microRNA-34a體外調控鼻咽癌鱗狀腫瘤干細胞表型
江文靜 蔣學范 胡未鳴
浙江省人民醫院耳鼻喉科,浙江杭州310000
microRNA-34a體外調控鼻咽癌鱗狀腫瘤干細胞表型
江文靜蔣學范胡未鳴▲
浙江省人民醫院耳鼻喉科,浙江杭州310000
目的探討microRNA-34a(miR-34a)對鼻咽癌鱗狀腫瘤干細胞表型的體外調控作用。方法利用原代培養的人類鼻咽癌細胞,采用流式分選法定量并收集ALDH(aldehyde dehydrogenase)+腫瘤干細胞。通過RT-qPCR分析miR-34與腫瘤干細胞相關因子(Sox2、Nanog、Oct3/4)在ALDH+和ALDH-細胞中的表達情況。進一步用miR-34a擬態轉染評估其對鼻咽癌腫瘤干細胞標記物以及相關因子的表達調控能力。結果原代鼻咽癌細胞中表達ALDH的細胞約占15.43%左右。與ALDH-細胞相比,miR-34a表達水平在大多數ALDH+細胞中顯著下調(-13.2 vs-4.1倍),3種腫瘤干細胞相關因子表達顯著增加(最高36.8倍)。ALDH+細胞轉染miR-34a擬態24 h、48 h、72 h后miR-34a mRNA水平顯著增加,48 h時達峰值水平(4.49倍,P<0.01),而3種腫瘤干細胞相關因子表達水平顯著降低。結論恢復miR-34a表達顯著抑制人類原代鼻咽癌干細胞表型的形成。調控鼻咽癌和腫瘤干細胞中miR-34a的表達可能降低腫瘤治療后的轉移和復發率。
鼻咽癌;腫瘤干細胞;microRNA-34a;轉染;擬態;醛脫氫酶
[Abstract]Objective To investigate the role of miR-34a in regulating cancer stem cell(CSC)phenotype of nasopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro.Methods The cells were isolated from patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC)and cultured in vitro.Flow-cytometry was used to quantify and enrich for ALDH+cancer stem cells(CSCs).RT-qPCR was performed to analyze expression patterns of miR-34a and CSC-related transcription factors(CSC-TFs)(Sox2,Nanog,Oct3/4)for ALDH+and ALDH-cells.Transfection of miR-34a mimics was used to evaluate its regulatory potential for CSC marker profiles as well as CSC-TFs expression in NPC-CSC.Results The expression of ALDH was found in around 15.43%of primary NPC cells.miR-34a expression levels were significantly downregulated in the majority of ALDH+cells derived from primary NPC as compared to ALDH-cells(-13.2 vs-4.1 fold).For CSC-related TF expression,ALDH+cells showed a significantly increased level compared to ALDH-cells(up to 36.8 fold).miR-34a mRNA level in ALDH+cells after transfection with miR-34a mimics significantly increased after 24 h,48 h and 72 h,and the peak of miR-34a level was found 48 h post-transfection(4.49 fold,P<0.01).Transfection of miR-34a mimics significantly reduced the CSC-related TF expression level in ALDH+cells.Conclusion Restoration miR-34a significantly inhibited the formation of CSC-phenotype in human primary NPC cells.Therapeutic modulation of miR-34a in NPC and CSCs may reduce the rate of metastasis and recurrence of tumors after therapy.
