波束中心近似對機載干涉SAR運動補償的影響分析
李銀偉 鄧 袁 向茂生
?
波束中心近似對機載干涉SAR運動補償的影響分析
李銀偉*①②鄧 袁①②向茂生①
①(中國科學院電子學研究所微波成像技術國家級重點實驗室 北京 100190)②(中國科學院大學 北京 100039)
為了定量分析波束中心近似對機載干涉SAR運動補償的影響,該文首先建立斜視條件下波束中心近似時運動補償殘余誤差的數學模型,其形式類似于斜距誤差。隨后推導斜視條件下二次斜距誤差對干涉SAR的影響,通過仿真驗證了理論推導的正確性。最后詳細討論不同波段、斜視角、軌跡偏移、地形變化和斜距情況下波束中心近似對干涉SAR運動補償后圖像質量和相干系數的影響。該文的分析結果為機載重軌干涉SAR數據處理中運動補償精度的估計提供了技術支持。
機載干涉SAR;波束中心近似;運動補償;殘余誤差;相干系數
1 引言
波束中心近似是指在同一方位時刻,對波束照射范圍內的所有目標均按照波束中心目標的運動補償量進行補償。而運動誤差的方位空變性將導致運動補償殘余誤差。DLR的Potsis等人[8]和JPL的Madsen[9]首次指出波束中心近似假設不成立,研究者相繼提出了子孔徑運動補償算法,如SATA[10], PTA[11]和FD[12],但這些算法沒有定量分析波束中心近似對干涉SAR的影響,無法確保在殘余運動估計時可完全忽略這些殘余誤差。文獻[13]定量地分析了正側視模型下波束中心近似對SAR圖像質量的影響,但載機平臺的抖動總會導致斜視角的出現,同時也沒有考慮對相干性的影響。另外,與只重視SAR圖像的系統相比,需要精確相位信息的干涉SAR對運動補償精度的要求更高。
針對上述問題,本文針對斜視條件下波束中心近似時的運動補償殘余誤差建立數學模型,得到其形式類似于斜距誤差。隨后詳細推導了斜視條件下二次斜距誤差對干涉SAR的影響,通過仿真驗證了理論推導的正確性。最后在此基礎上詳細討論了不同波段、斜視角、軌跡偏移、地形變化和斜距情況下殘余誤差對干涉SAR圖像質量和相干性的影響,為機載重軌干涉SAR數據處理中運動補償精度的估計提供了技術支持。
2 運動補償殘余誤差的數學模型
