聯(lián)咪唑及其衍生物修飾的多酸基化合物的合成、結(jié)構(gòu)和性質(zhì)
田愛香 侯 雪 孫 娜 肖 茹 應(yīng) 俊 楊 陽 寧亞莉 李天嬌 王秀麗
(1渤海大學(xué)化學(xué)系,錦州121000)
(2河北化工醫(yī)藥職業(yè)技術(shù)學(xué)院化學(xué)與環(huán)境工程系,石家莊050026)
聯(lián)咪唑及其衍生物修飾的多酸基化合物的合成、結(jié)構(gòu)和性質(zhì)
田愛香*,1侯 雪1孫 娜2肖 茹1應(yīng) 俊1楊 陽1寧亞莉1李天嬌1王秀麗*,1
(1渤海大學(xué)化學(xué)系,錦州121000)
(2河北化工醫(yī)藥職業(yè)技術(shù)學(xué)院化學(xué)與環(huán)境工程系,石家莊050026)
通過使用聯(lián)咪唑及其衍生物2種有機配體在水熱條件下合成了2個多酸基化合物[Ag4(biz)4][H2P2Mo5O23]·2H2O(1)和[Ag4(bbiz)4][HPWⅥ10WⅤ2O40](2)(biz=2,2-聯(lián)咪唑,bbiz=5-丁基-2,2-聯(lián)咪唑),并通過單晶X-射線衍射、元素分析和紅外光譜對其進行了表征。化合物1包含雙核銀簇[Ag2(biz)2]2+,[P2Mo5O23]6-多陰離子通過提供端基氧原子連接相鄰雙核銀簇而構(gòu)筑了一維鏈結(jié)構(gòu)。在化合物2中,每個Keggin型陰離子提供4個橋氧原子來連接4個雙核銀簇[Ag2(bbiz)2]2+,從而構(gòu)筑一個二維的層結(jié)構(gòu)。此外,對標(biāo)題化合物的電化學(xué)、光催化以及熒光性能也進行了研究。
多酸基化合物;2,2-聯(lián)咪唑;5-丁基-2,2-聯(lián)咪唑;電化學(xué)性能;光催化性能;熒光性能
0 Introduction
Over the past decades,the assembly of metalorganic frameworks(MOFs)has attracted great attention owing to not only their structural diversity but also their remarkable applications[1].Nowadays,polyoxometalates(POMs)have been regarded as excellent inorganic building blocks to construct POM-based MOFs (POMOFs)due to their discrete structures and promising physical and chemical properties,such as optics,electrochemical activity,gas storage,magnetism and catalysis[2].Among a wide variety of POM types, classical Keggin anions are commonly used and many Keggin-based compounds have been obtained[3].Compared with Keggin anions,the Strandberg-type anion owns smaller volume and fewer terminal and bridging O atoms.However,it still can be treated as the appropriate candidates for the construction of POMOFs owing to their higher charges and particular structural features.Up to now,a series of Strandberg-based compounds have been synthesized with some excellent properties[4].For example,Zhu′s group firstly reported three Strandberg-based compounds acting as efficient catalysts for the organic synthesis[5].In this work,we chose Keggin and Strandberg anions to explore whether the distinct volume and O atoms can influence the final structures.
To the best of our knowledge,the rigid organic ligands are extremely popular for construction of new POMOFs on account of their relatively fixed coordination modes in favor of target syntheses[6]. Among the various rigid ligands,2,2-biimidazole has been viewed as a preferred one to construct POMOFs, which owns longer N…N distance and can induce binuclear metal clusters with ease[7].In our previous work,we have discussed the influence of-CH3in bis (pyrazole)ligands on the architectures[8].In this work, we still try to explore the effect of introduction of alkyl chain-(CH2)nCH3group to organic ligands on the structures of target compounds.Thus,in this work, 2,2-biimidazole(biz)and its derivative 5-butyl-2,2-biimidazole(bbiz)were selected as organic linkers to construct new POMOFs(Scheme 1).The bbiz ligand is firstly used in POM field to our knowledge. Furthermore,owing to the diverse coordination modes of Ag+ions and easy aggregation to form multi-nuclear Ag+clusters,we chose Ag+as the central metal ion[9].
On the basis of the aforementioned points,in this work,we chose Keggin/Ag+/biz and Strandberg/Ag+/ bbiz systems to construct new POMOFs.Fortunately, we successfully obtained two new compounds under hydrothermal conditions:[Ag4(biz)4][H2P2Mo5O23]·2H2O (1)and[Ag4(bbiz)4][HPWⅥ10WⅤ2O40](2)(biz=2,2-biimidazole,bbiz=5-butyl-2,2-biimidazole).In addition,the electrochemical,photocatalytic and fluorescence properties of these two compounds have been studied.