[Key words]Nasopharyngeal carcinoma;Cancer stem cells;microRNA-34a;Transfection;Mimics;Aldehyde dehydrogenase
近年來,通路靶向抑制治療鼻咽癌(nasopharyngeal carcinoma,NPC)的報道已取得了一些進展,但其研究僅限于NPC細胞株,未充分考慮到腫瘤細胞株在逐代的培養過程中可能會發生某些生物學行為的改變,如細胞活性、藥物敏感性等等[1]。因此,為使研究更貼近臨床人體內實驗,本文探討了miR-34a和人類原代NPC干細胞生物學行為之間的關系。本研究首先采用流式分選法分選出ALDH+和ALDH-細胞,然后通過實時定量PCR檢測兩種細胞中CSCs相關的3種轉錄因子(CSC-TFs:Sox2、Nanog、Oct3/4)[2]及miR-34a的表達是否有差異,并將ALDH+細胞轉染miR-34a擬態,比較不同作用時間(24 h、48 h、72 h)后miR-34a及3種轉錄因子表達量的變化,探討miR-34a轉染對NPC干細胞增殖是否有抑制效應。
1 材料與方法
1.1鼻咽癌原代細胞培養
新鮮鼻咽鱗狀細胞癌組織由本院耳鼻喉科提供。本研究經患者知情同意和醫院倫理委員會審查通過,研究工作從2015年8月開展至今。步驟:①適量新鮮標本置于15 mL離心管中,裝2 mL含10℅FBS(Gibco公司)的RPMI-1640(Gibco公司)培養基。②去除外周壞死組織,無血清培養基充分漂洗3次。③將組織塊剪成0.5 mm大小,加入適量0.25℅胰酶,37℃消化8~10 min;含10℅FBS的培養基終止消化,吹打均勻后200目篩網過濾;將濾液接種于25 cm2培養瓶中,培養基3 mL,置于37℃、5%CO2、濕潤空氣的密閉式培養箱中培養。④96孔板單細胞克隆分離提純細胞。
1.2Aldefluor測定和FACS分選
