一類捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統的隨機動力學行為
馮 濤,孟新柱
(山東科技大學 數學與系統科學學院,山東 青島 266590)
一類捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統的隨機動力學行為
馮 濤,孟新柱
(山東科技大學 數學與系統科學學院,山東 青島 266590)
考慮了一類具有Beddington-DeAngelis功能性反應和Lévy跳的捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統的動力學行為。利用Lyapunov方法和伊藤公式,本文討論了系統全局正解的存在唯一性;研究了隨機系統在其確定性模型的平衡點周圍的長時間行為。研究結果表明,在一定條件下,隨機系統的解會在其確定性系統的平衡點周圍波動,且波動的幅度與隨機系統所受干擾的強度呈正相關。最后,本文運用Matlab數值模擬對前述理論進行了驗證。
捕食者-食餌系統;Beddington-DeAngelis功能性反應;漸近行為;隨機擾動;Lévy跳
近年來,隨機干擾對生態系統的影響逐漸成為生物數學領域的研究熱點[1-6]。在生態系統中,捕食者和食餌之間的相互作用經常受到一些環境因素的影響,例如海嘯、水源、地震、火山、疾病等。許多學者研究了傳染病對捕食者-食餌種群的影響[7-13]和環境干擾對捕食者-食餌種群的影響[14-17]。研究傳染病和環境噪聲對捕食者-食餌種群的影響具有重要的生物學意義。本文結合傳染病與環境噪聲對生物種群的影響,研究了一類帶有Beddington-DeAngelis功能性反應和Lévy跳的捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統的動力學行為。
1 數學模型
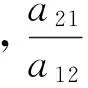
文獻[13]研究了如下具有Beddington-DeAngelis功能性反應和捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統:
(1)
令
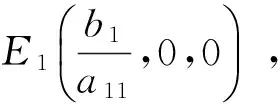
實際上,生態系統中的物種可能會遭受到一些較大的不確定因素的干擾,比如火山噴發、地震、海嘯和氣候驟變等,一般把這類較大的干擾因素稱為有色噪聲干擾,數學上使用Lévy跳表示。考慮這類有色噪聲干擾后,模型(1)變為:
(2)
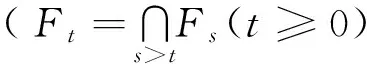
2 全局正解的存在唯一性
本文的研究對象為生物種群,由于負數解不存在生物學意義,因此本節首先證明模型(2)存在全局唯一正解。
假設 2.1 假定以下條件成立[15]:
(i) 1+γi(u)>0,
其中,i=1,2,3,這兩個假設意味著Lévy噪聲的強度不會無限大。
