陜西梁山地區中二疊世早期腕足動物多樣性演變
柯妍 曾勇
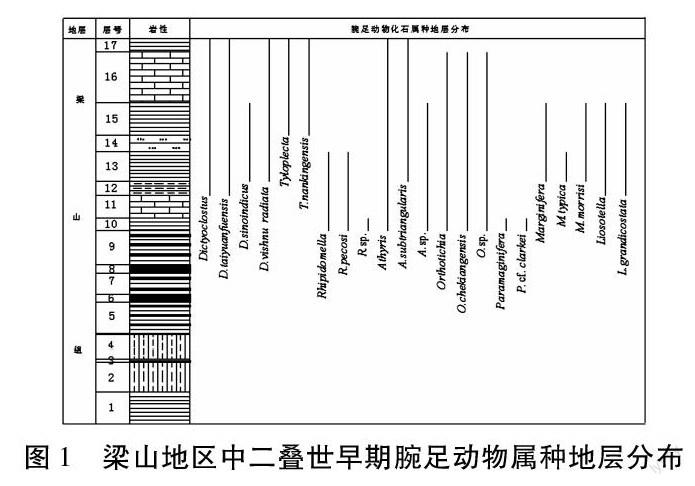

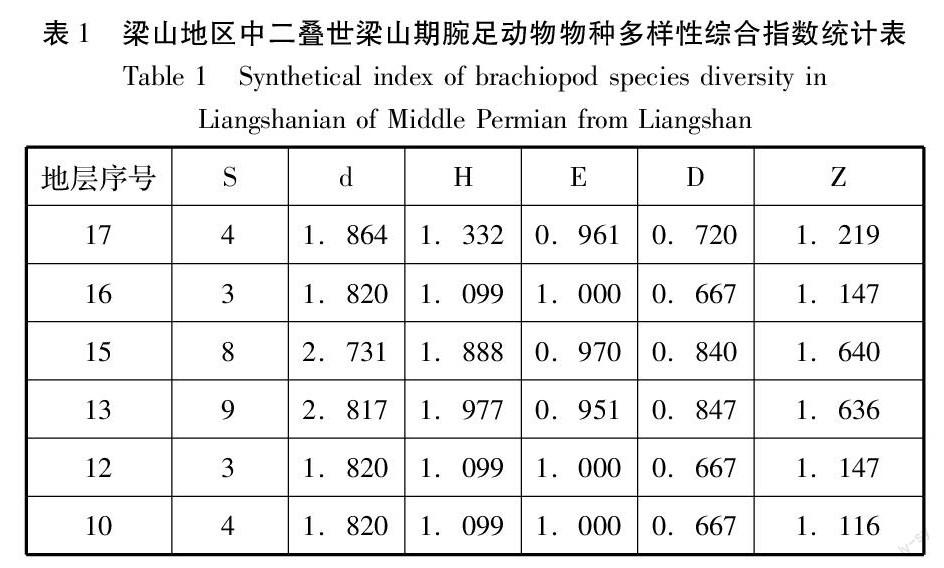
摘要:利用陜西漢中梁山地區中二疊世早期梁山組地層中的腕足動物化石進行了物種多樣性演變的統計分析,從分析結果可以發現,本區中二疊世梁山期腕足動物的物種多樣性經歷了輻射上升—衰退下降—輻射上升期的過程,物種多樣性綜合指數由本期初始的1.116上升到最高峰的1.640而后下降為本期末的1.219。結合本地區的巖相和沉積環境,認為這可能是受當時的環境影響。
關鍵詞:陜西梁山地區;中二疊世早期;腕足動物;物種多樣性;演變
Abstract: Brachiopod diversity evolution of the early middle-Permian is statistical analyses on the fossils from the Liangshan Formation in Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi province. From the analysis results, it can be found that the brachiopod species diversity of the study area experienced a process which could be divided in to three phase: radiation rise, recession fall, and radiation rise again. The synthetically index of species diversity is up to a peak of 1.640 from the initial value in this period of 1.116 and finally dropped to the 1.219 at the end of this period. It could be subject to the sedimentary environmental impact on the lithofacies of this area.
Key words: Liangshan area in Shaanxi Province; Early Middle Permian; Brachiopod; species diversity; evolution
1.引言
生物多樣性是一個涉及基因、物種和生態系統等三個方面的學科領域,它既包括了生物個體及其新攜帶的遺傳信息,也包括它們與其生境所組成的生態系統以及各組成部分之間的相互聯系。因此,聯合國環境規劃署在《全球生物多樣性評估》一書中給出了生物多樣性的定義:生物多樣性是所有生物種類、種內遺傳變異和它們與生存環境構成的生態系統總稱[1]。當前, 公認的生物多樣性是從三 個層次上進行描述的, 即遺傳多樣性、物種多樣性、生態系統與景觀多樣性[2、3].雖然生物多樣性是現代生物學家提出來的, 但由于它涉及到生物物種的起源、生物物種和生態類型的發展、演化、滅絕等變化的規律, 因此, 古生物學家和古生態學家也加入到這一研究領彧中來。
本文以陜西梁山地區的中二疊世早期腕足動物為對象, 用數理統計的方法對該時期腕足類物種多樣性指數進行研究, 以期達到總結其在演化過程中相互關系的規律的目的。……

