新疆溫宿縣土壤重金屬含量分布及污染風險評價
付彥博,竇曉靜,賴寧,黃建,王新勇,王治國
(新疆農業科學院土壤肥料與農業節水研究所,烏魯木齊 830091)
新疆溫宿縣土壤重金屬含量分布及污染風險評價
付彥博,竇曉靜,賴寧,黃建,王新勇,王治國
(新疆農業科學院土壤肥料與農業節水研究所,烏魯木齊 830091)
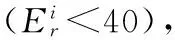
土壤;重金屬;污染評價;生態風險
0 引言
【研究意義】重金屬是土壤環境污染物質之一[1],由于其滯留持久、高富集等特性,成為威脅區域生態系統健康的重要因素。隨著工農業的快速發展,環境中重金屬污染加劇,土壤重金屬污染問題已成為全球廣泛關注的環境問題[2, 3]。人類活動是土壤重金屬污染的主要驅動因子,重金屬的污染直接影響土壤性質(物理、化學),抑制土壤微生物活動,導致農作物的產、品質降低,最終危及人類健康[4]。旨在對新疆溫宿縣林果土壤重金屬含量、分布狀況及風險進行評價,為新疆重金屬污染防治、修復等技術提供理論依據。【前人研究進展】新疆(干旱區)的相關研究主要集中于污灌農田、礦區、山地、綠洲城市工業園等。任力民等[8]以農田為研究對象,在新疆全疆(13個地州)進行土壤重金屬含量調查,結果表明,6種重金屬(Hg、Cd、Pb、As、Cr和Cu)含量均低于國家二級標準限值,污染評價均為安全等級。陳牧霞等[9]發現新疆污灌區重金屬Cu、Zn、Ni、Cr、Pb以殘渣態為主。土壤中李長春和姚峰等[10, 11]均選定五彩灣露天礦區為研究靶區,利用GIS手段厘定重金屬的空間分布特征和主要來源,評價重金屬污染等級。綜合結果顯示,此區域土壤中Cr污染最為嚴重,煤礦區域各個單元的污染程度:工業區>開采區>排土場>辦公生活區。余艷華等[12]研究了新疆奎屯地區土壤重金屬的污染狀況,發現部分地區土壤As和Cd存在超標的情況,羅艷麗等[13]篩選出藨草(ScirpusL)和蘆葦(Phragmites)為此區域的耐As植物。烏魯木齊市周邊[14-17]農田、菜地土壤重金屬含量進行調查,土壤中重金屬有明顯積累,含量超過綠色食品土壤環境質量要求。【本研究切入點】近年來,土壤重金屬含量已廣泛成為區域環境質量評價的依據之一[5-7],但在西北干旱區相關研究較少。以新疆南部阿克蘇溫宿縣研究靶區,重點分析17個樣區(138個采樣點)土壤重金屬(As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr)的含量,同時評價土壤中5種重金屬污染水平。【擬解決的關鍵問題】以新疆土壤背景值、國家土壤環境質量二級標準(GB15618-1995)為基礎,采用單因子污染指數法和內梅羅綜合污染指數法,闡明溫宿縣土壤重金屬含量及分布特征,對污染指數進行定量比較及評級,為土壤重金屬污染防治、修復等技術提供參考。
1 材料與方法
1.1 材 料
溫宿縣(40°52~42°15′N,79°28′~81°30′E)位于新疆西部天山中段的托木爾峰南麓,塔里木盆地北緣。屬典型的大陸性氣候,年均氣溫10.1℃,年均降水量 65.4 mm,年均無霜期185 d。
