老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)患者甲狀腺功能的變化
郝建萍
(河北省康保縣人民醫(yī)院心內(nèi)科,河北康保,076650)
老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)患者甲狀腺功能的變化
郝建萍
(河北省康保縣人民醫(yī)院心內(nèi)科,河北康保,076650)
目的探討老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)患者甲狀腺功能的變化。方法分析2009年1月—2013年1月在本院接受治療的糖尿病患者臨床資料,依據(jù)是否發(fā)生高血糖高滲狀態(tài)分為觀察組(高血糖高滲狀態(tài))65例和對(duì)照組(無高血糖高滲狀態(tài))45例。結(jié)果觀察組血糖水平、血鉀水平、血鈉水平、血滲透壓、剩余堿均顯著高于對(duì)照組(P<0.05)。觀察組T3水平、T4水平及FT4水平均顯著低于對(duì)照組(P<0.05)。至治療后4d,觀察組T3、T4及FT4均顯著高于治療前(P<0.05)。結(jié)論老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)會(huì)導(dǎo)致繼發(fā)性甲狀腺功能低下及一系列電解質(zhì)酸堿平衡紊亂,治療后甲狀腺功能可恢復(fù)。
糖尿病;老年;甲狀腺功能;高血糖高滲狀態(tài)
糖尿病系由胰島素相對(duì)不足或絕對(duì)不足而引起,以血糖升高為特異性表現(xiàn)的代謝性疾病[1]。該病發(fā)病機(jī)制復(fù)雜,目前尚不十分清楚,認(rèn)為與遺傳、環(huán)境污染、高脂高糖飲食及高齡等因素相關(guān)[2]。2型糖尿病主要累及中老年人群,而中國(guó)是老年人口大國(guó),老年糖尿病患者的數(shù)量逐年增多[3-4]。在糖尿病病程中會(huì)發(fā)生多種并發(fā)癥,高血糖高滲狀態(tài)是其中一種較為兇險(xiǎn)的急性并發(fā)癥,處理不當(dāng)可危及患者生命[5]。作者在前期臨床觀察中發(fā)現(xiàn),老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)患者甲狀腺功能會(huì)產(chǎn)生一定變化,本文擬進(jìn)一步明確甲狀腺功能指標(biāo)是否可用以指導(dǎo)此類患者的診療。
1 資料與方法
分析2009年1月—2013年1月在我院接受治療的糖尿病患者臨床資料,臨床資料完整。所有患者年齡均≥60歲,均經(jīng)臨床、影像學(xué)等檢查明確診斷為2型糖尿病;未合并自身免疫性疾病、甲狀腺功能性疾病、惡性腫瘤等疾病。依據(jù)是否發(fā)生高血糖高滲狀態(tài)分為觀察組:高血糖高滲狀態(tài);對(duì)照組:無高血糖高滲狀態(tài)。
2組患者均在同一組醫(yī)師指導(dǎo)下接受治療,對(duì)照組行常規(guī)處理,觀察組給予補(bǔ)液、胰島素降血糖、糾正電解質(zhì)酸堿平衡紊亂及對(duì)癥支持治療。糖尿病診斷依據(jù)1999年世界衛(wèi)生組織制定的糖尿病診斷標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。高血糖高滲狀態(tài)定義為:血糖常>33.6 mmol/L,血漿滲透壓>330 mOsm/L。
比較2組患者一般資料、血液學(xué)指標(biāo),以及甲狀腺功能指標(biāo),包括:三碘甲狀腺原氨酸素(T3)、游離三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(FT3)、總甲狀腺素(T4)、游離甲狀腺素(FT4)促甲狀腺素(TSH)。
2 結(jié) 果
2.1 一般資料
本研究共回顧性分析在我院接受治療的老年糖尿病患者198例,其中符合研究條件的患者110例,觀察組65例,對(duì)照組45例,2組患者性別比例、年齡、病程及體質(zhì)指數(shù)(BMI)比較差異均無統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。見表1。
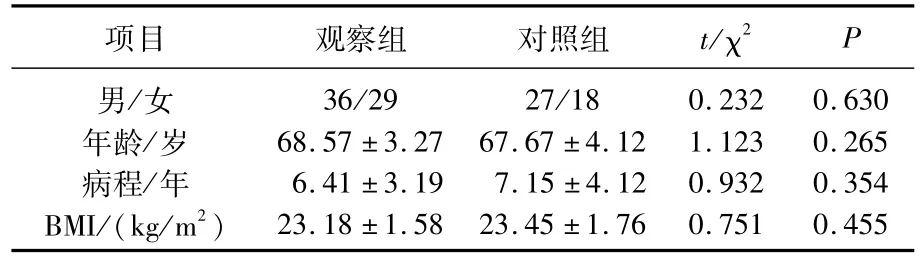
表1 2組患者一般資料比較
2.2 2組患者血液學(xué)指標(biāo)比較
2組患者血氯水平、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)碳酸氫鹽及血pH比較差異均無統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。觀察組血糖、血鉀、血鈉水平及血滲透壓、剩余堿均顯著高于對(duì)照組,差異均有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(t分別為8.991、7.092、9.362、13.390和6.177,P均<0.001)。見表2。
2.3 2組患者甲狀腺功能指標(biāo)比較
2組患者血FT3及TSH比較差異無統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。觀察組T3、T4、FT4水平均顯著低于對(duì)照組,差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(t分別為3.414、 3.597和4.225,P均<0.001)。見表3。

表2 2組患者血液學(xué)指標(biāo)比較

表3 2組患者甲狀腺功能指標(biāo)比較
2.4 觀察組患者T3、T4及FT4的變化
經(jīng)治療后,觀察組患者T3、T4及FT4呈現(xiàn)逐步升高的趨勢(shì);至治療后4 d,觀察組患者T3、T4及FT4均顯著高于治療前,相比較差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。見圖1。
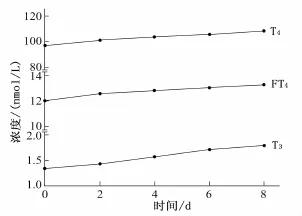
圖1 觀察組患者T3、T4及FT4變化
3 討 論
糖尿病是一種終身性慢性疾病,以中老年人群高發(fā),其治療中會(huì)產(chǎn)生各種急慢性并發(fā)癥[6]。高血糖高滲狀態(tài)是其中較為危急的并發(fā)癥,如救治不及時(shí)可導(dǎo)致高滲性昏迷,甚至是死亡[7]。老年患者機(jī)體功能處于衰退階段,其自穩(wěn)調(diào)節(jié)能力較弱,更易產(chǎn)生并發(fā)癥且難以處理[8]。高血糖、高滲狀態(tài)會(huì)導(dǎo)致全身性應(yīng)激,此時(shí)機(jī)體產(chǎn)生一系列神經(jīng)體液調(diào)節(jié)[9],下丘腦、垂體功能紊亂,激發(fā)甲狀腺功能異常,甲狀腺激素與白蛋白異常結(jié)合,可出現(xiàn)甲狀腺功能低下癥狀[10],從而更加劇患者全身內(nèi)環(huán)境的紊亂。
本研究顯示,觀察組除血糖(mmol/L)及血滲透壓(mOsm/kg)顯著高于對(duì)照組外,血鉀、血鈉、及剩余堿均出現(xiàn)明顯紊亂,說明高血糖高滲狀態(tài)加劇了患者電解質(zhì)及酸堿平衡的紊亂。2組患者甲狀腺相關(guān)功能比較發(fā)現(xiàn),觀察組T3、T4及TSH均顯著低于對(duì)照組,說明高血糖高滲狀態(tài)導(dǎo)致了患者甲狀腺功能低下。經(jīng)治療后,觀察組T3、T4及FT4呈現(xiàn)逐步升高趨勢(shì);至治療后4 d,觀察組T3、T4及FT4均顯著高于治療前,逐步恢復(fù)到正常水平。本研究顯示,老年糖尿病合并高血糖高滲狀態(tài)可導(dǎo)致繼發(fā)性甲狀腺功能低下及一系列電解質(zhì)酸堿平衡紊亂,治療后甲狀腺功能可恢復(fù)。
