城市模型反射率測量方法與運用
譚康豪 覃英宏 蘇益聲 梁槚 龐如月
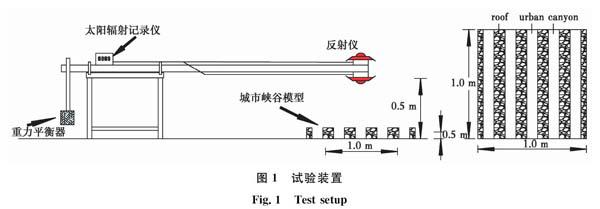
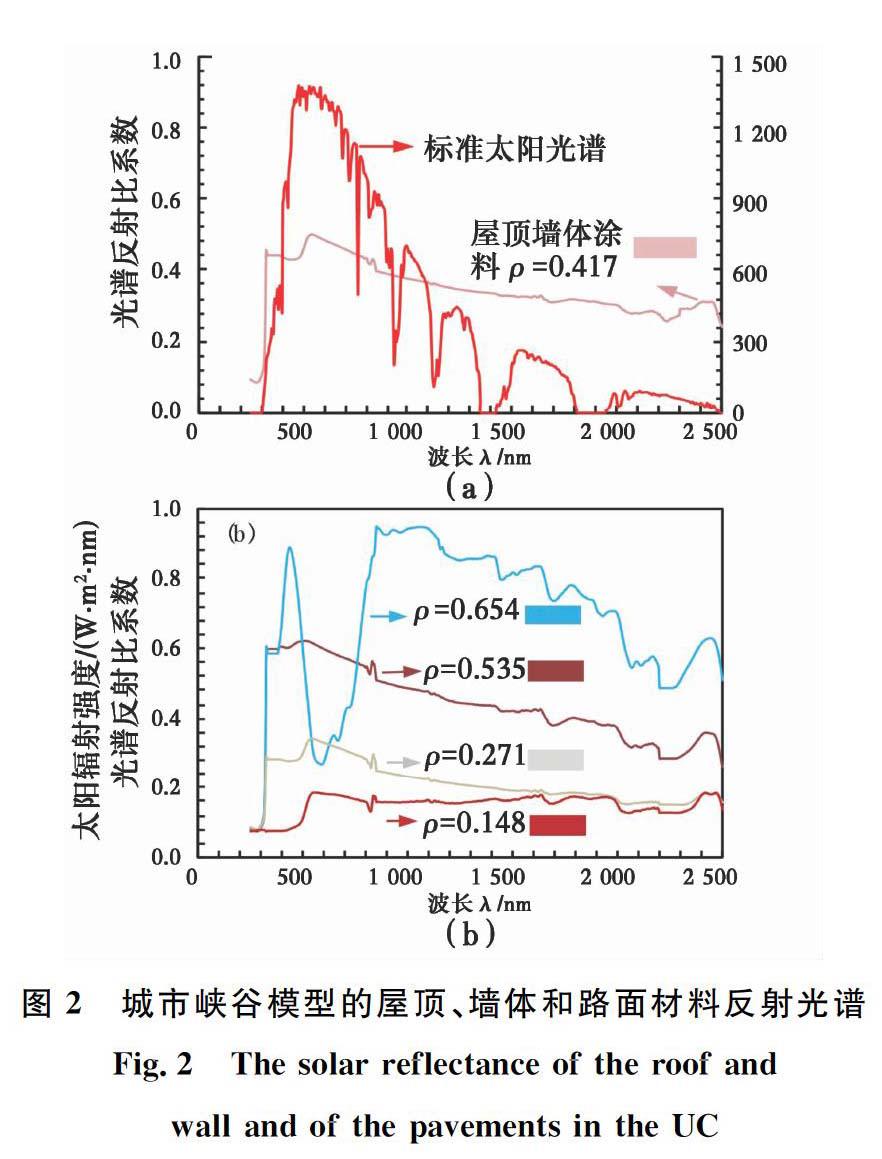
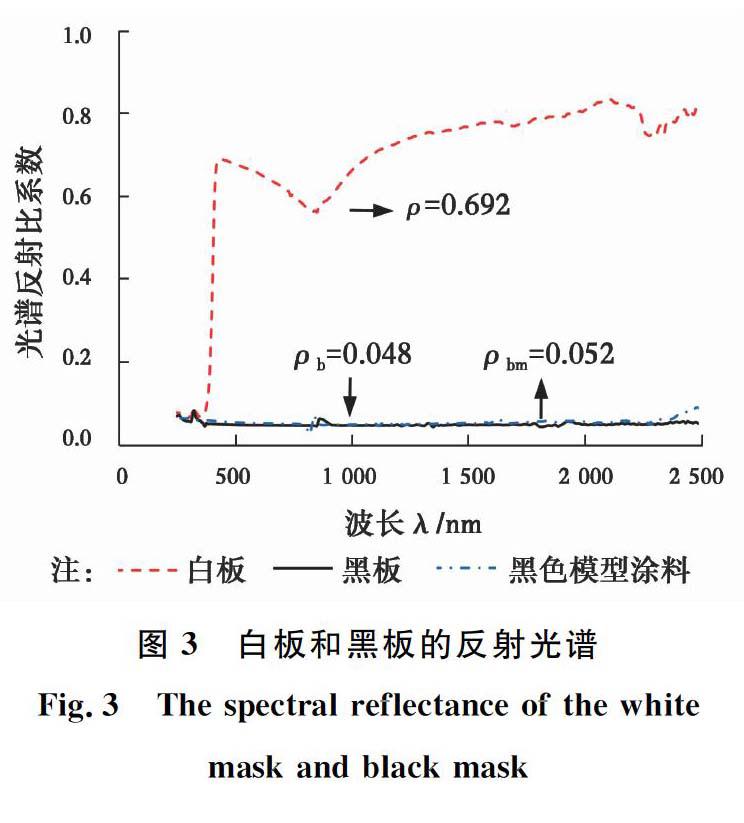
摘要:介紹了一種測試城市模型反射率的試驗方法。制作10個條形和十字形的城市模型進行測試,觀測路面不同反射率對城市反射率的影響,并將實測模型反射率與ASTM E191806規范計算結果進行對比。研究發現:瞬時太陽輻射強度變化值在規范允許范圍內,模型計算的反射率與ASTM E191806測量值的誤差在0~0.1之間。當峽谷縱橫比(建筑物高度與路面寬度之比)為10時,路面反射率從0.15提高到0.65,城市峽谷反射率增幅在0~0.30之間;提高路面反射率并不能有效提高城市峽谷反射率,尤其是縱橫比較大的深峽谷。城市峽谷中的多重反射抑制城市反射率的提高。同時,反射路面將給行人增加額外的輻射通量,可能帶來熱不適感和眩光刺眼等問題。因此,應謹慎看待反射路面作為一個緩解城市熱島效應策略。
關鍵詞:城市峽谷;熱島效應;多重反射;反射率;縱橫比;反射路面
中圖分類號:TU761
文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:16744764(2016)02011107
Abstract: A new method of measuring the albedo of urban prototype is proposed. The method is used to measure ten urban prototypes with different pavement reflectivity and with southnorth orientation, westeast orientation and crossstreet orientation, respectively. The results are compared with those obtained by the ASTM E191806 and the modified ASTM E191806. It is found that when the variation of the incident solar intensity is less than 20 W/m2 (a tolerant error stated by ASTM