將溫宿縣林果按各鄉鎮劃分為17個區,每個區分根據林果面積分布和土壤類型進行樣點布設,共布設1 300個樣點,選取138個具有代表性樣點進行重金屬樣品采集測定。每個樣地采用多點取樣混合一個代表樣,在每個樣地中分別取土壤層0~20 cm的土壤0.5 kg,共138份。將土壤樣品晾干后粉碎,過孔徑篩(2 mm),保存待消煮測定。列出樣品基本信息。表1
表1 樣品信息
Table 1 The information of samples
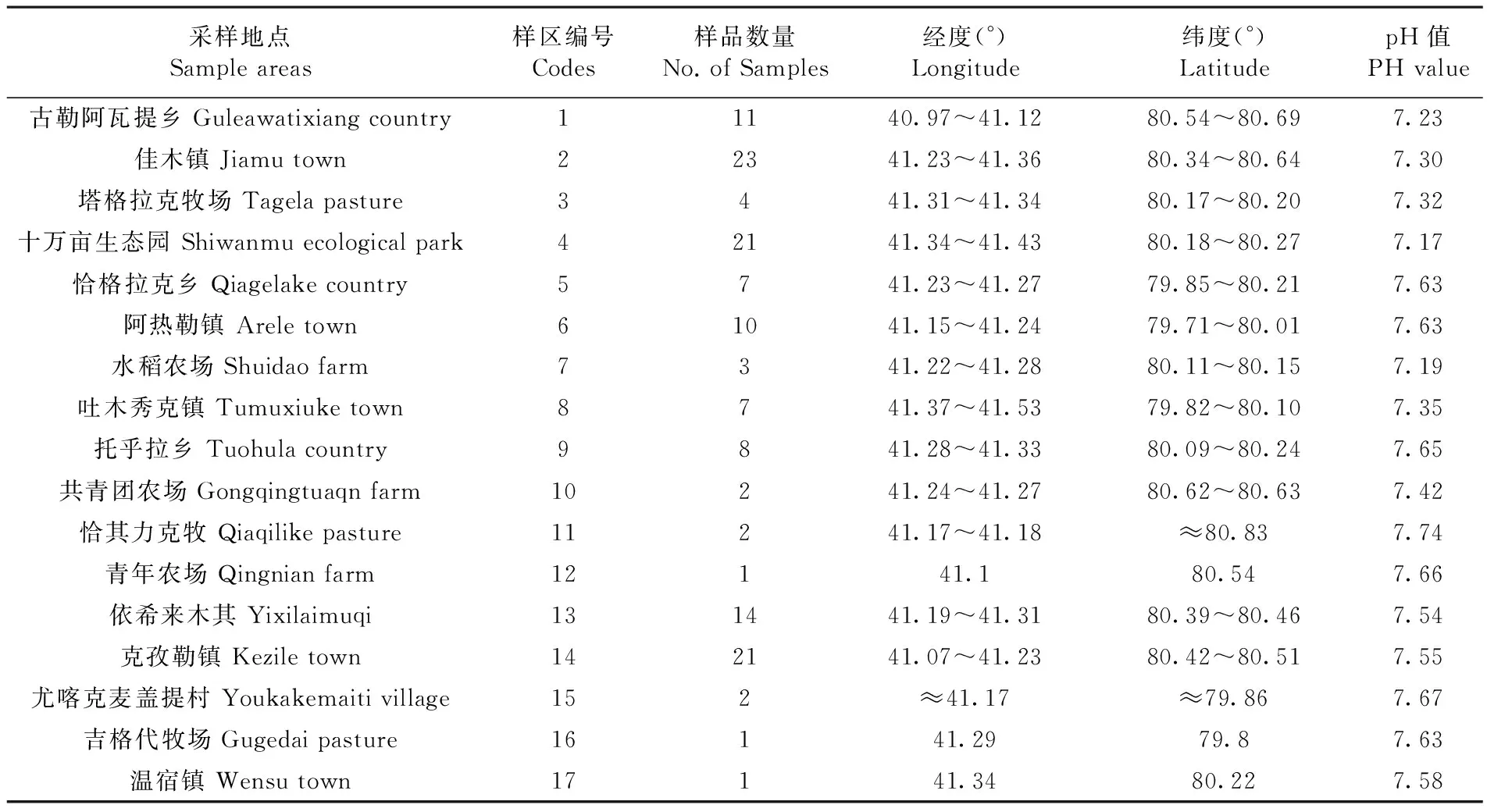
采樣地點Sampleareas樣區編號Codes樣品數量No.ofSamples經度(°)Longitude緯度(°)LatitudepH值PHvalue古勒阿瓦提鄉Guleawatixiangcountry11140.97~41.1280.54~80.697.23佳木鎮Jiamutown22341.23~41.3680.34~80.647.30塔格拉克牧場Tagelapasture3441.31~41.3480.17~80.207.32十萬畝生態園Shiwanmuecologicalpark42141.34~41.4380.18~80.277.17恰格拉克鄉Qiagelakecountry5741.23~41.2779.85~80.217.63阿熱勒鎮Areletown61041.15~41.2479.71~80.017.63水稻農場Shuidaofarm7341.22~41.2880.11~80.157.19吐木秀克鎮Tumuxiuketown8741.37~41.5379.82~80.107.35托乎拉鄉Tuohulacountry9841.28~41.3380.09~80.247.65共青團農場Gongqingtuaqnfarm10241.24~41.2780.62~80.637.42恰其力克牧Qiaqilikepasture11241.17~41.18≈80.837.74青年農場Qingnianfarm12141.180.547.66依希來木其Yixilaimuqi131441.19~41.3180.39~80.467.54克孜勒鎮Keziletown142141.07~41.2380.42~80.517.55尤喀克麥蓋提村Youkakemaitivillage152≈41.17≈79.867.67吉格代牧場Gugedaipasture16141.2979.87.63溫宿鎮Wensutown17141.3480.227.58
1.2 方 法
1.2.1 樣品測定
土壤樣品測定采用HCl+ HNO3+HF +HClO4全消毒法[18],秤取8.0 g土壤樣品,用HCl+ HNO3+HF +HClO4(40+20+20+6 mL)消毒,定容至100 mL保存,待測定。待測液中,As、Hg含量用原子熒光光譜法測定,Cd含量用石墨爐原子吸收分光光度法測定,Pb、Cr含量用火焰原子吸收分光光度法測定。
1.2.2 重金屬污染評價
根據不同樣區和不同樣點的整體調查,對研究區域采用污染指數[19, 20]和潛在生態風險指數進行綜合評價。