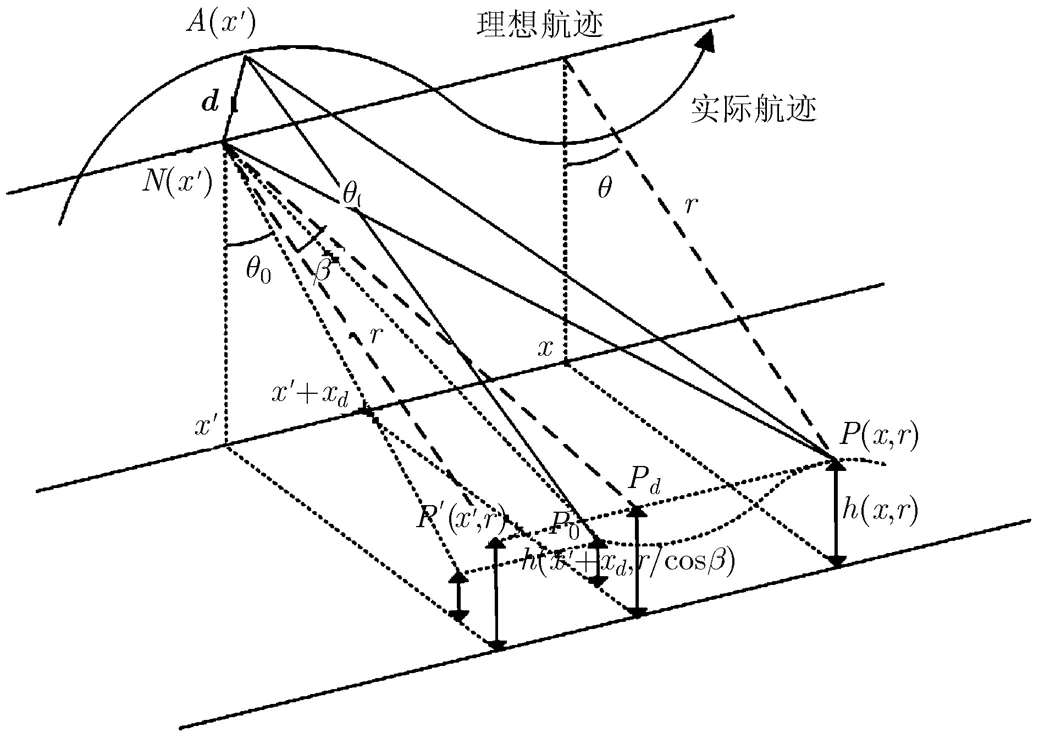
圖1 斜視條件下機載SAR系統的運動補償幾何關系圖
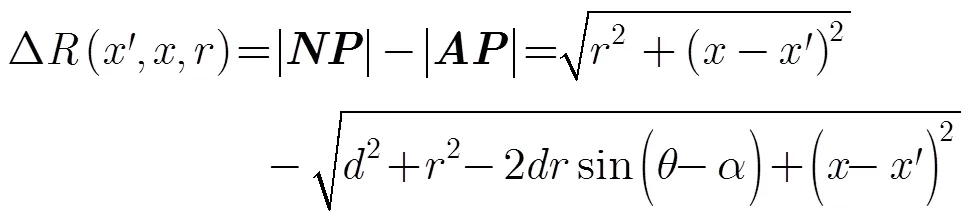
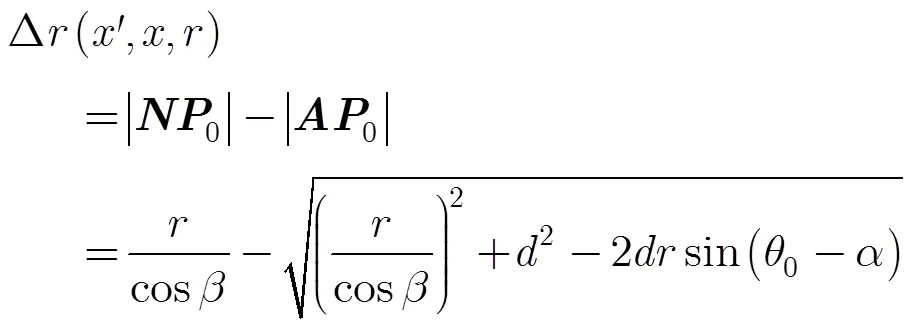
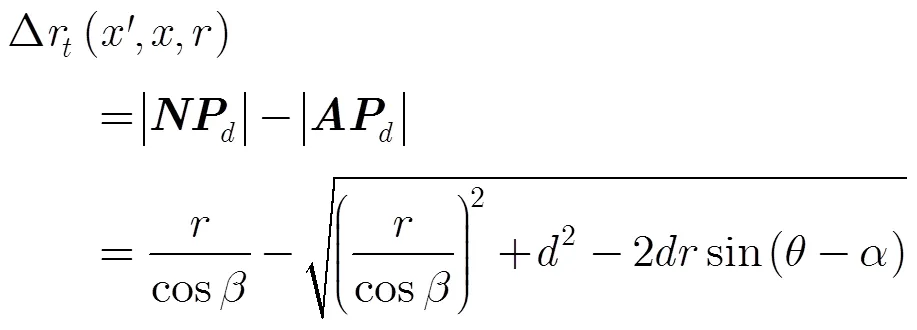
則波束中心近似導致的運動補償殘余誤差為
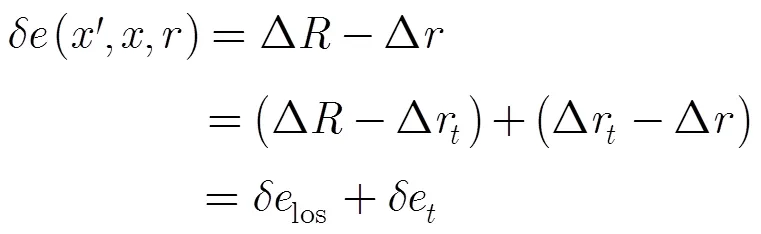
其中
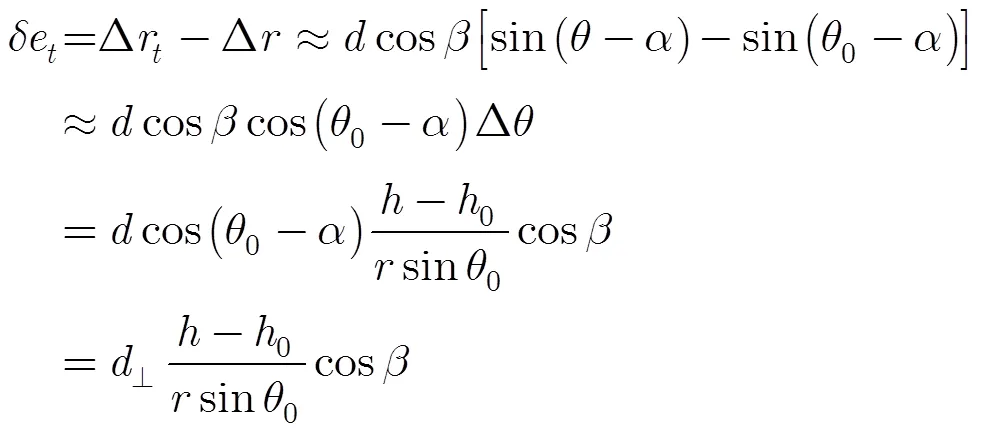
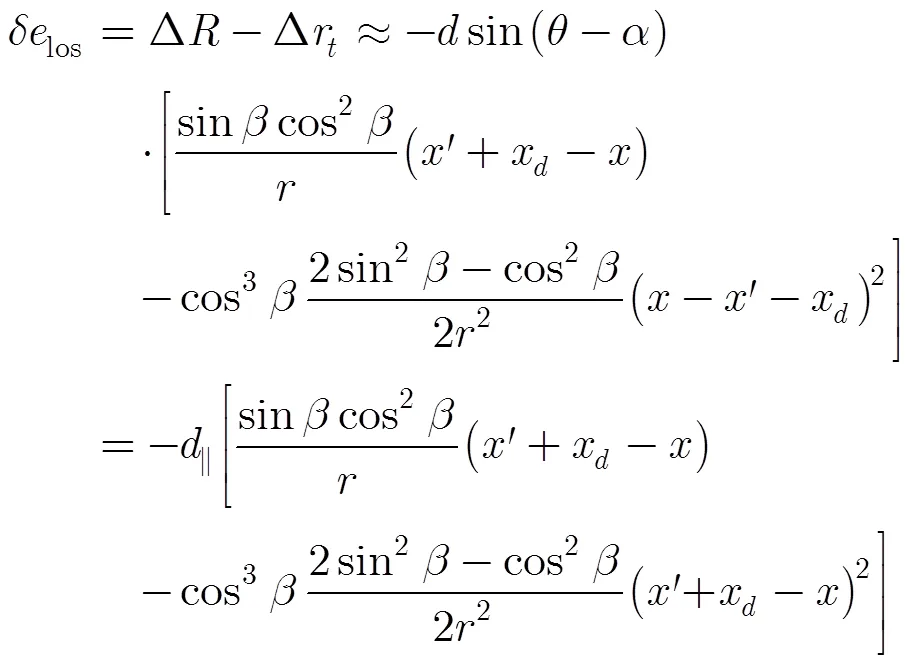
3 斜距誤差對干涉SAR的影響
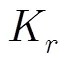

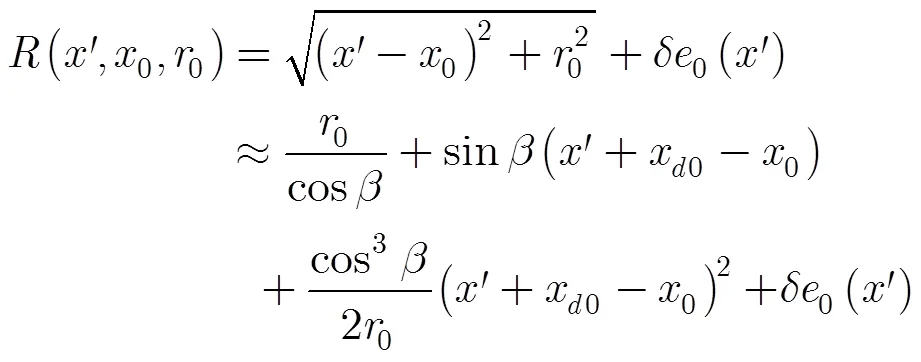
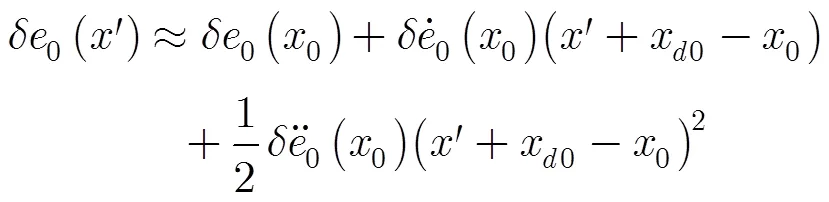
則對式(7)進行距離壓縮,并且對其進行方位向FFT,得到距離壓縮后的2維頻域信號
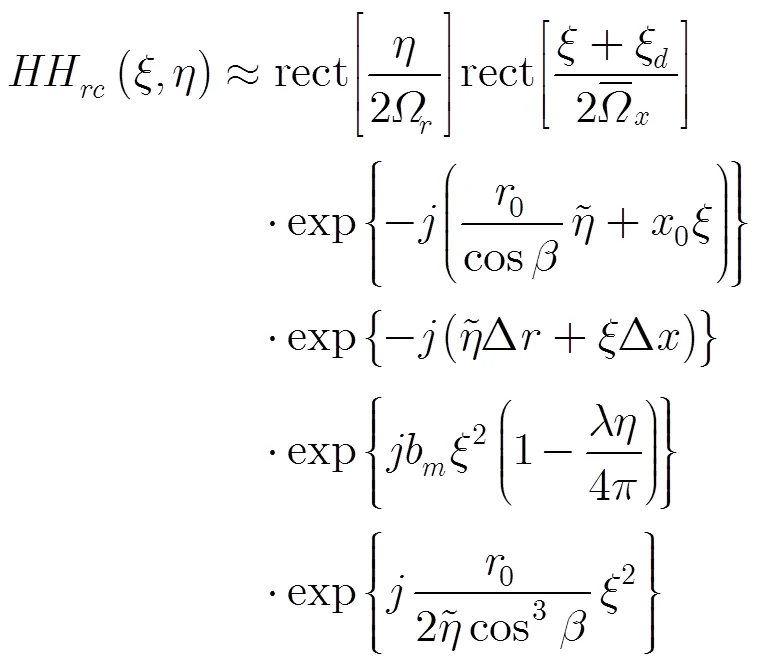
假設方位向處理帶寬足夠大,對2維頻域信號進行距離徙動校正(Range Cell Migration Correction, RCMC)和方位向壓縮可得其2維頻域表達式為
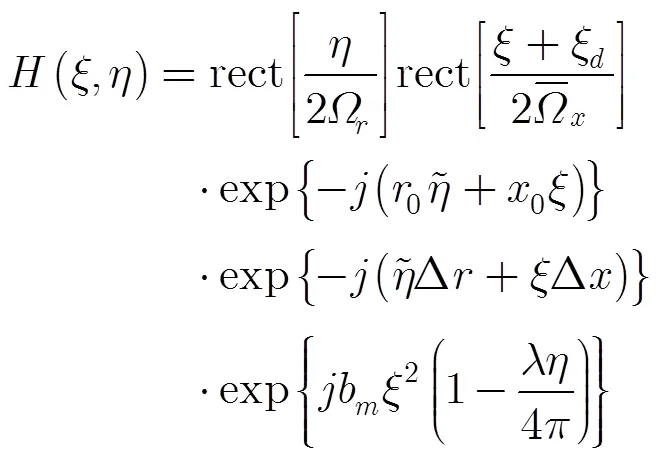
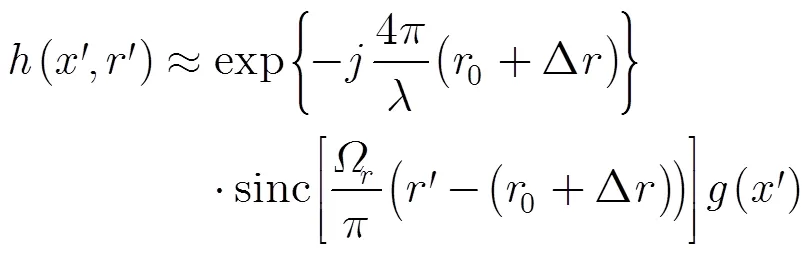
其中
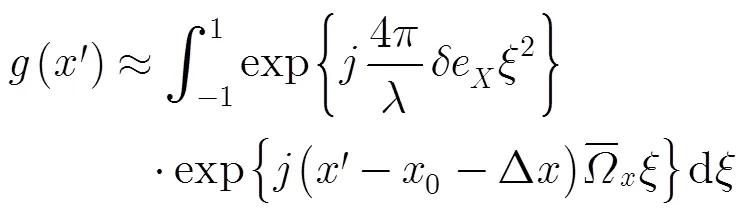
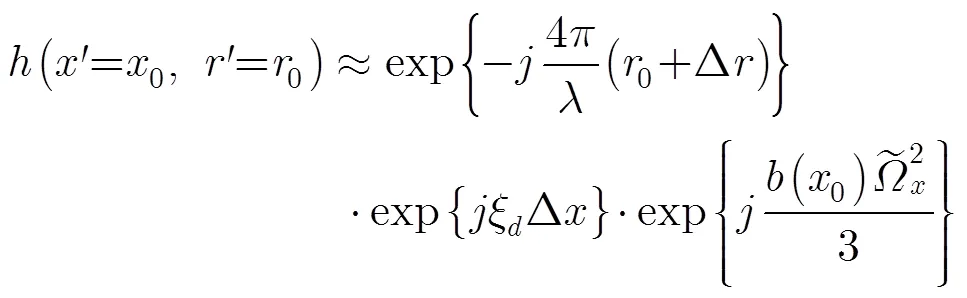
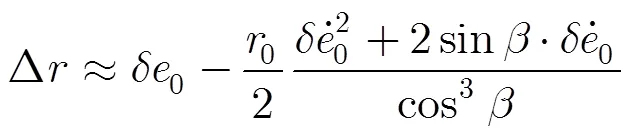
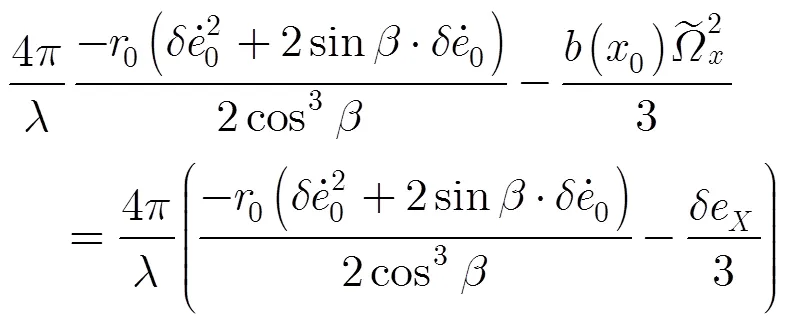