E1918A), the ASTM E191806 can either underestimate or overestimate the albedo of the urban canyon prototype up to 0.10. For an urban canyon (UC) with an aspect ratio of 1.0, an change from 0.15 to 0.65 of pavement albedo would cause an increase of the albedo of the UC from about 0.15 to 0.35 if the albedo of the roof and wall is about 0.40. Raising the albedo of the pavement in a UC is not an effective way to increase the albedo of the urban area, especially for UC with great aspect ratio. For low aspect ratio UC, raising the albedo of the pavement or of the parking lot introduces a sizable additional diffuse reflected radiation to the pedestrians. Therefore, it should be cautious to developing reflective pavements as an urban cooling strategy.
Keywords:urban canyon; urban heat island; multiple reflection; albedo; aspect ratio; reflective pavement
城市結構單元一般包括建筑墻體、屋頂及道路,道路與建筑兩側的空氣形成類似于峽谷的地貌特征,稱為“城市街道峽谷”(Urban canyon)。城鎮化的進程使得城市下墊面發生重大改變,以前的透水性地面被不透水性地面所取代,由于干燥致密的混凝土路面無法進行有效地蒸發降溫,存儲于城市下墊面的熱量只能以濕熱的形式散失到城市環境中。城市熱島效應的成因與許多因素有關,其中最根本的誘因來自太陽直接輻射。由于太陽輻射為不可控因素,控制城市峽谷的熱吸收量很大程度依賴于整個城市峽谷反射率的改變。……

