THREE SOLUTIONS FOR A FRACTIONAL ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS WITH CRITICAL AND SUPERCRITICAL GROWTH?
Jinguo ZHANG(張全國)
School of Mathematics,Jiangxi Normal University,Nanchang 330022,China
Xiaochun LIU(劉曉春)
School of Mathematics and Statistics,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China
THREE SOLUTIONS FOR A FRACTIONAL ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS WITH CRITICAL AND SUPERCRITICAL GROWTH?
Jinguo ZHANG(張全國)
School of Mathematics,Jiangxi Normal University,Nanchang 330022,China
E-mail:jgzhang@jxnu.edu.cn
Xiaochun LIU(劉曉春)
School of Mathematics and Statistics,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China
E-mail:xcliu@whu.edu.cn
In this paper,we deal with the existence and multiplicity of solutions to the fractional elliptic problems involving critical and supercritical Sobolev exponent via variational arguments.By means of the truncation combining with the Moser iteration,we prove that our problem has at least three solutions.
fractional elliptic equation;variational methods;three solutions;Moser iteration
2010 MR Subject Classifcation35J60;47J30
1 Introduction
In this paper,we consider the existence and multiplicity of solutions for the fractional elliptic problem
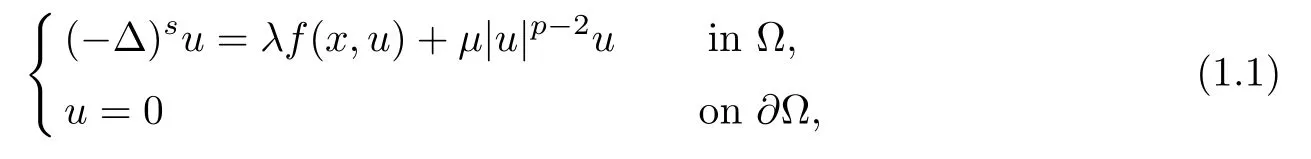
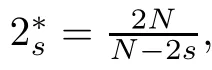
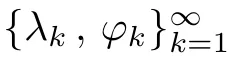
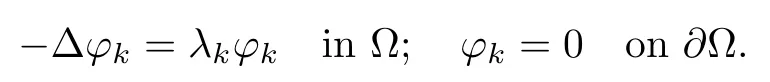
For any u∈L2(?),we may writeWith this spectral decomposition,the fractional powers of the Dirichlet Laplacian(??)scan be defned forby

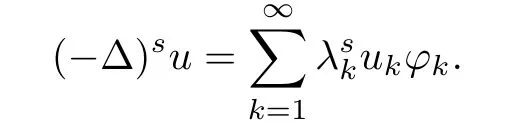
By density,the operator(??)scan be etended to the Hilbert Space
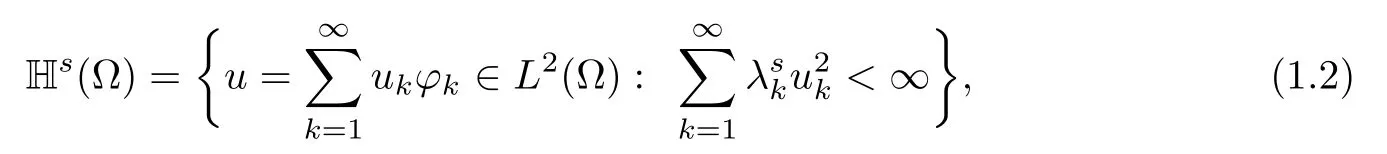
which is equipped with the norm
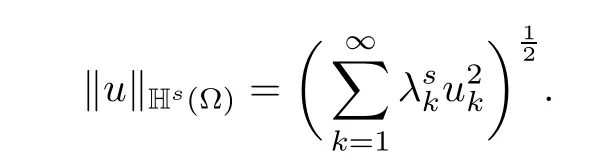
The theory of Hilbert scales presented in the classical book by Lions and Magenes[11]shows that
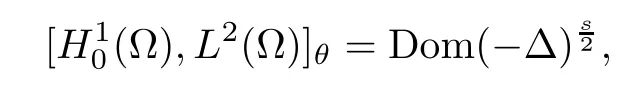
where θ=1?s.This implies the following characterization of the space Hs(?),
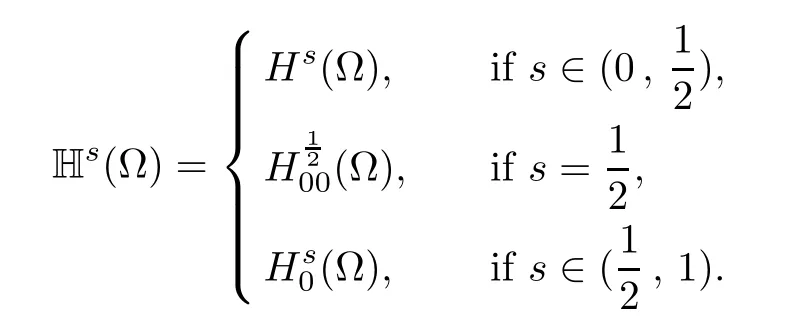
One of the main difculties in the study of problem(1.1)is that the fractional Laplacian is a nonlocal operator.To localize it,Cafarelli and Silvestre[1]developed a local interpretation of the fractional Laplacian in RNby considering a Dirichlet to Neumann type operator in the domain{(x,y)∈RN+1:y>0}.A similar extension,in a bounded domain with zero Dirichlet boundary condition,was establish by Cabr′e and Tan in[2],Tan[3]and by Br¨andle,Colorado, de Pablo and S′anchez[4].For anythe solutionof
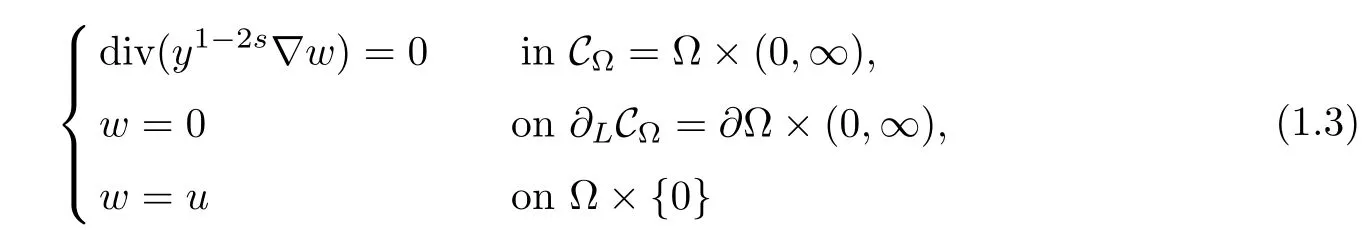
is called the s-harmonic extension w=Es(u)of u,and it belongs to the space
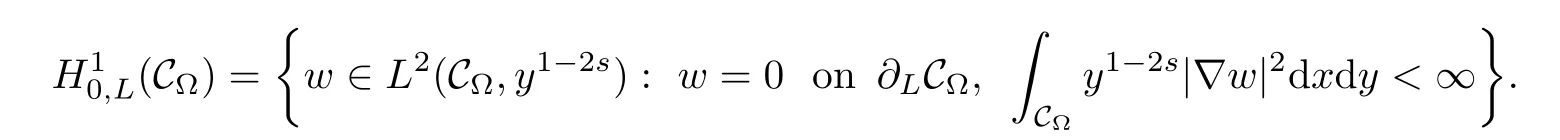
It is proved that
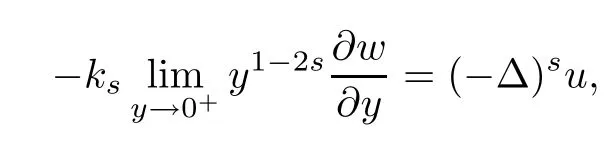
where ks=21?2sΓ(1?s)/Γ(s).Here H10,L(C?)is a Hilbert space endowed with the norm
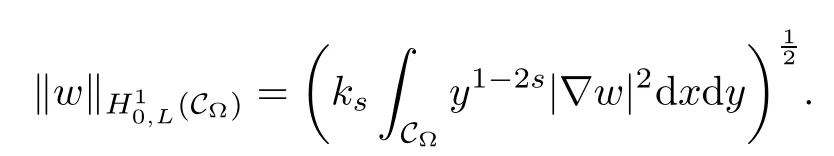
Therefore,the nonlocal problem(1.1)can be reformulated to the following local problem
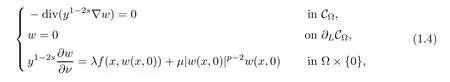
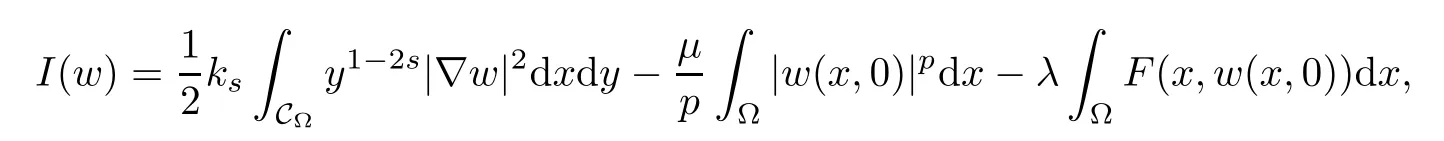
In this paper,we study the existence and multiplicity of solutions for the problem with critical and supercritical growth.In our problem,the frst difculty lies in that the fractional Laplacian operator(??)sis nonlocal,and this makes some calculations difcult.To overcome this difculty,we do not work on the space Hs(?)directly,and we transform the nonlocal problem into a local problem by the extension introduced by Cafarelli and Silvestre in[1].The second difculty lies in which problem(1.4)is a supercritical problem.We can not use directly the variational techniques because the corresponding energy functional is not well-defned on Hilbert spaceTo overcome this difculty,one usually uses the truncation and the Moser iteration.This spirt has been widely applied in the supercritical Laplacian equation in the past decades,see[5–10]and references therein.
