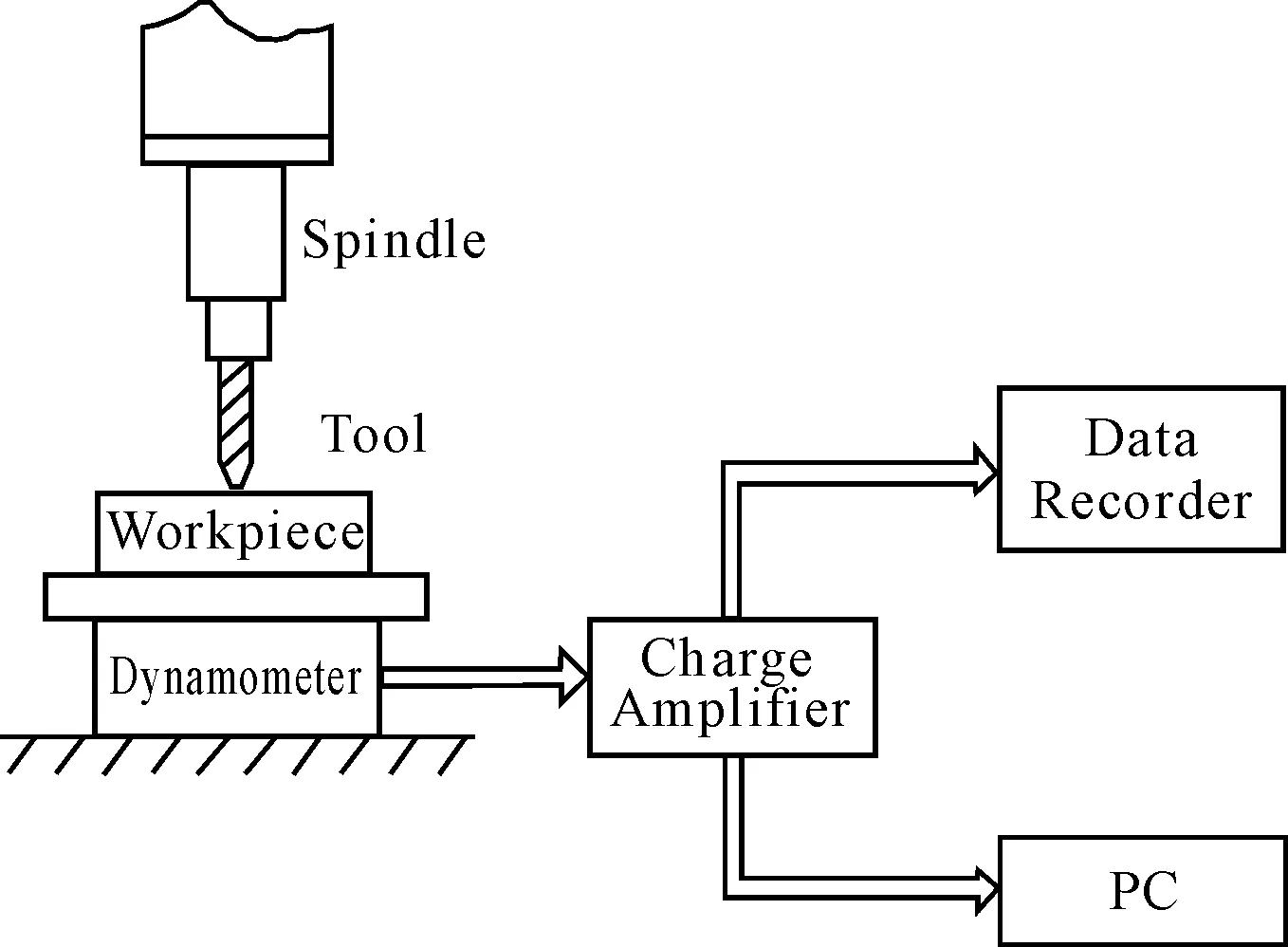
Figure 3. Experimental setup for cutting processing
The tool wear states are classified into three categories: the initial processing status of the tool is named as sharp state (pattern 1), the wear processing status of the tool is named aswearstate (pattern 3), and the status between sharp state and wear state is named asslightwearstate(pattern 2)[8].