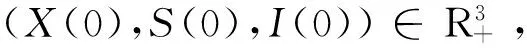
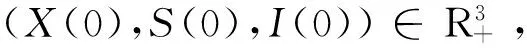
證明由引理2.1可知,只需要證明τe=∞。定義一個充分大的正常數k0,使得
定義停時
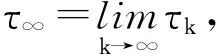
(3)
V(X,S,I)=X-1-lnX+S-1-lnS+I-1-lnI。
(4)
由伊藤公式得
(5)
其中
(6)
其中,H0>0是常數。
對方程(5)的兩端從0到τk∧N積分并取期望,得
(7)
(8)
結合方程(7)和方程(8),得
其中1nk 是Ωk的指標函數。令k→+∞,得
+∞≥V(X(0),S(0),I(0))+H0N≥+∞。
顯然與假設矛盾。故τ∞=∞。
3 模型(2)解的漸近性質
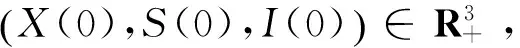
其中
證明定義
由伊藤公式得
(9)
其中
(10)
對方程(9)兩端由0到t積分并取期望,得
(11)
對方程(11)兩端同時除以t,令t→∞并取上界,得
證畢。
推論 3.1當σ1,γ1=0時,模型(2)等同于模型(1)。由定理3.1中(10)可知,此時
所以模型(1)的平衡點E1(K,0,0)是全局漸近穩定的。
注 3.1由定理3.1可知,如果干擾強度σ1,γ1足夠小,模型(2)的解會在模型(1)的邊界平衡點E1(K,0,0)周圍震蕩,且震蕩的幅度與干擾的強度呈正相關。
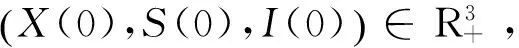
其中
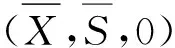
定義
由伊藤公式得
(12)
其中
同理可得
(13)
其中
同理
(14)
結合方程(12)~(14),得
(15)
其中
(16)
對方程(15)兩端由0到t積分并取期望,得
(17)
對方程(17)兩端同時除以t,令t→∞并取上界,得
證明完畢。
推論3.2當σi,γi=0(i=1,2)時,模型(2)等同于模型(1)。由定理3.2中方程(16)知,此時
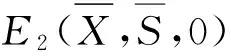
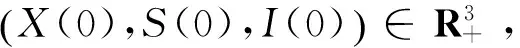
其中
證明由于(X*,S*,I*)是系統(1)的正平衡點,所以
定義
由伊藤公式得
(18)
其中
同理可得
(19)
其中
同理
(20)
其中
結合方程(18)~(20),得
(21)
其中
對方程(21)兩端由0到t積分并取期望,得
(22)
對方程(22)兩端同時除以t,令t→∞并取上界,得
證明完畢。
推論 3.3當σi,γi=0(i=1,2,3)時,模型(2)等同于模型(1)。由定理3.3知,此時
所以模型(1)的正平衡點E3(X*,S*,I*)是全局漸近穩定的。