The aim of this paper is to study problem(1.4)when p≥2?s.In order to state our main results,we formulate the following assumptions
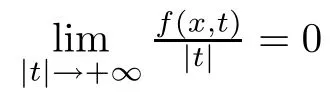
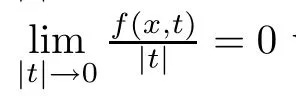
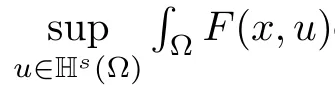
Set
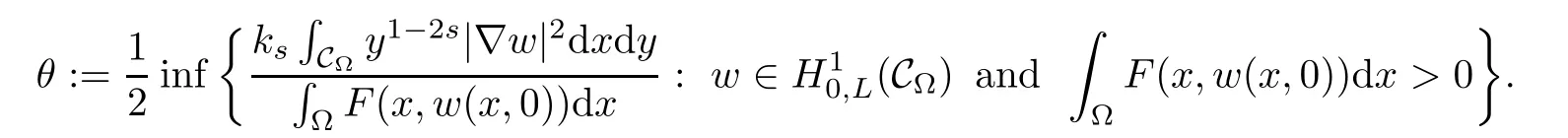
The main results are as follows.
Theorem 1.1Assume that(f1)–(f3)hold.Then there exists a δ>0 such that for any μ∈[0,δ],there are a compact interval[a,b]?(1θ,+∞)and a constant γ>0 such that problem(1.4)has at least three solutions infor each λ∈[a,b],whosenorms are less than γ.
For the general problem
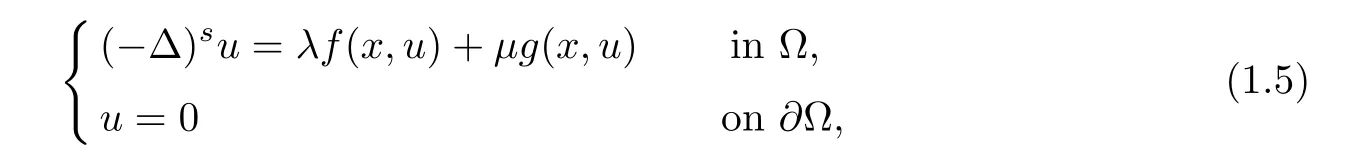
where ??RNis a bounded smooth domain,and
(g)|g(x,u)|≤C(1+|u|p?1),where
If f satisfes conditions(f1)–(f3),we also have similar result.
Theorem 1.2Assume that(f1)–(f3)and(g)hold.Then there exists a,δ>0 such that for anyμ∈[0,δ],there are a compact interval[a,b]?(1θ,+∞)and a constant γ>0 such that problem(1.5)has at least three solutions infor each λ∈[a,b],whose-norms are less than γ.
The paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we introduce a variational setting of the problem and present some preliminary results.In Section 3,some properties of the fractional operator are discussed,and we apply the truncation and the Moser iteration to obtain the proof of Theorems 1.1 and 1.2.
For convenience we fx some notations.Lp(?)(1 Let us recall some function spaces,for details the reader to[12,13].For 0 The Sobolev space Hs(?)of order is defned by which,equipped with the norm is a Hilbert space.Let Hs0(?)be the closure of C∞c(?)with respect to the norm k·kHs(?),i.e., If the boundary of ? is smooth,the space Hs(?)can be defned as interpolation spaces of index θ=1?2s for pair[H1(?),L2(?)]