振動深松試驗臺作業參數減阻減振優化
孫亞朋,董向前,宋建農,劉彩玲,王繼承,張 超
?
振動深松試驗臺作業參數減阻減振優化
孫亞朋,董向前,宋建農※,劉彩玲,王繼承,張 超
(農業部土壤-機器-植物系統技術重點實驗室,中國農業大學,北京 100083)
振動深松具有降低耕阻的作業優勢,但振動對駕駛員造成的負面影響是制約其推廣使用的主要因素之一。該文采用二次回歸通用旋轉設計,考察深松鏟振頻、振幅、前進速度3個工作參數與耕阻、振動2個試驗指標的關系,利用Design-Expert響應面分析法,得到2個指標的回歸模型,并進行優化分析。綜合分析得到一組減阻減振的優化解:振幅21 mm、振頻4.2 Hz、前進速度3.4 km/h,在該組工作參數下,與非振動深松相比,振動深松的耕阻最大值變化較小,耕阻最小值、平均值分別減小46.2%、16.6%。
農業機械;優化;振動;深松;響應面法
0 引 言
深松是利用深松部件在不翻轉土壤的條件下,疏松土壤、打破犁底層、加深耕作層。深松可以保持地表覆蓋物,減少表土翻動,對于北方寒冷的旱區,深松可以提高地溫,促進種子發芽,有利于作物的增產[1-5]。深松的作業深度超過犁底層或土壤自然形成的黏盤層分布深度[6],使耕層由翻地的20 cm左右加深到30~35 cm。但深松作業牽引阻力大,需要配備大馬力拖拉機,限制其推廣使用。
與非振動深松相比,振動深松充分利用拖拉機動力輸出軸的功率,有效降低牽引阻力,并提高松土效果,在保證松土質量的同時降低對拖拉機馬力的要求[7-17]。
國內外在深松減阻方面開展了大量研究。Shahgoli等[18-19]以單立柱鑿式深松鏟為試驗對象,分別對振頻、振動角進行單因素試驗,同時考慮耕阻和總功耗,得到最優作業頻率為3.3 Hz,最優振動角為1.5°。
在多因素試驗方面,李霞選取前進速度、振頻、振動角度3個因素,對單立柱振動深松鏟進行正交試驗,試驗得出當前進速度2 km/h,振動頻率10 Hz,振動角度12°時,牽引阻力和總功率最小。與不振動深松相比,振動深松機牽引阻力平均降幅為9.09%[20]。
王俊發等[21]選取振頻、前進速度、振幅3個因素進行二次正交旋轉試驗,得到優化參數為振幅20~25 mm,振頻2~3 Hz,鏟機速比1.7~2.2,牽引阻力降低30%。并且得出振動深松會增加總功耗,振頻越高,功耗越大。
目前對振動深松的研究,主要以減少耕作阻力為優化目標。振動深松機的振動傳遞到拖拉機,對拖拉機及機手造成不良影響,是振動深松推廣面臨的難題之一。農業機械注重提供安全、舒適的操作環境,提高振動深松減阻效果的同時需要降低振動對拖拉機的影響。