The real-time cutting processing signals under different cutting tool condition are shown in Figure 4. Signal I represents the sharp cutting tool condition. Signal II represents the slight wear cutting tool condition. Signal III represents the wear cutting tool condition. By using the fast Fourier transforms (FFT) processing, the time domain signals are shown in Figure 5. We can see that the time-frequency amplitude is different significantly for these three wear states.
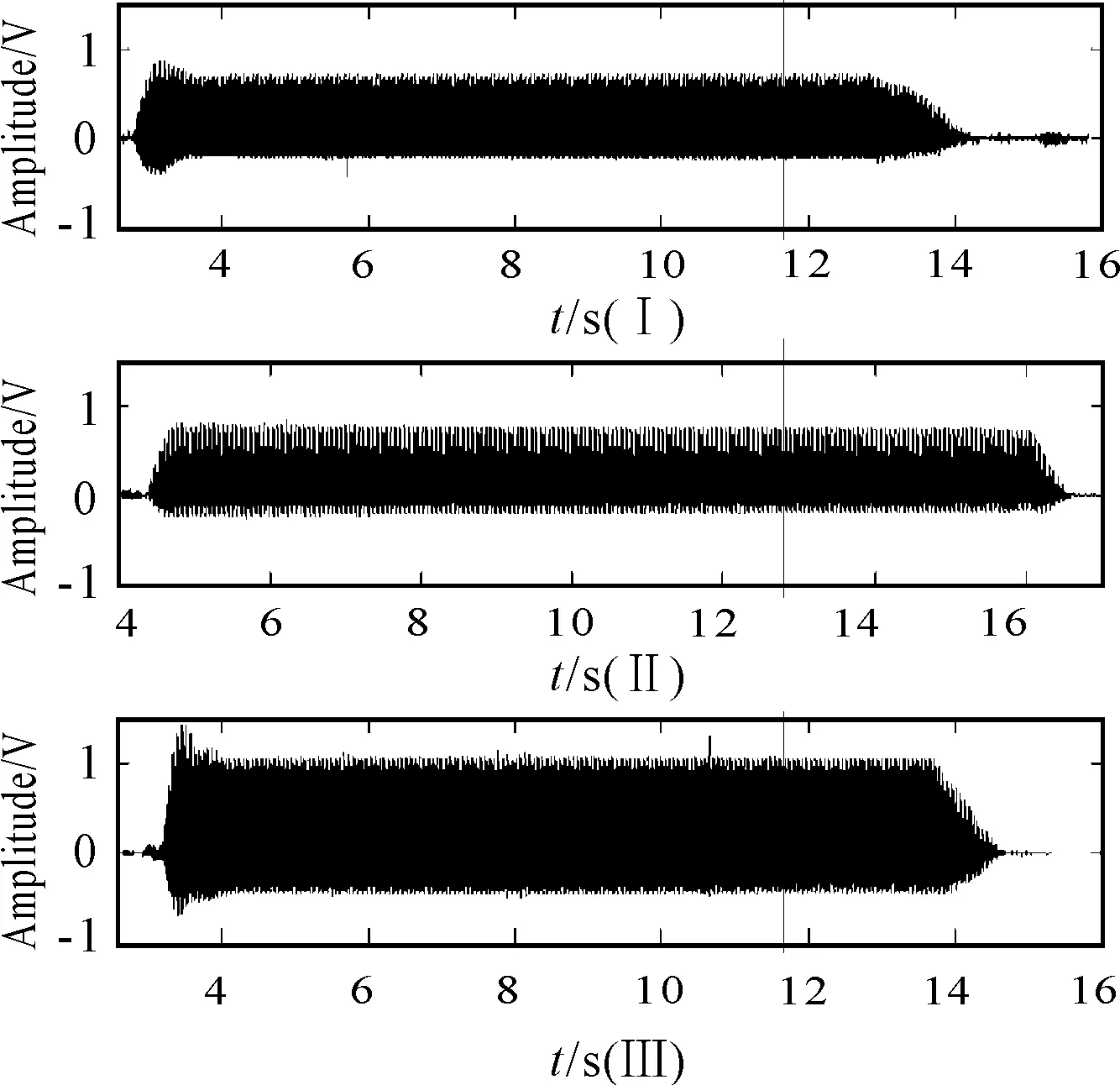
Figure 4. Dynamometer signals
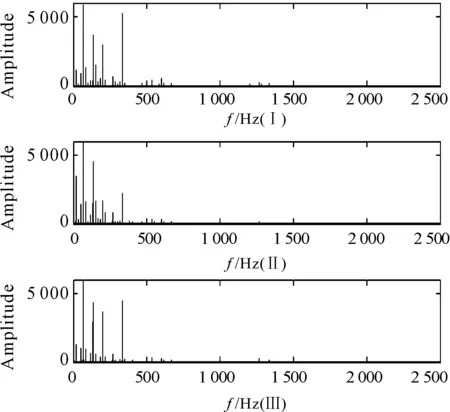
Figure 5. The chart of frequency spectrum
A four-level wavelet packet decomposition is used in this paper. The root mean square (RMS) of the wavelet coefficients at different scales is shown in Figure 6. It could be found that RMS results are significantly different for these three states. The RMS of the wavelet coefficients at different scales are taken as the feature observations vector.