θ.Analogously,for s∈[0,1]{12},the spaces Hs0(?) are defned as interpolation spaces of index θ=1?2s for pair[H10(?),L2(?)]θ,that is, and d(x)=dist(x,??)for all x∈?.It was known from[11]that for 0 Furthermore,we recall a result in[14]. Lemma 2.1There exists a trace operator fromin toFurthermore,the space Hs(?)given by(1.2)is characterized by Lemma 2.1 was proved in[14].In its proof,we see in fact that the mapping tr:Hs(?)is continuous,and this operator has its image contained inNext,we have the Sobolev embedding theorem. Lemma 2.2Given s>0 and1p>1 so that1p≥12?sN,the inclusion map i:Hs(?)→Lp(?)is well defned and bounded.If the above inequality is strict,then the inclusion is compact. By Lemma 2.1 and Lemma 2.2,we now that there exists a continuous linear mapping fromThen we will list following lemma. Lemma 2.3it holds where C>0 depends on r,s,N and ?. Theorems 1.1 and 1.2 will be proved in an idea from a recent result on the existence of at least three critical points by Ricceri[15,16].For the readers convenience,we state it as follows. Theorem 2.4Let X be a separable and refexive real Banach space and I?R be an interval.A C1functional Φ:X→R a sequentially weakly lower semi-continuous,bounded on each bounded subset of X,and belonging to X.The derivative of Φ admits a continuous inverse on X?.The functional J:X→R is a C1functional with compact derivative.Assume that the functional Φ?λJ is coercive for each λ∈I,and it has a strict local but not global minimum,sayThen there exists a number γ>0 for each compact interval[a,b]?I for whichsuch that the following property holds:there exists δ0>0,for every λ∈[a,b]and every C1functional Ψ:X→R with compact derivative,such that the equation has at least three solutions whose norm are less than γ for eachμ∈[0,δ0]. Let Obviously,condition(f3)implies Lemma 3.1Let f satisfyThen for every λ∈(0,∞),the functional Φ?