接下來,忽略基線去相干、噪聲去相干等因素,分析雙通道間相對的斜距誤差對相干系數的影響。假設主通道沒有受到運動誤差的影響,副通道受到二次斜距誤差的影響,則相干系數的幅度為
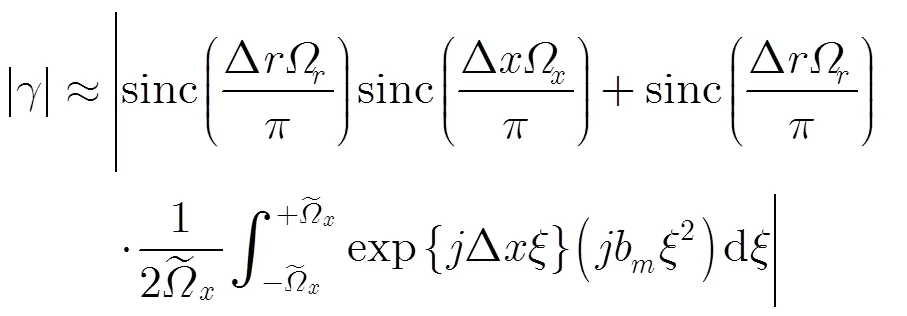
由式(15)可知,相干系數主要由兩部分構成:一部分是由線性項引起圖像偏移而導致的去相干,另一部分是由二次項引起圖像方位向散焦而導致的去相干。
4 仿真結果和分析討論
4.1 仿真結果
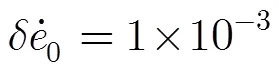
圖2給出了方位向理想脈沖響應函數(Impulse Response Function, IRF)和存在運動誤差情況下的散焦IRF。由圖2理想IRF和散焦IRF的3 dB分辨率得到其脈沖響應寬度(Impulse Response Width, IRW)展寬大約為9.8%,而根據理論計算得到其IRW展寬為8%,兩者結果比較吻合。同時二次誤差對PSLR和ISLR也都有影響。
表1仿真系統參數

中心頻率中心斜距中心視角波束寬度斜視角帶寬速度采樣率脈寬PRF 9.6 GHz5000 m40°3°2°100 MHz169 m/s150 MHz51186 Hz
表2線性誤差影響定位的仿真驗證
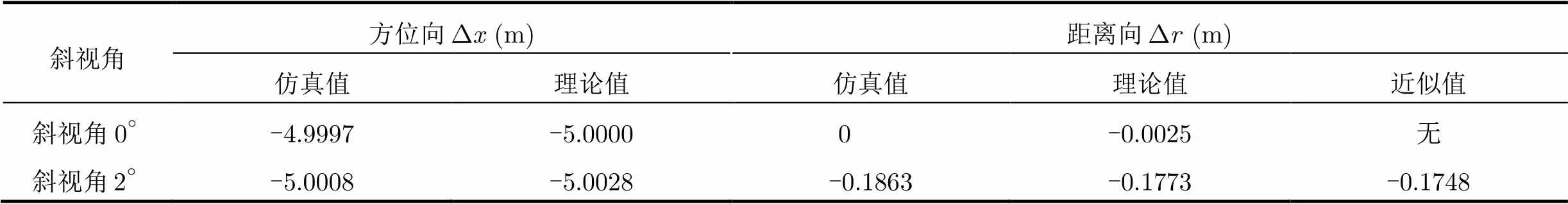
斜視角方位向(m)距離向(m) 仿真值理論值仿真值理論值近似值 斜視角-4.9997-5.00000-0.0025無 斜視角-5.0008-5.0028-0.1863-0.1773-0.1748
4.2 地形變化殘余誤差
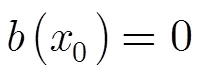

圖2 方位向理想IRF和散焦IRF對比圖
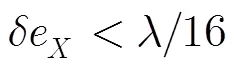
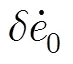
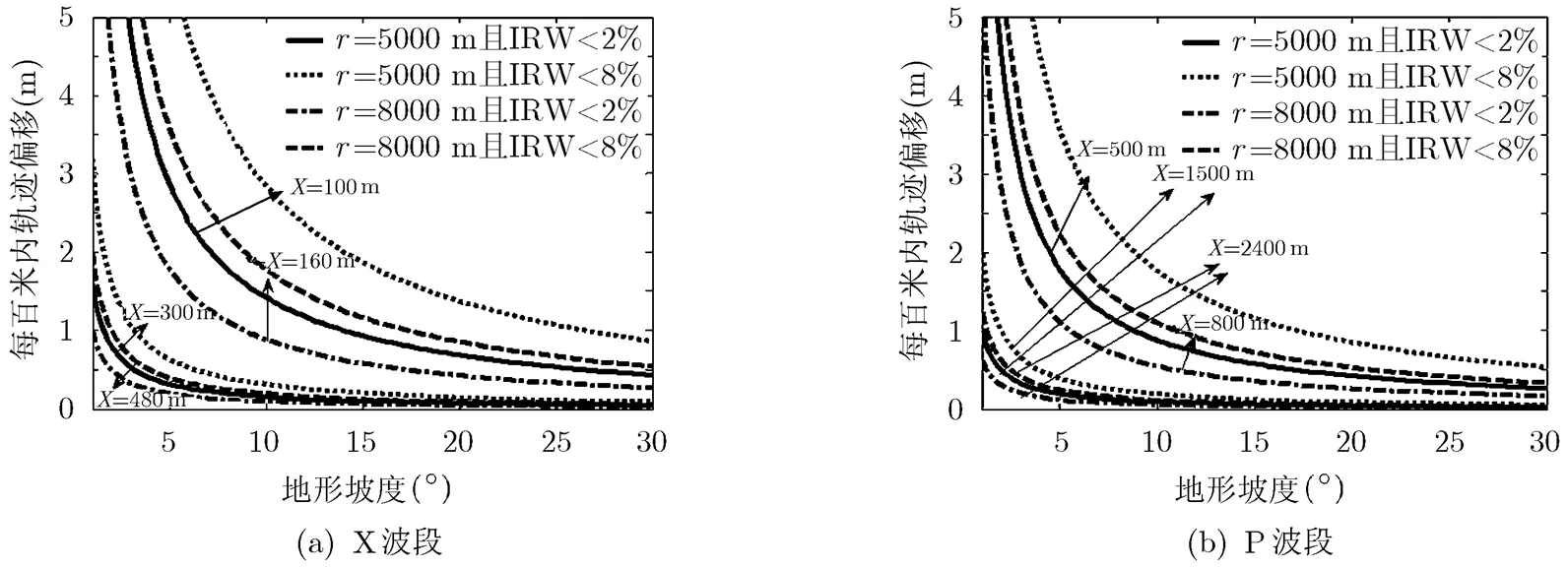
圖3 地形變化中二階誤差的散焦影響
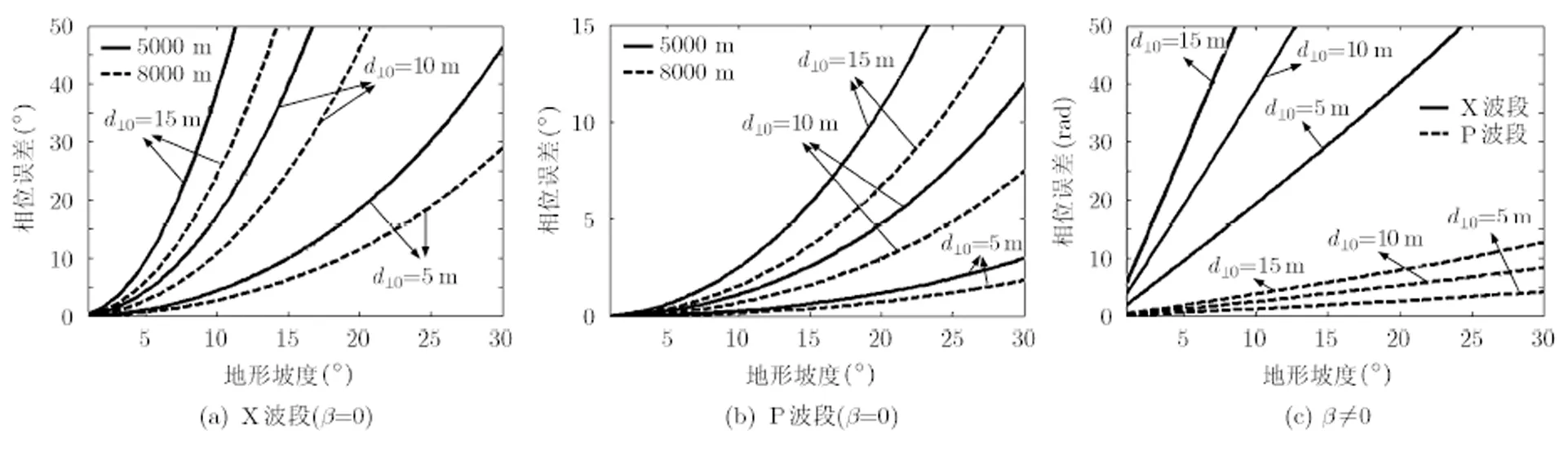