注 3.3由定理3.3知,如果干擾強度σi,γi=0(i=1,2,3)足夠小,模型(2)的解會在模型(1)的正平衡點E3(X*,S*,I*)周圍震蕩,且震蕩的幅度與干擾的強度呈正相關。
4 數值仿真
利用歐拉法和Matlab2014b[13],本文進行了數值模擬以支持獲得的結果。數值仿真中,使用以下參數:
初始值X(0)=3,S(0)=2,I(0)=2,p=q=1,Ζ=(0,+∞),λ(Ζ)=1,步長Δt=0.001。
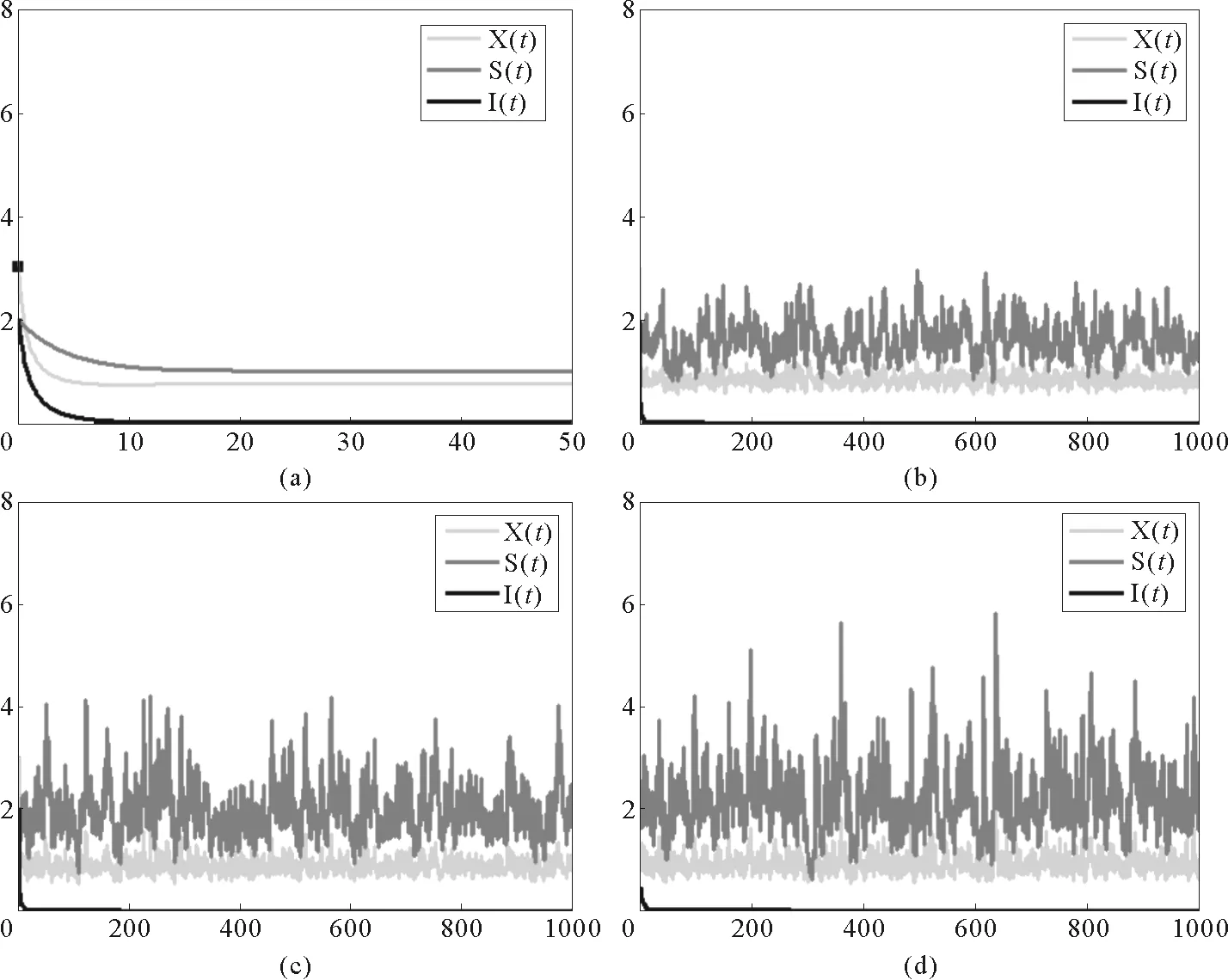
在圖1中,b1=0.6,b2=0.4,b3=0.2,a11=0.5,a12=0.6,a21=0.3,a22=0.1,a33=0.1,β=0.2。圖1(a)為確定性模型(1)的時間序列圖,(b)-(d)為隨機模型(2)的時間序列圖,干擾強度分別取:(b)σi=0.05,γi=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,γi=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,γi=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
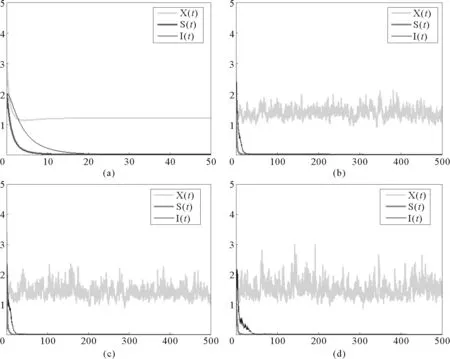
(a) 確定性模型(1);(b)-(d)為隨機模型(2),干擾強度分別取值:(b)σi=0.05,ri=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,ri=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,ri=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
在圖2中,b1=0.6,b2=0.12,b3=0.5,a11=0.5,a12=0.6,a21=0.8,a22=0.1,a33=0.4,β=0.1。圖2(a)為確定性模型(1)的時間序列圖,(b)~(d)為隨機模型(2)的時間序列圖,干擾強度分別取:(b)σi=0.05,γi=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,γi=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,γi=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
在圖3中,b1=1,b2=0.1,b3=0.1,a11=0.2,a12=0.6,a21=0.1,a22=0.1,a33=0.2,β=0.5。圖3(a)為確定性模型(1)的時間序列圖,(b)-(d)為隨機模型(2)的時間序列圖,干擾強度分別取:(b)σi=0.05,γi=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,γi=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,γi=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