1.2.2.1 污染指數法
單因子污染指數計算如公式(1),Pi為第i污染物的污染指數,Ci為第i污染物的實測值,Si為第i污染物的評價標準。
內梅羅(Nemerow)綜合污染指數的計算如公式(2),Ps為綜合污染指數,n為污染物總數,Pi為第i污染物的污染指數,Pmax所有污染元素指數中的最大值。
公式(1):Pi=Ci/Si.
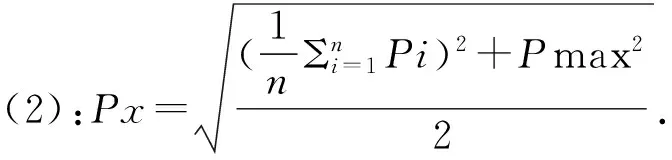
依據《土壤環境質量標準》(GB15618-1995)中的二級標準對果園土壤重金屬進行污染評價(pH=7.48<7.5,圖1中警戒線),列出土壤污染指數分級[21, 22]。表2
表2 土壤污染指數分級
Table 2 The Grading of soil pollution indexes
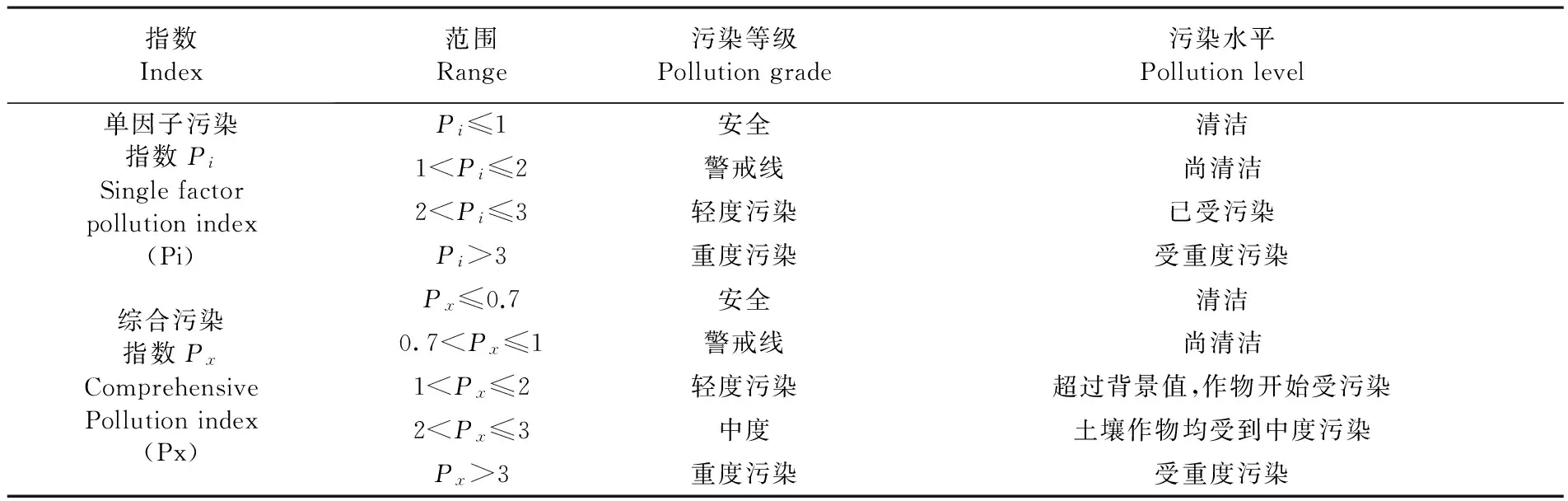
指數Index范圍Range污染等級Pollutiongrade污染水平Pollutionlevel單因子污染指數PiSinglefactorpollutionindex(Pi)Pi≤1安全清潔1
1.2.2.2 潛在生態風險指數法
采用Hakanson[23]潛在生態風險指數法評價溫宿縣土壤中重金屬的生態風險及危害,公式如下:

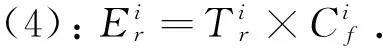

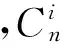
表3 重金屬生態風險、污染水平評估標準

Table 3 Assessment standards of potential ecological risk coefficient(Eir) and risk indices (RI) of heavy metals
1.3 數據統計
試驗數據使用Microsoft Excel 2010(Microsoft公司,美國)進行預處理,SPSS19.0(IBM公司,美國)進行單因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)和相關性分析。
2 結果與討論
2.1 溫宿縣土壤重金屬含量
研究表明,溫宿縣17個樣區土壤重金屬含量特征值為As平均含量11.96 mg/kg,標準差為3.56 mg/kg,變異系數為29.77%;Hg平均含量0.032 mg/kg,標準差為0.03 mg/kg,變異系數為9.38%;Cd平均含量0.17 mg/kg,標準差為0.04 mg/kg,變異系數為23.53%;Pb平均含量22.93 mg/kg,標準差為3.74 mg/kg,變異系數為16.31%;Cr平均含量43.38 mg/kg,標準差13.60 mg/kg,變異系數為28.11%。溫宿縣138個采樣點5種土壤重金屬差異不大(9.38%~29.77%),平均值和背景值的比值均接近1(0.5~1.7)。溫宿縣果園的重金屬含量基本上與新疆土壤背景值相似,土壤均未受到污染。表4
表4 溫宿縣果園土壤重金屬含量
Table 4 The heavy metal contents of Urumqi soil
