異丙酚抑制高糖誘導的臍靜脈內皮細胞黏附分子表達
游 莉 姜 輝 朱敏敏
(復旦大學附屬腫瘤醫院麻醉科 上海 200032)
異丙酚抑制高糖誘導的臍靜脈內皮細胞黏附分子表達
游 莉▲姜 輝▲朱敏敏△
(復旦大學附屬腫瘤醫院麻醉科 上海 200032)
目的 研究異丙酚抑制高糖誘導的臍靜脈內皮細胞黏附分子的表達并探討其可能的機制。方法 采用Histopaque-1077溶液提取人外周血單核細胞。采用一氧化氮(NO)試劑盒檢測臍靜脈內皮細胞NO生成。采用Western blot檢測內皮細胞黏附分子、內皮型一氧化氮合酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)(總蛋白,單體及雙體)、eNOS磷酸化水平及caveolin-1表達。結果 高糖上調血管內皮細胞黏附分子1(vascular cell adhesion molecule,VCAM-1)的表達,促進單核細胞-內皮黏附,并減少NO生成。異丙酚改善高糖環境下NO生成,并抑制VCAM-1表達及單核細胞-內皮黏附。異丙酚的作用可被eNOS抑制劑L-NAME所拮抗。異丙酚能上調高糖環境下eNOS-Ser1177磷酸化水平及雙體/單體比值,下調高糖環境下eNOS-Thr495磷酸化水平及caveolin-1表達。結論 異丙酚通過調節高糖環境下eNOS的磷酸化水平、單體/雙體比值及caveolin-1表達,改善內皮細胞NO生成,進而抑制內皮細胞黏附分子的表達及單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附。
丙泊酚; 高糖; 臍靜脈; 內皮細胞; 黏附分子
圍術期常見高血糖,主要由圍術期的生理性應激反應及糖輸注過多引起[1-2]。高糖可上調血管內皮細胞黏附分子(vascular cell adhesion molecule,VCAM)的表達[3-5],如VCAM-1。黏附分子表達增加誘導單核細胞-內皮黏附[3],從而導致內皮損傷。對于圍術期高血糖患者,抑制VCAM表達可改善內皮損傷,從而改善高血糖患者預后。
