減氮增銨對滴灌玉米氮素營養及產量的影響
王雪薇 ,夏文豪, 劉 濤, 唐 誠, 褚貴新
(新疆生產建設兵團綠洲生態農業重點實驗室/石河子大學農學院,新疆石河子 832000)
?
減氮增銨對滴灌玉米氮素營養及產量的影響
王雪薇 ,夏文豪, 劉 濤, 唐 誠, 褚貴新
(新疆生產建設兵團綠洲生態農業重點實驗室/石河子大學農學院,新疆石河子 832000)
摘要:【目的】增銨營養具有明顯改善旱地作物氮素營養與提高作物產量的效應。【方法】設置N(0 )(不施氮)、N(375 )(全氮)、75%N(375)+CP (減氮25%+增銨)以及N(375)+CP (全氮增銨)4個處理,在覆膜滴灌條件下,研究尿素減量及其與氯甲基吡啶,隨水分次滴施對玉米氮素營養、產量及氮素養分資源利用效率的影響。【結果】減氮增銨處理75%N(375)+CP可促進植株干物質的積累,較N0增加了22%;75%N(375)+CP處理的玉米葉鞘含量比N(375)處理降低了16.7%;75%N(375)+CP處理產量較N0處理增加了18.6%,且使滴灌玉米的氮素利用效率和氮肥偏生產力,較全氮施肥分別提高了41.6%和26.8%。【結論】在滴灌水氮一體化供應條件下,通過硝化抑制劑增銨減少氮肥用量25%(75~95 N kg/hm2),可顯著提高氮素養分利用效率。
關鍵詞:玉米;籽粒產量;減氮增銨;氮素利用率;氮素營養
0引 言

1材料與方法
1.1材 料
該試驗為滴灌小區試驗,于2014年在新疆沙灣縣烏蘭烏蘇氣象站試驗地進行(E85°49′、N44°17′),年降雨量約為187.7 mm,供試土壤為灌耕灰漠土(CalcaricFluvisal),質地為壤土,耕層(0~20 cm),土壤pH 8.52,有機質18.73 g/kg,全氮0.96 g/kg,速效磷23.87 g/kg,速效鉀340.95 g/kg。玉米品種為春玉米良玉66 號。供試氮肥為尿素(含N 46.6%)375 kg/hm2、磷肥為磷酸一銨(含P2O561%、含N 12%)90 kg /hm2,鉀肥為硫酸鉀(含K2O 51%)90 kg/hm2。
1.2 方 法
1.2.1試驗設計
采用滴灌小區試驗,隨機區組設計。設置4個處理,分別為:T1:N0(CK)、T2:N375(當地滴灌高產玉米常規施氮量)、T3:75%N375+CP、T4:N375+CP(其中N375:純氮施量375 kg/hm2,75%N375:純氮施量281.25 kg/hm2,CP:氯甲基吡啶 上海碧晶),重復3次。40+80 (cm)寬窄行覆膜種植,株距14.5 cm,每小區4膜,1膜2行,鋪設1條滴灌帶,理論種植密度為112 500株/hm2,小區面積38.4 m2(4.8 m×8.0 m)。氮肥和磷肥全部作追肥隨水滴施,生育期內滴水10次,施肥8次,各生育時期田間管理措施等同當地一般大田。4月25日播種至10月2日收獲。表1