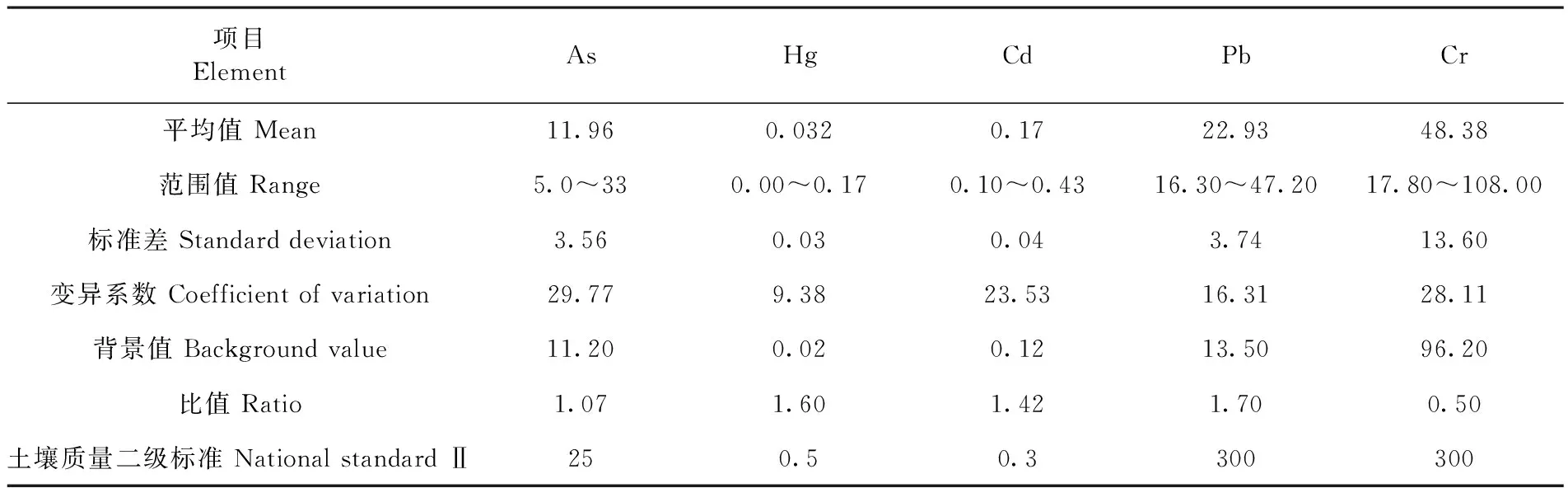
注:背景值為新疆土壤背景值,比值為平均值/背景值[24, 25]Note: It’s the Xinjiang soil background value, the ratio is average/ background values
2.2 溫宿縣土壤重金屬含量分布特征
研究表明,138個土壤樣品As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr 5種重金屬含量均低于國家土壤環境質量二級標準限值(國家《土壤環境質量標準》(GB15618-1995)),即該區域土壤重金屬含量不存在污染的風險。其中Hg、Pb和Cr的土壤重金屬含量均明顯低于國家二級標準限值,土壤樣點As和Cb的含量與警戒值較為接近。圖1
2.3 土壤重金屬的相關性
2.3.1 相關性
溫宿縣5種重金屬含量的相關分析表明,土壤中5種重金屬之間的相關關系較為簡單,As-Hg、As-Cd、As-Cr、Hg-Cd、Hg-Cr、Cd-Pb、Cd-Cr 均呈極顯著正相關(P<0.01),Hg-Pb呈極顯著負相關,As-Pb之間沒有顯著性相關關系(P>0.05)。說明土壤中重金屬As- Hg- Cd- Cr的相關性較好,具有較強的同源性,Pb有較強的異源性。表5
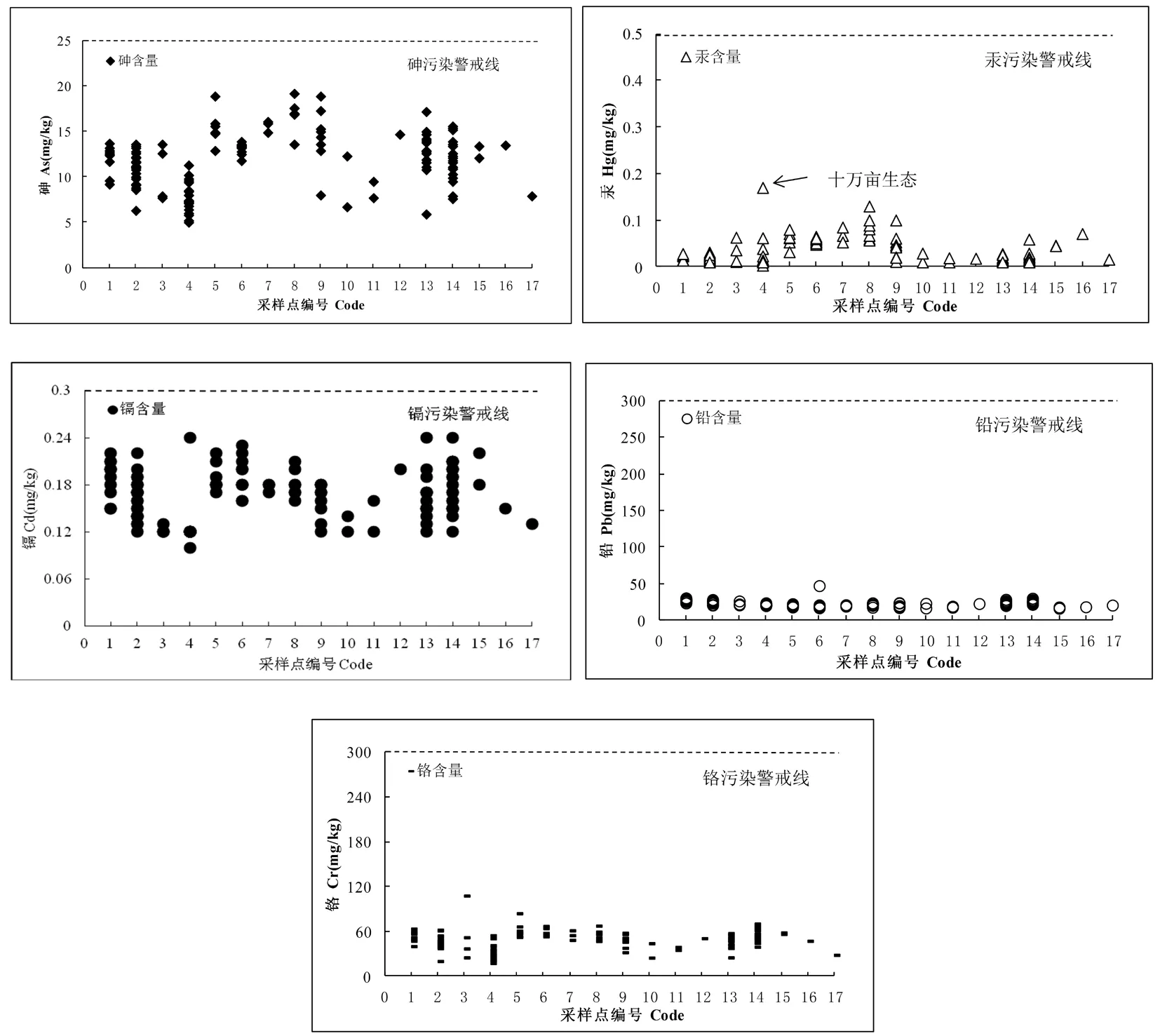
注:虛線為各重金屬元素含量的國家土壤環境質量二級標準(GB15618-1995)限值
Note: The dotted line is the second grade of nation soil environmental quality standards limit for heavy metal content (GB15618-1995)
圖1 土壤重金屬含量
Fig.1 Soil heavy metals contents of each survey point
表5 土壤重金屬含量的相關關系矩陣
Table 5 Correlation matrix of heavy metals contents in soils

注:**極顯著性相關;*顯著性相關Note: The sign ** indicates differences at significant level of P=0.01, and * with P=0.05
2.3.2 主成分分析
溫宿縣土壤重金屬主成分因子分析表明,將土壤污染物的信息進行了集中和提取,識別出起主導作用的成分。主成分分析可知,5種重金屬辨識出2 個主成分,分別解釋總因子的54.6%和25.3%,累計貢獻率達到54.6%和80.0%。因此,此分析數據可以解釋5種重金屬元素來源的絕大部分信息。第1主成分分析可知,重金屬As、Hg、Cd和Pb具有較大載荷(高于背景值),第2主成分分析可知,只有重金屬Cr具有較高的載荷,各元素之間的相關性較強。表6
表6 重金屬元素主成分因子載荷矩陣