一氧化氮(NO)是調節內皮功能重要信號分子,在維持血管內皮功能中發揮關鍵作用。高糖環境下內皮細胞生成NO的功能受損。研究表明NO生成減少可導致VCAM大量表達并促進單核細胞-內皮黏附,誘導內皮損傷[6-7],而改善NO生成可使VCAM的表達減少[8]。異丙酚能改善缺氧再灌注誘導的VCAM表達[9],但其是否能改善高糖誘導的VCAM表達尚不明確。本文旨在研究異丙酚是否能改善高糖誘導的VCAM表達,并探討其可能的調節機制(圖1)。
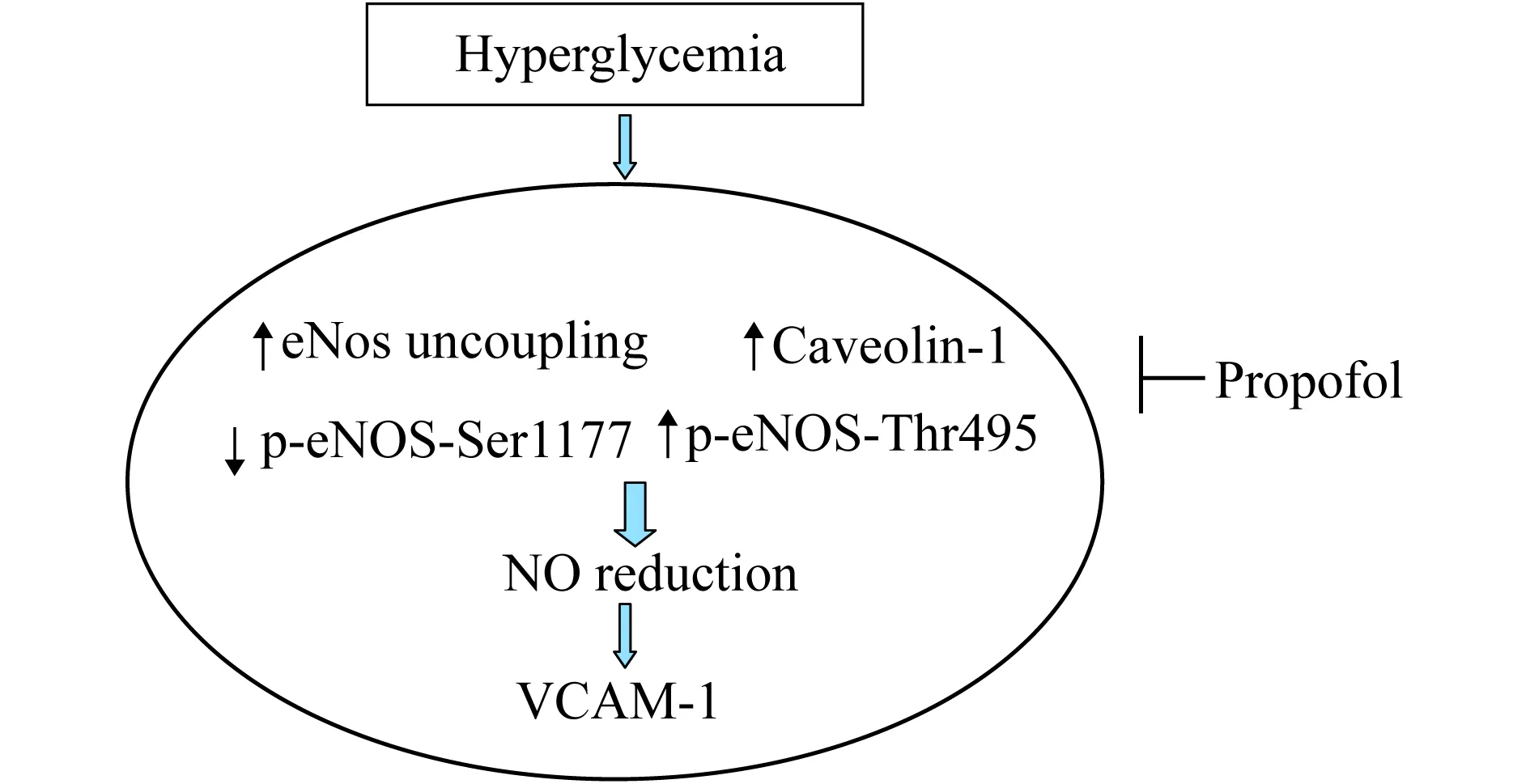
圖1 科學假說示意圖:異丙酚調節高糖誘導的VCAM表達
材料和分組 將臍靜脈內皮細胞分為5組:第1組(對照組)用5mmol/L葡萄糖培養細胞4 h;第2組(高糖組)用30 mmol/L葡萄糖培養細胞4 h;第3組(丙泊酚+高糖組)用5μmol/L丙泊酚預處理細胞30 min,再用30 mmol/L葡萄糖培養細胞4 h;第4組[丙泊酚+內皮型一氧化氮合酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)抑制劑+高糖組]用5μmol/L丙泊酚、eNOS抑制劑L-NAME 100μmol/L預處理細胞30 min,再用30 mmol/L葡萄糖培養細胞4 h;第5組(eNOS抑制劑對照組)用L-NAME 100μmol/L預處理細胞30 min,再用5 mmol/L葡萄糖培養細胞4 h。
單核細胞-內皮細胞黏附實驗 用Histopaque-1077 (美國Sigma公司)試劑分離單核細胞。將5 mL含有單核細胞的肝素化血液轉移到含有Histopaque-1077 (5 mL)的離心管中,室溫下400×g離心30 min,吸出單核細胞并用PBS清洗,離心后用DEMN培養基重懸單核細胞。將單核細胞懸液加入各處理組含內皮細胞的培養皿中,37 ℃孵育30 min。細胞用PBS清洗3遍,去除未與內皮細胞發生黏附的單核細胞,顯微鏡下觀察并計數。