在這種情況下,a11=0.2>p(b1-a11X*)=0.062 24,平衡E3(X*,S*,I*)=(4.69,0.66,1.15)R1=6.72>1。圖3顯示系統(2)的解在系統(1)的平衡點E3周圍浮動,且浮動的幅度與干擾的強度σi,γi(i=1,2,3)的取值呈正相關關系。這與定理3.3中的結論一致。
(a) 確定性模型(1);(b)-(d)為隨機模型(2),干擾強度分別取值:(b)σi=0.05,ri=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,ri=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,ri=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
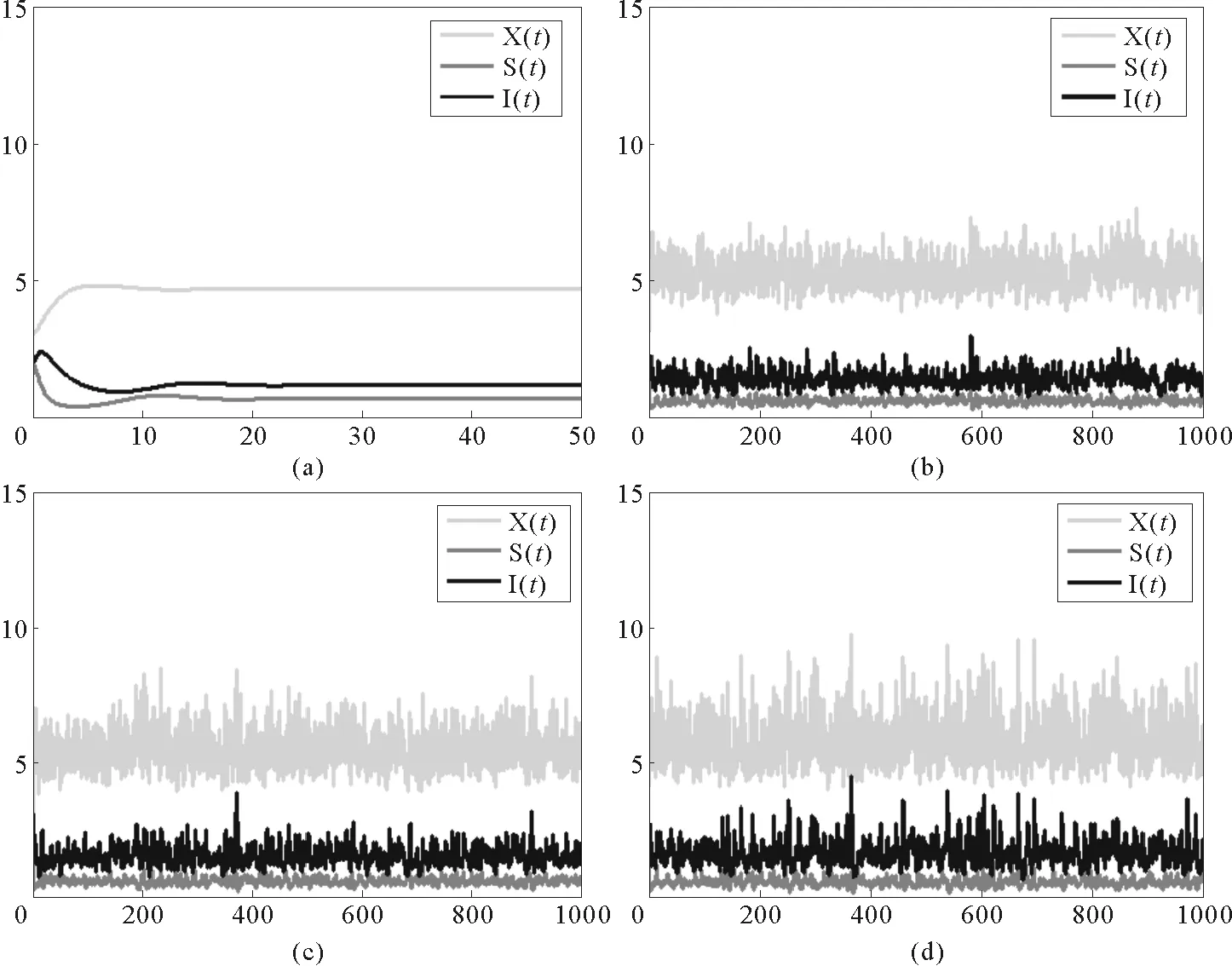
(a) 確定性模型(1);(b)-(d)為隨機模型(2),干擾強度分別取值:(b)σi=0.05,ri=0.1,(c)σi=0.05,ri=0.15,(d)σi=0.05,ri=0.2,其中i=1,2,3。
5 總結
本文研究了一類帶有Beddington-DeAngelis功能性反應和Lévy跳的捕食者染病的捕食者-食餌系統。運用李雅普諾夫方法和推廣的伊藤公式,本文首先證明了系統(2)全局正解的存在唯一性,然后討論了模型(2)的解在其確定性模型的平衡點周圍的漸近行為。Lévy跳在生物學上表示一些大的環境干擾,比如地震、火山、海嘯等。當這類噪聲干擾發生的時候,會對生物種群的穩定性產生一定的影響。文中干擾強度參數分別表示三個種群所受自然環境干擾的強度,比如地震、火山、暴雨等自然災害的強度。定理3.1~3.3的理論結果表明,當這類噪聲干擾不是特別大的時候,并不會使物種滅絕,但會使種群的數量在平衡狀態周邊浮動,且這種浮動的強度與噪聲干擾的強度呈正相關關系。也就是說,種群對環境的變化具有一定的適應能力,當環境變化的強度很小的時候,它們并不會導致物種的滅亡,而是使物種密度在一定范圍內波動。并且,當這種干擾強度不斷增大時,它們對物種密度產生的影響也會越大。
[1]MENG X Z,ZHAO S N,FENG T,et al.Dynamics of a novel nonlinear stochastic SIS epidemic model with double epidemic hypothesis[J].Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,2015,433:227-242.