Table 6 Factors matrix of heavy metals insoils
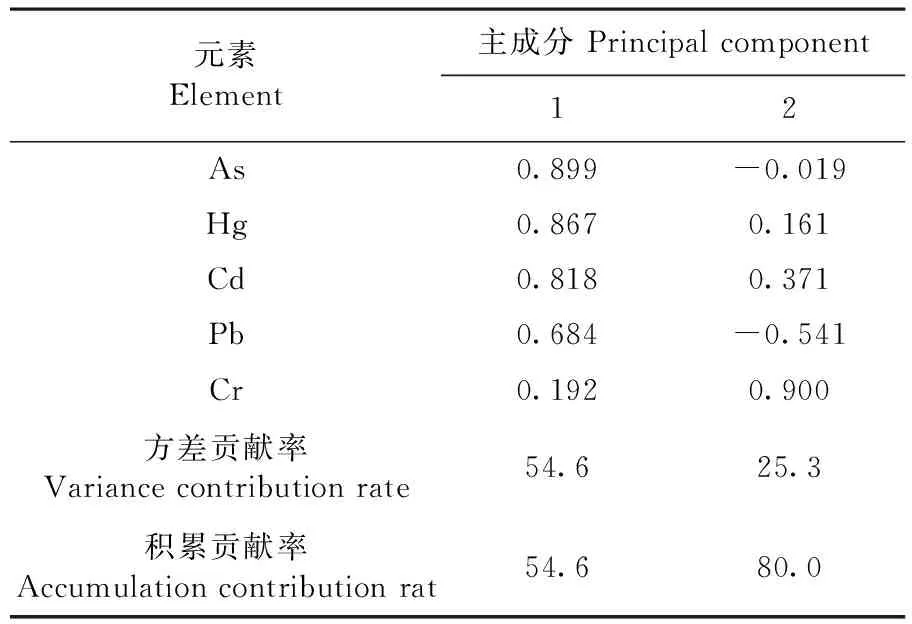
元素Element主成分Principalcomponent12As0.899-0.019Hg0.8670.161Cd0.8180.371Pb0.684-0.541Cr0.1920.900方差貢獻率Variancecontributionrate54.625.3積累貢獻率Accumulationcontributionrat54.680.0
2.4 土壤重金屬污染評價
采用污染指數法評價溫宿縣土壤中As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr重金屬元素的污染狀況,評價標準見表3,評價結果表明,由單因子污染指數來看,溫宿縣重金屬As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr的土壤中均屬于安全等級(Pi均≤1),為清潔水平;10萬畝生態園的土壤污染指數值最低(0.31),清潔程度最高,恰格拉克鄉的土壤污染指數值最高(0.77),但在安全等級以內;由5種重金屬元素的綜合污染指數可知,各樣區的溫宿縣重金屬As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr的土壤均屬于安全等級(Px均≤0.7),為清潔水平;由溫宿縣各樣區土壤重金屬單因子、綜合污染指數平均值可知,污染程度排序為:As(0.56)>Cd(0.38)>Cr(0.15)>Pb(0.07)>Hg(0.053),綜合污染屬于清潔水平(Px≤0.7)。表7
表7 土壤污染指數分級
Table 7 The Grading of soil pollution indexes
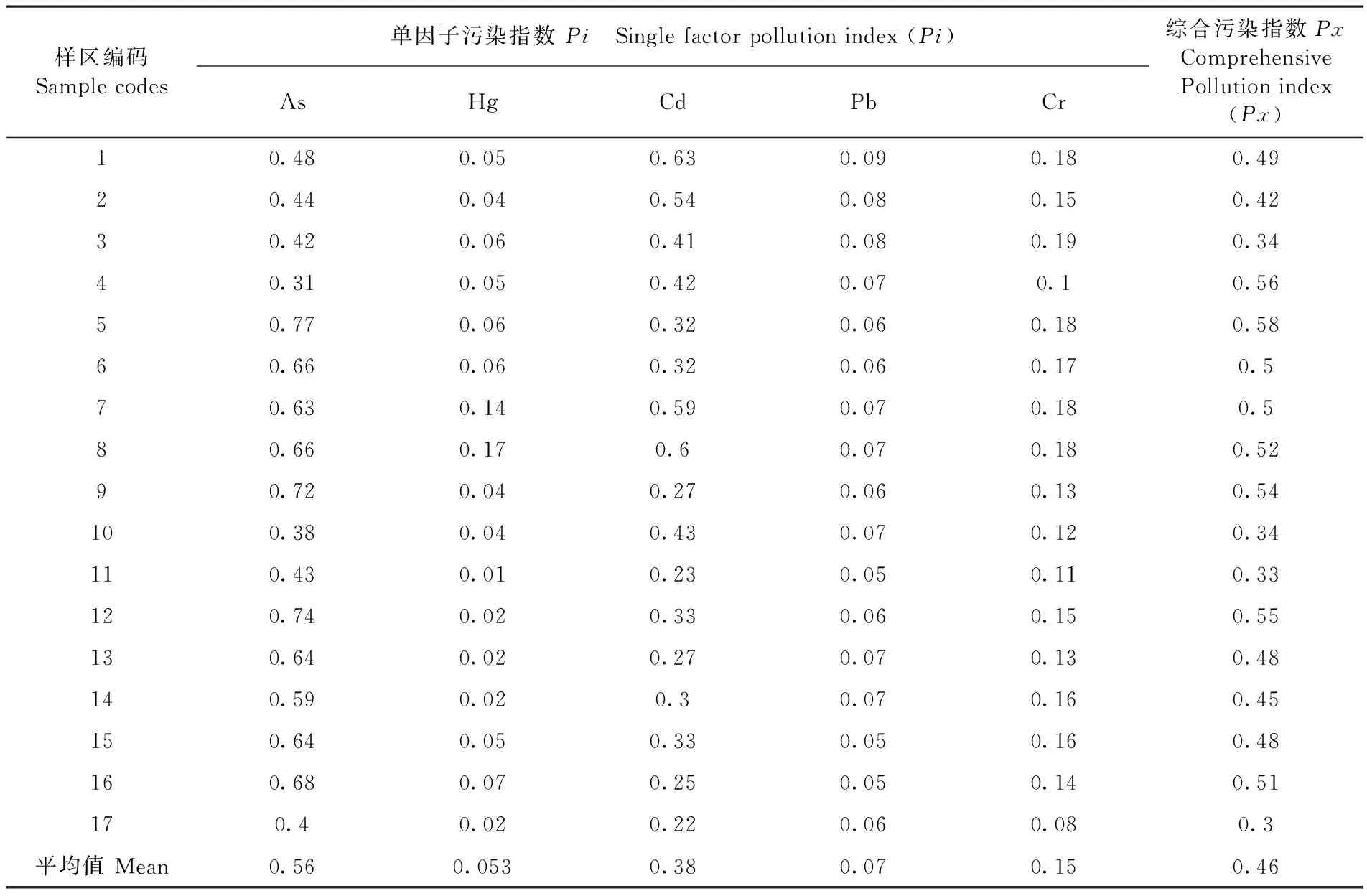
樣區編碼Samplecodes單因子污染指數Pi Singlefactorpollutionindex(Pi)AsHgCdPbCr綜合污染指數PxComprehensivePollutionindex(Px)10.480.050.630.090.180.4920.440.040.540.080.150.4230.420.060.410.080.190.3440.310.050.420.070.10.5650.770.060.320.060.180.5860.660.060.320.060.170.570.630.140.590.070.180.580.660.170.60.070.180.5290.720.040.270.060.130.54100.380.040.430.070.120.34110.430.010.230.050.110.33120.740.020.330.060.150.55130.640.020.270.070.130.48140.590.020.30.070.160.45150.640.050.330.050.160.48160.680.070.250.050.140.51170.40.020.220.060.080.3平均值Mean0.560.0530.380.070.150.46