目前的研究主要以單立柱深松鏟為研究對象,與單立柱深松鏟相比,框架式深松鏟可以實現全方位深松,進一步提高松土效果[7-12,22]。
在相關研究基礎上,本文以框架式深松鏟為研究對象,使用二次回歸通用旋轉設計,考察深松鏟振頻、振幅、前進速度3個工作參數與前進、豎直2個方向力的關系,利用Design-Expert響應面分析法,得到2個指標的回歸模型,并進行優化,將優化結果與非振動深松對比評價。
1 試驗設備與試驗方法
1.1 室內振動深松試驗臺
為進行振動深松試驗研究,中國農業大學土壤-機器-植物系統技術實驗室設計了室內振動深松試驗臺(圖1)。土壤-機器-植物系統技術實驗室主要由土槽、臺車和控制系統組成。土槽兩側為臺車軌道,臺車模擬拖拉機工作,可掛接農機具,并配備動力輸出軸(power take off,PTO)。臺車上配備六分力測力機構和土壤含水率、緊實度測量儀。通過控制系統設置前進速度、動力輸出軸轉速、耕深,輸出三向力、土壤參數報表[23]。
試驗裝置由機架、變速箱、偏心機構、連桿、拉桿、框架式深松鏟組成。試驗臺機架通過螺栓與臺車六分力測力機構連接,臺車動力輸出軸的動力經萬象聯軸器傳遞至變速箱輸入端,經變速箱減速、變向,動力由變速箱輸出端傳遞至偏心機構,偏心機構由2個偏心圓盤組成,偏心機構轉動產生的偏心激振力,經連桿帶動拉桿及深松鏟繞鉸接點上下振動(圖2)。
框架式深松鏟以全方位深松機V型深松部件為原型,為降低激振難度,采用小幅寬鏟型(圖3)。深松鏟底刀起土角為35°,側刀切土角為2°,側刀后傾角為23°,側刀在橫垂面內的傾角為77°,底刀和左、右側刀均采用下磨刃。
1.2 土壤制備
為了模擬田間土壤條件,增加試驗結果的可比性,室內試驗要求土槽土壤含水率、緊實度基本一致,土壤表面平整,為了達到此要求,試驗前對土槽土壤進行如下整理:
1)在試驗前一天,使用臺車底部灑水裝置灑水潤土;
2)用振動深松機均勻深松土槽土壤,設置松土深度為300 mm,實際松土深度為330 mm,保證土壤制備范圍≥試驗松土范圍;
3)用旋耕機旋碎大土塊;
4)用沖擊壓實裝置[24]夯實土壤,6遍。
使用臺車配備的HYD-ZS在線水分測量儀、SZ-3土壤硬度計,測量得到試驗土壤條件(表1)。
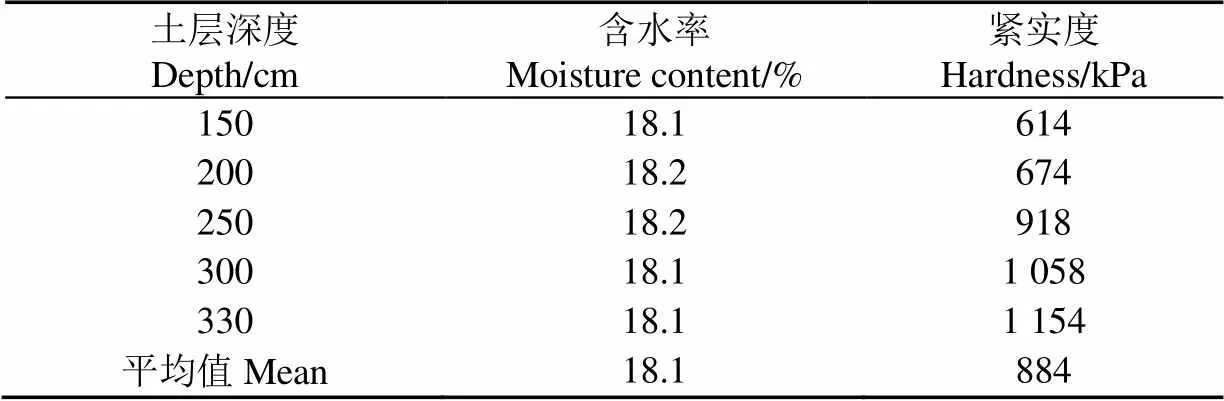
表1 試驗土壤條件
2 試驗設計
2.1 試驗因素水平與指標
在對框架式深松鏟的振頻單因素研究中,以耕阻為優化指標,在低速小振幅條件下(1 km/h,12.7 mm)得到最佳振頻4.4 Hz[25];在預試驗中,同時增大振幅、振頻,則振動加劇,臺車穩定性降低,影響試驗正常進行。綜合考慮耕阻和振動2個指標,得到一組水平范圍:振幅水平范圍15~43 mm,振頻水平范圍1~5 Hz,前進速度水平范圍1~4 km/h。根據深松要求,設置耕深為300 mm。