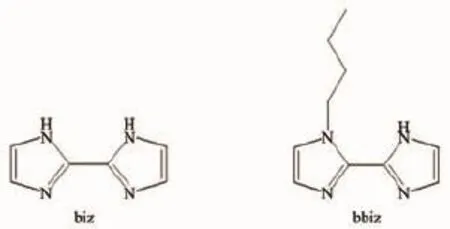
Scheme 1 2,2-biimidazole(biz)and its derivative 5-butyl-2,2-biim idazole(bbiz)
1 Experimental
1.1 M aterials and M ethods
All reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used without purification.Elemental analyses(C,H,and N)were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 2400 CHN elemental analyzer.The FTIR spectra were recorded from 4 000~400 cm-1on aMagna FTIR 560 Spectrometer with pressed KBr pellets.Electrochemical measurements were performed with a CHI 440 electrochemical workstation.A conventional three-electrode system was used.A saturated calomel electrode(SCE)was used as a reference electrode,and a Pt wire as a counter electrode.Chemically bulk-modified carbon-paste electrodes(CPEs)were used as the working electrodes.UV-Vis absorption spectra were obtained using a SP-1900 UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
1.2 Syntheses of com pounds 1 and 2
[Ag4(biz)4][H2P2Mo5O23]·2H2O(1):A mixture of Na2MoO4·2H2O(0.134 g,1.0 mmol),AgNO3(0.17 g, 1.0 mmol)and biz(0.2 g,1.5 mmol)was dissolved in 10 mL of distilled water at room temperature.The suspension was stirred for 40 min in air and then pH value of the mixture was adjusted to about 1.3 with 1.0 mol·L-1H3PO4.The suspension was transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave(20 mL)and kept under autogenous pressure at 160℃for 3 days. After slow cooling(10℃·h-1)to room temperature, yellow clavate crystals of 1 were obtained(45%yield based on Mo).Elemental analysis(%)calcd.for C24H30Mo5N16Ag4O25P2(1 915.71):C 15.04,H 1.46,N 11.7. Found:C 15.08,H 1.49,N 11.65.
[Ag4(bbiz)4][HPWⅥ10WⅤ2O40](2):The synthetic method was similar to that of compound 1,except that H3PW12O40·13H2O(0.08 g,0.47 mmol)was used instead of Na2MoO4·2H2O,while bbiz(0.015 g,0.05 mmol)was used instead of biz.Brownness block crystals were filtered and washed with distilled water (47%yield based on W).Elemental analysis(%) calcd.for C40H56Ag4N16O40PW12(4 069.54):C 11.79,H 1.37,N 5.5.Found:C 11.83,H 1.34,N 5.53.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
Crystallographic data for compounds 1 and 2 were collected on a Bruker Smart ApexⅡdiffractometer with Mo Kα(λ=0.071 073 nm)by usingan φ-ω scan mode at 293 K.All the structures were solved by direct methods and refined on F2by fullmatrix least-squares methods using the SHELXTL package[10].All the hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms were generated geometrically,while the hydrogen atoms attached to water molecules were not located but were included in the structure factor calculations.A summary of the crystallographic data and structural refinement for the title compounds are given in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and angles of 1 and 2 are listed in Table S1.