2.5 潛在生態風險評價
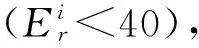
從綜合潛在生態危險指數來看,5種重金屬的RI值的范圍為79.78~236.10。有58.8%的樣區處于低生態風險程度(RI<150),41.2%的樣區處于中生態風險程度(150≤RI<300)。各樣區綜合潛在生態風險指數的平均值表明,溫宿鎮處于低生態風險程度(RI=139.94<150)。表3,表8
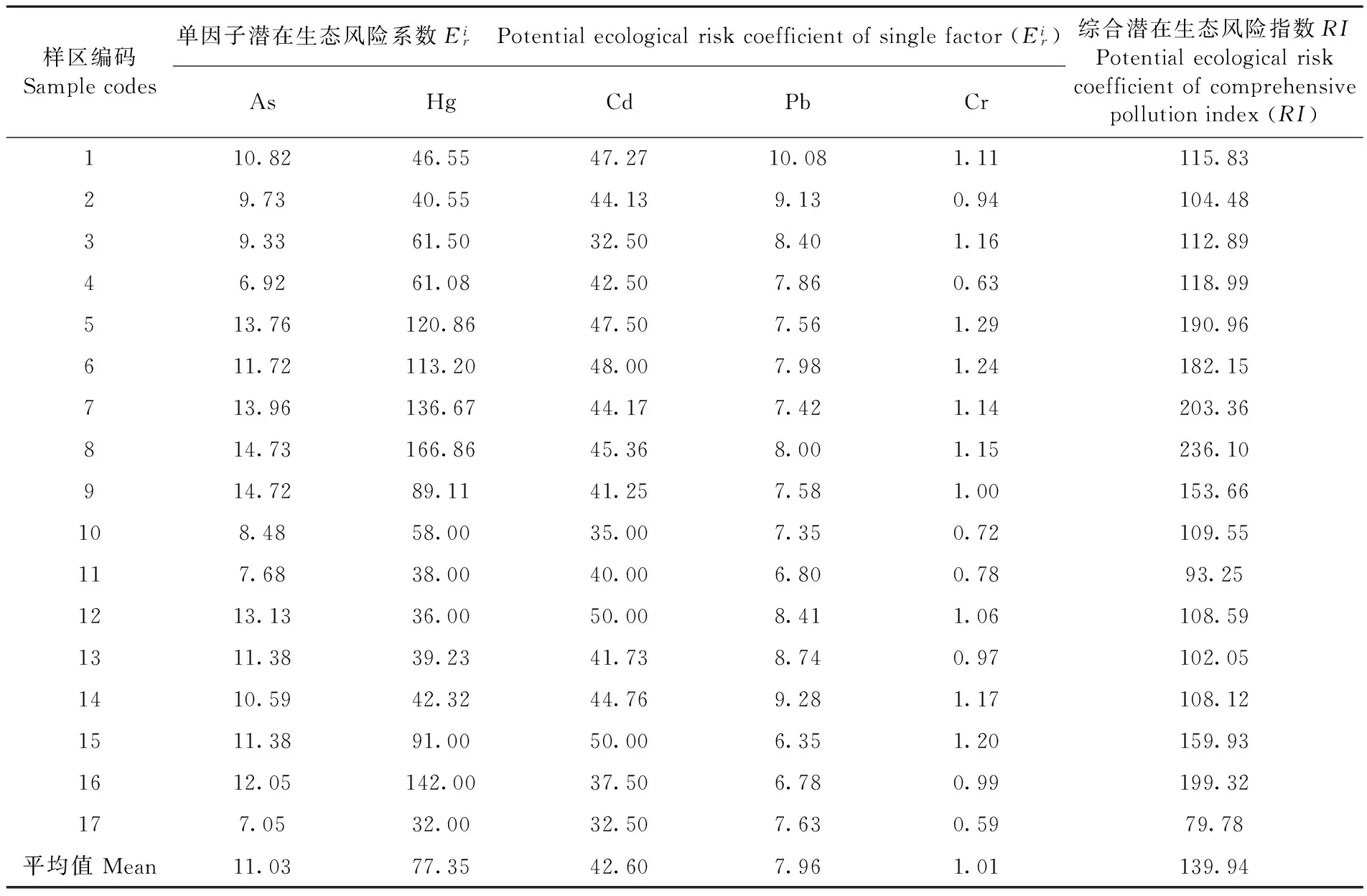
表8 重金屬潛在生態風險系數(Eir)和風險指數(RI)
3 討 論
工農業的快速發展,導致土壤環境中重金屬污染逐漸加劇,溫宿縣林果園主要種植紅棗、核桃,以農業活動為主。溫宿縣17個樣區138個土壤樣品的重金屬As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr的平均含量11.96、0.032、0.17、22.93 和43.38 mg/kg,與孫繼坤[24]得出的新疆土壤背景值相似,說明近30年,溫宿縣林果園的土壤環境良好,基本上未受到農業活動的影響。5種重金屬的含量分別均低于國家土壤環境質量二級標準限值,但部分地區的As和Cd含量較為接近警戒線,需做相應的預防、治理。
以污染指數、潛在生態風險指數法綜合評定溫宿縣重金屬情況,有更全面、更實時、更準確的優點。溫宿縣基本上不存在重金屬污染、生態危險狀況。其中,重金屬As的污染指數為0.56,較其他元素大,需注意治理、管理。潛在生態風險評價得出,As、Pb和Cr處于低生態風險程度,Hg和Cd處于中生態風險程度,綜合潛在生態風險評價屬于低生態風險程度,說明溫宿縣整體的生態環境良好。因此,溫度縣土壤環境處于安全、清潔等級,有利于進行農業活動,研究結果可為該區土壤重金屬污染防治、修復等技術的研究提供理論支撐。
4 結 論
新疆溫宿縣17個樣區138個土壤樣品的五種重金屬含量(As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr)均低于國家土壤環境質量二級標準限值,且土壤重金屬含量的變異系數比值均接近1(0.5~1.7),基本上與新疆土壤背景值相似,即該區域土壤重金屬含量不存在污染的風險,土壤均未受到污染。
溫宿縣土壤中5種重金屬之間基本上均呈極顯著相關關系(As-Pb除外),可辨識為2個主成分。PC1中重金屬As、Hg、Cd和Pb具有較大載荷,PC2中只有Cr具有較大載荷。
由單因子、綜合污染指數來看,溫宿縣重金屬As、Hg、Cd、Pb和Cr的土壤中均屬于安全等級(Pi均≤1,Px均≤0.7),為清潔水平;由溫宿縣各樣區土壤重金屬單因子、綜合污染指數平均值可知,污染程度排序為:As>Cd>Cr>Pb>Hg,綜合污染屬于清潔水平(Px≤0.7)。

References)
[1] 王岙, 白梅,崔勇. 吉林省部分地區食品中鉛、鎘污染狀況分析[J]. 中國食品衛生雜志,2006,(3):239-243.