以前進方向力的平均值為耕阻指標1(mean of resisting force)。預試驗中,豎直方向力的變化最大,為振動的主要來源。以豎直方向力的波幅振動指標2(range of vibratory force),為排除兩端極端值的影響,該波幅以四分位距表示。
2.2 二次回歸通用旋轉設計
在Design-Expert軟件中,選用響應面設計中的中心組合設計,設定因素數為3,中心點數為6,星號點值在旋轉條件下為1.682,設置編碼水平的±的實際值為試驗因素水平范圍的邊界值。
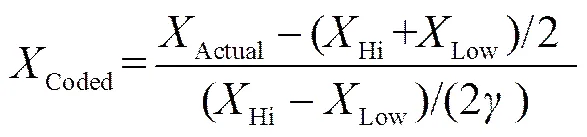
式中Coded為編碼值、、,Actual為實際值、、,Hi、Low為因素上、下水平±實際值。
計算得到因素水平編碼(表2)。設置響應為耕阻1和振動指標2,得到編碼值表示的試驗計劃表(表3),總試驗次數=20。中心點試驗順序的均勻分配可以探測試驗數據與時間的關聯,因此將試驗號隨機排序得到試驗順序。試驗現場如圖4所示。
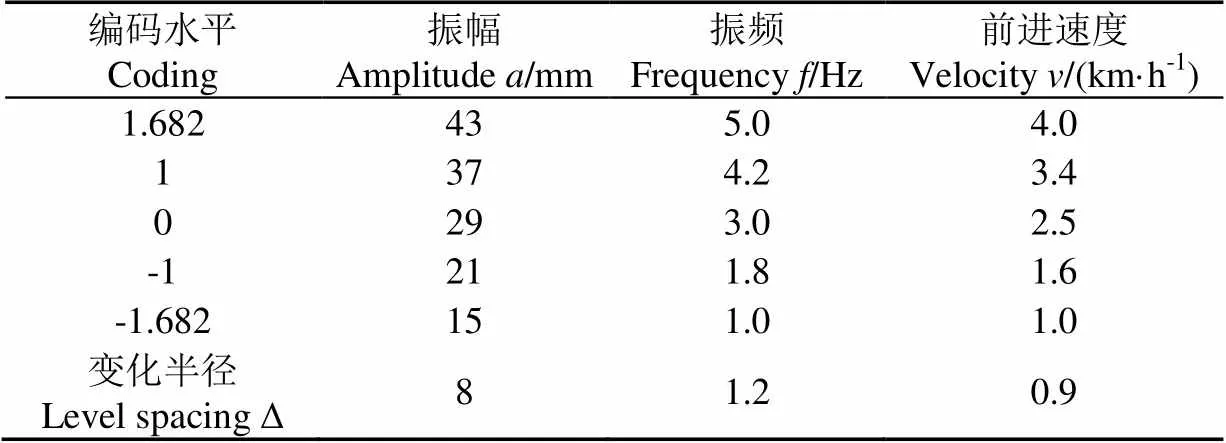
表2 因素水平編碼表
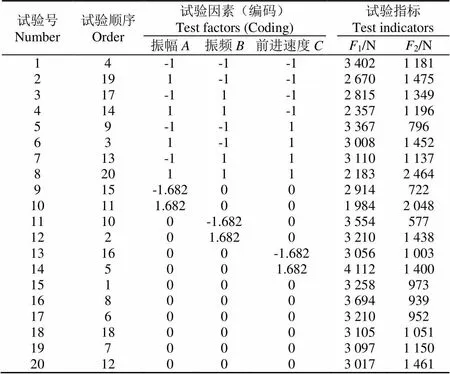
表3 試驗計劃與試驗結果
注:1為前進方向力的平均值,即耕阻指標;2為豎直方向力的波幅,即振動指標。
Note:1represents mean of resisting force;2represents amplitude of vibratory force.
3 試驗結果分析
3.1 回歸分析
試驗結果列入表3中試驗結果欄。回歸模型選用二次模型,回歸方法選用逐步回歸法,引入和剔除變量的檢驗水準設定為0.10,對1進行二次回歸建模(表4)。得到編碼方程
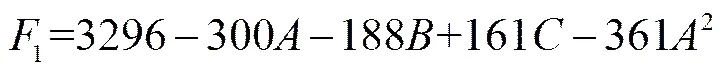
(3)
實際方程
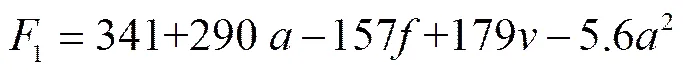
(5)
2的方差分析中,不顯著,但是回歸模型中包含顯著的交互作用項、,排除將使模型不滿足層級結構,因此將顯著交互作用項中的所有子項加入模型。
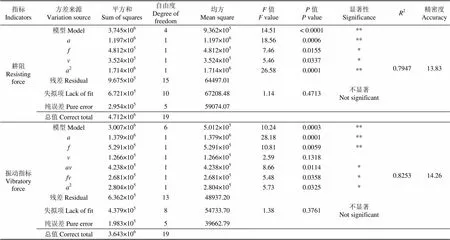
表4 耕阻F1與振動指標F2的方差分析表
注:**表示極顯著(<0.01);*表示顯著(0.01<<0.05)。
Note: ** means highly significant (<0.01); * means significant (0.01<<0.05).