圖4 地形變化中線性誤差導致的相位誤差
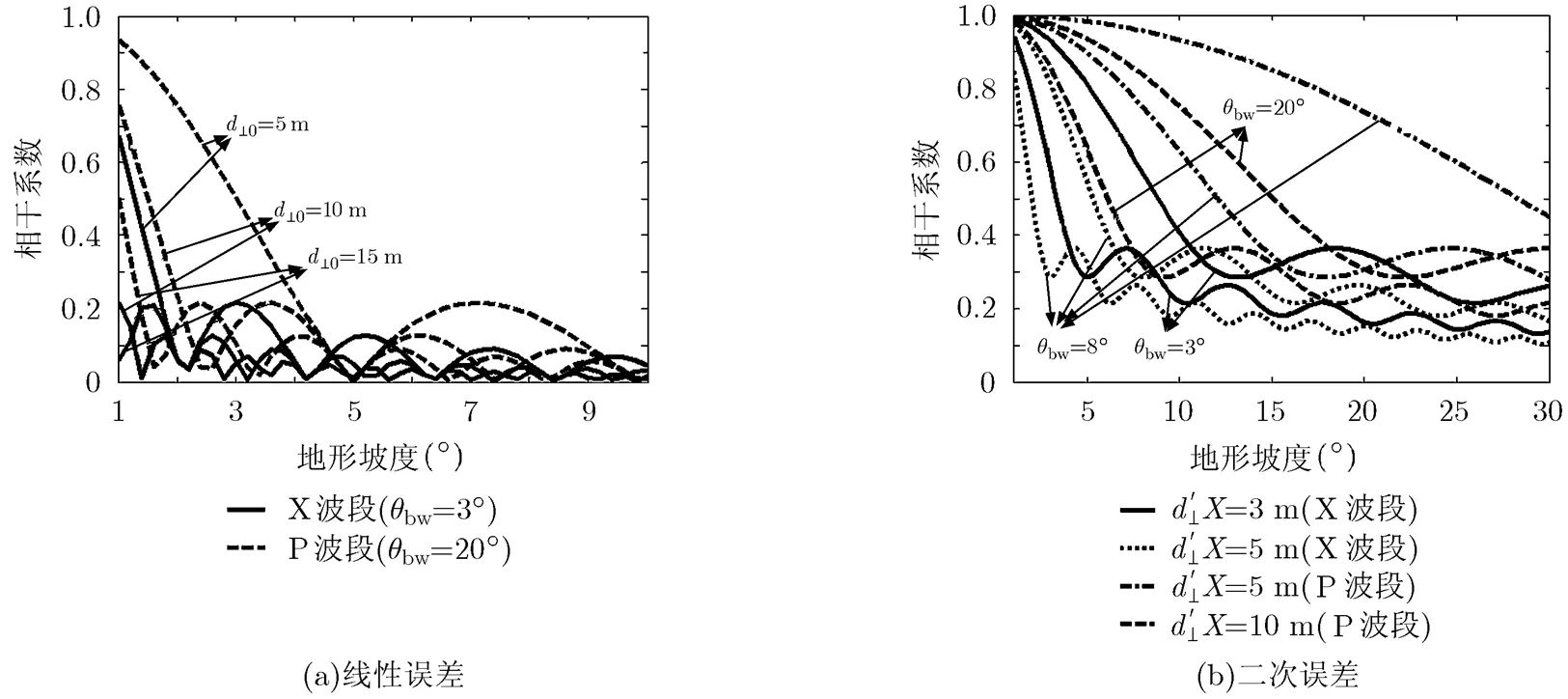
圖5 地形變化中殘余誤差導致的去相干
4.3 LOS近似殘余誤差
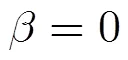
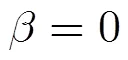
5 結論
本文針對波束中心近似對機載干涉SAR圖像質系數的影響進行了深入研究。詳細推導了斜視條件下二次斜距誤差對干涉SAR的影響,并通過仿真驗證了理論推導的正確性。在此基礎上,從理論上推導了斜視量和相干條件下波束中心近似造成的運動補償殘余誤差對干涉SAR的影響,從而得到了如下結論:波束中心近似殘余誤差會導致圖像散焦、定位偏移、相位誤差和去相干,且對寬波束高頻系統的影響更大;地形變化殘余誤差中斜視角的存在會使得相位誤差急劇增加;LOS近似殘余誤差的影響與斜距無關,且斜視角和軌跡偏移的增大會加劇其不利影響。該文的分析結果為機載重軌干涉SAR數據處理中運動補償精度提供了理論依據。同時在殘余運動誤差估計和補償中都假設相位誤差全是由IMU/GPS測量數據導致的,因此在殘余運動誤差估計之前必須要消除波束中心近似誤差的影響。
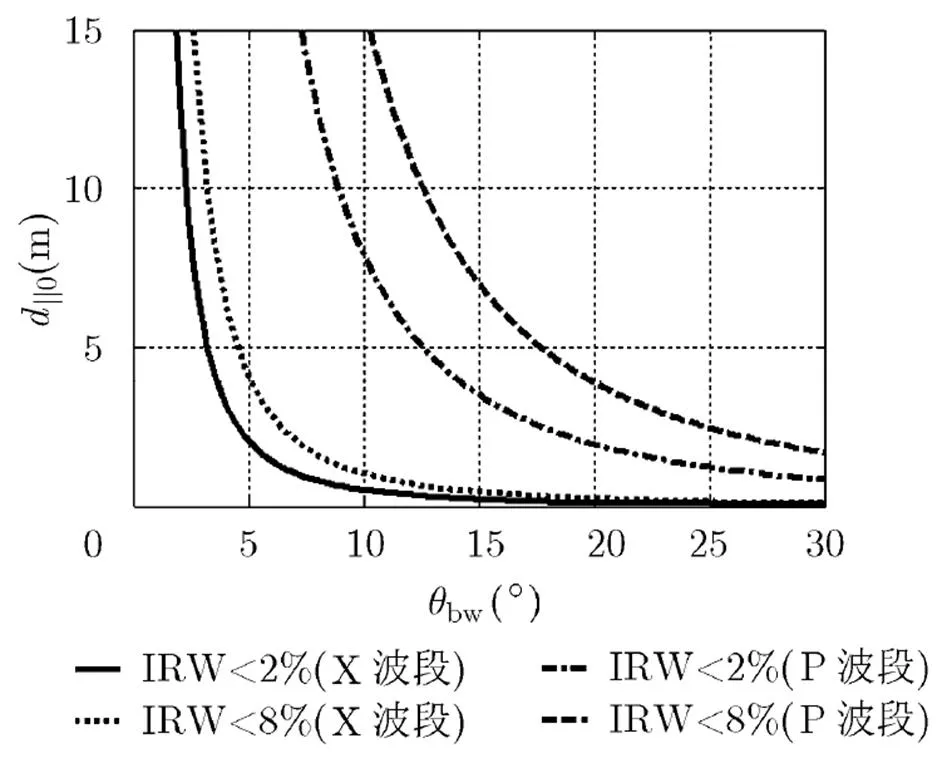
圖6 隨的變化
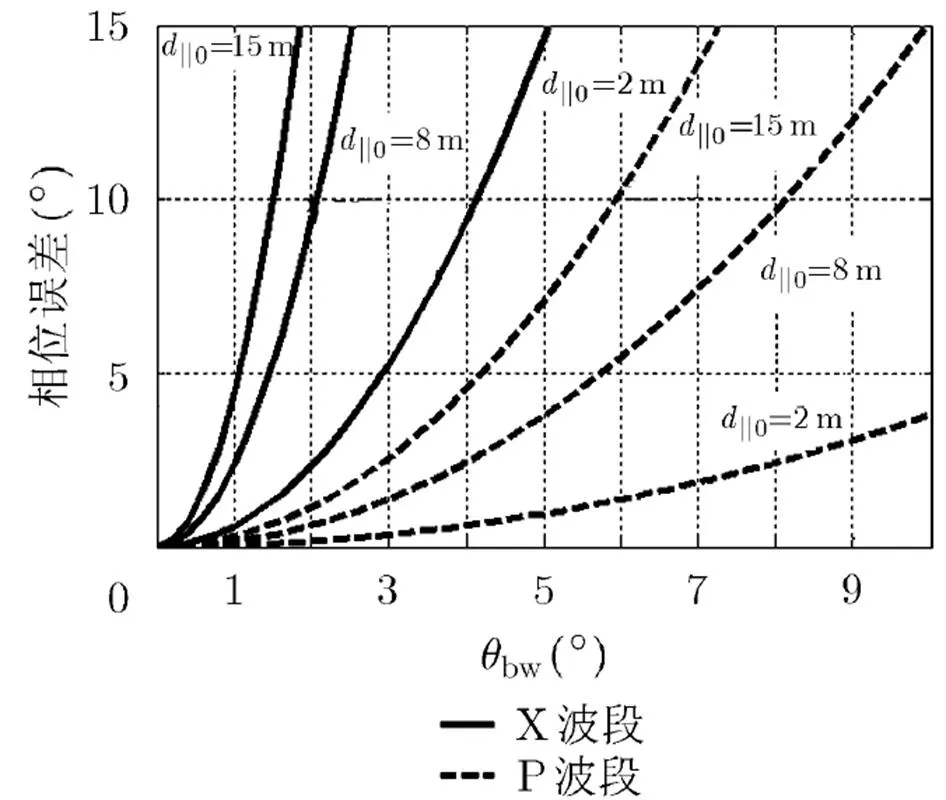
圖7 IRW<2%時的相位誤差
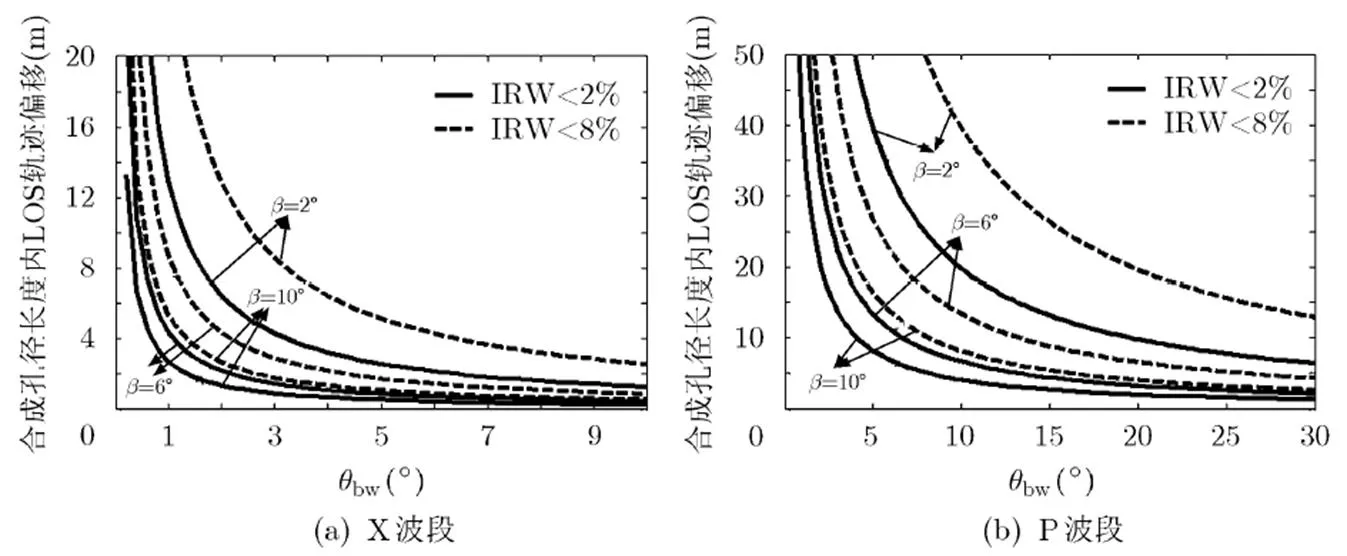
圖8 合成孔徑長度內軌跡偏移隨的變化曲線
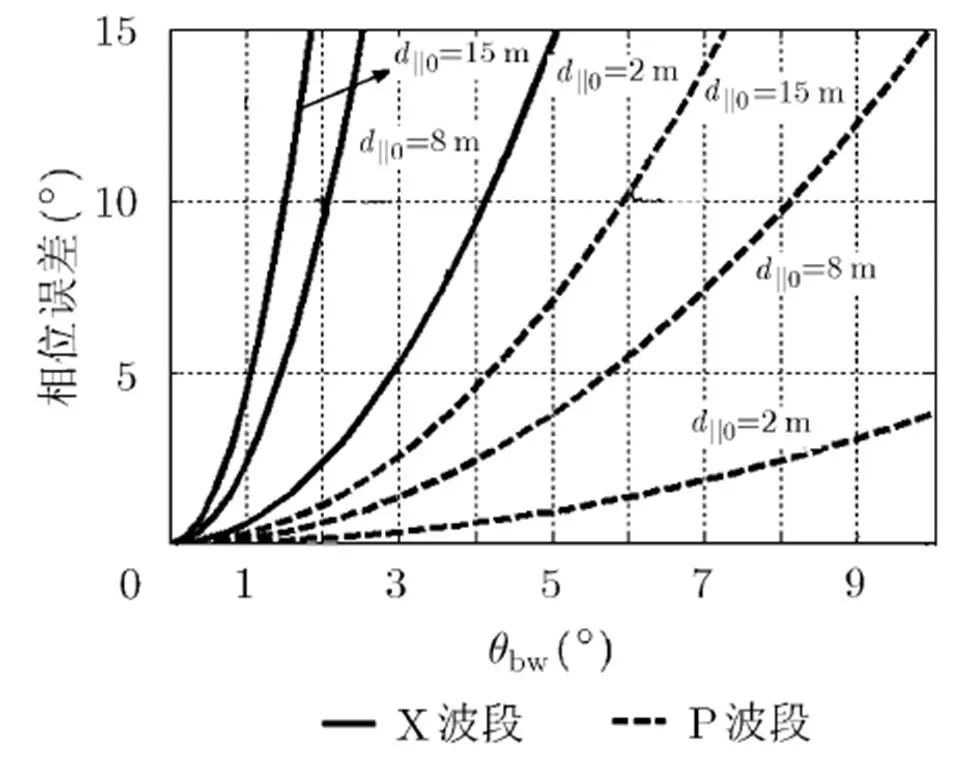
圖9 LOS近似中線性誤差導致的相位誤差
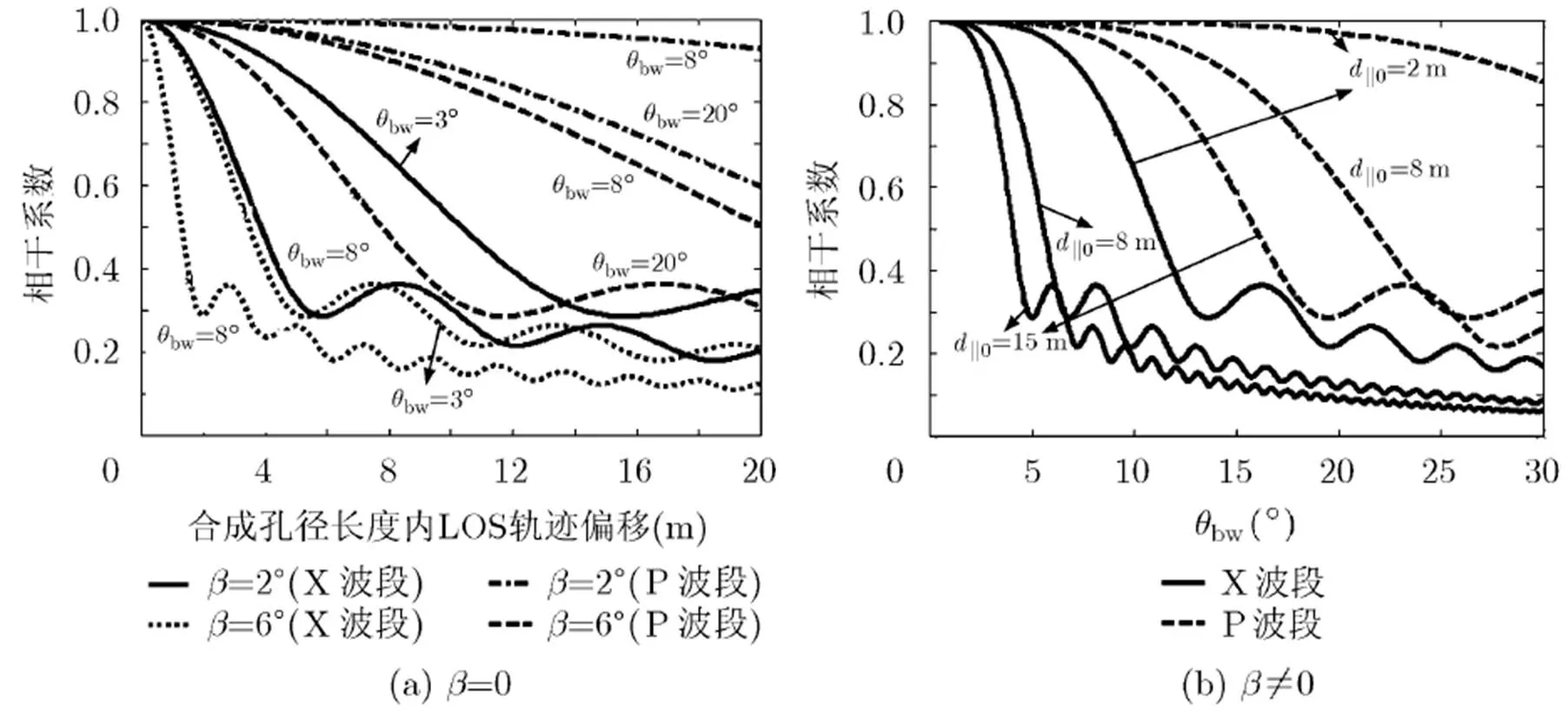
圖10 LOS近似中二次誤差導致的去相干
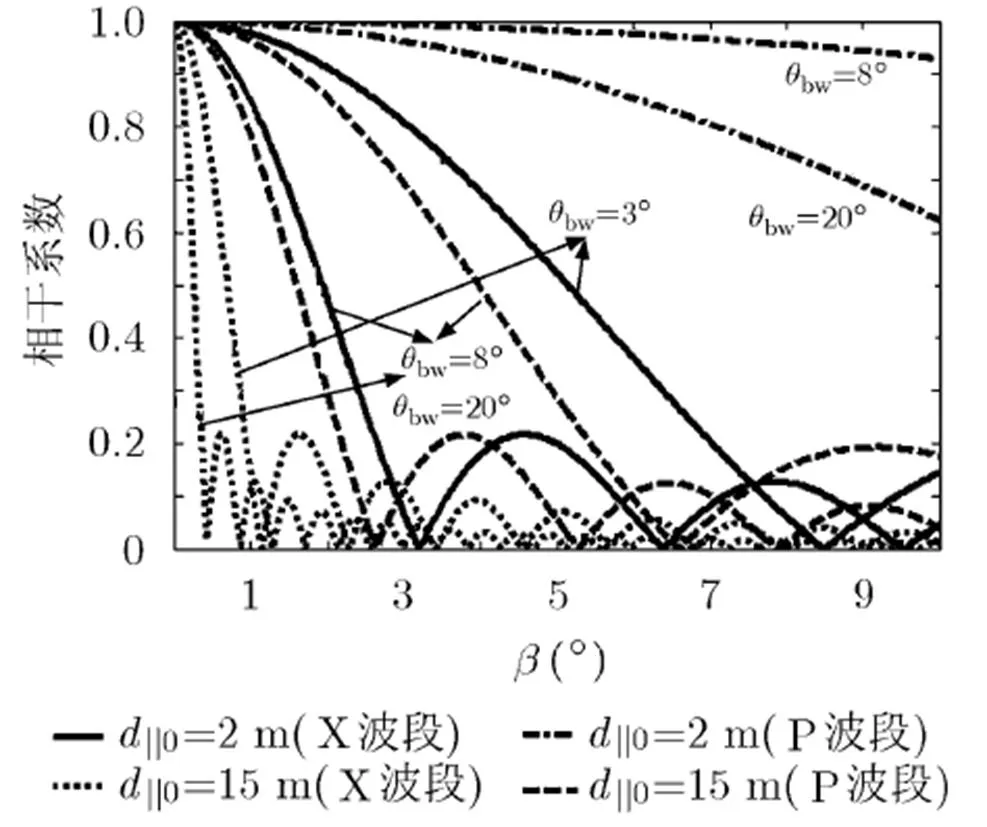
圖11 LOS近似中線性誤差導致的去相干