λJ is sequentially weakly lower continuous and coercive onand has a global minimizer ProofBy(f1)and(f3),for any ε>0,there exist M0>0 and C1>0 such that for allwe have which implies that and Then where the constants C2>0,C3>0.Let ε>0 small enough such thatand then we have Hence Φ?λJ is coerciveness. is weakly lower semi-continuous onWe can deduce that Φ?λJ is a sequentially weakly lower semi-continuous,that is,Φ?λJ∈X.Therefore,Φ?λJ has a global minimizerThe proof is completed. Next,we will show that Φ?λJ has a strictly local,but not global minimizer for some λ, when f satisfes(f1)–(f3). Lemma 3.2Let f satisfy(f1)–(f3).Then (i)0 is a strictly local minimizer of the functional Φ?λJ for λ∈(0,+∞). (ii)wλ66=0,i.e.,0 is not the global minimizer wλfor λ∈(1θ,+∞),where wλis given by Lemma 3.1. ProofFirst,we prove that In fact,by(f2),for any ε>0,there exists a δ>0,such that|w(x,0)|<δ and Considering inequality(3.2),(f1)and(f3),there exists r∈(1,2?s?1)such that Then from Sobolev embedding theorem,there exist C4,C5>0,such that This implies Next,we will prove(i)and(ii). Hence 0 is a strictly local minimizer of Φ?λJ. It yields that 0 is not a global minimizer of Φ?λJ. This completes the proof. Let K>0 be a real number whose value will be fxed later.Defne the truncation of where q∈(2,2?s).Then gK(w)satisfes for K large enough.Then,we study the truncated problem holds for every ?∈H10,L(C?). Let where is C1and its derivative is given by By Lemma 3.1 and Lemma 3.2,we know that all hypotheses of Theorem 2.4 are satisfed. So there exists γ>0 with the following property:for every λ∈[a,b]?