3.2 影響力主次分析
3.2.1 直觀分析
在編碼方程中,各因素水平編碼上、下水平分別為+1.682和-1.682,各自變量經過編碼處理,單位、區間一致,通過比較編碼方程中各因素系數的絕對值,可以考察各因素在相同編碼區間內對指標的影響大小。
對于耕阻1,式(2)中一次項的主次順序為>>,二次項的主次順序為>>。因為二次項在編碼區間內單調性不唯一,所以不能將一、二次項主次順序簡單疊加。
由耕阻1的方差分析可知,各因素間不存在交互作用,在其他因素取不同水平條件下,振幅變化規律一致。編碼方程(2)中,把其他因素固定在0水平,得到振幅的變化對耕阻1的擾動曲線(圖5),該曲線方程為
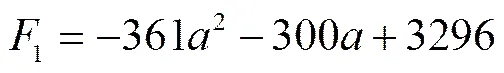
該曲線在=?0.4的曲率為0,即振幅在該編碼水平附近對指標擾動較小。
同理,可得到振頻、前進速度的變化對耕阻1的擾動曲線。曲線斜率越高,表明該因素的變化對指標的擾動越大,而相對平緩的曲線則說明因素對指標的擾動較小。由圖5可知,振幅小于“?0.4”水平時,擾動較小,響應與振幅呈正相關;大于“?0.4”水平時,擾動較大,耕阻與振幅呈負相關。響應與振頻呈負相關,與前進速度呈正相關,斜率分別為?188、161。雖然振幅在編碼水平為?0.4附近對指標擾動較小,但在整個編碼范圍內為擾動最大的因素。因此可以得到影響力排序(正相關→負相關)>(負相關)>(正相關)。
由振動指標2方差分析可知,振幅與前進速度,振頻與前進速度間存在交互作用,在前進速度取不同水平條件下,振幅的變化曲線不平行,變化規律改變。因此不能得出整個試驗范圍內的主次關系,只能得到其他因素在固定水平下的主次關系,圖5為其他因素在“0”水平下的擾動曲線,可以得到影響力排序為(正相關)>(正相關)>(正相關)。
3.2.2 通徑分析
對于存在交互作用項的2,采用通徑分析考察各因素影響力大小[26-29]。在通徑分析中,各因素與2的相關系數可分解為該因素對2的直接作用和間接作用,即
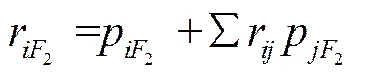
對于2的直接作用與間接作用分析見表5。由檢驗結果可知,的回歸系數不顯著,其他項均顯著。但是考慮到模型中交互作用項的層級結構,保留子項進行分析。
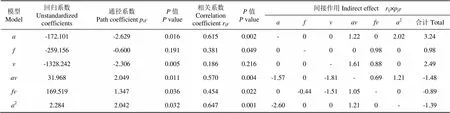
表5 振動指標F2通徑分析
1)振幅增大,一次項直接使2減小(?2.629),并且通過二次項2,使2增大(2.02)。另外,增大,交互作用項增大,間接使2增大(1.22),綜合作用為增強振動(0.615)。
2)振頻增大,直接作用系數不顯著,但是通過交互作用項(0.98)的間接作用系數顯著,使2增大。如果不考慮直接作用,顯然會高估對2的作用,因此考慮對2的直接作用(?0.6),使2減小。綜合作用為增強振動(0.381)。
3)前進速度增大,直接使振動減小(?2.306),并通過交互作用項(1.61)、(0.88)間接使振動增加。綜合作用為增強振動(0.186)。
綜合直接與間接作用將各因素影響力排序為(0.615)>(0.381)>(0.186),均為正相關。對于減小2,減小振幅比減小振頻更有效。
3.3 多目標優化分析與驗證
滿意度函數法是常用的多目標優化方法[30-31]。滿意度的計算公式如下:
單目標滿意度
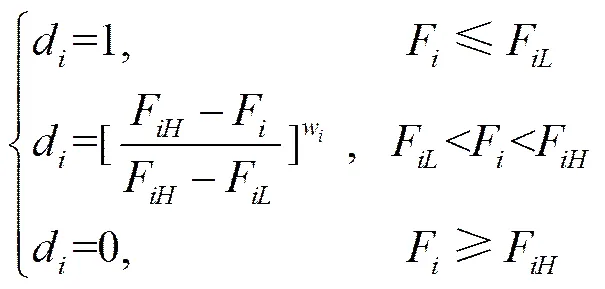
式中d為單目標滿意度;w為每個目標的權值(weight),本文中1、2的重要性相同,因此設置1=2=0.5;F為目標函數試驗值,N;F為各目標函數在自變量定義域內得到的最大值,N;F為最小值,N;回歸模型(3)、(5)在工作參數[?1,1]編碼水平范圍內得到1H=4 112 N,1L=1 984 N;2H=2 464 N,2L=577 N。
多目標滿意度
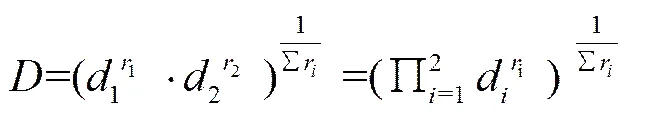
式中為多目標滿意度;r為各個目標相對于其他目標的重要值(importance),設置1=2=0.5。