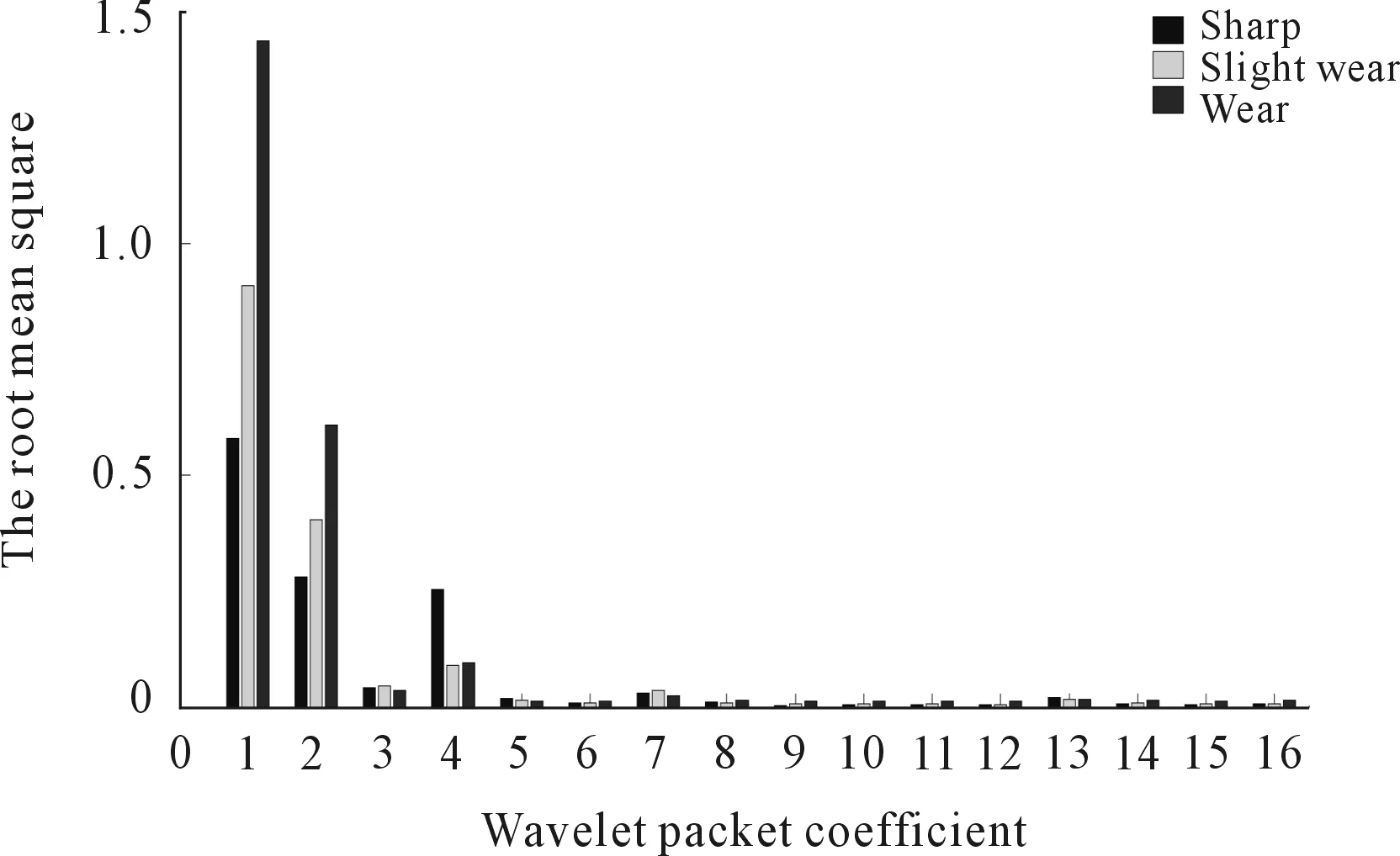
Figure 6. The RMS of wavelet coefficient in three wear states
3.Tool wear monitoring
Flow chart of the tool states recognition based on HMM is shown in Figure 7. It is composed of the wavelet-based feature extraction and the RMS of the wavelet coefficients for HMM input. Each HMM pattern is trained by the RMS from post treatment, and the test sample is recognized by the HMM based classification method. As shown in Table 1, 21 test samples are recognized. The same recognition procedure based on the BP neural network and the recognition results are presented in Table 2.
