Study on chemical failure of HMX under low temperature condition
AN Xiao-hong, ZHANG Xin-mao, LI Hua, GU Qiang
(1. College of Mechatronic Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China;2. Beijing North Vehicle Group Corporation, Beijing 100072, China)
安曉紅1, 張新貌1, 李 華2, 顧 強1
(1. 中北大學(xué) 機(jī)電工程學(xué)院, 山西 太原 030051; 2. 北京北方車輛集團(tuán)有限公司, 北京 100072)
?
Study on chemical failure of HMX under low temperature condition
AN Xiao-hong1, ZHANG Xin-mao1, LI Hua2, GU Qiang1
(1.CollegeofMechatronicEngineering,NorthUniversityofChina,Taiyuan030051,China;2.BeijingNorthVehicleGroupCorporation,Beijing100072,China)
In order to make unexploded ordnance lose explosive ability, the chemical failure of HMX that is usually used as detonating explosive and booster was studied so as to find the corresponding chemical reagents, which can decompose HMX into compounds without explosive properties. For this purpose, several decomposition experiments between HMX and NaOH, HMX and thick H2SO, HMX and mixed acid under different temperature conditions were carried out. According to the experimental results, it can be concluded that HMX can be decomposed by a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated nitric acid with the volume ratio of 3∶1. When its decomposed level reaches 60%, HMX will not be detonated, therefore the failure purpose is achieved.
unexploded ordnance; HMX; chemical failure; decomposition experiment
0 Introduction
All countries have paid considerable attention to the clearance of unexploded ordnance beacuse it may result in harm to the civilians. And a variety of solutions have been developed until now. Detonating explosive and booster are important explosive components in explosion sequence. The failure of explosion sequence will lead to fuse failure, therefore ammunition is unexplored. Destruction of fuse’s explosion sequence will ensure that the unexploded ordnance and waste ammunition lose their ability to explode[1]. HMX is main ingredient of common detonating explosive and booster. By analyzing the decomposition of HMX in chemical environment, the failure mechanism of fuse detonating explosive and booster can be known, which means that the fuse loses its explosion ability and the unexploded ordnance is safe[2-3].
Temperature is an important factor during the physicochemical process. At low temperatures, it is very difficult for some materials to produce chemical reaction or the reaction time is too long. In this paper, in order to ensure the feasibility of ammunition in reality, the chemical failure of HMX under low temperature conditions is studied.
1 Principle of HMX chemical failure