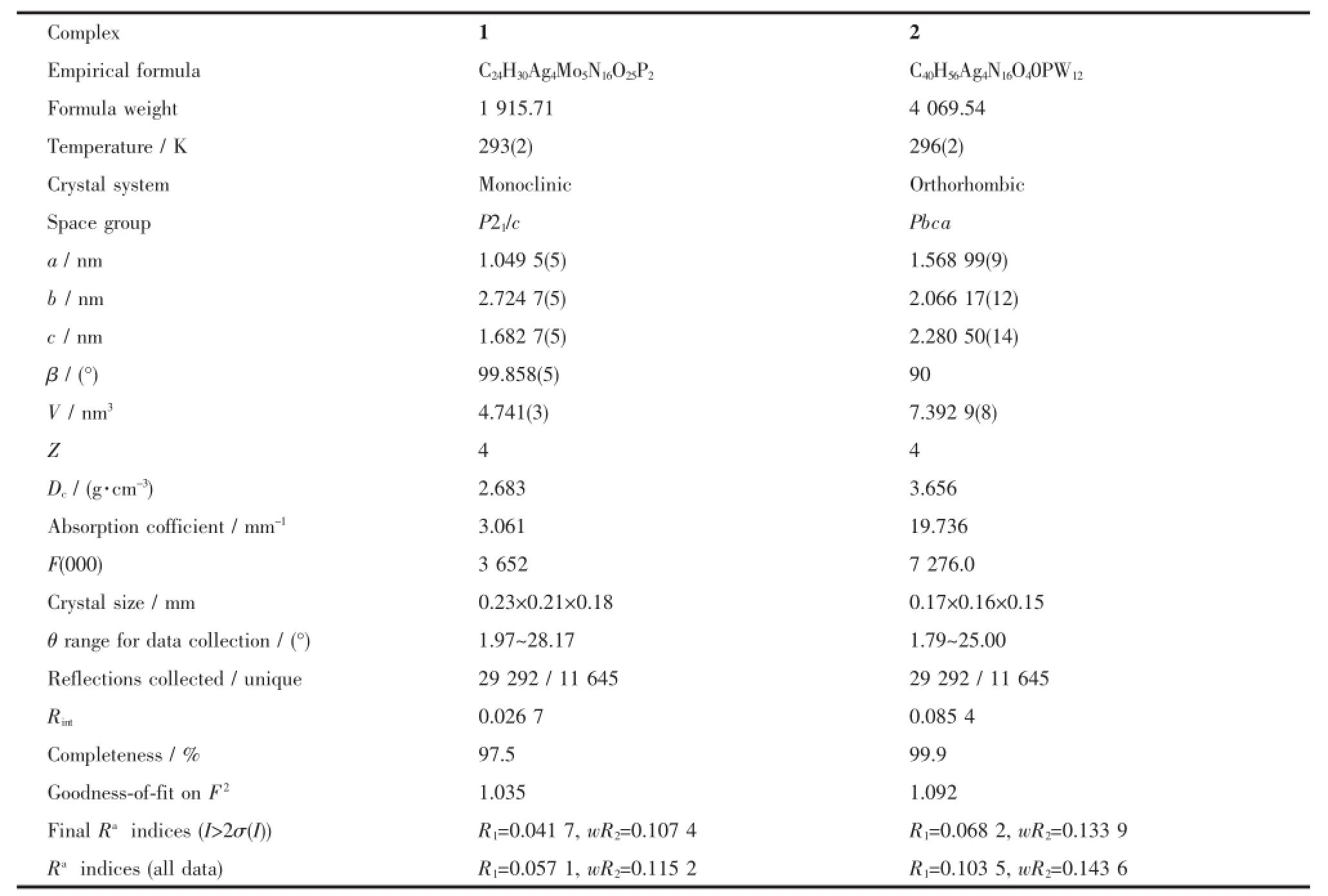
Table1 C rystal data and structure refinements for com pounds 1 and 2
CCDC:1027614,1;1027615,2.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Description of the structure
2.1.1 Crystal structure of compound 1
Crystal structure analysis reveals that compound 1 is composed of four Ag+ions,four biz ligands,one [P2Mo5O23]6-anion(abbreviated to P2Mo5)and two crystal water molecules,as shown in Fig.1.The P2Mo5anion shows a classical Strandberg type with five distorted edge-and corner-sharing MoO6octahedra capped two PO4tetrahedra on each side.The bond valence sum calculations indicate that all the Mo atoms are in the+6 oxidation state and all the Ag atoms are in+1 oxidation state[11].To balance the charge of the compound,two protons are added,then 1 is formulated as[Ag4(biz)4][H2P2Mo5O23]·2H2O.
In compound 1,there are four crystallographically independent Ag+ions(Ag1,Ag2, Ag3 and Ag4),which exhibit two coordination modes: (i)Both the Ag1 and Ag2 ions with T-type coordination geometries are three-coordinated by two N atoms(N3 and N7 for Ag1,N1 and N5 for Ag2) from two biz ligands and one Ag atom.(ii)The Ag3 and Ag4 ion adopts four-coordinated distorted seesaw coordination geometries,coordinated by two N atoms (N9 and N13 for Ag3,N11 and N19 for Ag4)from two biz ligands,one Ag ion and one terminal O atom(O14 for Ag3 and O19 for Ag4)from one P2Mo5anion.The distance and angles around the Ag+ions are 0.211 1(4)~0.214 5(3)nm for Ag-N,0.283 9(7)~0.287 5(8)nm for Ag-Ag,161.55(14)°~171.34(15)°for N-Ag-N, 84.18(10)°~89.77(10)°for N-Ag-Ag.The bond lengths and angles are listed in Table S1.
The biz ligand in compound 1 shows a single coordination mode:each imidazole group offers one N donor to link two different Ag+ions.Thus,two kinds of bi-nuclear Ag+clusters are formed containing[(Ag1) (Ag2)(biz)2]2+and[(Ag3)(Ag4)(biz)2]2+clusters. Furthermore,the P2Mo5anions provides two terminal oxygen atoms to link adjacent bi-nuclear[(Ag3)(Ag4) (biz)2]2+clusters to form an infinite jagged 1D chain in a ABAB mode(Fig.2).The adjacent chains further built a 2D supramolecular layer through hydrogen bonding interactions,such as C24…O4(0.310 6 nm)shown in Fig.S1.The[(Ag1)(Ag2)(biz)2]2+clusters acting as cationic complexes insert into adjacent 2D layers through hydrogen bonding interactions to stabilize the structure.