表1具體滴水施肥方案
Table 1 Schedule for water drip irrigation and fertigation of both N and P fertilizers
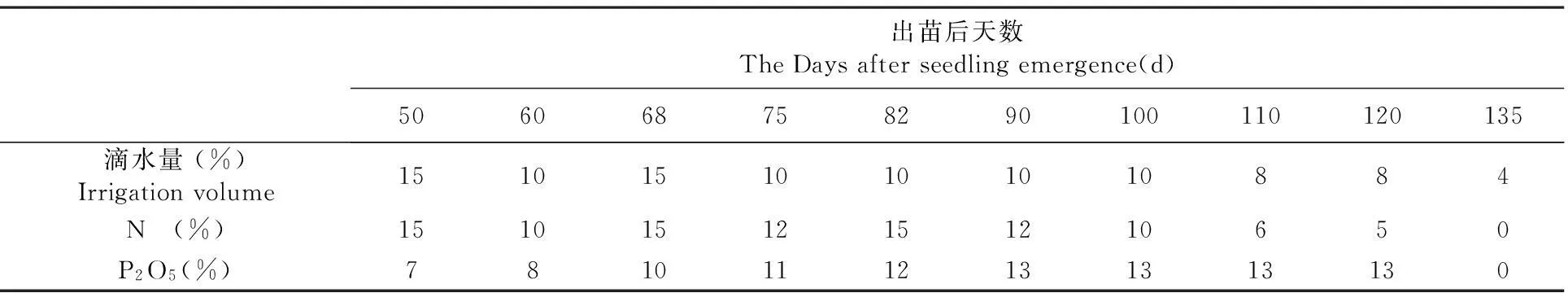
出苗后天數TheDaysafterseedlingemergence(d)506068758290100110120135滴水量(%)Irrigationvolume15101510101010884N (%)15101512151210650P2O5(%)78101112131313130
1.2.2樣品采集及測定項目1.2.2.1植物干物質量及養分含量
分別在玉米拔節期、抽雄吐絲期、灌漿期、乳熟期、完熟期滴水施肥前取植株樣,各小區隨機取3株,分器官在105℃殺青30 min,然后在75℃烘干恒重,稱重,測定干物質量;粉碎樣品測定植株氮含量及氮素吸收量。
1.2.2.2 植物中硝酸鹽含量
用RQ flex10反射儀(德國MERCK)測定玉米葉鞘的硝態氮含量。測試時期為拔節期、抽雄吐絲期、灌漿期。拔節期測定最上部完全展開葉的葉鞘部位,抽雄吐絲期和灌漿期測定穗位葉的葉鞘部位,各小區隨機抽取無損傷且長勢均勻的 3株進行測定。
1.2.2.3產量與產量構成要素
測產:在每個小區未取樣區劃2.4 m×4.0 m的樣方,收獲全部玉米,稱重并計算穗數。
考種:每個小區隨機取20株長勢相似的玉米,進行考種,測定產量構成要素及相關指標,計算產量。
氮肥偏生產力=施氮區玉米產量/施氮量;
氮肥利用率=(施氮區玉米地上部吸氮量-無氮區玉米地上部吸氮量)/施氮量×100%[12]。
1.3數據統計
采用Excel軟件進行數據的統計分析;用SPSS17.0軟件對數據進行單因素方差分析。
2 結果與分析
2.1不同施氮處理對植株干物質量的影響