NO生成檢測 采用NO試劑盒(南京建成生物工程研究所)檢測臍靜脈內皮細胞中NO的生成。
Western blot檢測 提取細胞蛋白,等量蛋白經6% SDS-PAGE膠分離,轉移到PVDF膜上。室溫下用含5%脫脂奶粉的TBST溶液封閉1 h,加入相應的一抗,4 ℃孵育過夜。一抗分別為VCAM-1、p-eNOS-Ser1177、p-eNOS-Thr495、eNOS、caveolin-1和β-actin。次日用TBST溶液于室溫下洗膜3次,每次10 min,加入相應的二抗室溫孵育1h,再用TBST洗膜3次,每次10 min,最后曝光顯影。二抗分別為鼠二抗和兔二抗。各組對應蛋白條帶的密度使用scan-gel-it軟件進行分析,β-actin作為內參。對照組中目的蛋白與β-actin蛋白條帶密度的比值設定為1。
結 果
高糖促進單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附(P<0.000 1),其作用可被異丙酚所抑制,并與異丙酚濃度存在劑量依賴關系(圖2A)。高糖可誘導內皮細胞表面VCAM-1表達(P =0.000 2),其作用可被異丙酚預處理所抑制,并同異丙酚預處理的濃度存在劑量依賴關系(圖2B、2C)。5 μmol/L異丙酚預處理可抑制高糖誘導單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附(P<0.000 1)及VCAM-1表達(P=0.001 3)。
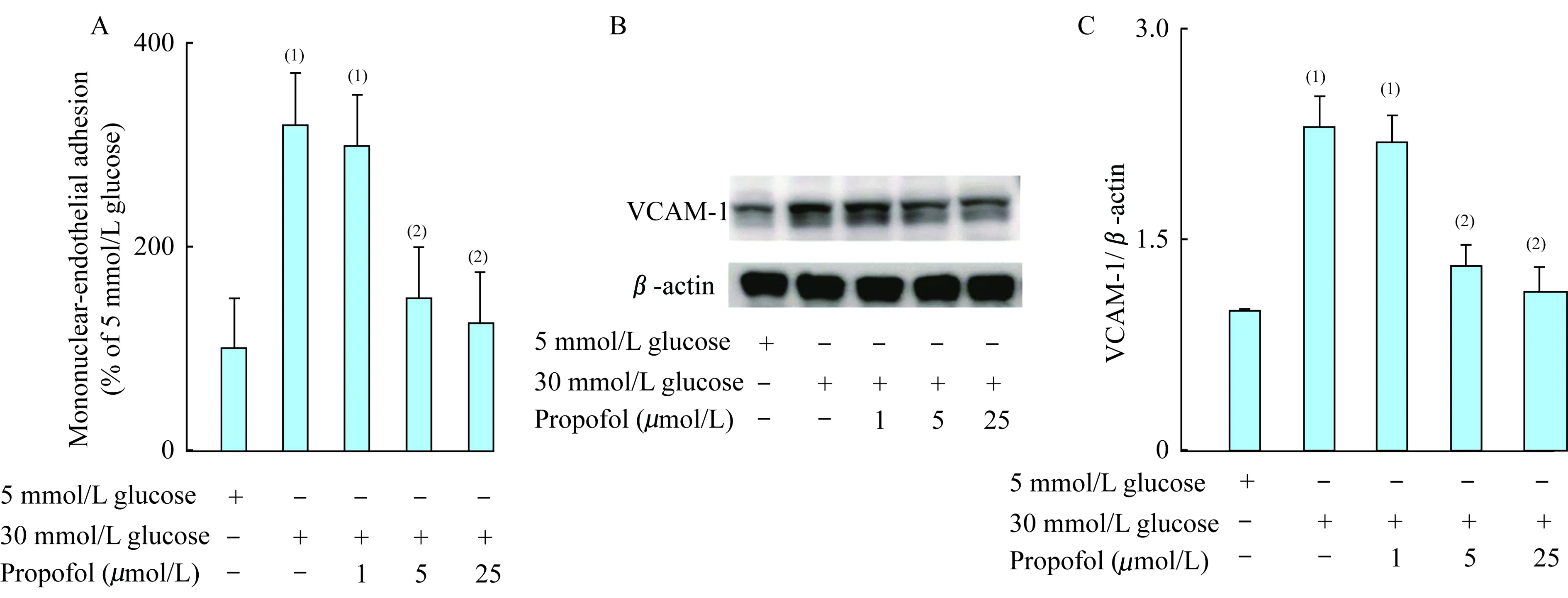
(1)5mmol/L glucose;(2)30 mmol/L glucose.