聯立式(8)、(9),得到多目標滿意度響應曲面(圖6)。低速前進時,在大振幅、大振頻(37 mm,4.2 Hz)條件下,滿意度最大;隨著前進速度的提高,在小振幅、大振頻(21 mm,4.2 Hz)條件下,滿意度最大。為了實現高速高效作業,選擇高速前進、小振幅、大振頻(3.4 km/h,21 mm,4.2 Hz)為多目標優化結果,并得到區間估計值(表6)。優化參數下的試驗值在區間估計范圍之內,表明模型具有較好的準確性。
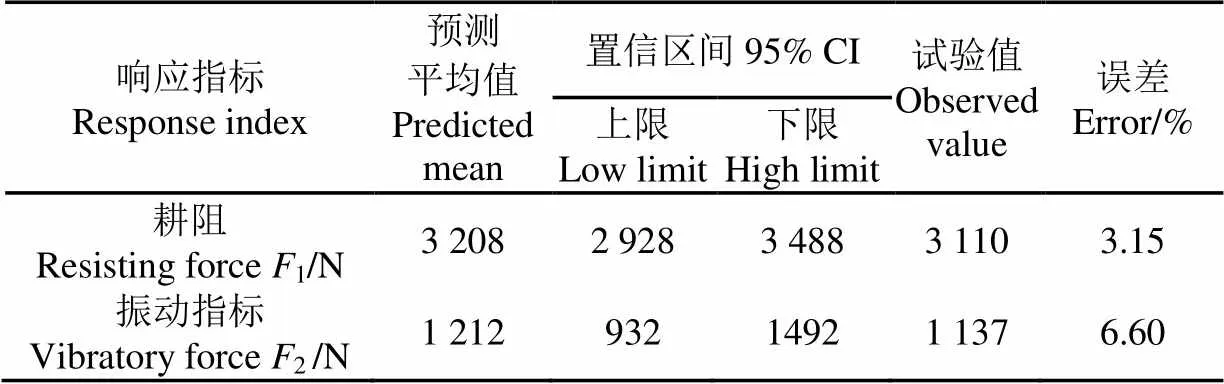
表6 預測與實際試驗指標對比
3.4 振動與非振動深松作業情況對比
為衡量振動深松減阻效果,將其與非振動深松作對比分析。在土壤條件、耕深和前進速度相同的條件下,分別進行振動、非振動2種深松試驗。與非振動深松相比,振動深松耕阻最小值減小46.2%;最大值減小1.5%,變化較小;平均值減小16.6%(表7);振動深松后大土塊較少(圖7),松土效果提高。
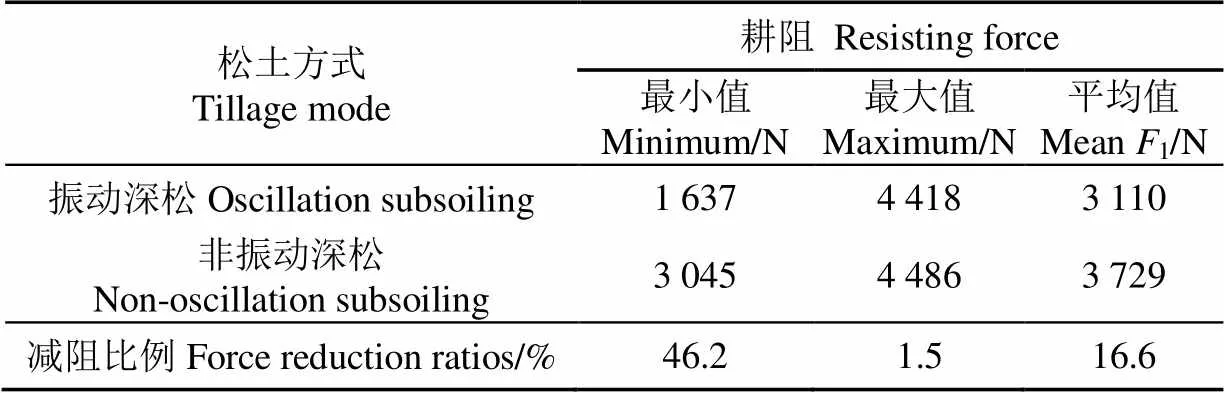
表7 振動與非振動深松作業對比
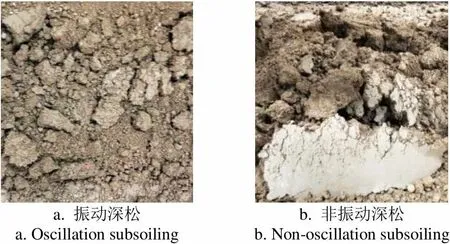
a. 振動深松 a. Oscillation subsoilingb. 非振動深松 b. Non-oscillation subsoiling
圖7 深松效果對比
Fig.7 Comparison of operation effect between oscillation and non-oscillation subsoiling
4 結 論
本文針對框架式振動深松鏟振頻、振幅、前進速度3個工作參數與耕阻、振動2個試驗指標的關系進行了分析討論,得出以下結論:
1)在沖擊壓實后的土壤條件下,振幅、振頻、前進速度與耕阻1、振動指標2之間符合三元二次回歸模型。
2)在試驗條件下,振幅、振頻、前進速度對1、2均具有顯著作用,特別是振幅對1有極顯著作用,振幅、振頻對2有極顯著作用。對于耕阻1,各因素無交互作用,作用大小依次為:振幅(負相關)>振頻(負相關)>前進速度(正相關);對于振動指標2,振幅與前進速度、振頻與前進速度有交互作用,各因素作用大小依次為:振幅(正相關)>振頻(正相關)>前進速度(正相關)。
3)在試驗條件下,得到耕阻、振動均較小的多目標優化組合方案為:振幅21 mm、振頻4.2 Hz、前進速度3.4 km/h。在該組合條件下,與非振動深松相比,振動深松耕阻平均值減小16.6%;最小值減小46.2%;最大值變化較小;振動深松后大土塊較少,松土效果提高,實現了在提高振動深松減阻效果的同時降低振動的目的。
[1] 鄭侃,何進,李洪文,等. 中國北方地區深松對小麥玉米產量影響的Meta分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2015,31(22):7-15.
Zheng Kan, He Jin, Li Hongwen, et al. Meta-analysis on maize and wheat yield under subsoiling in Northern China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(22): 7-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 張瑞富,楊恒山,高聚林,等. 深松對春玉米根系形態特征和生理特性的影響[J]. 農業工程學報,2015,31(5):78-84.
Zhang Ruifu, Yang Hengshan, Gao Julin, et al. Effect of subsoiling on root morphological and physiological characteristics of spring maize[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(5): 78-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 何進,李洪文,高煥文. 中國北方保護性耕作條件下深松效應與經濟效益研究[J]. 農業工程學報,2006,22(10):62-67.
