潰瘍性結腸炎患者腸道機械屏障變化與STAT3信號通路關系的研究
衛江鵬,劉 剛,張 霆,王建林,劉 彤
天津醫科大學總醫院普通外科,天津 300052
潰瘍性結腸炎患者腸道機械屏障變化與STAT3信號通路關系的研究
衛江鵬,劉 剛,張 霆,王建林,劉 彤
天津醫科大學總醫院普通外科,天津 300052
目的 探討潰瘍性結腸炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)患者腸道機械屏障變化與信號轉導及轉錄活化因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)信號通路的關系。方法 收集200例UC患者腸黏膜組織作為UC組,以50名健康體檢者腸黏膜標本為對照組。UC患者以Mayo評分分為輕度(68例)、中度(70例)和重度(62例)。免疫組化法檢測咬合蛋白(Occludin)、緊密連接蛋白l(Claudin-1)和STAT3蛋白表達,并對相關臨床指標進行統計學分析。結果 與對照組相比,UC組Occludin、Claudin-1的表達水平顯著降低(P<0.05),STAT3表達水平明顯升高(P<0.05)。三種蛋白的表達水平在輕、中、重度UC組間相比,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),其中Occludin和Claudin-1表達隨著UC分級增加顯著減少(rs=-0.914,rs=-0.933,P<0.05),STAT3表達隨著UC分級增加而顯著增多(rs=0.942,P<0.05)。Occludin及Claudin-1表達水平與STAT3表達水平呈負相關(r=-0.924,r=-0.983,P<0.05)。結論 STAT3信號通路可能通過影響腸黏膜上皮細胞間緊密連接蛋白Occludin和Claudin-1的表達引起UC腸黏膜機械屏障損傷。STAT3基因可能成為干預治療UC的一個潛在靶點。
潰瘍性結腸炎;腸上皮屏障功能;緊密連接蛋白;信號轉導及轉錄活化因子3
目前認為腸道屏障功能損傷在潰瘍性結腸炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)發生、發展過程中發揮重要作用,但其機制尚未完全明確。研究顯示信號轉導及轉錄活化因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)與UC發病密切相關[1]。本研究通過檢測UC患者腸黏膜STAT3蛋白、緊密連接蛋白1(Claudin-1)和咬合蛋白(Occludin)的表達,探討UC腸道機械屏障變化與STAT3信號通路的關系,進而分析UC的發病機制。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料收集2010年1月-2013年2月因具有UC癥狀在天津醫科大學總醫院內鏡室行電子結腸鏡檢查且腸鏡表現及病理診斷為UC患者的標本200例[診斷標準參照“炎癥性腸病診斷與治療的共識意見(2012)”[2]],男109例,女91例,年齡14~82歲,平均年齡(45±3)歲。根據Mayo[3]分級方法分為輕度68例,中度70例和重度62例。病變范圍:直腸53例,左半結腸78例,廣泛結腸69例。收集2012年1月-2013年2月天津醫科大學總醫院50名健康體檢者腸道黏膜標本作為對照組,男25名,女25名,年齡38~88歲,平均年齡(62±2)歲。此研究已通過天津醫科大學總醫院倫理委員會批準,所有患者均簽署知情同意書。
1.2 試劑與方法
1.2.1 主要試劑:兔抗人Occludin多克隆抗體購自英國Abcam公司;兔抗人Claudin-1多克隆抗體、兔抗人STAT3多克隆抗體、含5%BSA封閉液和SABC的羊抗兔/羊抗小鼠二抗試劑盒、3,3-二氨基聯苯胺(DAB)試劑盒均購自中國武漢博士德生物工程有限公司。
1.2.2 免疫組化法:將兩組結腸黏膜用4%多聚甲醛固定后,脫水制成蠟塊,所有組織蠟塊均以4 μm連續切片,兩組切片經脫蠟、水化、熱修復抗原后加5% BSA封閉液,依次加一抗、人生物素化二抗、鏈霉素親和素酶,常溫孵育,經DAB顯色及蘇木精復染,鹽酸乙醇分化、脫水、二甲苯透明、中性樹脂封片、顯微鏡鏡檢并拍照。由兩名病理科醫師采用獨立雙盲法在低倍鏡(40倍)下選取陽性細胞最密集區,然后在200倍視野下計數100個細胞,計算陽性細胞的百分率,最終以平均百分數字作為每張切片的結果[4]。
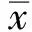
2 結果
2.1 兩組腸黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1和STAT3表達水平Occludin連續分布于腸道黏膜上皮細胞和腺體細胞,為棕黃色染色顆粒;Claudin-1主要分布于腸上皮緊密連接的細胞膜(包括細胞膜頂部),膜內近側的胞質區少量染色,為棕黃色染色顆粒。STAT3染色陽性表達為淋巴細胞或中性粒細胞胞漿或包膜呈棕黃色顆粒(見圖1)。UC組Occludin、Claudin-1的表達與對照組相比顯著降低,(31.46±11.27)%vs(43.37±5.89)%(t=7.23,P<0.05);(59.58±15.33)%vs(69.28±4.42)%(t=4.42,P<0.05)。與正常對照組相比,UC組STAT3表達水平顯著升高(42.73±8.38)%vs(87.24±9.81)%(t=7.22,P<0.05)。