(1θ,+∞),there exists δ0>0,such that forμ∈[0,δ0],problem(3.4)has at least three solutions w0,w1and w2inand where γ depends on λ,but does not depend onμor K. If these three solutions satisfy then in the view of the defnition gK,we have gK(x,w)=μ|w|p?2w,and therefore wk,k= 0,1,2,are also solutions of the original problem(1.4).This implies that problem(1.1)has at least three solutions uk(x)=trwk(k=0,1,2). Thus,in order to prove Theorem 1.1,it sufces to show that exists δ0>0 such that the solutions obtained by Theorem 2.4 satisfy inequality(3.6)forμ∈[0,δ0]. Proof of Theorem 1.1Our aim is to show that exits δ0>0 such that forμ∈[0,δ0], the solution wk,k=0,1,2,satisfy inequality(3.6).For simplicity,we will denote w:=wk, k=0,1,2. Set w+=max{w,0},w?=?min{w,0}.Then|w|=w++w?.We can argue with the positive and negative part of w separately. We frst deal with w+.For each L>0,we defne the following function For β>1 to be determined later,we choose in(3.5)that and Then we obtain From the defnition of wL,we have Set From(3.3)and|gK(x,w)|≤Kp?q|w|q?1,we can choose a constant C6>0 such that We deduce from(3.5),(3.7),(3.8)and(3.9)for β>1 that By the Sobolev embedding theorem,we obtain where S>0 is the best Sobolev embedding constant. Moreover,by the Sobolev embeddingwe have the above inequality that By Fatou’s Lemma on the variable L,we get i.e., By iterating this process and β t=2?s,we obtain Taking the limit as m→∞in(3.15),we have Next,we will fnd some suitable value of K andμsuch that the inequality holds.From(3.16),we get Then we can choose K to satisfy the inequality and fxμ0such that Thus we obtain(3.16)forμ∈[0,μ0],i.e., Similarly,we can also have the estimate for the w?,i.e., Now,let δ=min{δ0,μ0}.For eachμ∈[0,δ],from(3.17),(3.18)and|w|=w++w?,we have which implies that Therefore,we obtain inequality(3.6).The proof is completed. Proof of Theorem 1.2In fact,the truncation of gK(x,s)can be