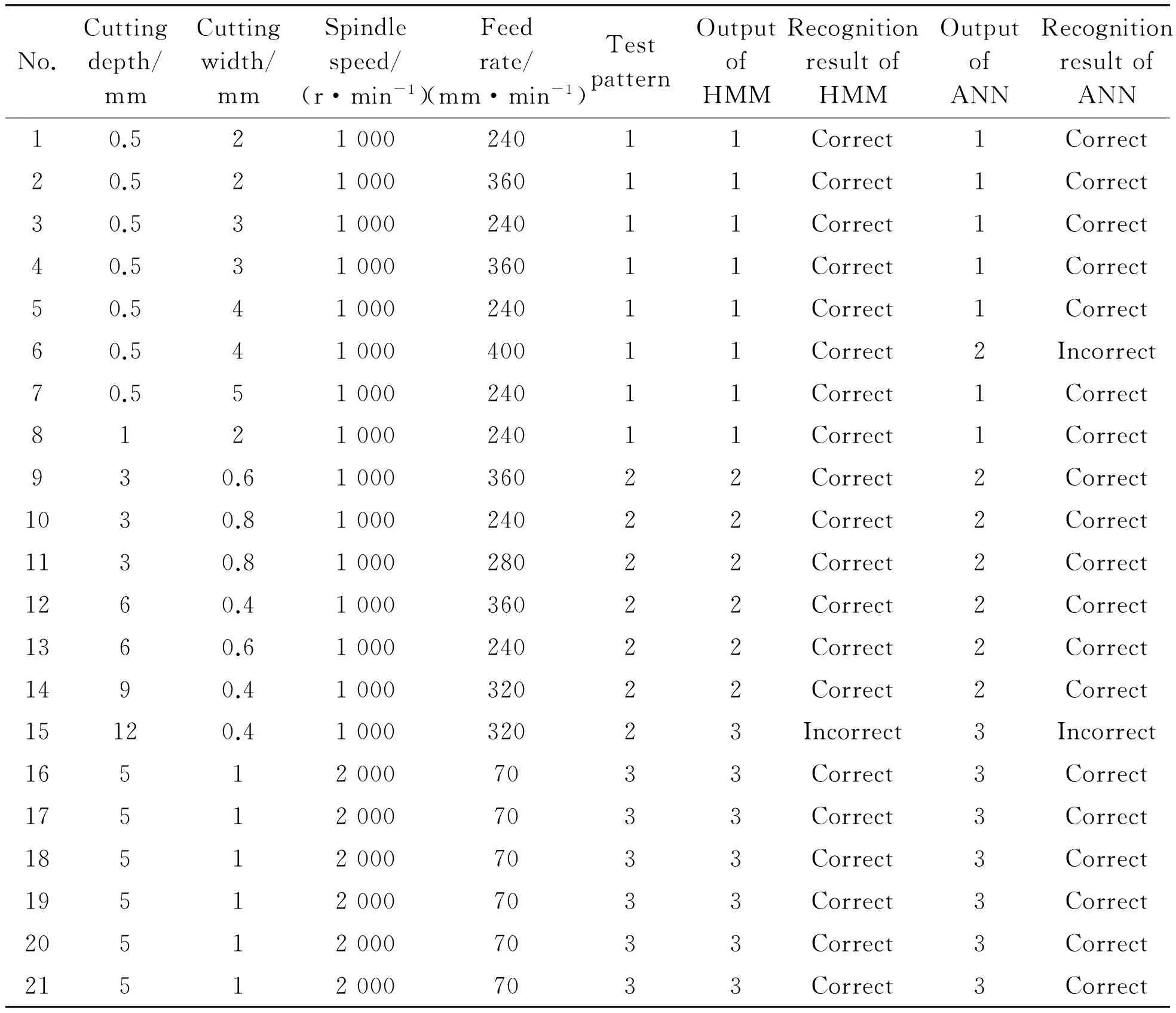
Table 2. Pattern classification results of the tool wear
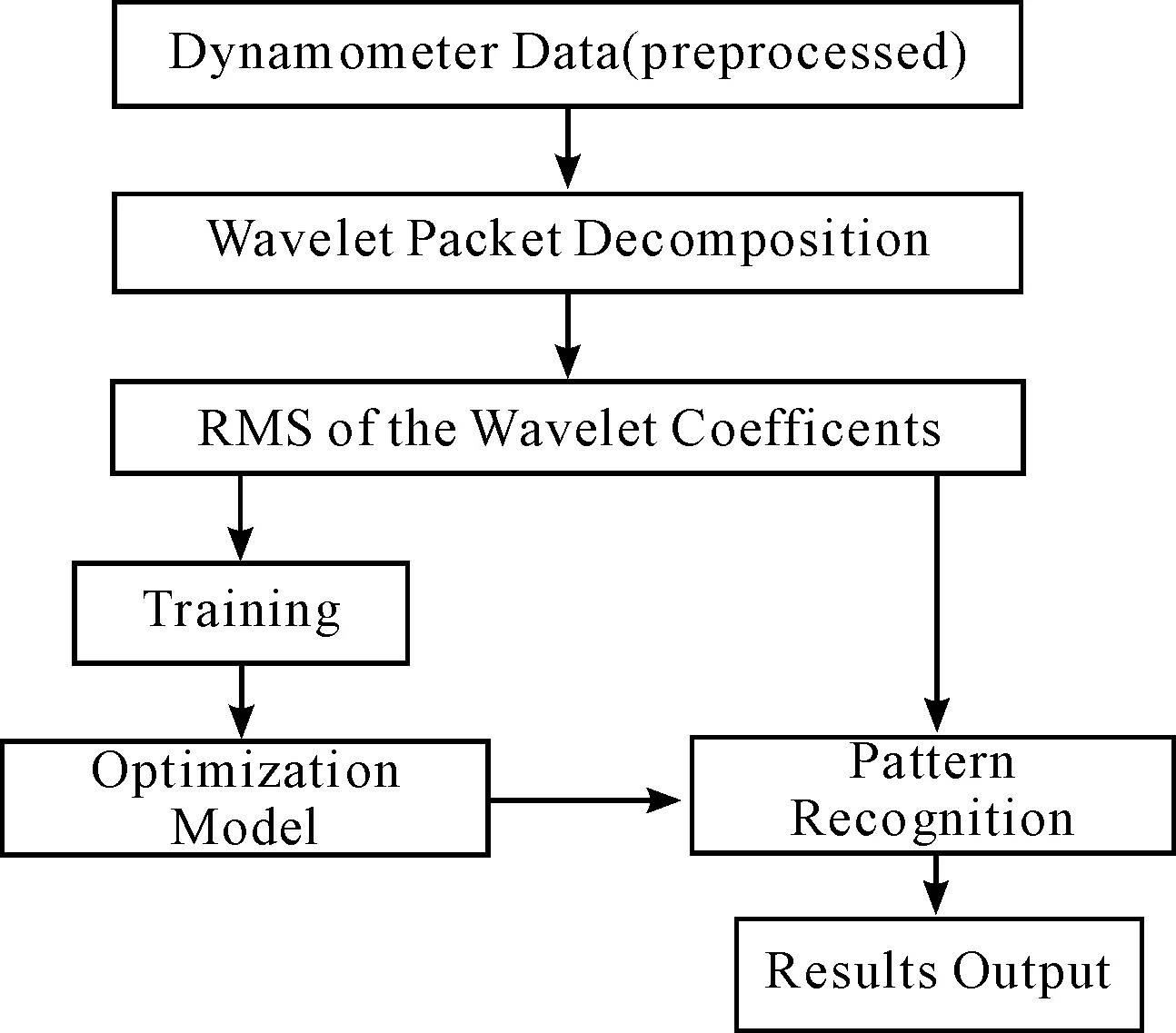
Figure 7. Flow chart of the tool states recognition
As shown in Table 2, most samples have been recognized correctly and the accuracy rate of HMM is 20/21=95%, the accuracy rate of HMM is 19/21=90%. The results show that the HMM-based classification has a higher recognition rate than that of ANN.