Aldefluor測定試劑盒(StemCell公司)檢測細胞活性;將細胞用胰蛋白酶消化制成單細胞懸液,不含Ca2+/Mg2+的PBS洗滌,重懸浮于含5 μL ALDH底物的1 mL Aldefluor緩沖液中(1×106個細胞/mL),暗室37℃孵育30~40 min。加入ALDH抑制劑(DEAB,50 mmol/L)作為陰性對照。所有樣本使用250×g離心5 min,棄上清。緩沖液洗滌細胞兩次后加入ALDH緩沖液,并置于冰上待用。將細胞懸浮于PBS緩沖中,107個細胞/mL,應用流式細胞儀Aria cell sorter進行分選(BD Biosciences公司)。
1.3實時定量PCR
Trizol試劑(Gibco公司)分離總RNA,Poly A尾和cDNA使用Ncode VILO miR cDNA(Invitrogen)合成。使用Chromo 4(BioRad)PRC儀及SYBR Green ERTM qPCR SuperMix試劑(Invitrogen公司)進行RT-qPCR分析。參照基因GAPDH。啟動序列見表1。
1.4microRNAs(miRs)的轉染
為轉染miR擬態(mimics),首先將ALDH+細胞制成單細胞懸液,然后接種于含完全培養基的6孔板中,密度8×104個細胞/孔。50 nmol/L miR-34a擬態(mimics)轉染細胞,陰性對照(NC)或空白對照(MOCK)用Lipofectamine RNAiMAX試劑(Invitrogen),且不含抗生素Opti-MEM(Invitrogen)。使用BLOCK-ITTM公司的Alexa Fluor紅色熒光指示劑處理后,通過熒光顯微鏡對轉染的細胞進行細胞計數以確定轉染效率。RT-qPCR評估對ALDH+細胞轉染前后miR-34a的表達及3種CSC-TFs的表達進行定量,后者分別在轉染后的24 h、48 h和72 h測定。
1.5統計學方法
數據用2△△Ct進行統計分析[3],相關CT值見表2~5。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1ALDH在NPC中表達情況
流式分選ALDH+腫瘤干細胞,見圖1。DEAB抑制下分采用流式分選法定性并分選ALDH+細胞。圖1左顯示DEAB抑制下ALDH+細胞分選情況,圖1右顯示無DEAB抑制劑下ALDH+細胞分選情況,R2區域顯示ALDH+細胞熒光強度(原代鼻咽癌細胞中表達ALDH的細胞均占15.43%左右)。
2.2RT-qPCR分析CSC相關轉錄因子(CSC-TFs: Sox2、Nanog、Oct3/4)mRNA及miR-34a的表達