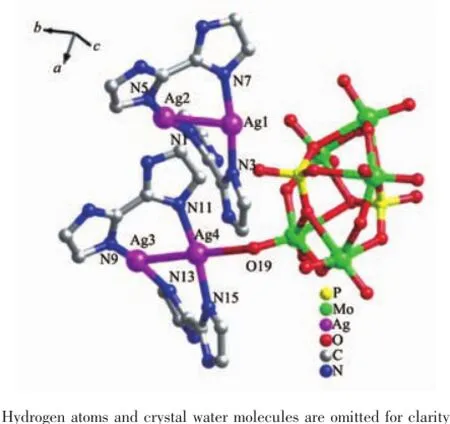
Fig.1 Ball and stick view of the asymmetric unit of 1
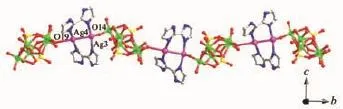
Fig.2 1D chain of compound 1 with the P2Mo5anions and bi-nuclear[(Ag3)(Ag4)(biz)2]2+clusters arranging alternately
2.1.2 Crystal structure of compound 2
Crystal structure analysis reveals that compound 2 consists of four Ag+ions,four bbiz ligands and one [PW12O40]3-anion(abbreviated to PW12)(Fig.3).The PW12presents a classical α-Keggin type anion.The central P atom is surrounded by a cube of eight O atoms with each site half-occupied[12].The valence sum calculations show that two of the twelve W atoms are in+5 oxidation state and all the Ag atoms are in+1 oxidation state[11].One proton is added to balance the charge of compound 2,then 2 is formulated as [Ag4(bbiz)4][HPWⅥ10WⅤ2O40].Under hydrothermal conditions,the organonitrogen species generally act not only as ligands but also as reductants,inducing the reduction of W in compound 2[13].
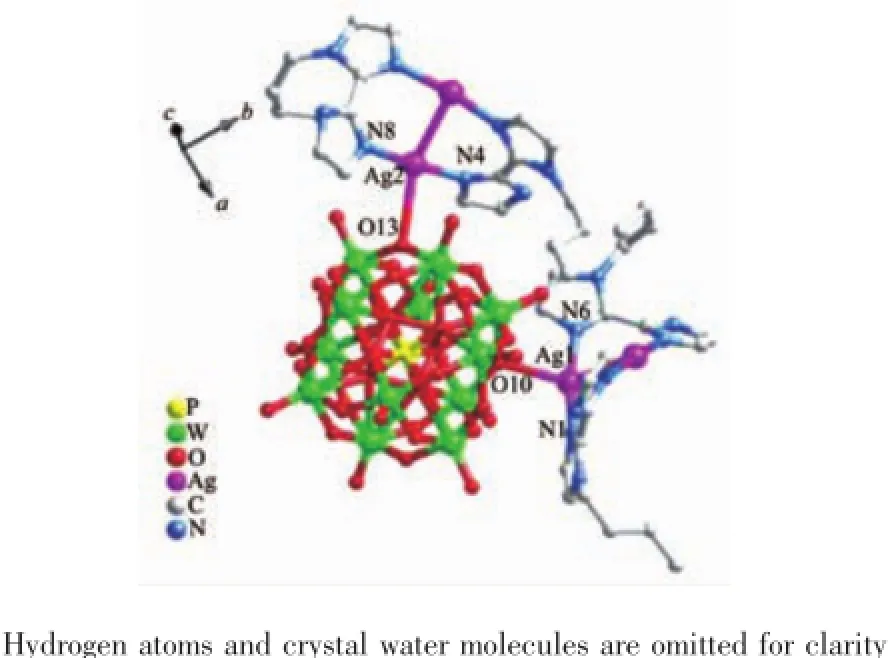
Fig.3 Ball and stick view of the asymmetric unit of 2
There are two crystallographically independent Ag+ions(Ag1 and Ag2)in compound 2.The Ag1 and Ag2 exhibit similar slightly distorted seesaw coordination geometries,coordinated by two nitrogen atoms(N1 and N6 for Ag1,N4 and N8 for Ag2)from two bbiz ligands,one bridging atom(O10 for Ag1 and O13 for Ag2)from one PW12anion and one Ag atom. The distance and angles around the Ag+ions are 0.206 4(9)~0.213 7(8)nm for Ag-N,0.282 8(11)nm for Ag-Ag,170.9(3)°~174.4(3)°for N-Ag-N,85.4(2)°~87.4(2)°for N-Ag-Ag.The bond lengths and angles are listed in Table S1.
The bbiz shows the same coordination mode with that in compound 1.There also exists a bi-nuclear [(Ag1)(Ag2)(bbiz)2]2+cluster.Each PW12anion offers four bridging O atoms(two O10 and two O13)to link four bi-nuclear Ag+clusters to construct a 2D layer of compound 2(Fig.4).