圖2 異丙酚抑制高糖誘導的單核細胞-內皮黏附及VCAM-1表達
Fig 2 Propofol inhibited high glucose induced monocyte endothelial adhesion and VCAM-1 expression
與對照相比,高糖抑制內皮細胞NO生成(P<0.001)。與高糖處理組相比,異丙酚預處理可以改善NO生成,并與異丙酚的預處理濃度存在劑量依賴關系(圖3)。5μmol/L異丙酚預處理可以改善高糖誘導的NO生成減少(P<0.000 1)。

(1)5 mmol/L glucose;(2)30 mmol/L glucose.
圖3 異丙酚改善高糖環境下臍靜脈內皮細胞NO生成
Fig 3 Propofol improved NO production in umbilical vein endothelial cell with high glucose
相比于5 mmol/L葡萄糖,30 mmol/L高糖可誘導內皮細胞表面VCAM-1的表達。異丙酚預處理可抑制高糖環境下VCAM-1表達,其作用可被eNOS抑制劑L-NAME所拮抗(P=0.002 9,圖4A、4B)。
相比于5mmol/L葡萄糖,30 mmol/L高糖抑制p-eNOS-Ser1177磷酸化水平(P<0.000 1)、上調p-eNOS-Thr495磷酸化水平(P=0.0005)及eNOS表達(P=0.000 4,圖5A、5B)、下調eNOS雙體/單體(P<0.000 1,圖5A、5C)、上調caveolin-1表達(P<0.000 1,圖5A、5D)。5μmol/L異丙酚預處理可以上調高糖環境下p-eNOS-Ser1177磷酸化水平(P=0.001 4)、下調p-eNOS-Thr495磷酸化水平(P=0.001 3,圖5A、5B)、上調eNOS雙體/單體(P=0.000 4,圖5A、5C)、下調caveolin-1表達(P=0.000 3,圖5A、5D)、對eNOS總體表達無影響(P=0.480 8,圖5A、5B)。
討 論
以上研究結果表明30 mmol/L高糖處理上調臍靜脈內皮細胞黏附分子表達,增加單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附。5μmol/L異丙酚的預處理通過改善高糖環境下內皮細胞NO生成,抑制高糖誘導的內皮黏附分子表達及單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附。高糖環境下,5μmol/L異丙酚通過調節內皮細胞eNOS的磷酸化水平、單體/雙體比值及抑制caveolin-1表達來改善NO生成。
以上實驗結果支持了高糖上調內皮黏附分子表達,從而促進單核細胞與內皮細胞的黏附,誘導內皮損傷[3-5];內皮細胞NO生成減少可誘導黏附分子的表達[6-7];改善NO生成可以抑制黏附分子的表達,且可被eNOS抑制劑L-NAME所阻斷[8];高糖通過抑制內皮細胞NO生成,上調黏附分子的表達并促進單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附,誘導內皮損傷。
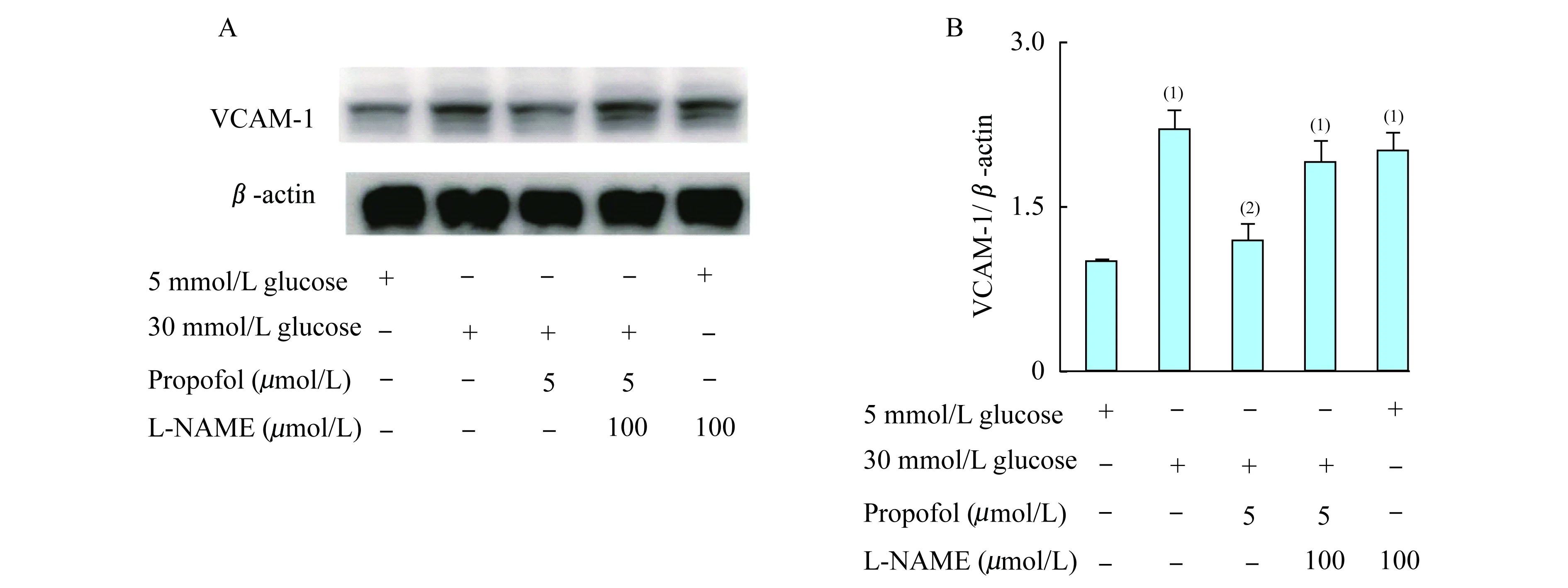
(1)5 mmol/L glucose;(2)30 mmol/L glucose.
圖 4 eNOS抑制劑L-NAME拮抗異丙酚的作用
Fig 4 Effect of propofol converted by the eNOS inhibitor of L-NAME

(1)5 mmol/L glucose;(2)30 mmol/L glucose.
圖5 異丙酚對高糖環境下eNOS磷酸化水平、雙體/單體比值、總表達及caveolin-1表達的影響