Octogen’s scientific name is central tetramethylene four nitramine, usually referred to as HMX. It is a kind of white granular crystal. And its structure is nitramine structure with eight membered rings, as shown in Fig.1[4-5].
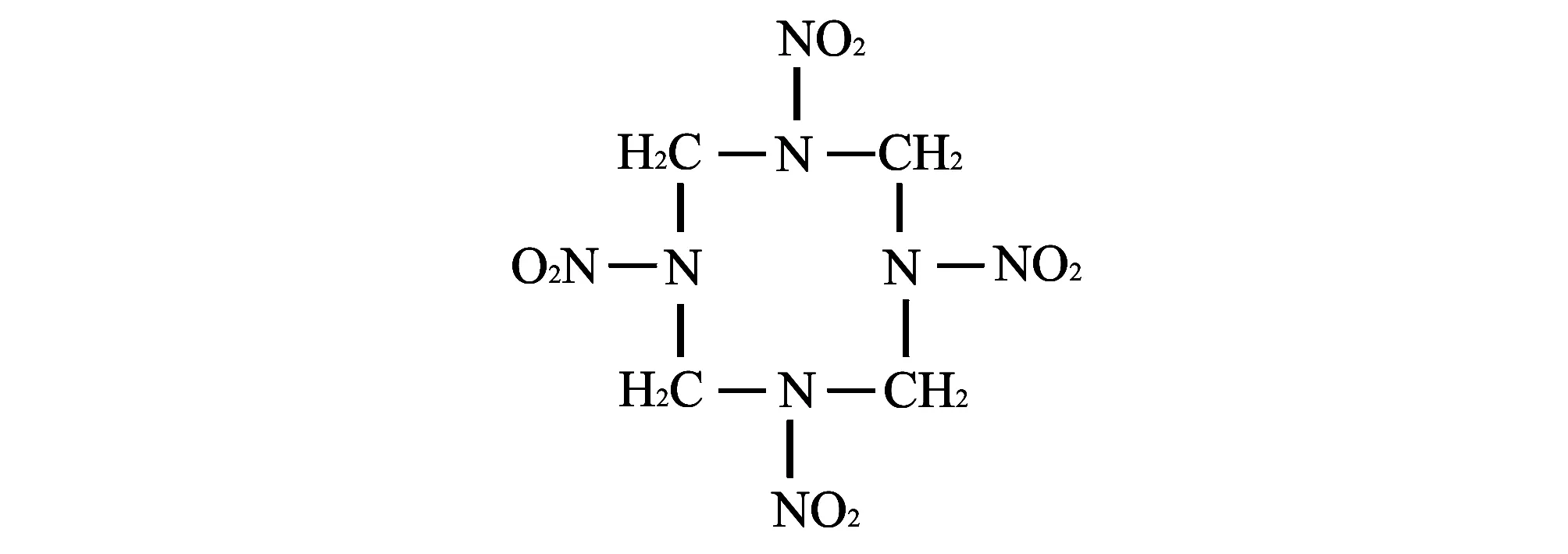
Fig.1 Chemical structure of HMX
HMX is a kind of explosive with high melting point of 276-280 ℃ and density of 1.902-1.905 g/cm3, and its stable crystalline form at normal temperature isβtype (all kinds of HMX in practical application areβtype). Due to high density, its detonation velocity and detonation pressure are high. Its chemical stability is good, and it has certain heat resistance, therefore it is the best explosive. Its toxicity is not heavy, but still potentially dangerous[6-7].
Based on the principle that oxidant can decompose organic material[8-11], the decomposition experiments of HMX were conducted. With a strong oxidizer, low-energy organic and inorganic salt could be obtained in the process of HMX decomposition. Reactants were mixed with undecomposed detonating explosive and booster with different ratios. In order to meet the requirements of practial application, the experiment of the effect of degradation degree on explosive performance was carried out.
2 HMX oxidative decomposition experiments
2.1 HMX hydrolysis experiments in sodium hydroxide
The first experiment is about the hydrolysis reaction of HMX and alkaline chemical reagent-sodium hydroxide. The hydrolysis reaction was carried out in a constant temperature water bath (a boiling water bath, in which there is 10.5% sodium hydroxide). According to the experimental data, the curve of the effect of temperature on the hydrolysis of HMX in alkaline solution with concentration of 10.5% are plotted, as shown in Fig.2.
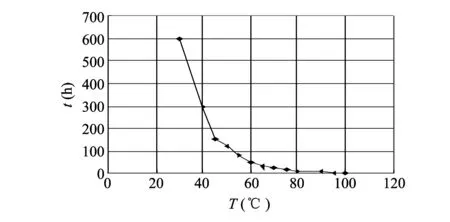
Fig.2 Curve of effect of temperature on hydrolysis of HMX in alkaline solution with concentration of 10.5%
The experiments show that there is almost no decomposition when the temperature is below the normal temperature.
2.2 Decomposition of HMX and concentrated sulfuric acid at 0 ℃
To observe the decomposition reaction between HMX and concentrated sulfuric acid (single acid) at 0 ℃, the following tests were performed.
Firstly, a clean conical flask and 500 mg HMX were prepared. After that, a piece of folded paper containing medicines was put into the prepared conical flask. Secondly, the medicines were slowly slided into the flask along the filter paper and the concentrated sulfuric acid was added to the medicine slowly. At last, the flask was placed in a thermostat with 0 ℃. The observed experimental results are shown in Fig.3. The white solid powder floating on the liquid surface means there is no decomposition.