圖1 對照組和UC組腸黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1及STAT3蛋白表達(200×) A:對照組Occludin(強陽性);B:UC組Occludin(陰性);C:對照組Claudin-1(強陽性);D:UC組Claudin-1(陰性);E:對照組STAT3(陰性);F:UC組STAT3(強陽性)
2.2 UC組腸黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1和STAT3表達水平與臨床參數的關系UC組腸黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1陽性細胞表達率由輕度到重度顯著減少,STAT3表達由輕度到重度顯著增加(P<0.05);Occludin、Claudin-1與Mayo分級呈負相關(rs=-0.914,P<0.05),STAT3與Mayo分級呈正相關(rs=0.942,P<0.05)。Occludin、Claudin-1和STAT3在不同性別、年齡和病變范圍的表達間比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05,見表1)。Pearson相關分析顯示:UC組腸道黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1表達與STAT3表達水平呈負相關(rs=-0.924,rs=-0.983,P<0.05)。
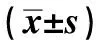
表1 UC組Occludin、Claudin-1、STAT3表達與臨床病理參數的關系
3 討論
研究表明STAT3是介導細胞因子信號通路的重要轉錄因子,可與多種細胞因子相結合并通過JAK/STAT途徑發揮誘導細胞信號轉導作用[5]。Murano等[6]的實驗發現腸黏膜中STAT3信號通路被激活后可促進腸上皮細胞編碼多種促炎因子。此外,其他一些研究表明炎癥介質可通過STAT3信號通路促進髓樣相關蛋白8(myeloid-related protein 8,MRP8)的表達,進而引起腸黏膜研中性粒細胞的趨化及黏附[7],加重UC炎癥反應。本實驗結果顯示,UC患者腸黏膜STAT3蛋白表達水平較對照組明顯升高,隨著病程進展STAT3表達量明顯增加,這與Li等[8]的研究結果一致,因而推測STAT3參與了UC的發病,并在疾病進展過程中發揮重要作用,可能成為未來UC治療的新靶點[9]。
Claudin-1與Occludin組成腸道上皮緊密連接并通過控制大分子物質和離子的通過,對維護上皮細胞兩側物質的差異及保持細胞極性,保持腸道穩態具有重要作用[10]。本研究顯示UC患者腸黏膜Claudin-1和Occludin表達水平顯著降低,隨著病程進展,表達量進一步減少。此結果表明腸道黏膜Claudin-1和Occludin表達減少引起機械屏障損傷而導致的腸道菌群移位、內毒素吸收可能是UC發生和發展的重要分子學基礎。Kim等[11]在Caco-2細胞模型實驗中發現當STAT3核轉位增多時會導致包括Occludin在內的多種腸屏障結構蛋白基因表達降低,導致腸道緊密連接受損。本研究中,STAT3、Occludin及Claudin-1與UC疾病分級密切相關;且Claudin-1和Occludin蛋白表達與STAT3蛋白表達水平呈顯著負相關。可以推測,STAT3通過影響Claudin-1和Occludin蛋白的表達,進而導致上皮細胞間緊密連接減少,上皮細胞間隙通透性增強,引起腸道菌群及內毒素移位,最終出現腸道穩態失衡,影響UC的發病及病程進展。
綜上,腸黏膜上皮Claudin-1和Occludin的表達減少是UC發病及進展的重要分子學基礎,STAT3作為一種可介導多種信號通路的轉錄因子,通過調控基因表達來影響Claudin-1和Occludin的表達水平,進而破壞腸黏膜機械屏障的完整性參與了UC的發病,并在疾病進展過程中發揮關鍵作用。如何通過靶向干預STAT3的表達,進而阻斷這一機制的發生,減輕腸黏膜機械屏障的損傷,對UC的診斷治療具有重要意義,未來或成為對UC研究的新熱點。
[1]Cénit MC, Alcina A, Márguez A, et al. STAT3 locus in inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis susceptibility [J]. Genes Immun, 2010, 11(3): 264-268.
