真菌性鼻竇炎大鼠鼻竇黏膜組織Maspin、IKKα表達水平及意義
李 琴,謝 瓊
(華中科技大學同濟醫學院附屬荊州醫院耳鼻喉科,湖北 荊州 434020)
真菌性鼻竇炎大鼠鼻竇黏膜組織Maspin、IKKα表達水平及意義
李 琴,謝 瓊*
(華中科技大學同濟醫學院附屬荊州醫院耳鼻喉科,湖北 荊州 434020)
目的 探討真菌性鼻竇炎(FRS)大鼠鼻竇黏膜組織Maspin、IKKα表達水平及意義。方法 40只SD級大鼠建立真菌性鼻竇炎模型,按照隨機數字表法分為鼻塞組、FRS組、免疫抑制劑組、侵襲性FRS組,每組各10只,另選擇10只健康大鼠作為空白對照組;對照組正常喂養;鼻塞組僅鼻腔塞入止血棉,腹腔與鼻腔內給予等體積0.9% NaCl注射液;FRS組腹腔注射等量0.9% NaCl注射液,鼻腔注射煙曲霉菌孢子懸液;免疫抑制劑組腹腔注射環磷酰胺,鼻腔內注射等量0.9% NaCl注射液;侵襲性FRS組腹腔注射環磷酰胺、鼻腔注射煙曲霉菌孢子懸液建立侵襲性FRS大鼠模型。采用酶聯免疫吸附試驗檢測血清白細胞介素6(IL-6)、腫瘤壞死因子α(TNF-α)表達水平;免疫組織化學染色法檢測各組大鼠鼻腔組織Maspin、IKKα蛋白表達水平,熒光定量PCR法檢測各組大鼠鼻腔組織Maspin mRNA、IKKα mRNA表達水平。結果 各組大鼠血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較差異有顯著性(P< 0.05),其中FRS組血清IL-6、TNF-α顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組和侵襲性FRS組【(69.3±10.9)ng/L vs(45.2±7.1) ng/L,(46.4±6.7) ng/L,(21.3±4.5) ng/L,(20.9±4.3) ng/L;(30.4±4.8) ng/L vs(14.8±2.7) ng/L,(13.9±1.4) ng/L,(7.9±0.6) ng/L,(7.8±0.4) ng/L】(P< 0.05),對照組血清IL-6、TNF-α又顯著高于免疫抑制劑組和侵襲性FRS組(P<0.05),免疫抑制劑組、侵襲性FRS組間血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較差異無顯著性(P> 0.05)。免疫組織化學染色結果顯示FRS組、侵襲性FRS組Maspin蛋白表達水平顯著低于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,IKKα蛋白表達水平顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組(P< 0.05);其中侵襲性FRS組Maspin蛋白表達顯著低于FRS組,IKKα蛋白表達則顯著高于FRS組(P< 0.05)。FRS組、侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA表達水平顯著低于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,IKKα mRNA表達水平顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組(P< 0.05);其中侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA表達顯著低于FRS組,IKKα mRNA表達顯著高于FRS組(P< 0.05)。結論 IKKα活化后下調Maspin表達是導致FRS發病的主要原因,這一過程可能也是侵襲性FRS分子作用機制之一。
真菌性鼻竇炎;侵襲性真菌性鼻竇炎;乳腺絲氨酸蛋白酶抑制劑;IκB激酶α;侵襲;細胞因子
近年來隨著廣譜抗菌藥物、免疫抑制劑、激素等廣泛使用,導致真菌性感染疾病發生率呈上升趨勢[1,2],其中真菌性鼻竇炎(fungal rhinosinusitis,FRS)是常見的真菌感染性疾病。按照組織侵犯程度不同,FRS分為侵襲性FRS和非侵襲性FRS兩種類型[3],侵襲性FRS病情較重,一旦急性發病可以在短時間內向周圍毗鄰器官侵襲而導致患者死亡,因此掌握侵襲性FRS的發病機制,對制訂預防措施、改善患者預后具有重要意義。導致FRS的誘因較多,其中免疫功能與FRS的發病、疾病分型密切相關。當患者免疫功能低下時,極易誘發FRS,因此器官移植、老年人群、長期使用糖皮質激素者均是FRS感染的高發人群[4]。國外研究[5]證實乳腺絲氨酸蛋白酶抑制劑(mammary serine proteinase inhibitor,Maspin)是導致真菌侵襲的主要病毒素;而最近研究發現IκB激酶α(IκB kinase α,IKKα)在晚期惡性腫瘤中能夠被炎性因子激活[6],進而下調Maspin蛋白的表達,最終介導腫瘤的浸潤轉移。然而在FRS中是否存在炎性介質介導IKKα活化,并下調Maspin蛋白這一過程目前尚不得而知。鑒于此,本研究對FRS大鼠呼吸道上皮細胞炎性因子、IKKα、Maspin表達情況進行研究,旨在探討侵襲性FRS的發病機制,現將研究成果總結如下。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