Fig 5 Effects of propofol on eNOS phpsphorylation level,morphom/disome ratio,expressions of total eNOS and caveolin-1
eNOS是內皮細胞生成NO的主要來源。eNOS的功能主要由eNOS的表達[10]、磷酸化水平[11]、單體/雙體比值[12]及caveolin-1[13]調節。本研究發現高糖雖然上調eNOS的表達,但其可以抑制eNOS正性調節位點Ser1177磷酸化水平,上調抑制性磷酸化位點Thr495磷酸化水平,增加eNOS單體/雙體的比值,并上調caveolin-1的表達。eNOS主要以雙體形式存在,生成NO而發揮正常的生理功能;但在高糖環境下eNOS發生脫偶聯,此時eNOS不再生產NO,而生成超氧陰離子[14-15]。以上實驗研究一方面表明高糖可影響eNOS的磷酸化水平而減少內皮細胞NO的生成;另一方面,在內皮細胞中大量存在eNOS大量富集的caveolae結構,調控并保持適當的NO水平,在I型糖尿病中caveolin-1表達上調減少NO生成[13],caveolin-1是eNOS上游的負調控因子,與eNOS形成復合物,此時eNOS失去了催化NO產生活性的能力。
異丙酚是臨床上常用的靜脈全麻藥,除鎮靜、催眠外,還具有抗氧化、抗凋亡、抗炎等作用。本研究發現異丙酚具有改善高糖環境下內皮細胞生成NO的作用,而該作用主要通過改善eNOS的功能來實現。首先,5μmol/L異丙酚能改善高糖環境下eNOS的磷酸化水平及單體/雙體比值。一方面支持高糖激活內皮細胞PKC-βⅡ,上調抑制性磷酸化位點eNOS-Thr495的磷酸化水平[16];另一方面支持高糖可以激活PP2A,下調正性磷酸化位點eNOS-Ser1177的磷酸化水平[17];同時支持異丙酚可以抑制PKC-βⅡ及PP2A的活性[18],從而改善高糖環境下eNOS的磷酸化水平。高糖環境下生成的過氧亞硝基陰離子可誘導eNOS發生脫偶聯,異丙酚是強大的過氧亞硝基陰離子清除劑[19],可改善高糖誘導的eNOS脫偶聯。其次,5μmol/L異丙酚能抑制高糖環境下caveolin-1的表達,在平滑肌細胞中異丙酚對eNOS/caveolin-1信號通路有調節作用,能促進NO生成[20]。本研究發現,5μmol/L異丙酚在臍靜脈內皮細胞中對eNOS/caveolin-1信號通路也有調節作用,并能促進NO生成。因此,5μmol/L異丙酚通過調節高糖環境下eNOS的磷酸化水平、單體/雙體比值及caveolin-1表達,改善內皮細胞NO生成,進而抑制VCAM-1的表達及單核細胞-內皮細胞的黏附。雖然eNOS是內皮細胞生成NO的重要來源之一,但是既往研究表明異丙酚不影響高糖環境下eNOS的表達及偶聯狀態[21]。
本研究的不足之處在于,在人臍靜脈內皮細胞中進行的體外實驗不同于體內實驗,尤其是藥物有效性和毒性,且未觀察丙泊酚和高糖對單核細胞的影響。因此,需要進一步確定丙泊酚抑制高糖誘導的單核-內皮細胞黏附作用可否通過單核細胞起作用。
[1] WERB MR,ZINMAN B,TEASDALE SJ,etal.Hormonal and metabolic responses during coronary artery bypass surgery:role of infused glucose[J].JClinEndocrinolMetab,1989,69(5):1010-1018.
[2] WALTS LF,MILLER J,DAVIDSON MB,etal.Perioperative management of diabetes mellitus[J].Anesthesiology,1981,55(2):104-109.