[1] Moreira A and Huang Yong-hong. Airborne SAR processing of highly squinted data using a chirp scaling approach with integrated motion compensation[J]., 1994, 32(5): 1029-1040.
[2] 李銀偉, 向茂生, 毛永飛. 基于擴展波數域的機載雙天線干涉SAR自配準成像算法[J]. 電子與信息學報, 2012, 34(7): 1630-1636.
Li Yin-wei, Xiang Mao-sheng, and Mao Yong-fei. Auto-registration imaging algorithm based on extended wavenumber domain for airborne dual-antenna InSAR[J].&, 2012, 34(7): 1630-1636.
[3] Mao Yong-fei, Xiang Mao-sheng, Wei Li-deng,.. The effect of IMU inaccuracies on airborne SAR imaging[J].(), 2011, 28(4): 409-418.
[4] Mao Yong-fei, Xiang Mao-sheng, Wei Li-deng,.. Error analysis of SAR motion compensation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques, Manchester, United Kingdom, 2012: 377-380.
[5] Reigber A, Prats P, and Mallorqui J. Refined estimation of time-varying baseline errors in airborne SAR interferometry[J]., 2006, 3(1): 145-149.
[6] Macedo K A C de, Scheiber R, and Moreira A. An autofocus approach for residual motion errors with application to airborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry[J]., 2008, 46(10): 3151-3162.
[7] Zhong Xue-lian, Guo Hua-dong, Xiang Mao-sheng,.. Residual motion estimation with point targets and its application to airborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry[J]., 2012, 33(2): 762-780.
[8] Potsis A, Reigber A, and Mittermayer J. Sub-aperture algorithm for motion compensation improvement in wide beam SAR data processing[J]., 2001, 37(23): 1405-1407.
[9] Madsen S. Motion compensation for ultra wide band SAR[C]. IEEE Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 2001: 1436-1438.
[10] Prats P, Reigber A, and Mallorqui J. Topography-dependent motion compensation for repeat-pass interferometric SAR systems[J]., 2005, 2(2): 206-210.
[11] Macedo K A C de and Scheiber R. Precise topography and aperture-dependent motion compensation for airborne SAR[J]., 2005, 2(2): 172-176.