2.1.3 Effect of different anions on structures of 1 and 2
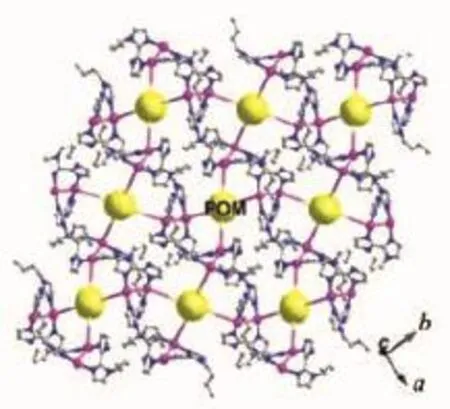
Fig.4 2D layer of compound 2(the biggest balls:Keggin anions)
We chose biz and P2Mo5for construction of 1 and chose bbiz and PW12for 2,in order to explore whether the butyl group in ligands and different anions have influences on the structures[14].Though the butyl group shows a few hydrogen interactions,it has no obvious effect on the structures.However,the different anions (P2Mo5for 1 and PW12for 2)really induce distinct structures of 1 and 2.In compound 1,the P2Mo5anion owns a smaller volume.Thus,in order to reduce the repulsions between bi-nuclear[(Ag3)(Ag4)(biz)2]2+clusters,the P2Mo5anion only offers two symmetrical terminal O atoms to link two bi-nuclear clusters(Fig. S2a).But the PW12anion in 2 owing to big volume can link four bi-nuclear Ag+clusters by providing four bridging O atoms(Fig.S2b).If the P2Mo5anion also supplies its two bridging O atoms instead of terminal ones,the repulsions of bi-nuclear Ag+clusters will increase.Furthermore,the coordination number of P2Mo5is also less than that of PW12.Thus,the different anions play a key role on construction of the structures of 1 and 2.
2.2 FTIR Spectra
The IR spectra of compounds 1 and 2 are shown in Fig.S3.In the spectrum of 1,characteristic bands at 785,862,957 and 1 060 cm-1correspond to ν(Mo-Oc-Mo),ν(Mo-Ob-Mo),ν(Mo=Od)and ν(P-O)of the P2Mo5anion,respectively[4c].In the spectrum of 2, 1 072,977,888,805 are attributed to the ν(P-Oa), ν(W-Od)andν(W-Ob-W)of the PW12anion, respectively[15].Bands in the regions of 1 563~1 245 cm-1for 1 and 1 537~1 168 cm-1for 2 are attributed to the bizand bbiz ligands,respectively.
2.3 Electrochem ical properties
The electrochemical behaviors of 1 and 2 were investigated with 1-and 2-modified CPE(1-and 2-CPE).The cyclic voltammograms for the CPEs in 0.1 mol·L-1H2SO4+0.5 mol·L-1Na2SO4aqueous solution at different scan rates are presented in Fig.5.Three reversible redox peaks appear in the potential range from+460 to-250 mV for 1-CPE,corresponding to three consecutive two-electron processes of P2Mo5.The mean peak potentials(E1/2=(Epa+Epc)/2)(scan rate:250 mV·s-1)are 224(Ⅰ-Ⅰ′),39(Ⅱ-Ⅱ′)and-165(Ⅲ-Ⅲ′)mV for the 1-CPE[16].The cyclic voltammograms of 2-CPE at different scan rates are presented in the potential range of+100 to-780 mV.There also exist three reversible redox peaksⅠ-Ⅰ′,Ⅱ-Ⅱ′andⅢ-Ⅲ′with the mean peak potentials(E1/2=(Epa+Epc)/2)of-178,-466,-661 mV(scan rate:250 mV·s-1).Redox peaksⅠ-Ⅰ′andⅡ-Ⅱ′correspond to two consecutive one-electron processes,whileⅢ-Ⅲ′corresponds to a two-electron process of PW12[8].The peak potentials of cyclic voltammograms for the CPEs change gradually following the scan rates from 40 to 500 mV·s-1:the cathodic peak potentials shift toward the negative direction and the corresponding anodic peak potentials to the positive direction with increasing scan rates.When the scan rate is up to 500 mV·s-1, the peak currents are proportional to the scan rates, which shows that the redox process of the 1-and 2-CPEs are surface-confined(Fig.S4).