[3] MORIGI M,ANGIOLETTI S,IMBERTI B,etal.Leukocyte-endothelial interaction is augmented by high glucose concentrations and hyperglycemia in a NF-kB-dependent fashion[J].JClinInvest,1998,101(9):1905-1915.
[4] MARLELLA R,ESPOSITO K,GIUNTA R,etal.Circulating adhesion molecules in humans: role of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia[J].Circulation,2000,101(19):2247-2251.
[5] BAUMGARTNER-PARZER SM,WAGNER L,PETTERMANN M,etal.Modulation by high glucose of adhesion molecule expression in cultured endothelial cells[J].Diabetologia,1995,38(11):1367-1370.
[6] DE CATERINA R,LIBBY P,PENG HB,etal.Nitric oxide decreases cytokine-induced endothelial activation.Nitric oxide selectively reduces endothelial expression of adhesion molecules and proinflammatory cytokines[J].JClinInvest,1995,96(1):60-68.
[7] CARTWRIGHT JE,WHITLEY GS,JOHNSTONE AP.Endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression and lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells: effect of nitricoxide[J].ExpCellRes,1997,235(2):431-434.
[8] XIE H,RAY PE,SHORT BL.Rho-kinase contributes to hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cerebral endothelial dysfunction[J].JCardiovascPharmacol,2006;48(1):814-819.
[9] CORCORAN TB,ENGEL A,SHORTEN GD.The influence of propofol on the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in reoxygenated human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J].EurJAnaesthesiol,2006,23(11):942-947.
[10] GRUMBACH IM,CHEN W,MERTENS SA,etal.A negative feedback mechanism involving nitric oxide and nuclear factor kappa-B modulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase transcription[J].JMolCellCardiol,2005,39(4):595-603.