研究表明,不同處理對玉米各個器官干物質積累有較大影響。完熟期玉米干物質的分配表現為:穗部(61.4%~62.1%)>莖稈(23.4%~25.8%)>葉片(12.7%~15.0%)。與對照處理(N0)相比,施氮可增加玉米莖、葉、穗干物質量(P< 0.05);N375、75%N375+CP和N375+CP處理的干物質分別比N0增加了7 648.8、6 565.1、9 732.0 kg/hm2,增幅分別為25%、22%、32%。各施氮處理之間的干物質量表現為N375+CP > N375> 75%N375+CP。N375和N375+CP處理的干物質分別比75%N375+CP處理增加了1 083.7和3 166.85 kg/hm2,增幅分別為2.9%和8.6%,但經方差分析處理間差異不顯著。由此可見,減氮增銨不會顯著降低玉米干物質積累量。圖1
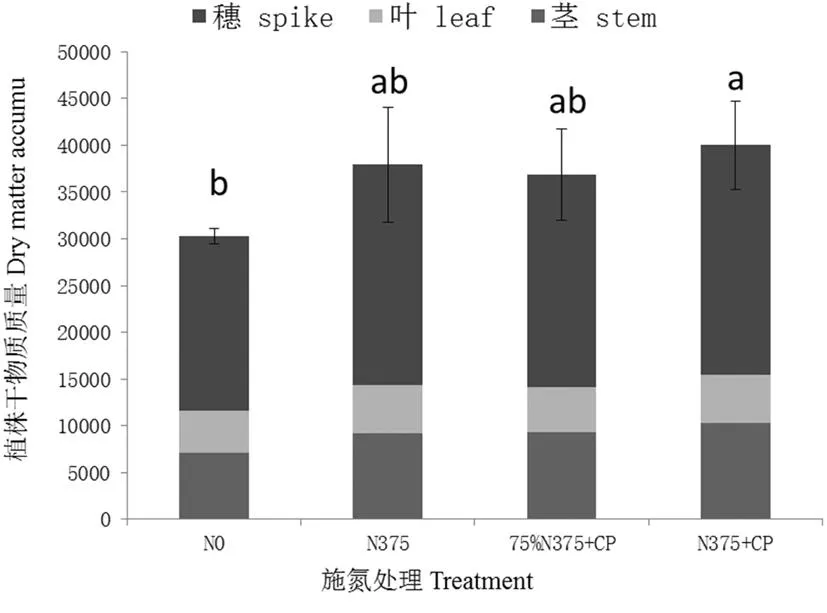
圖1不同施氮處理下玉米成熟期干物質量變化
Fig. 1 The effect of different N treatments on maize dry matter accumulation at maturity stage
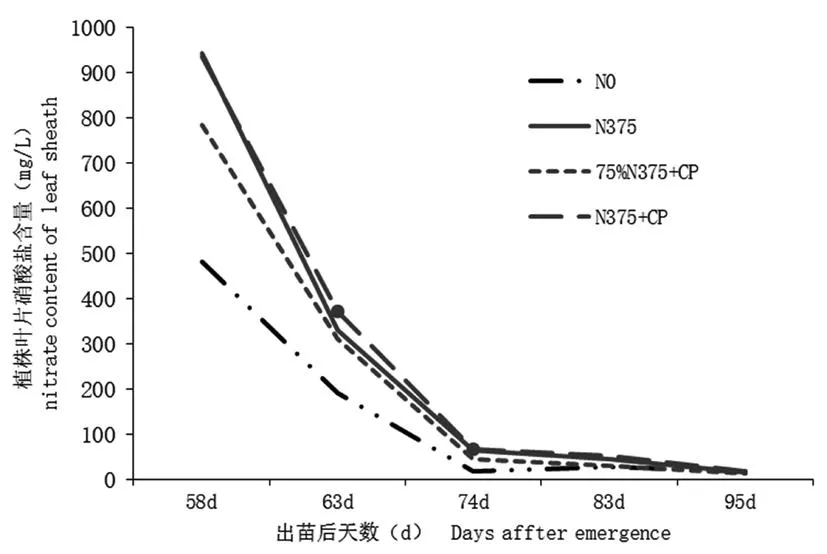
2.2不同施氮處理對葉片硝酸鹽含量的影響


2.3不同施氮處理對葉片含氮量和吸氮量的影響
研究表明,拔節期施氮處理植株葉片含氮量均顯著(P< 0.05)高于不施氮處理N0。N375+CP、N375和75%N375+CP處理葉片含氮量分別較N0處理增加了38.8%、32.9%、43.9%,差異顯著(P< 0.05),但3個施氮處理間差異不顯著。在拔節期和成熟期各施氮處理玉米植株吸氮量均顯著高于對照(P< 0.05)。如在拔節期,N375、75%N375+CP和N375+CP處理的葉片含氮量分別比對照增高了54.6%、44.3%和76.5%;在成熟期時N375、75%N375+CP和N375+CP處理的葉片含氮量分別比對照增高了60.7%、46.9%和67.5%;但施氮處理間植株葉片吸氮量不顯著。說明減氮增銨處理并不會降低植株葉片含氮量、吸氮量。表2
表2 不同施氮處理下葉片含氮量和吸氮量變化
Table 2 The effects of different N treatment on leaf total N content and maize N uptake
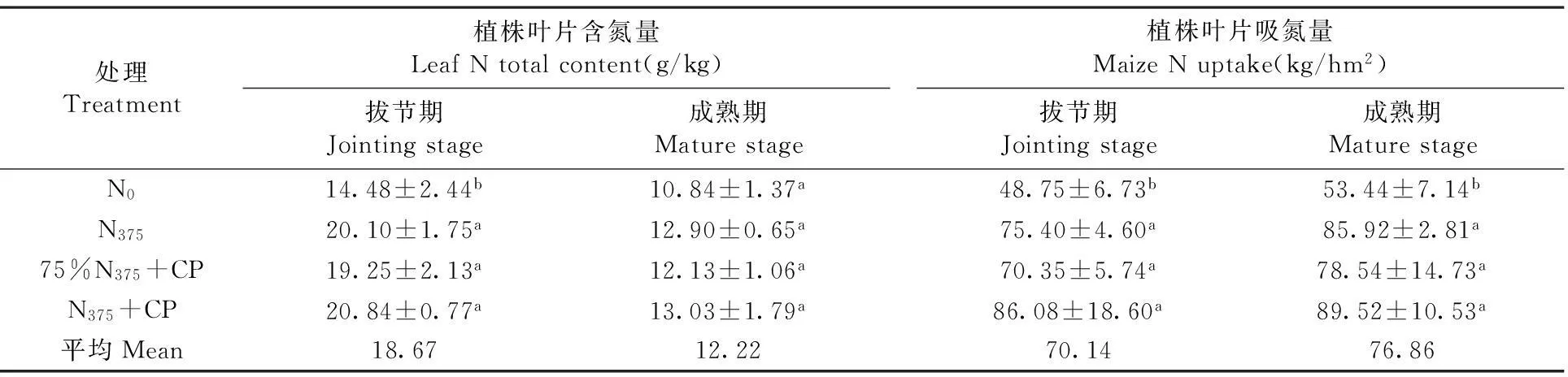