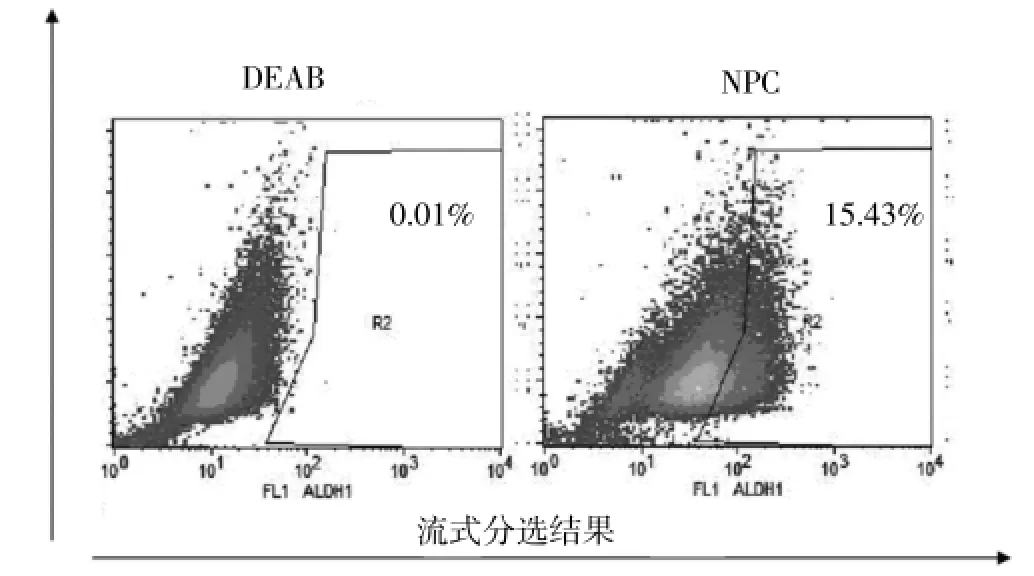
圖1 DEAB抑制下流式分選ALDH+和ALDH-細胞
RT-qPCR分析3種CSC-TFs的表達,ALDH+細胞中3種CSC-TFs的表達均顯著高于ALDH-細胞(最高36.8倍)(P<0.05或P<0.01),見圖2、表2;RT-qPCR分析miR-34a的表達,ALDH+細胞中miR-34a表達量顯著低于ALDH-細胞(-13.2 vs-4.1倍),見圖3、表3。

表1 RT-PCR引物序列(5’→3’)
2.3miR-34a超表達降低ALDH+細胞的干細胞特性
ALDH+細胞轉染前后miR-34a表達量比較,轉染后24 h、48 h、72 h其表達量顯著增加,其中48 h時表現更明顯(4.49倍),然而與對照組比較,Mock組轉染前后miR-34a表達量無明顯統計學差異,見圖4、表4。ALDH+細胞轉染后CSC相關轉錄因子(Nanog、Oct3/4)表達顯著降低,Sox2表達無明顯統計學差異,見圖5、表5。
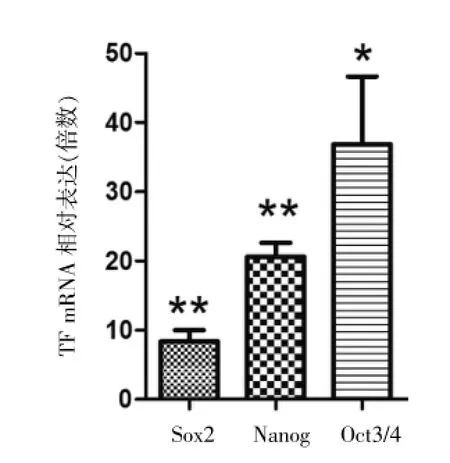
圖2 ALDH+細胞中CSC相關轉錄因子(CSC-TFs:Sox2]Nanog]Oct3/4)的表達顯著高于ALDH-細胞,*P<0.05,**P<0.01
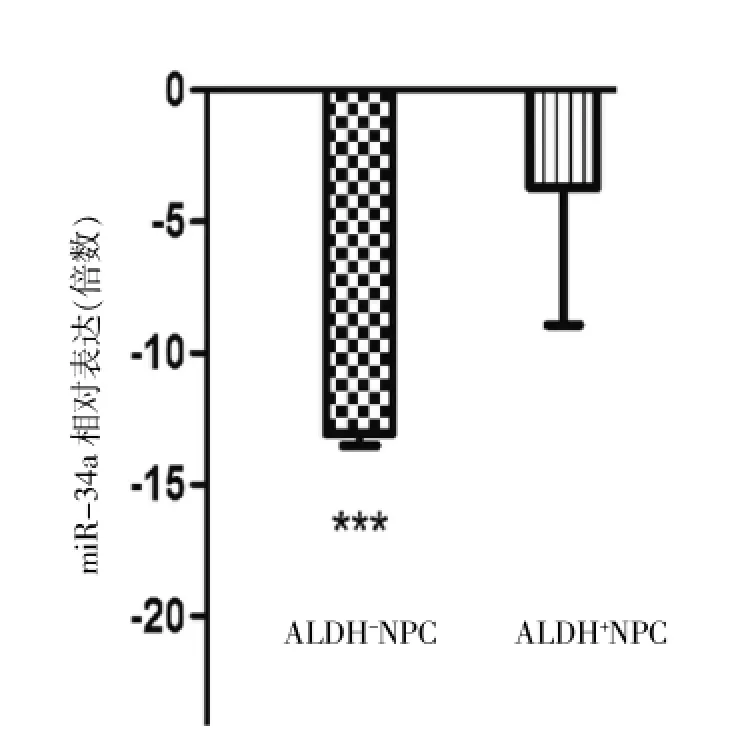
圖3 ALDH+細胞中miR-34a表達量顯著低于ALDH-細胞,***P<0.001
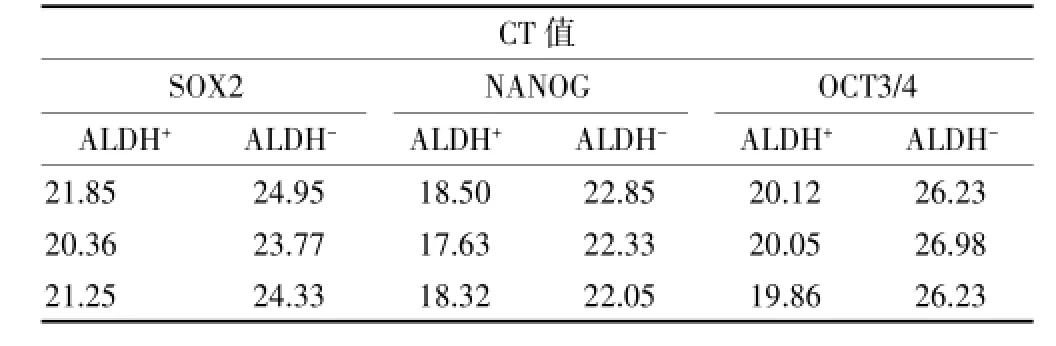
表2 ALDH+和ALDH-細胞中CSC相關轉錄因子表達CT值
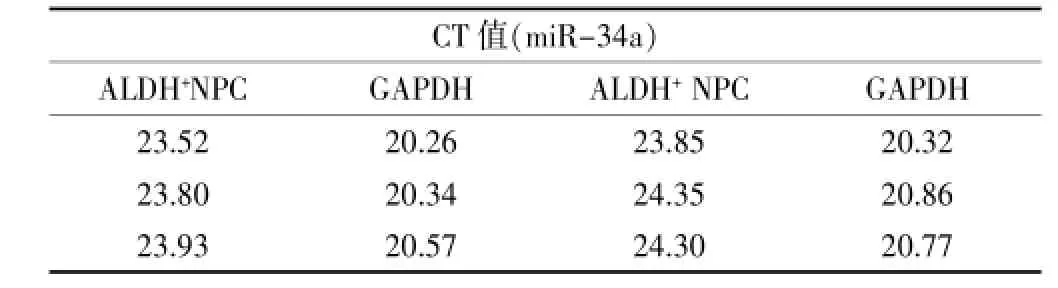
表3 ALDH+和ALDH-細胞miR-34a表達CT值
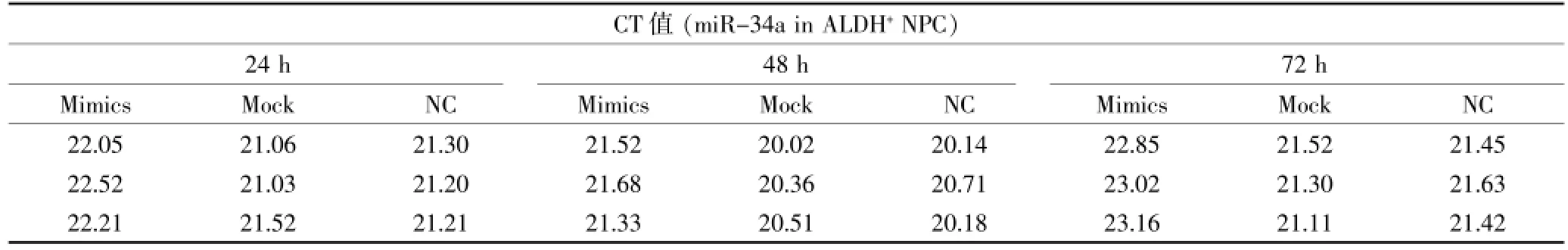
表4 miR-34a在3組ALDH+細胞且不同時間內表達的CT值
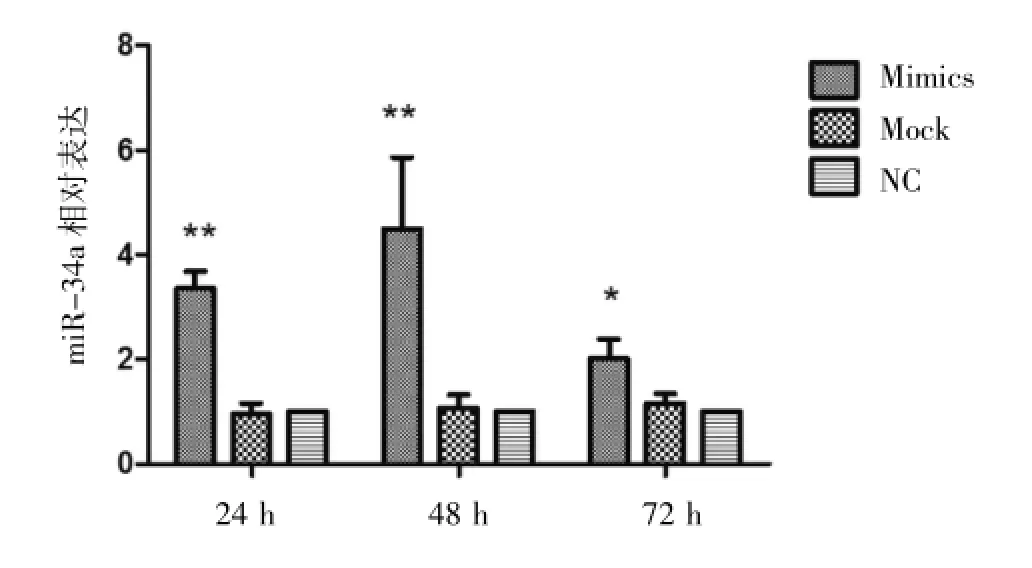