Fig.3 Reaction phenomenon when adding concentrated sulfuric acid at 0 ℃
The above two experiments show that when the temperature is below 0 ℃, there is no reaction between HMX and sodium hydroxide, HMX and concentrated sulfuric acid, respectively. To continue the experiment, stronger oxidation or strong acidic is needed.
2.3 Decomposition reaction of mixed acid and HMX with different proportions at normal temperature
Similar to the above experiments, in this experiment the conical flask was used. 500 mg HMX was slowly slided into the conical flask along the filter paper. Then 10 mL mixed acid was added drop by drop. This experiment was repeated using mixed acid with different proportions. The reaction results are shown in Table 1.
It can be seen from Table 1 that when the ingredients and proportions of the mixed acid are different, the reaction processes between the mixed acid and HMX are different. When concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrochloric acid are mixed at the volume ratio of 3∶1, the decomposition effect is the strongest. According to the experiments results, it is concluded that it is feasible to oxidize HMX by using mixed acid.
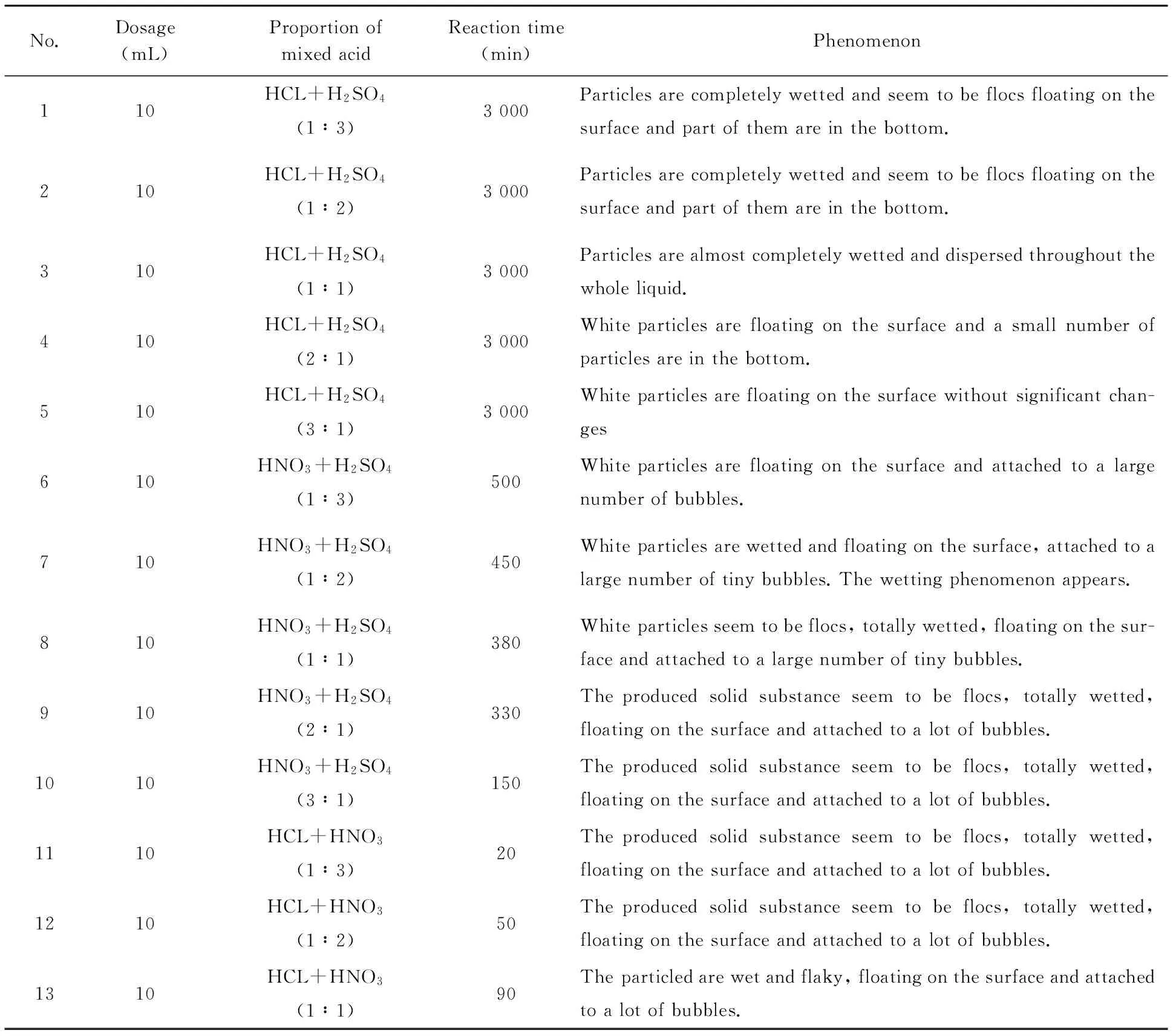
Table 1 Decomposition reaction of mixed acid with different proportions and HMX