處理Treatment植株葉片含氮量LeafNtotalcontent(g/kg)拔節期Jointingstage成熟期Maturestage 植株葉片吸氮量MaizeNuptake(kg/hm2)拔節期Jointingstage成熟期MaturestageN014.48±2.44b10.84±1.37a48.75±6.73b53.44±7.14bN37520.10±1.75a12.90±0.65a75.40±4.60a85.92±2.81a75%N375+CP19.25±2.13a12.13±1.06a70.35±5.74a78.54±14.73aN375+CP20.84±0.77a13.03±1.79a86.08±18.60a89.52±10.53a平均Mean18.6712.22 70.1476.86
注:同一列中不同字母表示差異達到顯著水平(P<0.05),下同
Note:Different letters on the same column mean significant difference atP<0.05,the same as below
2.4不同施氮處理對玉米產量與構成要素影響
研究表明,從玉米產量構成要素分析,千粒重各處理之間差異不顯著,施氮處理對玉米千粒重無顯著影響。從產量分析,與對照(N0)相比,施氮可以顯著提高玉米產量。75%N375+CP、N375、N375+CP處理玉米產量分別較N0處理增加了18.6%、24.4%和28.9%。雖然75%N375+CP處理的玉米產量在3個施肥處理中最低,但經統計各施氮處理間差異未達到顯著水平;說明減氮增銨并不會降低滴灌玉米產量。表3
表3不同施氮處理下玉米產量與構成要素
Table 3The effect of different N treatment on maize yield and its component
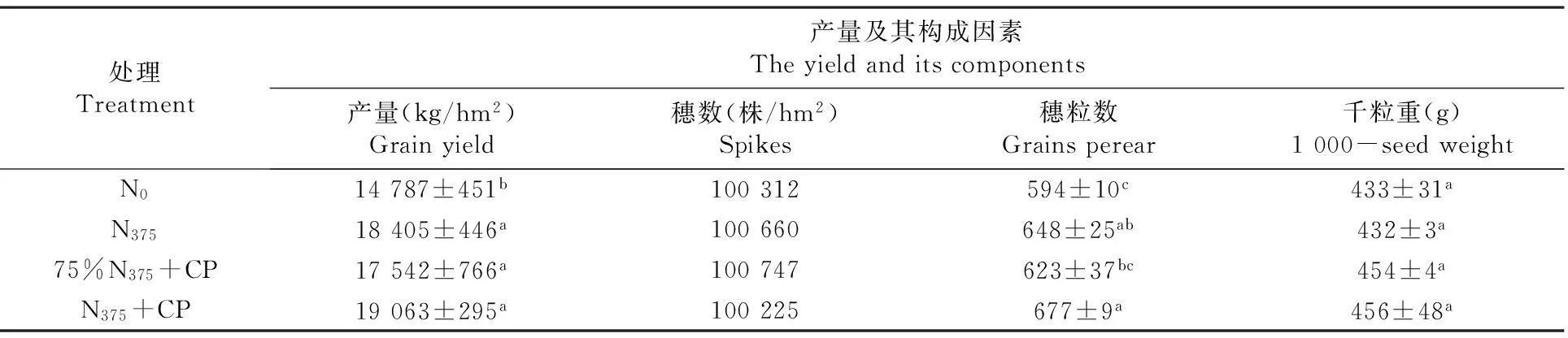
處理Treatment產量及其構成因素Theyieldanditscomponents產量(kg/hm2)Grainyield穗數(株/hm2)Spikes穗粒數Grainsperear千粒重(g)1000-seedweightN014787±451b100312594±10c433±31aN37518405±446a100660648±25ab432±3a75%N375+CP17542±766a100747623±37bc454±4aN375+CP19063±295a100225677±9a456±48a
2.5不同施氮處理對滴灌玉米氮肥利用效率的影響