[12] Zheng X, Yu W, and Li Z. A novel algorithm for wide beam SAR motion compensation based on frequency division[C]. IEEE Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, CO, 2006: 3160-3163.
[13] Fornaro G, Franceschetti G, and Perna S. On center-beam approximation in SAR motion compensation[J]., 2006, 3(2): 276-280.
李銀偉: 男,1985年生,博士生,研究方向為SAR成像、運動補償、干涉SAR信號處理.
鄧 袁: 男,1989年生,碩士生,研究方向為多基線干涉SAR信號處理.
向茂生: 男,1964年生,研究員,博士生導師,長期從事干涉SAR技術及方法的研究工作.
Effects of Center-beam Approximation on Motion Compensation for Airborne Interferometric SAR
Li Yin-wei①②Deng Yuan①②Xiang Mao-sheng①
①(,,,100190,)②(,100039,)
In order to analyze quantitatively the effects of Center-Beam Approximation (CBA) on MOtion COmpensation (MOCO) for airborne Interferometric SAR (InSAR), a mathematical model of MOCO residual error under the condition of squint is firstly established. The form of residual error is similar to the slant range error. Then, the effects of quadratic slant range error on InSAR are deduced on condition that the squint angle is not zero, and the accuracy of the theoretical derivation is verified with simulation data. Finally, the effects of CBA on image quality and coherence coefficient for airborne InSAR are discussed in detail for different bands, squint angles, trajectory deviations, topography variation and slant ranges. The research provides technical support for the estimation of MOCO precision in signal processing of airborne repeat-pass interferometric SAR.
Airborne Interferometric SAR (InSAR); Center-Beam Approximation (CBA); MOtion COmpensation (MOCO); Residual error; Correlation coefficient
TN959.3
A
1009-5896(2014)02-0415-07
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00479
李銀偉 liyinwei19@163.com
2013-04-11收到,2013-10-18改回
國家973計劃項目(2009CB724003)資助課題