given by Let hK(x,w)=λf(x,w)+μgK(x,w),?w∈H10,L(C?).The truncated problems associated to hKis the following Similar as in the proof of Theorem 1.1,by Theorem 2.4 we can prove that there exists δ>0 such that the solutions w for the truncated problems(3.19)satisfy kwkL∞≤K forμ∈[0,δ]; and in view of the defnition gK,we have Therefore wk,k=0,1,2,are also solutions of problem(3.19).This implies that problem(1.5) has at least three solutions uk(x)=trwk(k=0,1,2). [1]Cafarelli L,Silvestre L.An extension problem related to the fractional Laplacian.Comm Partial Difer Equ,2007,32:1245–1260 [2]Cabr′e X,Tan J.Positive solutions for nonlinear problems involving the square root of the Laplacian.Adv Math,2010,224:2052–2093 [3]Tan J.The Brezis-Nirenberg type problem involving the square root of the Laplacian.Calc Var,2011,42: 21–41 [4]Barrios B,Colorado E,de Pablo A,S′anchez U.On some critical problems for the fractional Laplacian operator.J Difer Equ,2012,252:6133–6162 [5]Cohabrowski J,Yang J.Existence theorems for elliptic equations involving supercritical Sobolev exponent. Adv Difer Equ,1997,2:231–256 [6]Ambrosetti A,Brezis H,Cerami G.Combined efectsof concave and convex nonlinearities in some elliptic problems.J Funct l Anal,1994,122:519–543 [7]Moser J.A new proof of De Giorgi’s theorem concerning the regularity problem for elliptic diferential equations.Comm Pure Appl Math,1960,13:457–468 [8]Francisco J,Correa S A,Figueiredo Giovany M.On an elliptic equation of p-Kirchhoftype via variational methods.Bull Australian Math Soc,2006,74:263–277 [9]Figueiredo G,Furtado M.Positive solutions for some quasilinear equations with critical and supercritical growth.Nonlinear Anal:TMA,2007,66(7):1600–1616 [10]Zhao L,Zhao P.The existence of solutions for p-Laplacian problems with