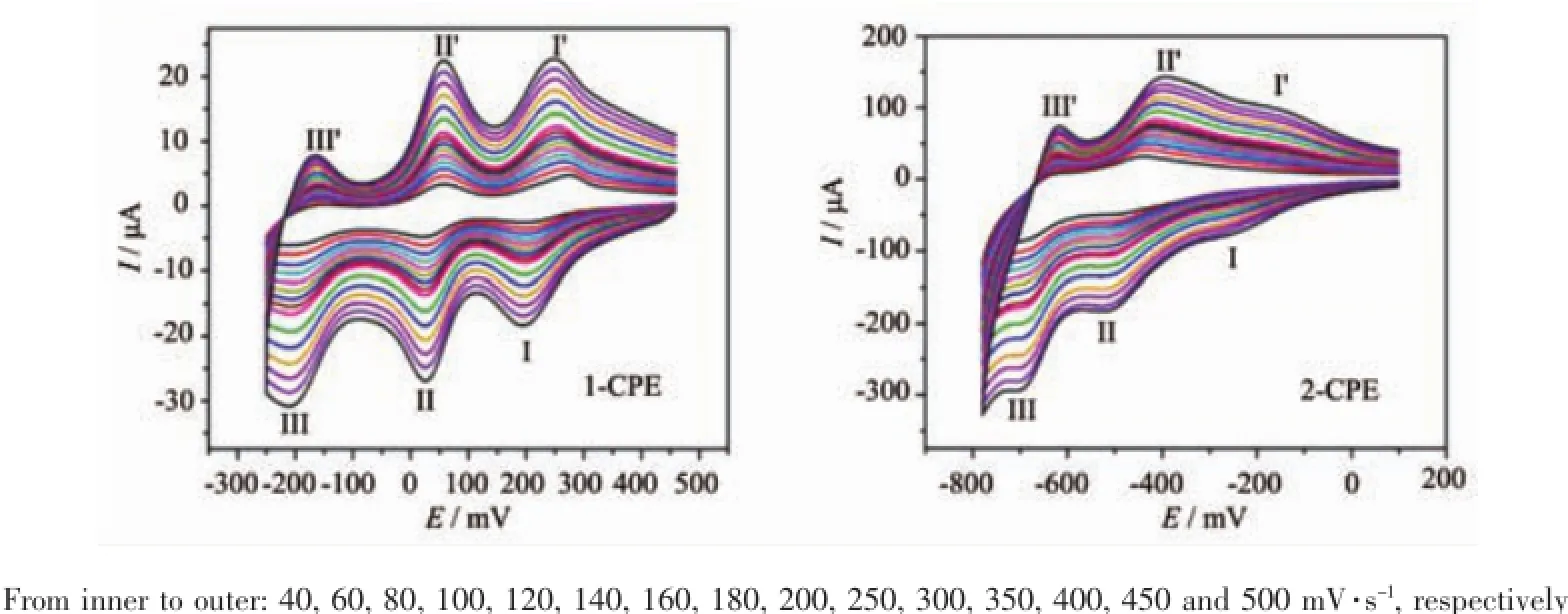
Fig.5 Cyclic voltammograms of the 1-and 2-CPEs in 0.1mol·L-1H2SO4+0.5 mol·L-1Na2SO4aqueous solution at different scan rates
Fig.6 shows cyclic voltammograms for the electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide at 1-and 2-CPEs in 0.1 mol·L-1H2SO4+0.5 mol·L-1Na2SO4aqueous solution.It can be clearly seen that with addition of H2O2,all three reduction peak currents of 1-and 2-CPEs gradually increase,while the corresponding oxidation peak currents decrease. These phenomena indicate that the three reductive species of P2Mo5in 1 and PW12in 2 all possess electrocatalytic activities for the reduction of hydrogen peroxide.In a word,compounds 1 and 2 may be used as good potential electrocatalysts.
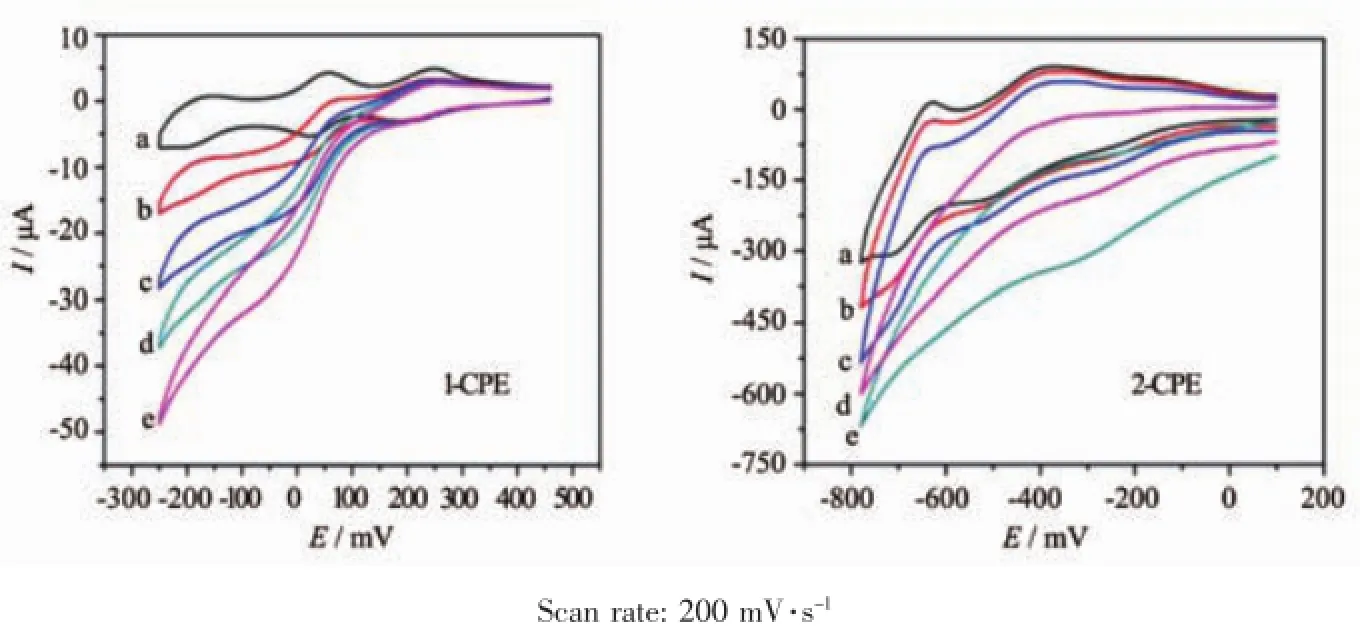
Fig.6 Cyclic voltammograms of the 1-and 2-CPEs in 0.1 mol·L-1H2SO4+0.5 mol·L-1Na2SO4aqueous solution containing 0(a),2(b),4(c),6(d)and 8(e)mmol·L-1H2O2
2.4 Photocatalytic activity
Some POM-based compounds exhibit photocatalitic activities to degrade organic dyes[17]. Therefore,the photocatalytic activities of compounds 1 and 2 were investigated by the degradation of methylene blue(MB)and Rhodamine-B(RhB)solution under UV irradiation,as shown in Fig.7 and Fig.8.In the process of photocatalysis,100 mg title compounds was suspended in 0.02 mmol·L-1MB or RhB aqueous solution 250 mL and magnetically stirred for about 10 min to ensure the equilibrium in the dark.Every 20 min,the sample of 5 mL was taken out,which wasobtained for analysis by UV-Visible spectroscopy.The absorption peaks of MB photocatalyzed by 1 and 2 decreased obviously with increasing of reaction time and the conversions of MB are 80.99%for compound 1 and 93.38%for 2 after 100 min(Fig.S5a).Fig.8 and Fig.S5b show that the conversions of RhB are 72.46% for 1 and 80.83%for 2,respectively.This results show that the title compounds own good photocatalytic activities for the degradation of MB and RhB, especially compound 2.