2.4 Effect of mixed acid on decomposition reaction of HMX at low temperature
In order to investigate the reaction performance between mixed acid and HMX at low temperature, the following tests were carried out.
Firstly, 500 mg HMX was slowly slided into the conical flask along the filter paper. Then 10 mL mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrochloric acid at the volume ratio of 3∶1 was added drop by drop. After that, conical flask was put into a thermostat with 10 ℃. The experiments were repeated at the temperatures of 0, -10 and -20 ℃, respectively. The experiment results were shown in Table 2.
It can be seen that acid mixture can decompose HMX and decomposition rate becomes slowly as the temperature falls.

Table 2 Effect of temperature on the decomposition reaction
3 Effect of degradation degree on explosive performance
Normally, when the decomposition rate of detonating explosive and booster is 100%, detonating explosive and booster fails. However, in reality, detonating explosive and booster fails even when the decomposition rate is below 100%. Therefore, to obtain the relationship between decomposition degree and failure of detonating explosive and booster, the decomposition degree of detonating explosive and booster was analyzed. Thereout, the amount of reagent can be determined, which not only saves the amount of reagent, but also helps to design the fuse device.
3.1 Verification of degradation products’ explosiveness
When the reaction between HMX and mixed acid terminated, the remained liquid in the conical flask was filtered and dried. Then the solid residue and filter paper were ignited in an open field.
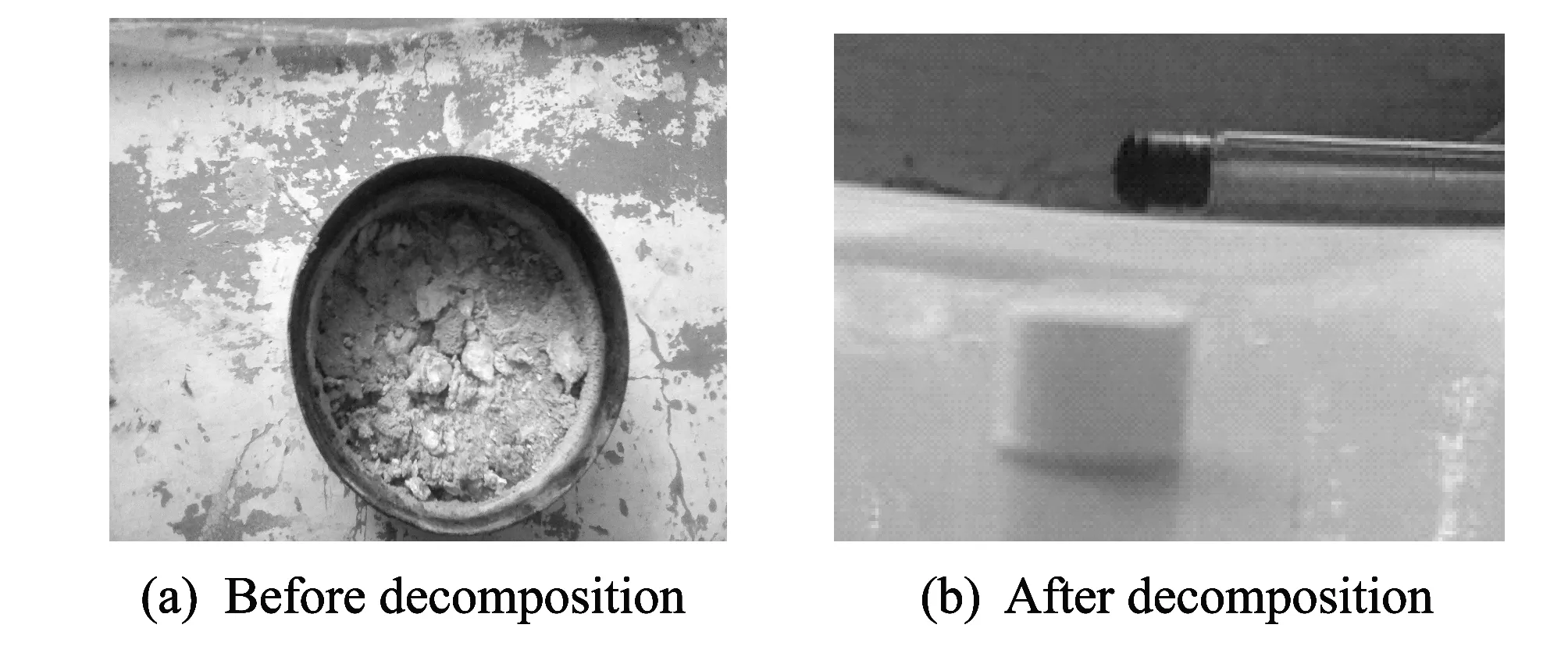
Fig.4 Comparison of detonating drugs decomposition
The experiment results show that the decomposition products can not be ignited and there is no obvious intense heat and light phenomenon, which means that the decomposition products are completely non-flammable and non-explosive. In Fig.4, performance comparison of detonating drugs before and after decomposition is shown.
3.2 Effect of degradation degree on explosive performance
At different rates, the product of HMX and mixed acid were mixed using detonating explosive and booster directly, as shown in Table 3. Then it was detonated by detonator. If it could be detonated, it meant that in such a decomposition degree, the ammunition could be detonated, and vice versa.
Table 3 Degradation degree and test table of detonators can be detonated or not
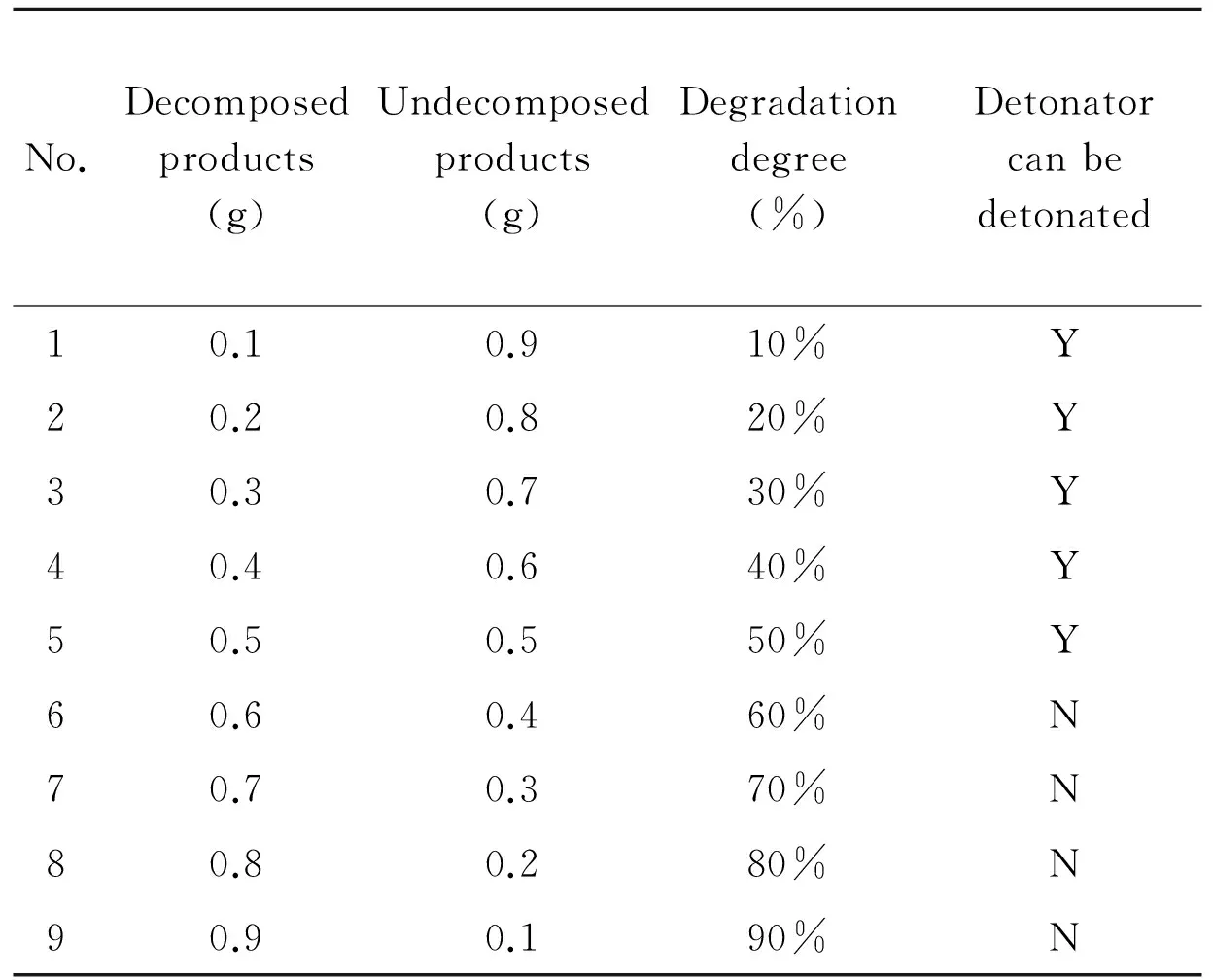
No.Decomposedproducts(g)Undecomposedproducts(g)Degradationdegree(%)Detonatorcanbedetonated10.10.910%Y20.20.820%Y30.30.730%Y40.40.640%Y50.50.550%Y60.60.460%N70.70.370%N80.80.280%N90.90.190%N
It can be seen from experimental results that when the degree of decomposition of HMX is more than 60%, it can not be detonated. The detonating explosive and booster will fail.
4 Conclusions
1) Under the condition of the normal and low temperatures, the detonating explosive and booster can be decomposed in the mixed acid (concentrated hydrochloric acid and nitric acid).
2) The solid residue of HMX and mixed acid are non-explosive.
3) When the degree of decomposition is more than 60%, detonators can not detonate HMX.
Therefore, by using special equipment, these reagents are added to ammunition’s fuse. If the ammunition is not exploded after launching or expires, these reagents will react with detonating explosive and booster, thus the detonating explosive and booster will lose their detonate ability and it meets the requirement of autonomic failure. Obviously, this will improve the safety of the use of cluster munitions greatly, and reduce the harmfulness of unexploded ordnance and scrap ammunition to the minimum.
[1] WANG De-wu, CAO Yan-wei, DONG Jing. Summary of cluster bomb technology development under the background of international armament control. Journal of Detection & Control, 2010, 32(4): 1-6.