critical and supercritical growth. Rocky Mountain J Math,2014,44(4):1383–1397 [11]Lions J L,Magenes E.Probl′emes aux Limites non Homog′enes et Applications,Vol 1.Trav et Rech Math, Vol 17.Paris:Dunod,1968 [12]Tartar L.An introduction to Sobolev Spaces and Interpolation Space.Lect Notes Unione Mat Ital,Vol 3. Berlin:Springer,2007 [13]Nochetto R H,Ot′arola E,Salgado A J.A PDE approach to fractional difussion in general domain:a priori error analysis.Found Comput Math,2015,15:733–791 [14]Capella A,D′avila J,Dupaigne L,Sire Y.Regularity of radial extremal solutions for some nonlocal semilinear equation.Comm Partial Diferential Equations,2011,36:1353–1384 [15]Ricceri B.A three points theorem revisited.Nonlinear Anal,2009,70:3084–3089 [16]Ricceri B.A further three points theorem.Nonlinear Anal,2009,71:4151–4157 ?Received February 29,2015;revised April 28,2016.Supported by NSFC(11371282,11201196)and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi(20142BAB211002).2 Preliminaries and Functional Setting
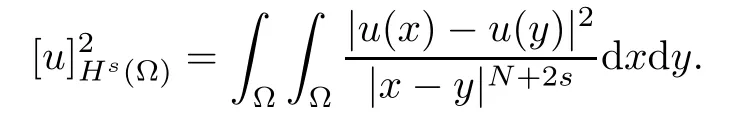
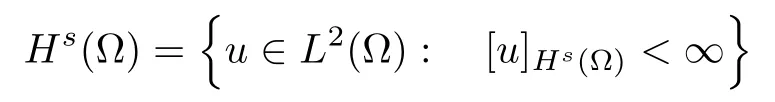
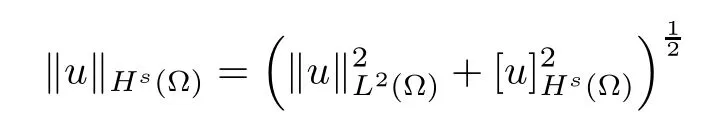
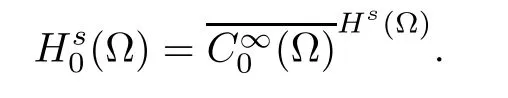
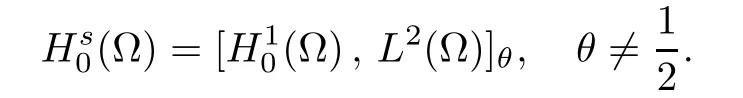
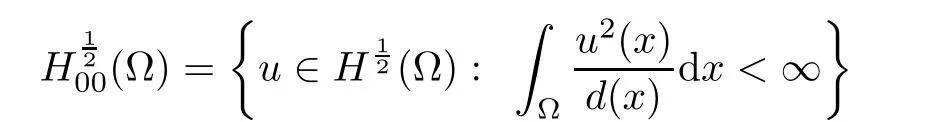
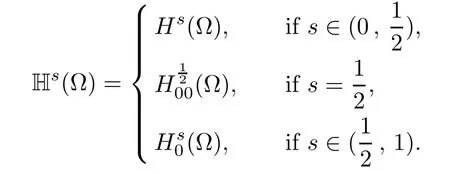
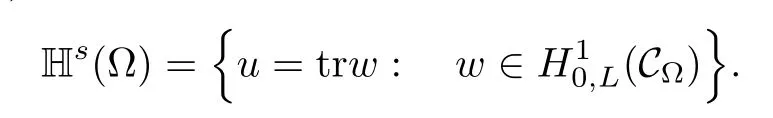
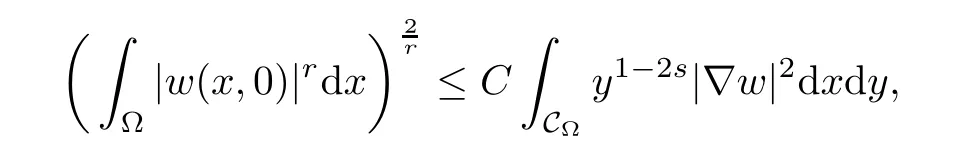
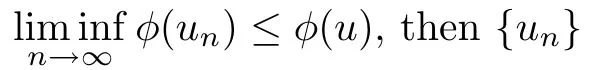

3 Proof of Main Results

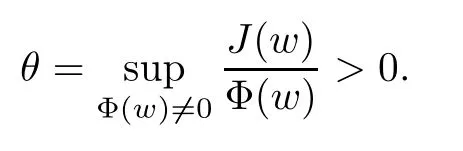
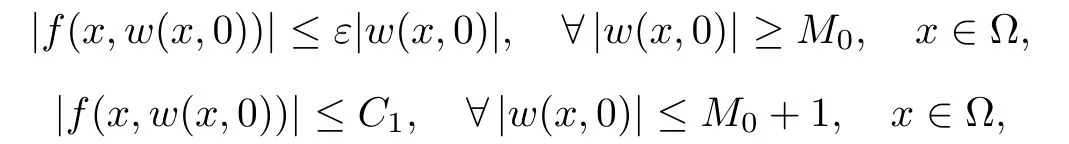
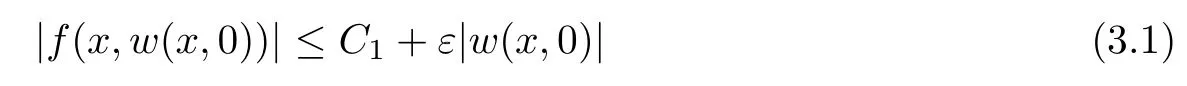
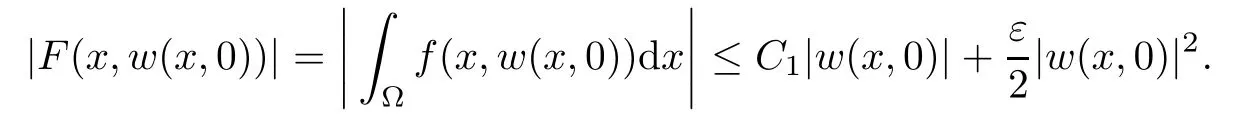
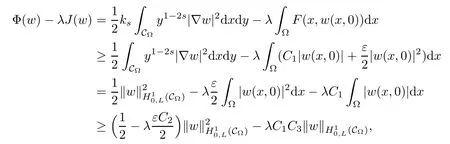
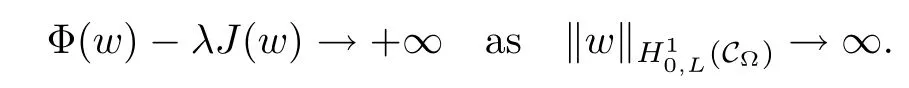
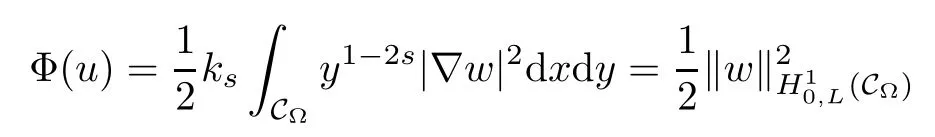
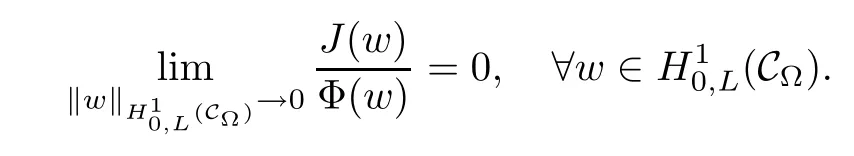