WANG Ao, BAI Mei, CUI Yong. (2006). Situation of Lead and Cadmium in Foods in Jilin Province during the Period 2001-2004 [J].ChineseJournalofFoodHygiene, (3):239-243. (in Chinese)
[2] Jrup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination.BritishMedicalBulletin, 68(486):167-182.
[3]黃益宗, 郝曉偉, 雷鳴, 等. 重金屬污染土壤修復技術及其修復實踐[J]. 農業環境科學學報, 2013,32(3):409-417.
HUANG Yi-zong, HAO Xiao-wei, LEI Ming, et al. (2013). The Remediation Technogy and Remediation Practice of Heavy metals-contaminated Soil [J].JournalofAgro-EnvironmentScience, 32(3):409-417. (in Chinese)
[4]呂建樹, 張祖陸, 劉洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金屬來源解析及環境風險評價[J]. 地理學報,2012,67(7):971-984.
LU Jian-shu, ZHANG Zu-lu, LIU Yang, et al. (2012). Sources Identification and Hazardous Risk Delineation of Heavy Metals Contamination in Rizhao City [J].ActaGeographicaSinica, 67(7):971-984. (in Chinese)
[5]馬陶武, 朱程, 王桂巖, 等. 銅銹環棱螺對沉積物中重金屬的生物積累及其與重金屬賦存形態的關系[J]. 應用生態學報,2010,21(3):734-742.
MA Tao-wu, ZHU Chen, WANG Gui-yan, et al. (2010). Bioaccumulation of Sediment Heavy Metals in Bellamya Aeruginosa and its Relations with the Metals Geochemical Fractions [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcolo-gy, 21(3):734-742. (in Chinese)
[6]吳新民, 李戀卿, 潘根興, 等. 南京市不同功能城區土壤中重金屬Cu、Zn、Pb和Cd的污染特征[J]. 環境科學,2003,24(3):105-111.
WU Xin-min, LI Luan-qing, PAN Gen-xin et al. (2003). Soil Pollution of Cu,Zn,Pb and Cd in Different City Zones of Nanjing [J].EnvironmentalScience, 24(3):105-111. (in Chinese)
[7]穆葉賽爾·吐地, 吉力力·阿布都外力,姜逢清. 天山北坡土壤重金屬含量的分布特征及其來源解釋[J]. 中國生態農業學報,2013,21(7):883-890.
Muyessar Turdi, Jilili Abuduwaili, JIANG Feng-Qing. (2013). Distribution Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metal Content in Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains and its Source Explanation [J].ChineseJournalofEco-Agriculture, 21(7):883-890. (in Chinese)
[8]任力民, 賈登泉,王飛. 新疆農田土壤重金屬含量調查與評價[J]. 新疆農業科學,2014,51(9):1 760-1 764.
REN Li-min, JIA Deng-quan, WANG Fei. (2014). Preliminary Survey and Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Farmland Soil [J].XinjiangAgriculturalSciences, 51(9):1,760-1,764. (in Chinese)
[9]陳牧霞, 地里拜爾·蘇力坦, 楊瀟, 等. 新疆污灌區重金屬含量及形態研究[J]. 干旱區資源與環境,2007,21(1):150-154.
CHEN Mu-xia, Dilibar Sultan, YANG Xiao, et al. (2007). Research on Concentration and Chemical Speciation of Heavy Metals in Sewage Irrigated Soil of Xinjiang [J].JournalofAridLandResourcesandEnvironment, 21(1):150-154. (in Chinese)
[10]李長春, 張光勝, 姚峰, 等. 新疆準東煤田五彩灣露天礦區土壤重金屬污染評估與分析[J]. 環境工程,2014,(7):142-146.
LI Chang-chun, ZHANG Guang-sheng, YAO Feng, et al. (2014).Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Area of Xinjiang Zhundong Wucaihu Surface Coal Mine [J].EnvironmentalEngineering, (7):142-146. (in Chinese)
[11]姚峰, 包安明, 古麗·加帕爾, 等. 新疆準東煤田土壤重金屬來源與污染評價[J]. 中國環境科學,2013,33(10):1 821-1 828.
YAO Feng, BAO An-ming, GULI Jiapaer, et al. (2013). Soil Heavy Metal Sources and Pollution Assessment in the Coalfield of East Junggar Basin in Xinjiang[J].ChinaEnvironmentalScience, 33(10):1,821-1,828. (in Chinese)
[12]余艷華, 蔣平安, 羅艷麗, 等. 新疆奎屯墾區土壤砷污染現狀評價[J]. 土壤通報,2008,39(6):1 445-1 448.
YU Yan-hua, JIANG Ping-an, LUO Yan-li, et al. (2008). Evaluation of Arsenic Pollution of Soil in Kuitun Reclamation Area of Xinjiang [J].ChineseJournalofSoilScience, 39(6):1,445-1,448. (in Chinese)
[13]羅艷麗, 余艷華, 鄭春霞, 等. 新疆奎屯墾區土壤砷含量及耐砷植物的篩選[J]. 干旱區資源與環境,2010,24(2):192-194.
LOU Yan-li, YU Yan-hua, ZHENG Chun-xia, et al. (2010). Arsenic Concentrations in Soils and Plants in Kuitun Farm, Xinjiang[J].JournalofAridLandResourcesandEnvironment, 24(2):192-194. (in Chinese)
[14]卡哈爾·吾甫爾, 阿孜古麗·玉蘇甫, 阿不都拉·阿巴斯, 等. 烏魯木齊南郊亞花松蘿重金屬含量及其大氣污染評價的研究[J]. 新疆農業科學,2010,47(9):1 780-1 785.
Kahar Gupur, Arzigul Yusup, Abdulla Abbas, et al. (2010). Study of the Heavy Metal Content of Usnea Subfloridanaand Assessment of the Air Pollution of Southern Suburb of Urumqi,Xinjiang[J].XinjiangAgriculturalSciences, 47(9):1,780-1,785. (in Chinese)
[15]易治伍, 王靈, 錢翌, 等. 烏魯木齊市農田土壤重金屬含量及評價[J]. 干旱區資源與環境,2009,23(2):150-154.
YI Zhi-wu, WANG Ling, QIAN Yi, et al. (2009). Heavy Metal Content Sand Evaluation of Farmland Soil in Urumqi[J].JournalofAridLandResourcesandEnvironment, 23(2):150-154. (in Chinese)
[16]劉玉燕,劉浩峰. 新疆米泉市污灌區土壤重金屬污染及防治[J]. 昌吉學院學報,2007,(3):45-48.