[2]Chinese cooperative group for the study on IBD, Chinese society of gastroenterology. Consensus on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in China (2012, Guangzhou) [J]. Chin J Dig, 2012, 32(12): 796-813. 中華醫學會消化病學分會炎癥性腸病學組. 炎癥性腸病診斷與治療的共識意見(2012年,廣州)[J]. 中華消化雜志, 2012, 32(12): 796-813.
[3]D′Haens G, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. A review of activity indices and efficacy end points for clinical trials of medical therapy in adults with ulcerative colitis [J]. Gastroenterology, 2007, 132(2): 763-786.
[4]Cates JM, Troutman KA Jr. Quality management of the immunohistochemistry laboratory: a practical guide [J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2015, 23(7): 471-480.
[5]Morikawa T, Baba Y, Yamauchi M, et al. STAT3 expression, molecular features, inflammation patterns, and prognosis in a database of 724 colorectal cancers [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17(6): 1452-1462.
[6]Murano T, Okamoto R, Ito G, et al. Hes1 promotes the IL-22-mediated antimicrobial response by enhancing STAT3-dependent transcription in human intestinal epithelial cells [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 443(3): 840-846.
[7]Lee MJ, Lee JK, Choi JW, et al. Interleukin-6 induces S100A9 expression in colonic epithelial cells through STAT3 activation in experimental ulcerative colitis [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e38801.
[8]Li F, Zou Y, Li X. Up-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 is associated with aggravation of ulcerative colitis [J]. Surgeon, 2010, 8(5): 262-266.
[9]Neufert C, Pickert G, Zheng Y, et al. Activation of epithelial STAT3 regulates intestinal homeostasis [J]. Cell Cycle, 2010, 9(4): 652-655.
[10]Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Mendivil-Rangel EJ, Fonseca-Camarillo G. Differential expression of occludin in patients with ulcerative colitis and healthy controls [J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2012, 18(10): E1999.
[11]Kim CY, Kim KH. Curcumin prevents leptin-induced tight junction dysfunction in intestinal Caco-2 BBe cells [J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2014, 25(1): 26-35.
(責任編輯:王豪勛)
The relationship between the change of intestinal mechanical barrier function in patients with ulcerative colitis and STAT3 pathway
WEI Jiangpeng, LIU Gang, ZHANG Ting, WANG Jianlin, LIU Tong
Department of General Surgery, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin 300052, China
Objective To investigate the relationship between the change of mechanical barriers in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway.Methods Specimens were obtained in 200 patients with UC and 50 controls respectively, samples were classified into three groups as mild (68 cases), moderate (70 cases) and severe (62 cases) according to Mayo classification. Immunohistochemistry was performed to examine the expressions of Occludin, Claudin-1 and STAT3. The result and the clinical data were analyzed. Results Compared with control group, the expressions of Occludin and Claudin-1 significantly decreased (P<0.05), STAT3 significantly increased in UC group (P<0.05). The levels of three proteins were different in each active subgroups (P<0.05). Occludin and Claudin-1 were decreased significantly with the increase of UC classification (rs=-0.914,rs=-0.933,P<0.05), STAT3 was significant increased with the increase of UC classification (rs=0.942,P<0.05). With the increase of STAT3, Occludin and Claudin-1 levels were decreased significantly (r=-0.924,r=-0.983,P<0.05).Conclusion STAT3 may be involved in intestinal mucosa barrier damage through inhibition of Occludin and Claudin-1 expressions, resulting in the occurrence and development of UC.
Ulcerative colitis; Epithelial barrier function; Tight junction proteins; Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
黎介壽院士腸道屏障研究專項基金(LJS201008);天津市衛生局科技基金(2011KZ66)
衛江鵬,碩士,研究方向:炎癥性腸病的臨床與基礎。E-mail:EdficRango@163.com
劉剛,博士,主任醫師,研究方向:炎癥性腸病的臨床與基礎。E-mail:landmark1503@sina.com
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2016.01.011
R574.62
A
1006-5709(2016)01-0047-04
2015-03-05