研究表明,滴灌玉米的氮肥利用率在39.0%~44.6%,不同施肥處理間氮肥利用率順序表現為75%N375+CP>N375+CP>N375。75%N375+CP的氮肥利用效率分別較N375和N375+CP處理提高了41.6%和27.4%,且差異顯著(P<0.05)。氮肥偏生產力變化范圍為47.1%~64.0%,3個施氮處理的氮肥偏生產力與氮肥利用率呈相同趨勢。75%N375+CP的氮肥偏生產力也表現為最高,分別較N375和N375+CP處理提高了26.8%和22.8%,且三者差異顯著(P<0.05)。說明在滴灌條件下通過減氮增銨可顯著提高滴灌玉米氮素養分利用效率。圖3
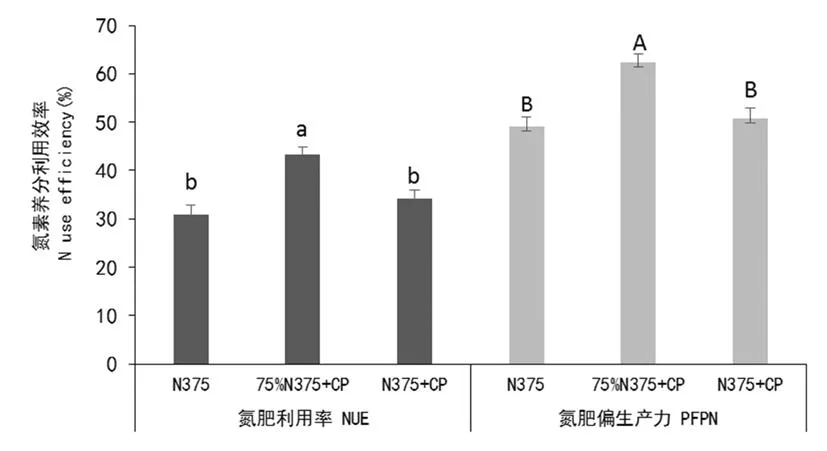
圖3不同施氮處理下玉米氮肥利用率及氮肥偏生產力變化
Fig. 3 The effect of different N treatment on maize apparent N fertilizer recovery rate and partially fertilizer production per N of nitrogen fertilizer
3 討 論

4 結 論
在天山北坡滴灌玉米種植區,以當地滴灌高產玉米施氮量(375 kg/hm2)為基礎,通過減氮增銨(75%N375+CP)可促進植株干物質的積累,且可改善植株氮素營養,提高玉米植株吸氮量;減肥增銨處理的玉米氮素利用效率和氮肥偏生產力,較全氮施肥提高了41%和26.8%。在現有常規施肥量的情況下,通過增銨措施、氮肥施量減少25%并不會導致減產。在滴灌水氮一體化條件下,通過硝化抑制劑增銨減少氮肥用量25%(75~95 N kg/hm2)不僅不會降低玉米的氮素營養與產量,且可顯著提高氮素養分利用效率。
參考文獻(References)
[1]吳美玲. 減施氮對不同品種玉米產量和氮效率的影響研究[D]. 長春:吉林農業大學碩士論文, 2014.
WU Mei-ling. (2014).Researchoneffectofreducingnitrogenonyieldandnitrogenefficiencyofdifferentvarietiesofmaize[D]. Master Dissertation. Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun. (in Chinese)
[2] 吳建新, 左強, 王甲辰, 等. 不同施肥措施對球莖茴香產量、品質及氮平衡的影響[J]. 北方園藝, 2010, (10): 15- 18.