[11] MICHELL BJ,CHEN ZP,TIGANIS T,etal.Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase[J].JBiolChem,2001,276(21): 17625-17628.
[12] RODRIGUEZ-CRESPO I,GERBER NC,ORTIZ DE MONTELLANO PR.Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression in Escherichia coli,spectroscopic characterization,and role of tetrahydrobiopterin in dimerformation[J].JBiolChem,1996,271(19):11462-11467.
[13] XU L,WENJUAN X,YANG W,etal.Upregulation of caveolin-1 contributes to aggravated high-salt diet-induced endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in type 1 diabeticrats[J].LifeSci,2014,113(1-2): 31-39.
[14] XIA Y,TSAI AL,BERKA V,etal.Superoxide generation from endothelial nitric-oxide synthase: a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent and tetrahydrobiopterin regulatory process[J].JBiolChem,1998,273(40):25804-25808.
[15] VASQUEZ-VIVAR J,KALYANARAMAN B,MARTASEK P,etal.Superoxide generation by endothelial nitric oxide synthase: the influence of cofactors[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,1998,95(16):9220-9225.
[16] PANENI F1,MOCHARLA P,AKHMEDOV A,etal.Gene silencing of the mitochondrial adaptor p66(Shc) suppresses vascular hyperglycemic memory in diabetes[J].CircRes, 2012,111(3):278-289.
[17] MICHELL BJ,CHEN Z,TIGANIS T,etal.Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase[J].JBiolChem, 2001,276(21):17625-17628.
[18] ZHU M,CHEN J,WEN M,etal.Propofol protects against angiotensin II-induced mouse hippocampal HT22 cells apoptosis via inhibition of p66Shc mitochondrial translocation[J].NeuromolecularMed,2014,16(4):772-781.
[19] MATHY-HARTERT M,MOUITHYS-MICKALAD A,KOHNEN S,etal.Effects of propofol on endothelial cells subjected to a peroxynitrite donor (SIN-1) [J].Anaesthesia,2000,55(11):1066-1071.
[20] GRIM KJ,ABCEJO AJ,BARNES A,etal.Caveolae and propofol effects on airway smooth muscle[J].BrJAnaesth,2012,109(3): 444-453.
[21] ZHU M,CHEN J,TAN Z,etal.Propofolprotects against high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J].AnesthAnalg,2012,114(2):303-309.
Propofol inhibits high glucose induced expression of endothelial adhesion molecule in umbilical vein endothelial cells
YOU Li▲, JIANG Hui▲, ZHU Min-min△
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,ShanghaiCancerCenter,FudanUniversity,Shanghai200032,China)
Objective To study high glucose induced expressiont of endothelial adhesion molecule inhibited by propofol in umbilical vein endothelial cells,and to investigate its mechanism. Methods Human peripheral mononuclear cells were prepared with Histopaque-1077 solution.Nitric oxide (NO) production was measured with an assay kit.Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) expression,endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) total protein,dimer and monomer expression,eNOS phosphorylation and caveolin-1 were measured by Western blot. Results High glucose induced VCAM-1 expression,increased mononuclear-endothelial adhesion and reduced NO production.Propofol improved NO level,and inhibited VCAM-1 expression and mononuclear-endothelial adhesion.The protective effect of propofol would be blocked by an eNOS inhibitor of L-NAME.Propofol increased high glucose-mediated eNOS-Ser1177phosphrylation and dimmer/monomer ratio,and attenuated high glucose-induced eNOS-Thr495phosphrylation and caveolin-1 expression. Conclusions Propofol improved high glucose mediated eNOS phosphrylation,dimer/monomer ratio and caveolin-1 expression,so that NO production was improved and VCAM-1 expression and mononuclear-endothelial interaction were inhibited.
propofol; high glucose; umbilical vein; endithelial cell; adhesion molecule
R34,R614.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2017.01.013
2016-01-18;編輯:段佳)
▲YOU Li and JIANG Hui contributed equally to this article
△Corresponding author E-mail:zhu_mm@126.com