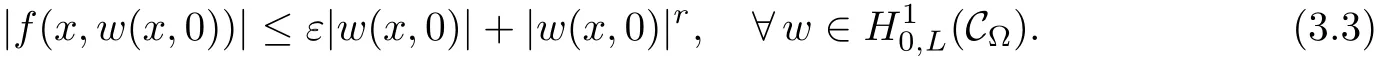
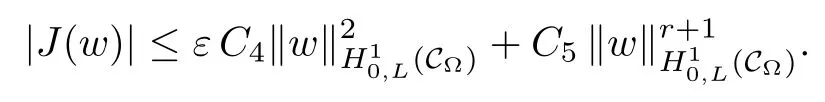
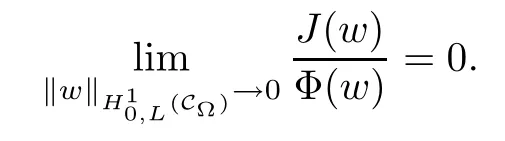
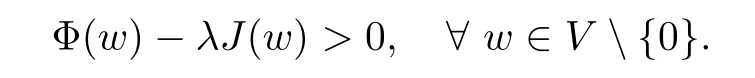
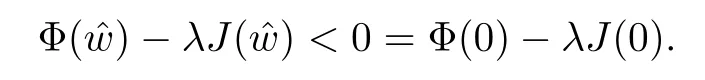
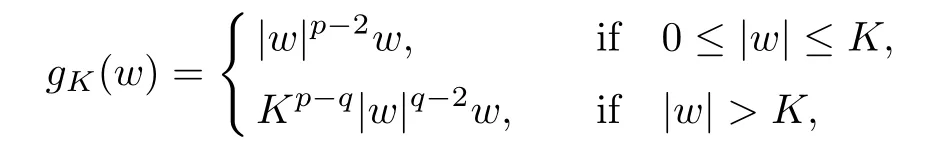
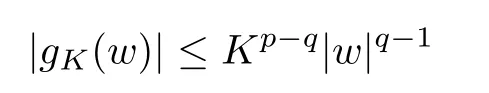
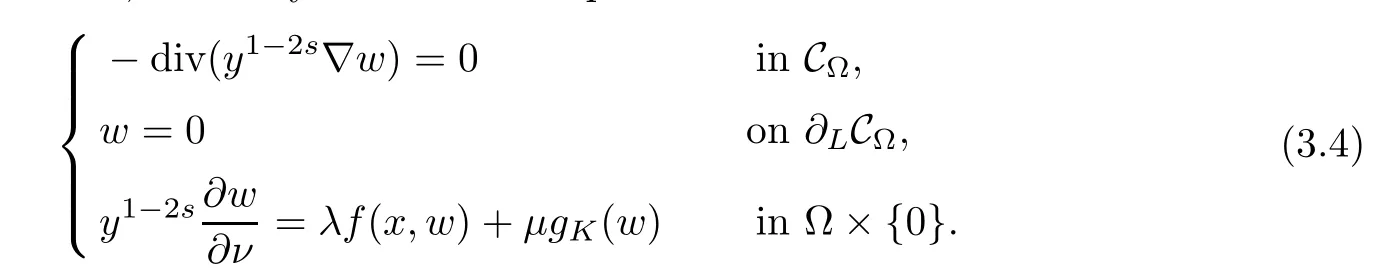
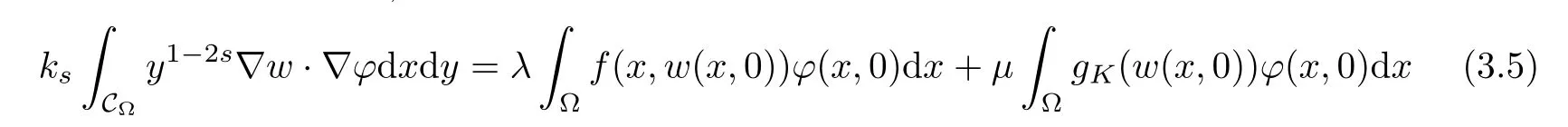
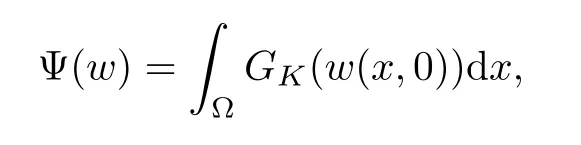
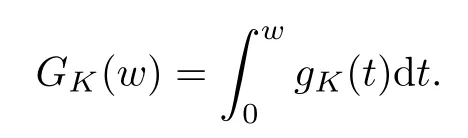

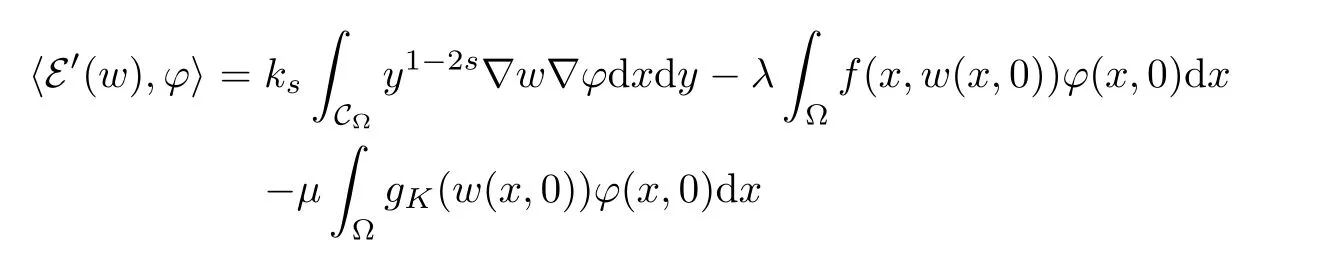
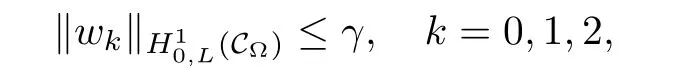
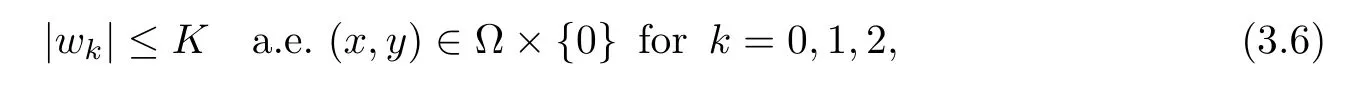
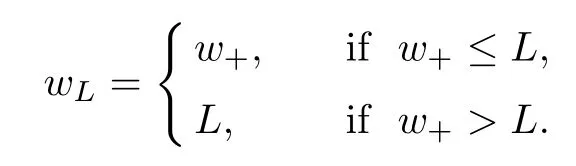
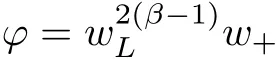
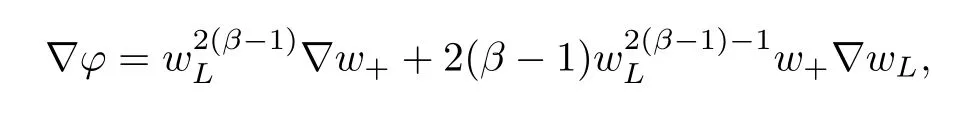
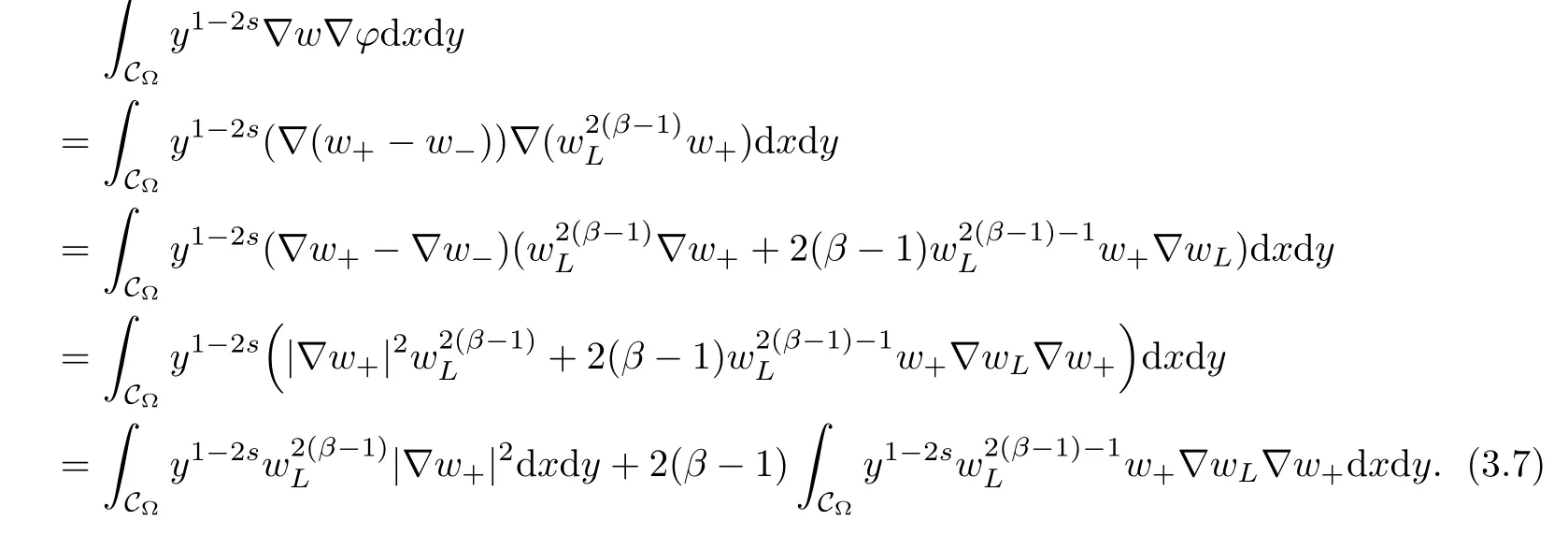
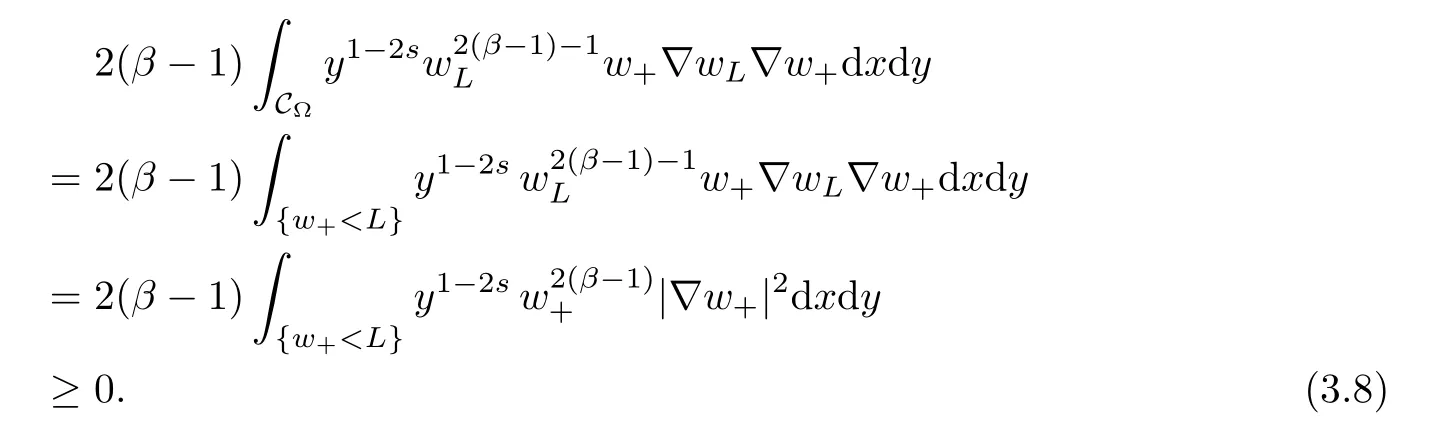
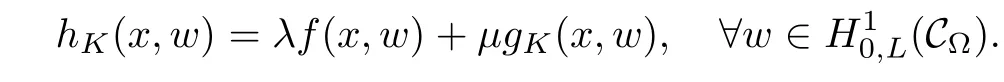
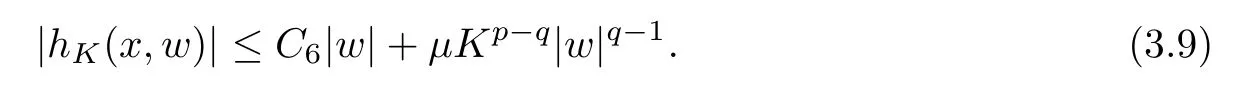
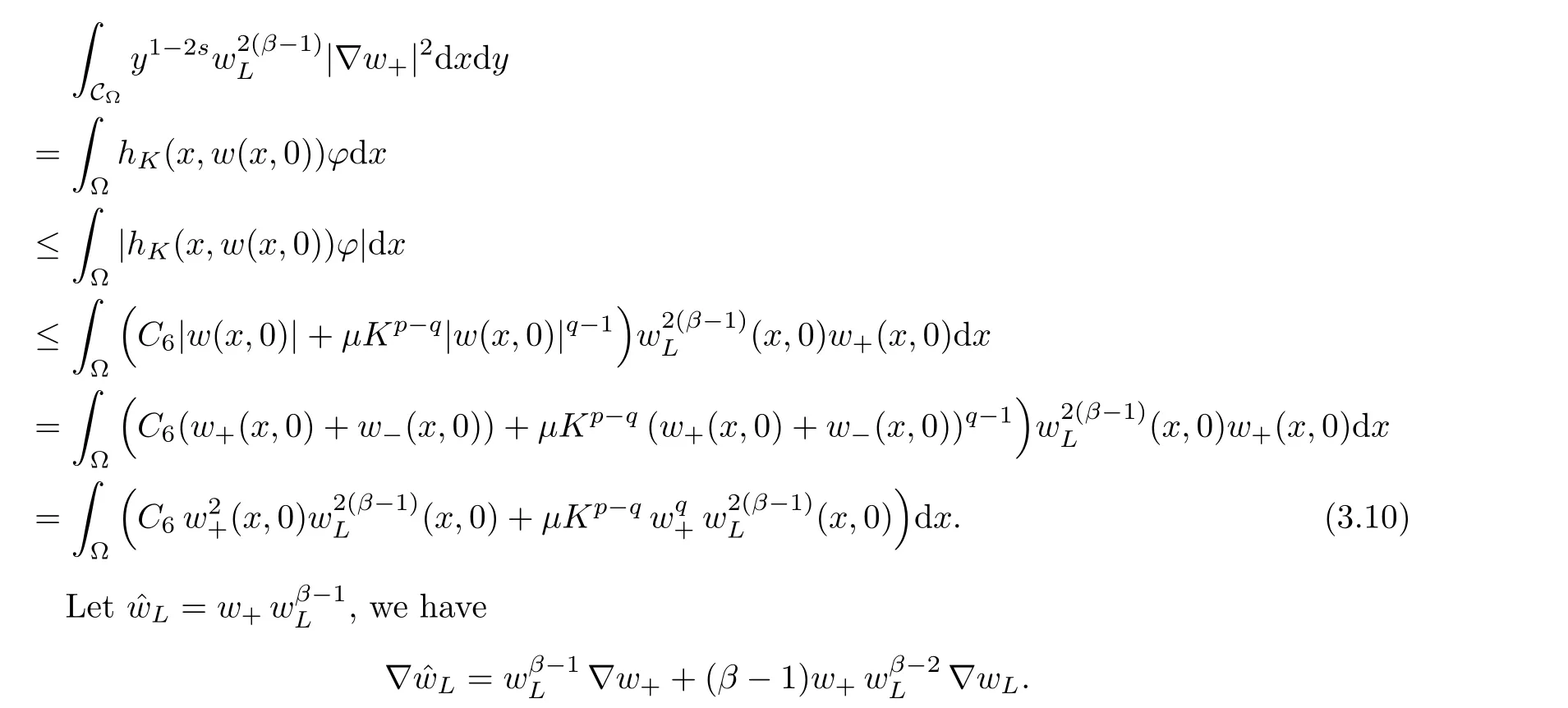
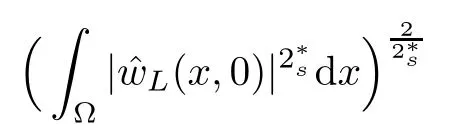
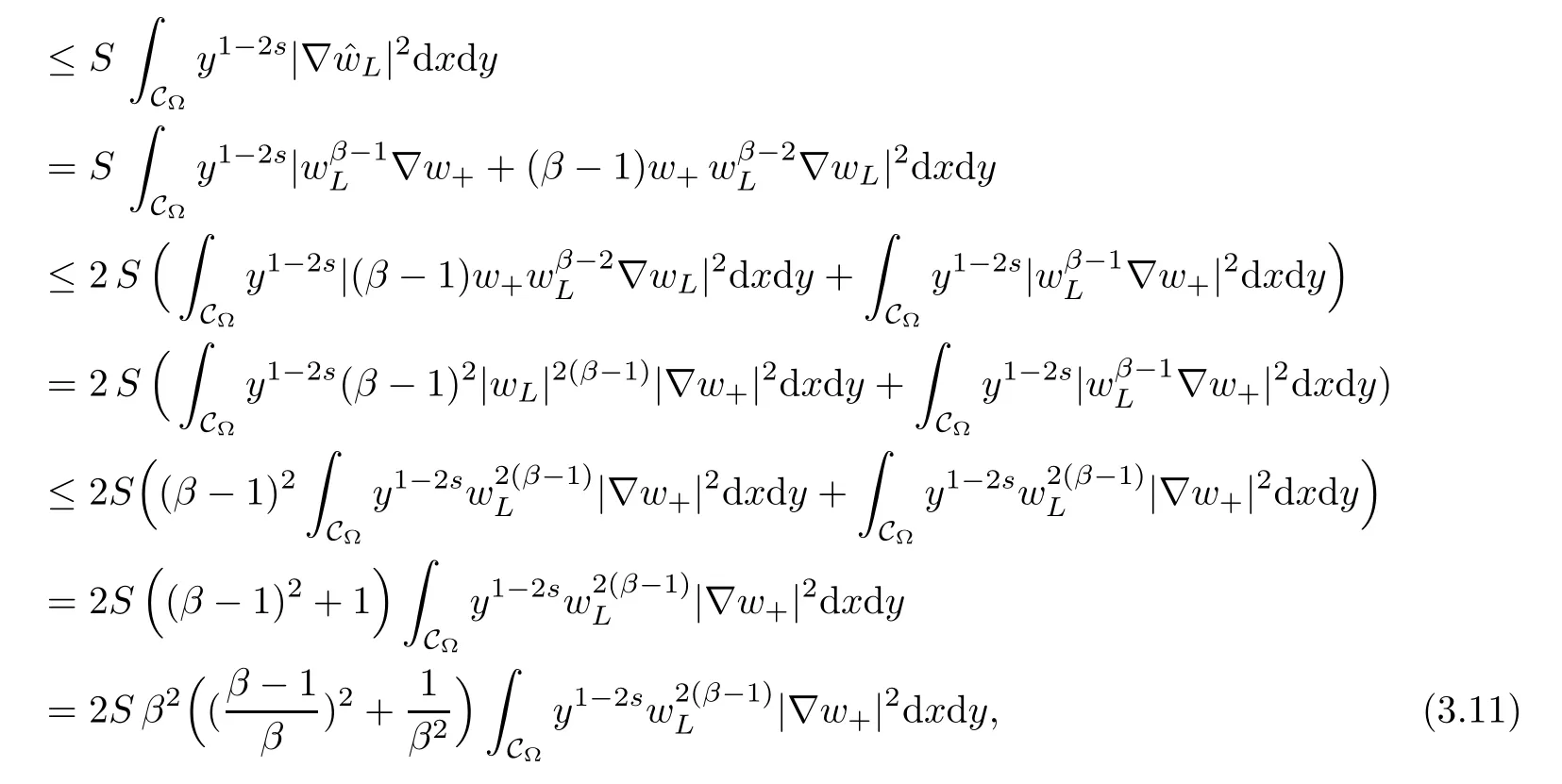
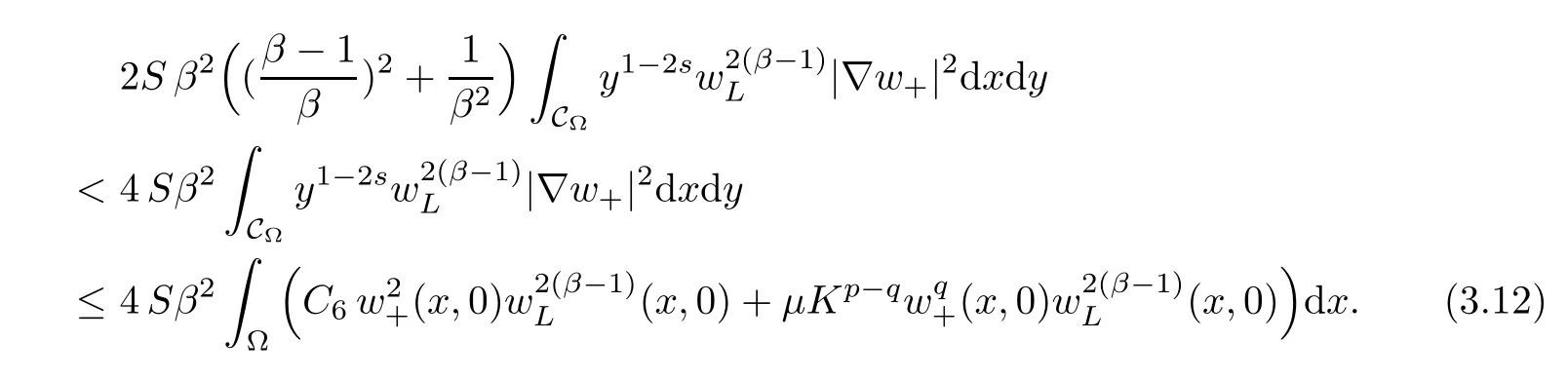
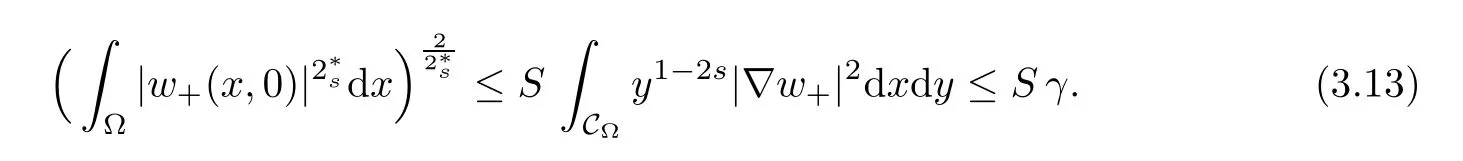
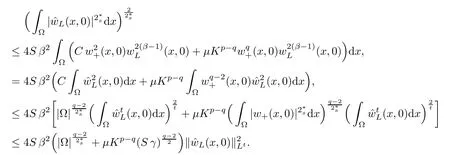
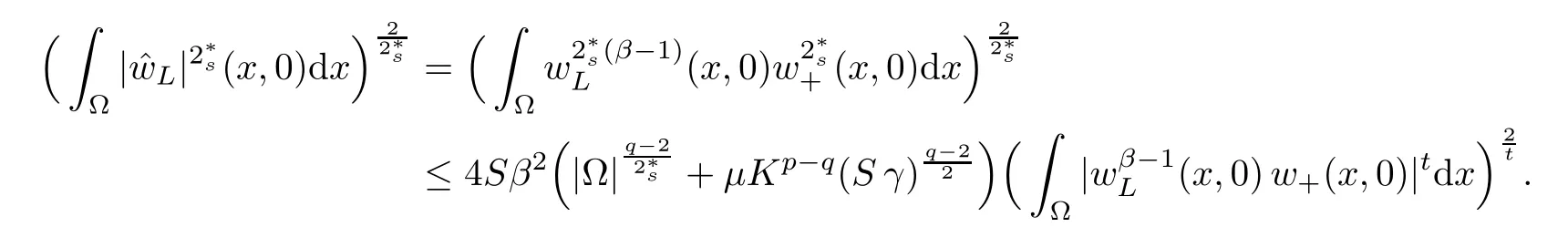


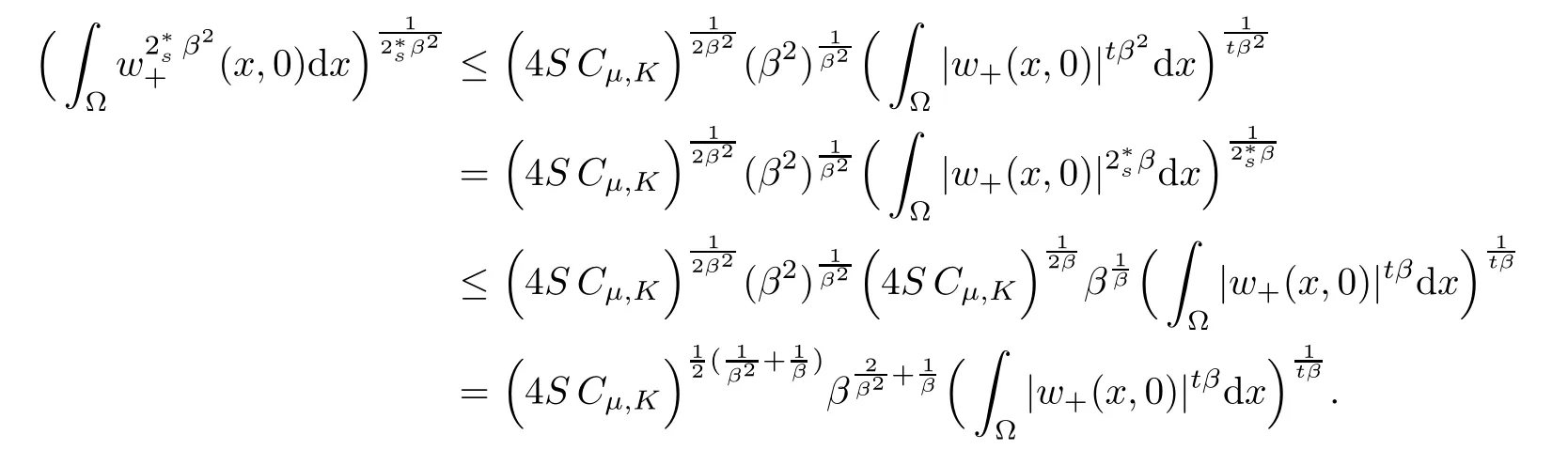
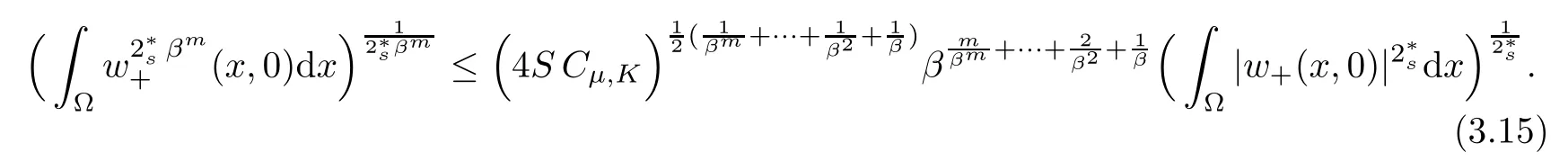
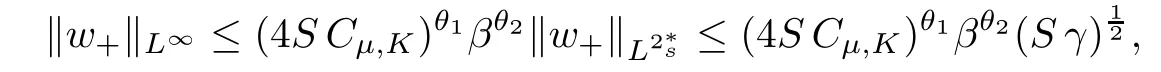

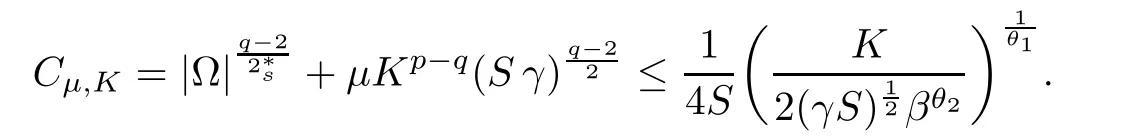
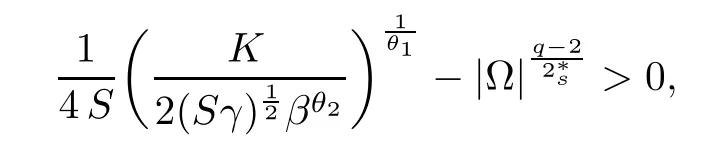
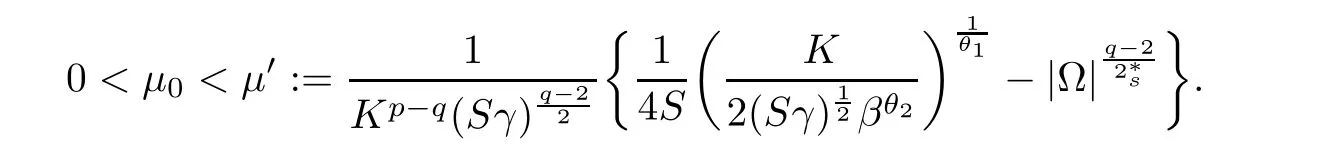
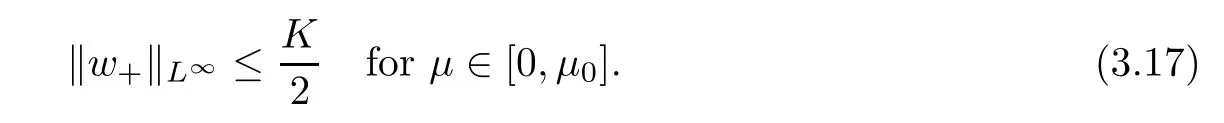
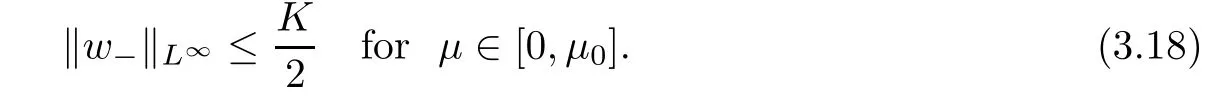
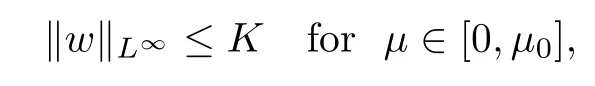
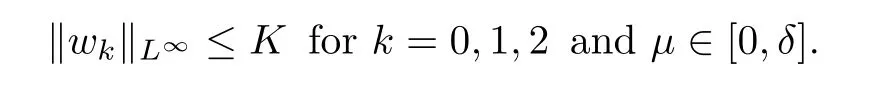
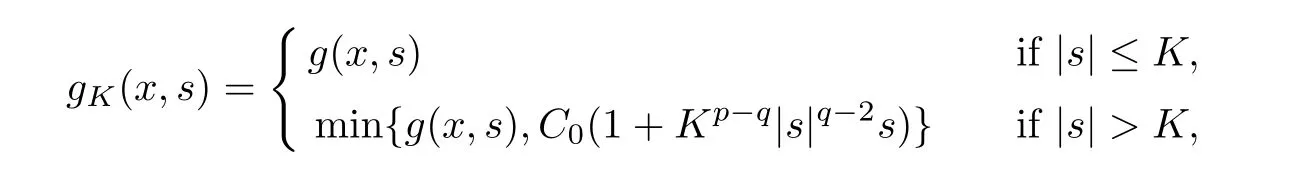
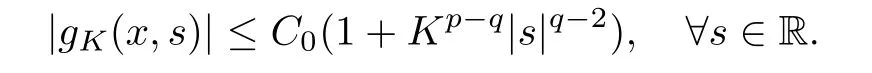
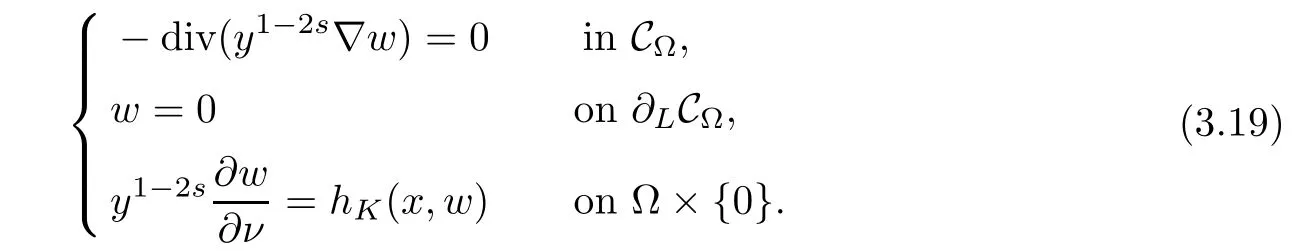
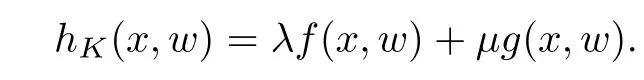
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