He Jin, Li Hongwen, Gao Huanwen. Subsoiling effect and economic benefit under conservation tillage mode in Northern China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2006, 22(10): 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 郭志軍,佟金,周志立,等. 深松技術研究現狀與展望[J]. 農業工程學報,2001,17(6):169-174.
Guo Zhijun, Tong Jin, Zhou Zhili, et al. Review of subsoiling techniques and their applications[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2001, 17(6): 169-174. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 張祥彩,李洪文,王慶杰,等. 我國北方地區機械化深松技術的研究現狀[J]. 農機化研究,2015(8):261-264.
Zhang Xiangcai, Li Hongwen, Wang Qingjie, et al. Research on mechanized subsoiling technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015(8): 261-264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王志窮,王維新,李霞,等. 保護性耕作條件下深松技術的國內外發展現狀[J]. 農機化研究,2016(6):253-258.
Wang Zhiqiong, Wang Weixin, Li Xia, et al. Development status of subsoiling at home and abroad under conservation tillage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016(6): 253-258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 徐宗保,董欣,李紫輝,等. 振動式深松中耕作業機的研制與試驗研究[J]. 農機化研究,2010(1):182-184.
Xu Zongbao, Dong Xin, Li Zihui, et al. Development and experimental study of the machine of vibrating deeploose and Intertillage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010(1): 182-184. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 湯明軍,王維新,李霞,等. 振動深松機的研究進展與展望[J]. 農機化研究,2016(4):258-263.
Tang Mingjun, Wang Weixin, Li Xia, et al. Research progress and prospect of vibrating subsoiler[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016(4): 258-263. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 付俊峰,張東興,李霞,等. 振動深松機的改進設計與試驗研究[J]. 中國農業大學學報,2011,16(6):158-162.