圖4 ALDH+細胞轉染前后miR-34a表達量比較,轉染后24 h]48 h]72 h其表達量顯著增加,其中48 h時表現更為明顯,*P<0.05,**P<0.01

圖5 ALDH+細胞轉染后CSC相關轉錄因子(Nanog,Oct3/4)表達顯著降低,Sox2表達無明顯統計學差異,*P<0.05,**P<0.01
3 討論
CSCs是腫瘤組織細胞的一小部分,它們具有無限的增殖潛能[4]。同時,CSCs是腫瘤細胞真正的“種子”,在某些腫瘤中表現出重要的生物學特性[5],它們與腫瘤的發生、致癌性、轉移和復發等密切相關,并對傳統的放化療具有抵抗性[6-7]。Ginestier等[8]發現將人類乳腺癌ALDH+細胞接種于非肥胖糖尿病/重癥聯合免疫缺陷的小鼠體內能形成腫瘤,因此推測這些細胞可能包含CSCs。隨后,利用ALDH1活性能從乳腺癌中鑒別并分離出CSCs[9]。ALDH在人類頭頸部鱗狀細胞癌細胞株中分離出的CSC中也呈現高表達[10]。本研究中我們采用流式分選獲取具有CSC表型的ALDH+和ALDH-細胞,進一步證實了ALDH+細胞中3種CSCTFs的表達均顯著高于ALDH-細胞。
microRNAs(miRs)是非編碼短單鏈RNAs,在正常和腫瘤細胞中調控目的mRNAs基因的翻譯,頻繁失調能促進腫瘤進展。miR-34a屬于腫瘤抑制因子,它直接作用于p53轉錄后水平。在p53缺陷的人類胰腺癌細胞中,miR-34a過度表達抑制細胞增殖,細胞周期進展及自我更新,表明miR-34a可能恢復p53功能,直接作用于與CSC分化和自我更新相關的下游靶基因[11]。MiR-34a也能抑制前列腺癌[12]和乳腺癌[13]腫瘤干細胞相關特性和功能的表達。最新研究顯示,miR-34a調節結腸癌干細胞的不對稱分裂,從而促進腫瘤生長[14]。此外,miR-34a不僅抑制非小細胞肺癌H1299細胞株的增殖,并能促進其凋亡[15]。越來越多的研究表明,針對miRNA靶向抑制CSCs在殺滅腫瘤細胞的同時也能預防腫瘤復發[16]。本研究也證實miR-34a在ALDH+細胞中表達水平顯著低于ALDH-細胞,同時miR-34a能抑制原代NPC中ALDH+細胞相關轉錄因子的表達。近來相關研究也表明miR-34a在頭頸部CSC中下調可能誘發腫瘤生長和發生[17]。