[2] DONG San-qiang, FENG Shun-shan, YU Wen-li. Weapons and ammunition end unexploded status of safety design and discussion. Winged Missiles Journal, 2008, (9): 48-51.
[3] FENG Guo-tian. Introduction of the research for booster charge. Initiators & Pyrotechnics, 1999, (2): 49-51.
[4] LI Quan-liang. Study on the technology of synthesis of HMX. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2007.
[5] SUI Xian-hui, BI Kai-bo, SUN Song-tao, et al. Present situation and development of ship to ship missile warhead. Guidance & Fuze, 2013, 34(2): 44-48.
[6] OU Rong-wen. HMX. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1978.
[7] WANG Bao-guo, ZHANG Jing-lin, CHEN Ya-fang, et al. PBX booster explosive based on HMX /TATB. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2007, 15(1): 9-11.
[8] ZHANG Xiao-lian, ZHANG Jing-lin, WANG Jin-ying. Experimental study on effect of modifier pvp on crystal growth of HMX. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2013, 21(1): 44-48.
[9] LI Li-jie, JIN Shao-hua, CHEN Shu-sen, et al. Study of thermal stability of HMX affected by 1,9-acetoxyl-2,4,6 ,8-tetranitro-tetraaza nonane. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(10): 1562-1568.
[10] MEI Chu-sheng, MA Zhong-liang, ZHANG Yong-li, et al. Study on influencing factors on HMX’s Thinning. Journal of North University of China(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 34(2): 166-169.
[11] WANG Xiao-yan, ZHANG Jing-lin, ZHANG Jian-ren. Ultrafine HMX prepared by solvent-nonsolvent method. Blasting, 2013, 30(3): 125-128.
奧克托今炸藥在低溫條件下的化學(xué)失效研究
為了使未爆彈藥失去爆炸能力, 本文對導(dǎo)爆藥、 傳爆藥的主體炸藥奧克托今進(jìn)行了化學(xué)失效研究, 旨在尋求相應(yīng)化學(xué)試劑使得奧克托今能夠被分解成不具有爆炸性質(zhì)的化合物。 通過分析奧克托今與氫氧化鈉、 濃硫酸(單一酸)以及混酸在不同溫度條件下的分解實驗, 確定了奧克托今低溫條件下被降解的最佳化學(xué)藥劑組分及不能被引爆的分解程度: 體積比為3∶1的濃硝酸與濃鹽酸的混酸溶液能夠分解奧克托今, 且當(dāng)分解程度達(dá)到60%以上時, 炸藥已經(jīng)不能被雷管引爆, 從而達(dá)到失效的目的。
未爆彈藥; 奧克托今; 化學(xué)失效; 分解實驗
AN Xiao-hong, ZHANG Xin-mao, LI Hua, et al. Study on chemical failure of HMX under low temperature condition. Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation, 2015, 6(3): 229-233. [
安曉紅1, 張新貌1, 李 華2, 顧 強1
(1. 中北大學(xué) 機(jī)電工程學(xué)院, 山西 太原 030051; 2. 北京北方車輛集團(tuán)有限公司, 北京 100072)
10.3969/j.issn.1674-8042.2015.03.005]
AN Xiao-hong (907308000@qq.com)
1674-8042(2015)03-0229-05 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8042.2015.03.005
Received date: 2015-05-06
CLD number: TJ450.4 Document code: A
 Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation
2015年3期
Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation
2015年3期
- Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation的其它文章
- Modal analysis of 4-cylinder engine crankshaft based on ANSYS Workbench
- Simulation of small-aperture deep hole drilling based on ABAQUS
- Investigation on nonlinear rolling dynamics of amphibious vehicle under wind and wave load
- Numerical simulation of two-phase flow field in underwater sealing device based on dynamic mesh
- Analysis of movement laws of fragment and shock wave from a blast fragmentation warhead
- Application of adaptive Kalman filter in rocket impact point estimation