Fu Junfeng, Zhang Dongxing, Li Xia, et al. An improved design and field experiments for a vibration subsoiler[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2011, 16(6): 158-162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李霞,付俊峰,張東興,等. 基于振動減阻原理的深松機牽引阻力試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2012,28(1):32-36.
Li Xia, Fu Junfeng, Zhang Dongxing, et al. Experiment analysis on traction resistance of vibration subsoiler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(1): 32-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Sakai K, Hata S I, Takai M, et al. Design parameters of 4-shank vibrating subsoiler[J]. Transactions of The ASAE, 1993, 36(1): 23-26.
[12] Niyamapa T, Salokhe V M. Force and pressure distribution under vibratory tillage tool[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2000, 37(3): 139-150.
[13] 邱立春,李寶筏. 自激振動深松機減阻試驗研究[J]. 農業工程學報,2000,16(6):72-76.
Qiu Lichun, Li Baofa. Experimental study on the self-excited vibration subsoiler for reducing draft force[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2000, 16(6): 72-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李艷龍,劉寶,崔濤,等. 1SZ-460型杠桿式深松機設計與試驗[J]. 農業機械學報,2009,40(S1):37-40.
Yanlong Li, Bao Liu, Tao Cui, et al. Design and field experiment on 1SZ-460 lever-type subsoiler[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(S1): 37-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王俊發,劉孝民,陳玉芳,等. 振動深松機理的探討[J]. 佳木斯大學學報:自然科學版,2000,18(4):335-338.
Wang Junfa, Liu Xiaomin, Chen Yufang, et al. Study on vibrating tillage mechanism[J]. Journal of Jiamusi University: Natural Science Edition, 2000, 18(4): 335-338. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 蔣建東,高潔,趙穎娣,等. 基于ALE有限元仿真的土壤切削振動減阻[J]. 農業工程學報,2012(增刊1):33-38.
Jiandong Jiang, Jie Gao, Yingdi Zhao, et al. Numerical simulation on resistance reduction of soil vibratory tillage using ALE equation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012(Supp.1): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 辛麗麗,李傳琦,梁繼輝,等. 考慮分段土壤作用力的振動減阻分析[J]. 農業機械學報,2014(2):136-140.
Xin Lili, Li Chuanqi, Liang Jihui, et al. Vibrating drag reduction considering acting force of piecewise soil[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2014(2): 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Shahgoli Gholamhossein, Fielke John, Desbiolles Jacky, et al. Optimising oscillation frequency in oscillatory tillage[J]. Soi & Tillage Research, 2010, 106(2): 202-210.
[19] Shahgoli Gholarnhossein, Saunders Chris, Desbiolles Jacky, et al. The effect of oscillation angle on the performance of oscillatory tillage[J]. Soi & Tillage Research, 2009, 104(1): 97-105.
[20] 李霞,張東興,王維新,等. 受迫振動深松機性能參數優化與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2015,31(21):17-24.
Li Xia, Zhang Dongxing, Wang Weixin, et al. Performance parameter optimization and experiment of forced-vibration subsoiler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(21): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王俊發,魏天路,劉孝民. 振動深松的試驗研究[J]. 農業機械學報,2001,32(3):33-35.
Wang Junfa, Wei Tianlu, Liu Xiaomin. Experimental study on vibrating subsoiling[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2001, 32(3): 33-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 谷謁白,劉向陽. 1SQ-250型全方位深松機的研制與試驗[J]. 北京農業工程大學學報,1994,14(4):42-48.
Gu Yebai, Liu Xiangyang. Development and experiment on 1SQ-250 model of bulk subsoiler[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural Engineering University, 1994, 14(4): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 吳儉敏,朱立成,米義,等. 新型土槽試驗臺的研制[J]. 農機化研究,2011(3):92-95.
Wu Jianmin, Zhu Licheng, Mi Yi, et al. The development of the new soil bin test-bed[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2011(3): 92-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王繼承,董向前,孫亞朋,等. 一種可調頻振動壓實裝置[P]. CN204803877U.
Wang Jicheng, Dong Xiangqian, Sun Yapeng, et al. Frequency modulation vibrating compacting device[P]. CN204803877U. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 董向前,宋建農,王繼承,等. 草地振動松土機運動特性分析與振動頻率優化[J]. 農業工程學報,2012,28(12):44-49.
Dong Xiangqian, Song Jiannong, Wang Jicheng, et al. Vibration frequency optimization and movement characteristics analysis of vibration shovel for meadow[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(12): 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 杜家菊,陳志偉. 使用SPSS線性回歸實現通徑分析的方法[J]. 生物學通報,2010,45(2):4-6.