LIU Yu-yang, LIU Hao-feng. (2007). Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Its Prevention and Cure in Polluted Irrigated Area in Miquan City, Xinjiang [J].JournalofChangjiUniversity, (3):45-48. (in Chinese)
[17]時亞坤, 李凱榮,閆寶環. 銅川三里洞煤礦煤矸石風化土壤重金屬分布及污染狀況分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2012,19(1):187-191.
SHI Ya-kun, LI Kai-rong, YAN Bao-huan. (2012). Distribution and Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Weathered Soil in Sanlidong Coal Mine of Tongchuan [J].ResearchofSoilandWaterConservation, 19(1):187-191. (in Chinese)
[18]高軍俠, 黨宏斌, 鄭敏, 等. 鄭州市郊農田土壤重金屬污染評價[J]. 中國農學通報,2013,29(21):116-120.
GAO Jun-xia, DANG Hong-bin, ZHENG Min, et al. (2013).Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment of Farmland Soil in Suburb in Zhengzhou City [J].ChineseAgriculturalScienceBulletin, 29(21):116-120. (in Chinese)
[19]王春光, 張思沖, 辛蕊, 等. 哈爾濱市東郊菜地土壤重金屬環境質量評價[J]. 中國農學通報,2010,26(2):262-266.
WANG Chun-guang, ZHANG Si-chong, XIN Rui, et al.(2010). Heavy Metal Environmental Assessment of Soil in East Suburb of Harbin [J].ChineseAgriculturalScienceBulletin, 26(2):262-266. (in Chinese)
[20]程芳, 程金平, 桑恒春, 等. 大金山島土壤重金屬污染評價及相關性分析[J]. 環境科學,2013,34(3):1 062-1 066.
CHENG Fang, CHENG Jin-ping, SANG Heng-chun, et al. (2013). Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Heavy Metals Pollution in Soil of Dajinshan Island [J].EnvironmentalScience, 34(3):1,062-1,066. (in Chinese)
[21]郭平, 謝忠雷, 李軍, 等. 長春市土壤重金屬污染特征及其潛在生態風險評價[J]. 地理科學,2005,25(1):108-112.
GUO Ping, XIE Zhong-lei, LI Jun, et al. (2005). Specificity of Heavy Metal Pollution and the Ecological Hazard in Urban Soils of Changchun City [J].ScientiaGeographicaSinica, 25(1):108-112. (in Chinese)
[22] Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach.WaterResearch, 14(8):975-1,001.
[23]張兆永, 吉力力·阿不都外力,姜逢清. 天山土壤微量(類)重金屬的來源解析及潛在生態危害評估[J]. 應用生態學報,2014,25(11):3 168-3 176.
ZHANG Zhao-yong, JILILI Abuduwailil, JIANG Feng-qing. (2014). Source Identification and Potential Ecological Hazards Assessment of Trace Metalloid/ Heavy Metals in the Soil of Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcology, 25(11):3,168-3,176. (in Chinese)
[24] 孫繼坤,胡志林,周鴻興,等. 天山山地土壤中微量元素的含量與分布 [J]. 土壤學報,1987,24(2):335-341.
SUN Ji-kun, HU Zhi-lin, ZHOU Hong-xing, et al. (1987). Content and distribution of trace elementsin the soil of the Tianshan Mountains [J].ActaPedologicaSnica, 24(2):335-341.(in Chinese)
[25] 中國環境監測總站. 中國土壤元素背景值 [M]. 北京: 中國環境科學出版社,1990.
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. (1990).China'sSoilElementBackgroundValues[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.(in Chinese)
Fund project:Supported by the special funds for basic science and technology research of nono "profit research institutions of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region "remediation measures of main heavy metal pollution in Xinjiang soil" (ky2014037),Excellent Youth Fund of Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences "The influence of biocharcoal on the adsorption characteristics of heavy metal cadmium" (xjnkq-2014004) and special funds for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements "Walnut orchard health management of precision fertilizer technology integration and demonstration(201454122)
Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Contents in Wensu County of Southwest Xinjiang
FU Yan-bo, DOU Xiao-jing, LAI Ning, HUANG Jian, WANG Xin-yong, WANG Zhi-guo
(ResearchInstituteofSoil,FertilizerandAgriculturalWaterConservation,XinjiangAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Urumqi830091,China)
【Objective】 To make clear the level of heavy metal contamination by analyzing the total quantity in Wensu County and conduct risk assessment of their safety.【Method】In 2004, 138 soil samples in 17 sampling points in Wensu County were collected, and the total content of heavy metals(As, Hg, Cd, Pb and Cr) was determined.【Result】The results showed that in Wensu county As was 11.96 mg/kg, Hg 0.032 mg/kg, Cd 0.17 mg/kg, Pb 22.93 mg/kg, Cr 43.38 mg/kg. The coefficient variability of heavy metals was really little. According to the state soil environmental quality standards as the evaluation standard, the integrated pollution indexes of various elements were: As>Cd>Cr>Pb>Hg. The pollution assessment showed that five kinds of heavy metals were all at security and clean level(Pi≤1), so was the comprehensive pollution indices of heavy metals(Px≤0.7). The average values of potential ecological risk assessment showed that the various elements were: Hg (77.35) > Cd (42.60) > As (11.03) >Pb (7.96) >Cr(1.01), a lower ecological risk level was estimated to soil heavy metals. The comprehensive range of potential ecological risk index of five finds of heavy metals was between 79.78 and 236.10, so a lower ecological risk level was determined, too.【Conclusion】In Wensu county, the heavy metal contamination (As, Hg, Cd, Pb and Cr) is lower than the warning level, and the degree of pollution is below the safe level. The single factor and comprehensive ecological risk assessment are also at a low ecological risk, which indicates that the soil environmental quality is overall good in Wensu County.
soil; heavy metals; pollution assessment; ecological risk
2016-08-26
自治區公益性科研院所基本科研業務費專項資金“新疆土壤主要重金屬污染修復措施研究”(ky2014037);新疆農業科學院優秀青年基金“生物炭對土壤重金屬鎘吸附特征的影響”(xjnkq-2014004);自治區科技成果轉化專項資金項目“核桃健康果園水肥精準管理技術集成與示范”(201454122)
付彥博(1986-),男,助理研究員,研究方向為土壤生態與農業節水,(E-mail)fuyanbo2010@163.com
王治國(1980-),男,副研究員,研究方向為土壤生態與農業節水,(E-mail)13565915020@126.com
10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2016.12.016
X825
:A
:1001-4330(2016)12-2280-10