腫瘤干細胞相關因子Nanog、Oct3/4、Sox2在miRNA誘導的結腸癌細胞中均呈現高表達[18]。然而,在我們的研究中miR-34a擬態轉染在增加miR-34a表達的同時,只減少ALDH+細胞中相關CSC表型Nanog、Oct3/4的表達,而Sox2表達無明顯統計學差異。
本研究顯示原代NPC細胞中含ALDH+細胞,即NPC干細胞。RT-qPCR分析結果顯示ALDH+細胞中3種CSC-TFs的表達均顯著高于ALDH-細胞,但miR-34a表達量顯著低于ALDH-細胞。由此推斷,miR-34a的表達在NPC干細胞中明顯少于非NPC干細胞。進一步對分選出的ALDH+細胞進行miR-34a擬態轉染,結果顯示轉染24 h、48 h、72 h后miR-34a表達量顯著增加,其中48 h時表現更明顯,然而對照組無明顯統計學差異,表明miR-34a表達呈一定時間依賴性。同時分別對ALDH+細胞轉染后3種CSC-TFs的表達進行分析,發現轉染后CSC相關表達因子Nanog、Oct3/4的表達顯著降低,而Sox2表達無明顯統計學差異。據此研究表明,miR-34a體外抑制鼻咽癌鱗狀腫瘤干細胞表型的表達。因此,使用針對相關通路靶向提高miR-34a表達從而抑制CSC的生長,將可能成為徹底清除人類腫瘤包括NPC在內的一個革新性治療策略。
此外,研究發現在口咽部鱗狀細胞癌中,人乳頭瘤病毒(human papillomavirus,HPV)是否感染對細胞生物學和臨床特性也起到一定作用,與HPV-DNA-細胞相比,HPV-DNA+腫瘤細胞中ALDH1A1的表達水平降低[19]。ALDH1A1作為一種腫瘤干細胞標記之一,與頭頸部鱗狀細胞癌的預后密切相關[20]。因此,在以后的研究中,圍繞HPV感染及治療將待進一步研究。
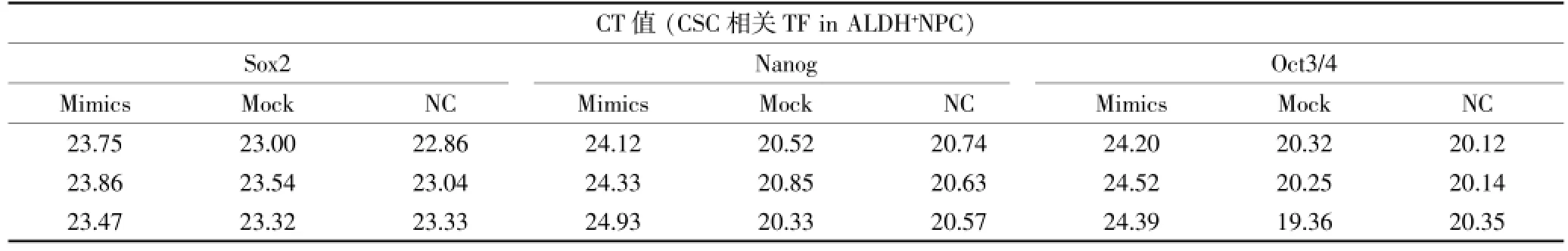
表5 ALDH+細胞中CSC相關轉錄因子在3組條件下表達的CT值
[1]W Jiang JP,Y Zhang.The Implications of Cancer Stem Cells for Cancer Therapy[J].Int J Mol Sci,2012,13(12):16636-16657.