Du Jiaju, Chen Zhiwei. Method of path analysis with SPSS linear regression[J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2010, 45(2): 4-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 徐向宏,何明珠. 試驗設計與Design-Expert、SPSS應用[M]. 北京:科學出版社,2010:79-84.
[28] 張琪,叢鵬,彭勵. 通徑分析在Excel和SPSS中的實現[J]. 農業網絡信息,2007(3):109-110.
[29] 任紅松,呂新,曹連莆,等. 通徑分析的SAS實現方法[J]. 計算機與農業·綜合版,2003(4):17-19.
Ren Hongsong, Lu Xi, Cao Lianpu, et al. The implemented method of SAS in path analysis[J]. Computer and Agriculture, 2003(4): 17-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 張昆,高振,李霜,等. 基于Desirability函數法對米根霉發酵制備富馬酸的多目標優化[J]. 中國生物工程雜志,2008,28(4):59-64.
Zhang Kun, Gao Zhen, Li Shuang, et al. Multiple target optimization on the fumaric Acid production by rhizopusoryzae based on desirability function[J]. China Biotechnology, 2008, 28(4): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 劉愛琴,羅超杰,周迪,等. 滿意度函數法對維生素A微膠囊的多目標優化[J]. 食品研究與開發,2014,35(8):46-50.
Liu Aiqin, Luo Chaojie, Zhou Di, et al. Multiple target optimization on vitamin A microencapsulation by desirability function approach[J]. Food Research And Development, 2014, 35(8): 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Parameter optimization of vibration subsoiler test bed for reducing resistance and vibration
Sun Yapeng, Dong Xiangqian, Song Jiannong※, Liu Cailing, Wang Jicheng, Zhang Chao
(,100083,)
The oscillatory tillage was proved to be more efficient than rigid tillage. Oscillation could reduce the drag resistance during tillage. But the oscillation had a bed effect on the tractor. Oscillation damaged the tractor and was harmful to tractor driver. The goals were to reduce the drag residence and the effect on the tractor. These two goals couldn’t be optimum at the same time. But it had a relative optimum combination. The Six-component test system on the experiment trolley could measure the forces in the directions of heading(), vertical () and crosswise (). Define the mean value of-direction force as the mean of resisting force1, the interquartile range of-direction force as the range of vibratory force2. The working parameter of oscillatory tillage that to be considered were amplitude e(), frequency () and velocity () in the experiments. Using quadratic general revolving combination design with 3 factors, the regression models between1,2and amplitude, frequency, velocity were founded. There were two three-factor quadratic regression models. The influence order could be found in the perturbation graph for non-interaction parameters, but couldn’t be found for interactive parameters, because the trend of perturbation curve changed when the interactive parameters was changed. The path analysis method could find both direct and indirect influences of interactive parameters. Using the interaction analysis method in the Design-Expert and the path analysis method in the SPSS, the influence order of three factors was determined,>>, to both1and2. There were no optimal solutions for this multi-objective optimization problem, but there were relative optimal solutions for it through the method of desirability function method. The higher the desirability value, the better the solution. From the 3D response surface of desirability at different velocities, in order to achieve high speed work, the relative optimal solution of both the goal of low resisting force and that of low vibratory force was small amplitude, high frequency and high speed, the values were 21 mm, 4.2 Hz and 3.4 km/h. The inaccuracy between the predicted value of regression model and the result of verification test was acceptable. The maximums of resisting forces during oscillation and non-oscillatory tillage were similar, but the force reductions of minimum and mean values were 46.2% and 16.6%. Comparing with the single objective optimal solution of1, the multi-objective optimization reduced the vibratory force. It achieves that resisting force decreases and at the same time the vibration on vertical direction decreases during oscillatory tillage.
agricultural machinery; optimization; vibration; subsoiling; response surface
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.24.006
S222.1
A
1002-6819(2016)-24-0043-07
2016-03-29
2016-10-18
教育部創新團隊發展計劃項目(IRT13039);中央高校基本科研業務費專項資金資助項目(2015GX003/2016TC007)
孫亞朋,男,山東濟寧人,博士生,主要從事農業機械與農業裝備研究。北京 中國農業大學農業部土壤-機器-植物系統技術重點實驗室,100083。Email:sunypeng@hotmail.com
宋建農,男,河北藁城人,教授,博士生導師,主要從事農業機械與農業裝備研究。北京 中國農業大學農業部土壤-機器-植物系統技術重點實驗室,100083。Email:songjn@cau.edu.cn