[1]Ballav C,Gough S C.Safety and Efficacy of Sitagliptin-Metformin in Fixed Combination for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J].Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes,2013,6:25.
[2]Bondan E F,Martins M F,Viani F C.Decreased astrocytic GFAP expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetes after gliotoxic lesion in the rat brainstem[J].Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol,2013,57(6):431.
[3] 黃毅,佟曉光.中國(guó)人口老齡化現(xiàn)狀分析[J].中國(guó)老年學(xué)雜志,2012,32(21):4853.
[4] 許樟榮.對(duì)老年糖尿病更應(yīng)給予高度關(guān)注[J].中華老年多器官疾病雜志,2012,11(7):481.
[5]Restrepo B I,Pino P A,Zarate I,et al.Dipstick urinalysis for diabetes screening in TB patients[J].Int Health,2013,5(2):157.
[6]Morita K,Saruwatari J,Miyagawa H,et al.Association between aldehyde dehydrogenase2 polymorphismsand theincidence of diabetic retinopathy among Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Cardiovasc Diabetol,2013,12(1):132.
[7]Al-Khalifah R,Al-Subaihin A,Al-Kharfi T,et al. Neonatal short-term outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus in saudi mothers:a retrospective cohort study[J].JClin Neonatol,2012,1(1):29.
[8]Ghadiri-Anari A,F(xiàn)azaelipoor Z,Mohammadi S M.Insulin refusal in Iranian patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Acta Med Iran,2013,51(8):567.
[9]Wenning P,Kreutz T,Schmidt A,et al.Endurance Exercise Alters Cellular Immune Status and Resistin Concentrations in Men Suffering from Non-insulin-dependent Type 2 Diabetes[J].Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes,2013,121(8):475.
[10]Kim Y S,Kwon J S,Hong M H,et al.Restoration of angiogenic capacity of diabetes-insulted mesenchymal stem cells by oxytocin[J].BMC Cell Biol,2013,14(1):38.
Clinical analysis of changes of thyroid function in elderly diabetic patientsw ith hyperglycem ic hyperosmolar status
HAO Jianping
(Department of Cardiology,The People′s Hospital of Kangbao County,Kangbao,Hebei,076650)
ObjectiveTo observe the changes of thyroid function in elderly diabetic patients with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar status(HHS).M ethodsClinicalmaterial of diabetic elderly patientswith hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state from 2009 to 2013 was retrospectively analyzed.Patients were divided into observation group and control group according to the occurrence of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.Therewere 65 elderly diabetics patientswith HHS in observation group and 45 diabetic elderly patientswithout HHS in the control group.ResultsPatients in the observation group had higher levels of blood glucose,serum potassium,blood sodium,blood osmotic and base excess than that in the control group and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The levels of T3,T4and FT4were lower in the observation group than that in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).After 4 days of treatment,patients in the observation group had higher levels of T3,T4and FT4than that of prior treatment,so the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).ConclusionHHS of elderly diabetic patients could lead to the secondary hypofunction of thyroid and a series of acid base disturbance.With the treatment,the function of thyroid could be recovered.
diabetes;the elderly;thyroid function;hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state
R 587.1
A
1672-2353(2014)05-111-02
10.7619/jcmp.201405038
2013-11-19