WU Jian-xin, ZUO Qiang, WANG Jia-chen, et al. (2010). Effects of different fertilization treatments on yield, quality and nitrogen balance of the bulb [J].NorthernHorticulture, (10): 15-18. (in Chinese)
[3] 馬群, 李國業, 顧海永, 等. 我國水稻氮肥利用現狀及對策[J].廣東農業科學, 2010, 37(11):126-129.
MA Qun, LI Guo-ye, GU Hai-yong, et al. (2011). Current situation and Countermeasures of rice nitrogen fertilizer use in China [J].XinjiangAgriculturalSciences, 37(11):126-129. (in Chinese)
[4] 劉建亮. 旱地高產高效玉米栽培體系水氮管理及調控[D]. 楊凌:西北農林科技大學博士論文, 2014.
LIU Jian-liang. (2014).Managementandregulationofwaterandnitrogenforhigh-yieldandhigh-efficiencydrylandmaizesystem[D]. PhD Dissertation. Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Yangling. (in Chinese)
[5] Pang, X. P., Gupta, S. C., Moncrief, J. F., Rosen, C. J., & Cheng, H. H. (1998). Evaluation of nitrate leaching potential in minnesota glacial outwash soils using the ceres-maize model.JournalofEnvironmentalQuality, 27(1):75-85.
[6] 譚賀. 不同氮肥運籌對春玉米干物質積累及氮吸收分配的影響[D]. 長春: 東北農業大學碩士論文, 2013.
TAN He. (2013).EffectsofDifferenceNitrogenManagementsonDryMatterAccumulation,NitrogenUptakeandDistributionofSpringMaize[D]. Master Dissertation. Northeast Agricultural University, Changchun. (in Chinese)
[7] 王秀斌, 徐新朋, 孫剛, 等. 氮肥用量對雙季稻產量和氮肥利用率的影響[J]. 植物營養與肥料學報, 2013,(6):1 279- 1 286.
WANG Xiu-bin, Xü Xin-ming, SUN Gang, et al. (2013). Effects of nitrogen fertilization on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double cropping rice [J].PlantNutritionandFertilizerScience, (6):1,279-1,286. (in Chinese)
[8] 姜雯, 周登博, 張洪生,等.不同施肥水平下聚天冬氨酸對玉米幼苗生長的影響[J]. 玉米科學, 2007, 15(5):121- 124.
JIANG Wen, ZHOU Deng-bo, ZHANG Hong-sheng, et al. (2007). The Effect of Poly aspartic Acid on Maize Growth at Seedling Stage Under Different Fertilizer Applied Condition [J].JournalofMaizeScience, 15(5):121-124. (in Chinese)
[9] 孫傳范, 戴廷波, 曹衛星. 不同施氮水平下增銨營養對小麥生長和氮素利用的影響[J]. 植物營養與肥料學報, 2003, (1):33-38,49.
SUN Chuan-fan, DAI Ting-bo, CAO Wei-xing. (2003). Effect of the Enhanced Ammonium Nutrition on the growth and nitrogen utilization of wheat under different N levels [J].PlantNutritionandFertilizerScience, (1):33-38,49. (in Chinese)
[10] 張維理, 田哲旭, 張寧,等. 我國北方農用氮肥造成地下水硝酸鹽污染的調查[J]. 植物營養與肥料學報, 1995, 1(2) : 80 - 87.
ZANG Wei-li, TIAN Zhe-xu, ZHANG Ning, et al. (1995). Investigation of nitrate pollution in ground water due o nitrogen fertilization in agriculture in north China [J].PlantNutritionandFertilizerScience, 1(2): 80 -87. (in Chinese)
[11] Liu, L. J., Sang, D. Z., Liu, C. L., Wang, Z. Q., Yang, J. C., & Zhu, Q. S. (2004). Effects of real-time and site-specific nitrogen managements on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency.AgriculturalSciencesinChina,(4):262-268.
[12] 王端, 紀德智, 馬琳,等. 春玉米產量和施氮量對氮素利用率的影響[J]. 中國土壤與肥料, 2013, (6):42- 46.