[2]Chickarmane V,Peterson C.A computational model for understanding stem cell,trophectoderm and endoderm lineage determination[J].Plo S One.2008,3(10):e3478.
[3]Pfaffl MW.A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2001,29(9):e45.
[4]Reya TM,Morrison SJ,Clarke MF,et al.Weissman I.L,Stem cells,cancer,and cancer stem cells[J].Nature,2001,414(11):105-111.
[5]Shipitsin M,Polyak K.The cancer stem cell hypothesis:In search of definitions,markers,and relevance[J].Lab Invest,2008,88(5):459-463.
[6]Li X,Lewis MT,Huang J,et al.Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy[J].J Natl Cancer Inst,2008,100(9):672-679.
[7]Diehn M,Cho RW,Lobo NA,et al.Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stemcells[J].Nature,2009,458(7239):780-783.
[8]Ginestier C,Hur MH,Charafe-Jauffret E,et al.ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome[J].Cell Stem Cell,2007,1(5):555-567.
[9]Douville JB,R Balicki D.Aldh1 as a functional marker of cancer stem and progenitor cells[J].Stem Cells Dev,2009,18(1):17-25.
[10]Okamoto A,Chikamatsu K,Sakakura K,et al.Expansion and characterization of cancer stem-like cells in squa mous cell carcinoma of the head and neck[J].Oral Oncol,2009,45(7):633-639.
[11]Ji Q,Hao X,Zhang M,et al.MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells[J].Plo S One,2009,4(8):e6816.
[12]Liu C,Kelnar K,Liu B,et al.The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by di rectly repressing CD44[J].Nature Medicine,2011,17(2):211-215.
[13]Park EY,Chang E,Lee EJ,et al.Targeting of miR34a-NOTCH1 Axis Reduced Breast Cancer Stemness and Chemoresistance[J].Cancer Research,2014,74(24):7573-7582.
[14]Wang L,Bu P,Ai Y,et al.A long non-coding RNA targets microRNA miR-34a to regulate colon cancer stem cell asymmetric division[J].Elife,2016,14(5):e14620.
[15]Ma ZL,Hou PP,Li YL,et al.MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer H1299 cell line by targeting TGFbetaR2[J].Tumour Biol,2015,36(4):2481-2490.
[16]Osaki M,Okada F,Ochiya T.miRNA therapy targeting cancer stem cells:A new paradigm for cancer treatment and prevention of tumor recurrence[J].Ther Deliv,2015,6(3):323-337.
[17]Sun Z,Hu W,Xu J,et al.MicroRNA-34a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro[J].Int J Oncol,2015,47(4):1339-1350.
[18]Miyazaki S,Yamamoto H,Miyoshi N,et al.A Cancer Reprogramming Method Using MicroRNAs as a Novel Therapeutic Approach against Colon Cancer:Research for Reprogramming of Cancer Cells by MicroRNAs[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2015,22(Suppl 3):1394-1401.
[19]Qian X,Wagner S,Ma C,et al.ALDH1-positive cancer stem-like cells are enriched in nodal metastases of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma independent of HPV status[J].Oncology Reports,2013,29(5):1777-1784.
[20]Qian X,Wagner S,Ma C,et al.Prognostic significance of ALDH1A1-positive cancer stem cells in patients with locally advanced,metastasized head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology,2014,140(7):1151-1158.
microRNA-34a regulates cancer stem cell phenotype of squamous nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro
JIANG WenjingJIANG XuefanHU Weiming
Department of Otorhinolaryngology,Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital,Hangzhou310000,China
R76
A
1673-9701(2016)21-0028-05
2016-05-07)
浙江省醫藥衛生科技計劃項目(2016KYB024)▲