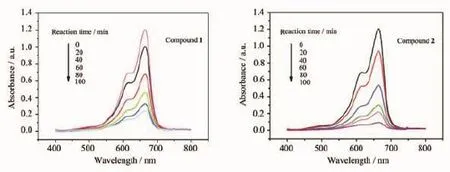
Fig.7 Absorption spectra of the MB solution during the decomposition reaction under UV irradiation in the presence of compounds 1 and 2
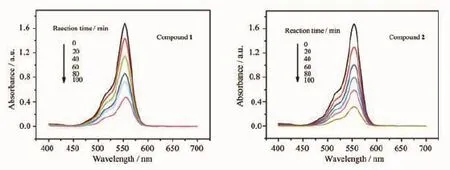
Fig.8 Absorption spectra of the RhB solution during the decomposition reaction under UV irradiation in the presence of compounds 1 and 2
2.5 Fluorescent properties
In this work,the fluorescent properties of the title compounds in the solid state at room temperature were investigated.Emission spectra of 1 and 2 are shown in Fig.S6.Two prominent emission peaks are observed at about 417 and 467 nm for 1,414 and 466 nm for 2(excitation at 340 nm).The emission peak would be assigned to ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT)[18].These observations exhibit that the title compounds may be candidates for photoluminescence materials.
3 Conclusions
In summary,by using biz and bbiz ligands two new POM-based compounds have been successfully synthesized.In compound 1,the bi-nuclear[Ag2(biz)2]2+clusters are linked by P2Mo5anions to form a 1D chain.Compound 2 displays a 2D layer constructed by tetra-dentate PW12anions and bi-nuclear [Ag2(bbiz)2]2+clusters.The different POM anions induce distinct structures of 1 and 2.Though the butyl group exhibits no obvious effect,further study on its influence on other structures is underway.
Acknow ledgements:Financial supports of this research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 21101015,21471021 and 21201021),Program of Innovative Research Team in University of Liaoning Province(No. LT2012020)and Talent-supporting Program Foundation of Education Office of Liaoning Province(No.LJQ2012097).