[3]YAGI A,TON T V.Dynamic of a stochastic predator-prey population[J].Applied mathematics and Computation,2011,218(7):3100-3109.
[4]劉文昌,孟新柱.具有脈沖毒素輸入的隨機收獲模型最優捕獲策略[J].山東科技大學學報(自然科學版),2015,34(5):98-103. LIU Wenchang,MENG Xinzhu.Optimal harvesting strategies for stochastic harvest model with impulsive toxicant input[J].Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science),2015,34(5):98-103.
[5]ZHANG Q M,JIANG D Q,LIU Z W,et al.Asymptotic behavior of a three species eco-epidemiological model perturbed by white noise[J].Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,2016,433:121-148.
[6]LIU M,WANG K.Persistence,extinction and global asymptotical stability of a non-autonomous predator-prey model with random perturbation[J].Applied Mathematical Modelling,2012,36:5344-5353.
[7]HAQUE M,JIN Z,EZIO V.An ecoepidemiological predator-prey model with standard disease incidence [J].Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences,2009,32:875-898.
[8]CHATTOPADHYAY J,ARINO O.A predator-prey model with disease in the prey[J].Nonlinear Analysis-Series A Theory and Methods and Series B Real World Applications,1999,36:747-766.
[9]XIAO Y N,CHEN L S.Modeling and analysis of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey[J].Mathematical Biosciences,2001,171:59-82.
[10]HADELER K P,FREEDMAN H I.Predator-prey populations with parasitic infection[J].Journal of mathematical biology,1989,27:609-631.
[11]HAN L T,MA Z E,HETHCOTE H W.Four predator prey models with infectious diseases[J].Mathematical and Computer Modelling,2001,34:849-858.
[12]HETHCOTE H W,WANG W D,HAN L T,et al.A predator-prey model with infected prey[J].Theoretical Population Biology,2004,66:259-268.
[13]LI S,WANG X P.Analysis of stochastic predator-prey models with disease in the predator and Beddington-DeAngelis functional response[J].Advances in Difference Equations,2015,(1):1-21.
[14]ZU L,JIANG D Q,O'REGAN D.Conditions for persistence and ergodicity of a stochastic Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model with regime switching[J].Communications Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation,2015,29:1-11.
[15]LI D,CUI J A,SONG G H.Permanence and extinction for a single-species system with jump-diffusion[J].Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,2015,430:438-464.
[16]LIU M,WANG K.Stochastic Lotka-Volterra systems with Levy noise[J].Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,2014,410:750-763.
[17]ZOU X L,WANG K,Numerical simulations and modeling for stochastic biological systems with jumps[J].Communications Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation,2014,19:1557-1568.
(責任編輯:傅 游)
Stochastic Dynamics of a Predator-prey System with Disease in Predator
FENG Tao,MENG Xinzhu
(College of Mathematics and Systems Science,Shandong University of Science and Technology,Qingdao,Shandong 266590,China)
This paper investigated the stochastic dynamics of an infected predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and Lévy jump. By using Lyapunov methods and It’s formula,this paper first discussed the existence and uniqueness of the global positive solution of the stochastic system,and then studied the asymptotic behaviors around the equilibrium points of its deterministic model. Results show that the solutions of the stochastic system fluctuate around the equilibrium points of its deterministic model under certain conditions,and the fluctuation intensity is positively correlated with the intensity of interference. Finally,numerical simulations were carried out to verify the theoretical findings.
predator-prey system; Beddington-DeAngelis functional response; asymptotic behaviors; random disturbance; Lévy jump
2016-05-16
國家自然科學基金項目(11371230,11501331);山東省自然科學基金項目(ZR2015AQ001,BS2015SF002);山東科技大學科研創新團隊項目(2014TDJH102)
孟新柱(1972—),男,山東菏澤人,教授,博士生導師,主要從事生物數學方面的研究,本文通信作者. E-mail:mxz721106@sdust.edu.cn
O175
A
1672-3767(2017)01-0099-12