WANG Rui, JI De-zhi, MA Lin, et al. (2013). Effects of corn yield and nitrogen application on nitrogen use efficiency [J].SoilandFertilizerinChina, (6):42- 46. (in Chinese)
[13] 戴廷波,曹衛星,孫傳范,等. 增銨營養對小麥光合作用及硝酸還原酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶的影響[J]. 應用生態學報,2003, 14(9):1 529-1 532.
DAI Ting-bo, CAO Wei-xing, SUN Chuan-fan, et al. (2003). Effect of enhanced ammonium nutrition on photosynthesis and nitrate reuctase and glutamine syntheses activities of winter wheat [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcology,14(9): 1,529-1,532. (in Chinese)
[14] 李彩鳳. 增銨營養對玉米品質影響初探[J]. 玉米科學,2003,11(3):82-84.
LI Cai-feng. (2003). Primarily Research on Quality of Maize Influenced by Enhanced Ammonium Nutrition [J].JournalofMaizeSciences, 11(3): 82-84. (in Chinese)
[15] 孫傳范, 戴廷波, 荊奇,等. 不同生育時期增銨營養對小麥生長及氮素利用的影響[J]. 應用生態學報, 2004, 15(5):753- 757.
SUN Chuan-fan, DAI Ting-bo, JING Qi, et al. (2004). Effect of enhanced ammonium nutrition(EAN)at different growth stages on wheat growth and nitrogen utilization [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcology, 15(5): 753- 757. (in Chinese)
[16] 田秀英, 王正銀. 尿素與復合氮肥增效劑配施對水稻氮素利用的影響[J]. 水土保持學報,2006, 20(6):120- 123.
TIAN XU-ying, WANG Zheng-yin. (2006). Effect of Urea Combined with Compound Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergists on Nitrogen Utilization of Rice [J].JournalofSoilandWaterConservation, 20(6): 120-123. (in Chinese)
Response of Reduing Nitrogen and Enhancing Ammonium to Maize N Nutrition and Yield under Drip Irrigation Condition
WANG Xue-wei, XIA Wen-hao, LIU Tao, TANG Cheng, CHU Gui-xin
(KeyLaboratoryofOasisEco-agricultureofXinjiangProductionandConstructionCorps/CollegeofAgronomy,ShiheziUniversity,ShiheziXinjiang832003,China)
Abstract:【Objective】 The project aims to study the effect of enhancing ammonium nutrition in upland crop nitrogen nutrition in arid areas and improve crop yield as well. 【Method】In the present study, the effect of decreasing urea supply rate and enhancing ammonium nutrition by chloromethyl pyridine on maize yield, corn plant N nutrition status and N fertilizer using efficiency were investigated under plastic mulched drip irrigation condition. Four treatments was designed: N0 (without N), N(375 )(375 kg/hm2), 75%N(375)+CP (25% of N was reduced plus chloromethyl pyridine) and N(375)+CP (375 kg/hm2 plus chloromethyl pyridine). 【Result】Plant dry matter accumulation was increased by 22% with 75%N(375)+CP treatment compared with N0; the leaf -N content of maize was decreased by 16.7% with 75%N(375)+CP treatment in contrast to N(375); the maize yield was increased by 18.6% with 75%N(375 )+ CP treatment compared with N0, and N fertilizer recovery rate and nitrogen partial factor productivity of maize was increased by 41% and 26.8% respectively, in 75%N(375)+CP treatment compared with N0. 【Conclusion】 In brief, a great fertilizer N recovery rate and better plant N status could be archived by corn, meanwhile, the maize yield is not down through the strategy of reducing N supply rate and enhancing ammonium nutrition under drip irrigation condition.
Key words:maize; grain yield; decreasing the nitrogen and increasing the ammonium; nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency; maize N nutrition
中圖分類號:S513;S14
文獻標識碼:A
文章編號:1001-4330(2016)03-0461-06
作者簡介:王雪薇(1993-),女,新疆人,碩士研究生,研究方向為植物營養,(E-mail)grammays17@163.com通訊作者:褚貴新(1969-),男,甘肅人,教授,博士生導師,研究方向為植物營養生理生態與新型肥料,(E-mail)chuguixinshzu@163.com
基金項目:國家“十二五”科技支撐項目(2012BAD42B02)
收稿日期:2015-10-26
doi:10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2016.03.010
Fund project:Supported by Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period. (2012BAD42B02)