4.Conclusion
Tool wear monitoring in machining process is very important for mechanical manufacturing process. In this paper, an approach based on wavelet packet coefficient and HMM for tool wear monitoring is proposed. Wavelet packet decomposition is used for signal processing. The RMS of the wavelet coefficients is adopted for the input of HMM. According to HMM-based recognition method, tool wear states are recognized. In future works, uncertainty in processing should be regarded in modeling and signal acquisition.
[1] Vallejo A J,Menéndez R M,Alique J R.On-line cutting tool condition monitoring in machining processes using artificial intelligence[J].Robotics,Automation and Control,2008,143-166.
[2] XIE F Y.A method of state recognition in machining process based on wavelet and hidden Markov model[J].In Proceedings of the ISMR 2012,2012:639-643.
[3] XIE F Y.On-line condition monitoring based on empirical mode decomposition and neural network[J].Machine Tool & Hydraulics,2013.
[4] Haber R E,Alique,A.Intelligent Process Supervision for Predicting Tool Wear in Machining Processes[J].Mechatronics,2003,13:825-849.
[5] Owsley L M,Atlas L E,Bernard G D.Self-Organizing Feature maps and hidden Markov models for machine-tool monitoring[J].IEEE Transactions on Signals Processing,1997,45:2787-2798.
[6] Chen H X.Fault degradation assessment of water hydraulic motor by impulse vibration signal with wavelet packet analysis and Kolmogorov-Smirnov test[Z].2008,22:1670-1684.
[7] Rabiner L R.A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition[J].Proceedings of the IEEE,1989,77:257-286.
[8] XIE F Y,Hu Y M,Wu B.A generalized interval probability-based optimization method for training generalized hidden Markov model[J].Signal Processing,2014,94(1):319-329.
基于小波包系數與隱馬爾科夫模型的刀具磨損監測*
邱 英,謝鋒云?
華東交通大學 機電學院, 南昌 330013
在機械自動化加工中,為了防止刀具損壞,刀具磨損過程的監測是非常重要的。然而,由于加工過程的復雜性,對刀具磨損狀態的監測十分困難。提出了一個基于小波包系數與隱馬爾科夫模型的刀具磨損監測方法。將加工信號在不同頻帶上小波包系數的均方根值作為特征觀測向量,即為隱馬爾科夫模型的輸入,并用隱馬爾科夫模型模式識別方法識別刀具磨損狀態。實驗結果顯示,提出的方法對刀具磨損狀態具有很高的識別率。
刀具磨損;小波包系數;隱馬爾科夫模型;均方根
TH133;TP391
2014-01-20
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2014.12.008
*Project supported by Jiangxi Province Education Department Science Technology Project (GJJ14365),Jiangxi Province Nature Science Foundation (20132BAB201047,20114BAB206003)
? Feng-yun XIE, PhD. E-mail: xiefyun@163.com
- 機床與液壓的其它文章
- Application of fusion control strategy in purification treatment for workshop wastewater*
- Research on the development trend of marine hydraulic crane
- Structural design and performance testing of the electromagnetic proportional pressure relief valve
- A Simple time-domain method for bearing performance degradation assessment*
- Approaches and development of the modeling of the spiral bevel and hypoid gear*
- Research of data transmission path of neutral file between Pro/E and ADAMS*