Supporting information is available at http://www.wjhxxb.cn
[1](a)Manna K,Zhang T,Carboni M,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc., 2014,136(38):13182-13185; (b)Ahmed A,Forster M,Clowes R,et al.Chem.Commun., 2014,50:14314-14316; (c)Phang W J,Lee W R,Yoo K,et al.Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2014,53(32):8383-8387
[2](a)Kikukawa Y J,Kuroda Y,Yamaguchi K,et al.Angew. Chem.Int.Ed.,2012,124(10):2484-2487; (b)Miao H,Xu X,Ju W W,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53(6): 2757-2759; (c)Zhang Z Y,Lin Q P,Kurunthu D,et al.J.Am.Chem. Soc.,2011,133(18):6934-6937; (d)Fu H,Qin C,Lu Y,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed., 2012,51:7985-7989 (e)Wang X L,Bi Y F,Chen B K,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2008, 47(7):2442-2448
[3](a)Balula S S,Cunha-Silva L,Santos I C M S,et al.New J. Chem.,2013,37:2341-2350; (b)Tian A X,Ying J,Peng J,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2009,48(1): 100-110; (c)Wang X L,Li N,Tian A X,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53(14):7118-7129
[4](a)Nagazi,I,Haddad A.J.Cluster Sci.,2014,25:627-638 (b)Jin H J,Zhou B B,Yu Y,et al.Chem.Eng.Commun., 2011,13,585-590 (c)Shi J,Wang C X,Yu K,et al.J.Coord.Chem.,2014,67 (13):2229-2237
[5]Li Z L,Wang Y,Zhang L C,et al.Dalton Trans.,2014,43: 5840-5846
[6](a)Wang L M,Wang Y,Fan Y,et al.Chem.Eng.Commun., 2014,16:430-440 (b)Yang H X,Guo S P,Tao J,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2009,9:4735-4744 (c)Sun J W,Li M T,Sha J Q,et al.Chem.Eng.Commun., 2013,15:10584-10589
[7](a)Wang Y,Zhang L C,Zhu Z M,et al.Transition Met. Chem.,2011,36:261-267 (b)Xu Y L,Zhou B B,Su Z H,et al.J.Coord.Chem., 2011,64:3670-3678
[8]Tian A X,Yang Y,Ying J,et al.Dalton Trans.,2014,43: 8405-8413
[9](a)Wang L,Yang W T,Zhu W,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014, 53(21):11584-11588 (b)Zhou K,Qin C,Wang X L,et al.Chem.Eng.Commun., 2014,16:10376-10379 (c)Li M T,Sha J Q,Zong X M,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2014,14(6):2794-2802
[10](a)Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,Program for Crystal Structure Solution.University of G?ttingen,Germany,1997. (b)Sheldrick G M.Acta Crystallogr.Sect.A,2008,64:112
[11]Brown I D,Altermatt D.Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.B,1985,41: 244-247
[12]Jr Evans H T,Popev M T.Inorg.Chem.,1984,23:501-504
[13]Liu C M,Zhang D Q,Zhu D B.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006,6: 524-529
[14](a)Wang X L,Li N,Tian A X,et al.Dalton Trans.,2013, 42:14856-14865 (b)Zhai Q G,Wu X Y,Chen S M,et al.Inorg.Chem., 2007,46:5046-5058 (c)Zhang P P,Peng J,Pang H J,et al.Chem.Eng. Commun.,2011,13:3832-3841
[15](a)Dobrick M S,Jansen M.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2006,22: 4498-4502 (b)Liu H Y,Wu H,Yang J,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2011,11(5):1786-1797
[16]Guo H X,Li X Z,Weng W.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2010,13:909-913
[17](a)Li T H,Li Q G,Yan J,et al.Dalton Trans.,2014,43: 9061-9069 (b)Tian A X,Yang Y,Sun N,et al.J.Coord.Chem.,2014, 67(9):1550-1561
[18]Wang X,Peng J,Liu M G,et al.Chem.Eng.Commun., 2012,14:3220-3226
Syntheses,Structures and Properties of Two POM-based Com pounds M odified by Biim idazole and Its Derivative
TIAN Ai-Xiang*,1HOU Xue1SUN Na2XIAO Ru1YING Jun1YANG Yang1NING Ya-Li1LI Tian-Jiao1WANG Xiu-Li*,1
(1Department of Chemistry,Bohai University,Jinzhou,Liaoning 121000,China)
(2Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering,Hebei Chemical&Pharmaceutical Vocational Technology College,Shijiazhuang 050026,China)
Through using two kinds of ligands(biimidazole and its derivative),two polyoxometalate-based compounds,[Ag4(biz)4][H2P2Mo5O23]·2H2O(1)and[Ag4(bbiz)4][HPWⅥ10WⅤ2O40](2)(biz=2,2-biimidazole,bbiz=5-butyl-2,2-biimidazole),have been synthesized under hydrothermal conditions and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction,elemental analyses and IR spectra.Compound 1 contains bi-nuclear[Ag2(biz)2]2+clusters,which are linked by[P2Mo5O23]6-anions through terminal O atoms to construct a 1D chain.In compound 2,each Keggin anion offers four bridging O atoms to link four bi-nuclear[Ag2(bbiz)2]2+clusters and a 2D layer of 2 is constructed. Additionally,the electrochemical,photocatalytic and fluorescent properties of the title compounds have been studied.CCDC:1027614,1;1027615,2.
POM-based compounds;2,2-biimidazole;5-butyl-2,2-biimidazole;electrochemical property;photocatalytic property; fluorescent property
10.11862/CJIC.114
2014-11-10。收修改稿日期:2015-01-22。
國家自然科學(xué)基金(No.21101015,21471021,21201021)資助項目。
*通訊聯(lián)系人。E-mail:tian@bhu.edu.cn;wangxiuli@bhu.edu.cn;會員登記號:S06N2283M1406(田愛香);S06N6675M1005(王秀麗)。
O614.122
A
1001-4861(2015)04-0839-09