50只雄SD級性Wistar大鼠【SCXK(鄂)2015-009】均購自華中科技大學同濟醫學院動物實驗中心【SYXK(鄂)2014-0049】,周齡10 ~ 14周,平均(12.5±3.1)周,體質量240 ~ 260 g,平均(252±5)g;于20 ~ 22℃、相對濕度55%的條件下籠中飼養,12 h晝夜交替,所有大鼠飲用水均經過高溫滅菌處理,所有大鼠自由進食進水。本實驗經醫院動物倫理委員會批準。
1.2 試劑與儀器
煙曲霉菌AF293由本實驗室按照美國臨床實驗室標準化研究所標準自制,培養基購自青島科瑞培養基有限公司,IKKα、Maspin單克隆抗體購自圣克魯斯生物技術公司(美國),RT逆轉錄試劑盒購自羅氏公司,羊抗兔IgG抗體購自武漢博士德生物工程有限公司, 白細胞介素6(interleukelin-6,IL-6)、腫瘤壞死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)購自上海基免實業有限公司;熒光定量PCR儀購自美國ABI公司,倒置顯微鏡購自日本奧林巴斯公司。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 動物分組與模型建立
將50只大鼠按照隨機數字表法分為5組:空白對照組、鼻塞組、FRS組、免疫抑制劑組、侵襲性FRS組,各10只。首先將煙曲霉菌AF293在培養基中以37℃條件下培養5 ~ 7 d,再將分生孢子收集后用磷酸緩沖鹽溶液(phosphate buffer saline,PBS)沖洗,以離心力800 g離心10 min后再次用PBS洗滌,取得煙曲霉菌孢子懸液,調整細胞懸液濃度1×107個/mL。空白對照組:不做任何處理,正常喂養。侵襲性FRS組:大鼠腹腔注射水合氯醛(濃度10%)3 mL/kg,待大鼠完全麻醉,將面積約為2 mm × 2 mm × 10 mm 大小的Merocel 高分子止血棉(美國施美德公司)塞入大鼠左側鼻腔,至第7日腹腔注射環磷酰胺100 mg/kg,每3日 1次,連續注射2次;至第11日大鼠吸入乙醚麻醉,將煙曲霉菌孢子懸液50 μL緩慢注射至左側鼻腔。第13日局部檢測鼻腔分泌物,以病原菌培養存在煙曲霉菌作為建模成功的標準。鼻塞組:僅在大鼠左側鼻腔塞入Merocel 高分子止血棉,腹腔與鼻腔內給予等體積0.9% NaCl注射液代替環磷酰胺和煙曲霉菌孢子懸液,注射方法同侵襲性FRS組。FRS組:鼻腔塞入Merocel 高分子止血棉,腹腔注射等量0.9% NaCl注射液代替環磷酰胺,鼻腔注射煙曲霉菌孢子懸液,注射方法同侵襲性FRS組。免疫抑制劑組:腹腔注射環磷酰胺,鼻腔內注射等量0.9% NaCl注射液代替煙曲霉菌孢子懸液,注射方法同侵襲性FRS組。建模成功后繼續飼養7 d,然后處死。本試驗大鼠造模均獲得成功。
1.3.2 血清細胞因子檢測
于模型建立第7日采集各組大鼠尾部靜脈血3 mL,離心5 min(離心半徑8 cm)分離血清,采用酶聯免疫吸附試驗檢測血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平,檢測操作參考試劑盒說明書。
1.3.3 鼻腔組織Maspin、IKKα蛋白檢測
待尾靜脈取血結束后,各組大鼠均腹腔注射100 mg/kg氯胺酮,大鼠麻醉后脫臼斷頭,將大鼠面部皮毛和軟組織完全剔除,取鼻吻部至雙眼前緣的平面組織,于4%甲醛中固定3 d,常規石蠟包埋制成鼻竇組織切片。從液氮中取出組織樣本,手術剪將樣本剪成小塊,超聲粉碎,打成勻漿,加入蛋白提取液4℃振蕩過夜,15000 r/min離心50 min,提取上清液,Bradford法檢測蛋白濃度。采用聚丙烯酰胺凝膠上樣,每個泳道加入30 μg總蛋白,常規方法轉移至PVDF膜,再加入5%脫脂牛奶封閉2 h。分別加入IKKα、Maspin單克隆抗體作為一抗,4℃封閉過夜。PBS洗滌3次,再加入1∶5000稀釋的二抗37℃孵育2 h。PBS沖洗后加入按照ECL化學發光顯影試劑盒顯影并測量光密度值,以目的蛋白與β-actin蛋白光密度的比值作為目的蛋白相對表達量。
1.3.4 鼻腔組織Maspin、IKKα mRNA表達檢測
取各組大鼠鼻黏膜組織30 ~ 50 mg,加入1 mL Trizol RNA總提取液,制成勻漿后再加入100 μL氯仿,振蕩混勻后800 g離心10 min, 70%乙醇洗滌3次,提取總RNA。按照RT反轉錄試劑盒說明書,取1 μg總RNA逆轉錄得到互補DNA,以β-actin作為內參,采用實時熒光定量PCR分別擴增Maspin、IKKα基因,設置反應體系:模板7.5 μL,上游引物0.5 μL,下游引物0.5 μL,cDNA1.5 μL,雙蒸水 8 μL,總反應體系18 μL。反應條件:95℃預變性5 min,92℃ 30 s,72℃延伸45 s,總計45個循環。Maspin mRNA引物序列:上游:5′-TCGCGAGCTT GCTTGGCGAC-3′,下游:5′-GCTGTCAGGCGCGC TGCGATA-3′,擴增片段長度201 bp;IKKα mRNA引物序列:上游:5′-GTGACATAAGTTCGGACTGCG-3′,下游:5′-TTTCGATTACATCGCGGAGCT-3′,擴增片段長度276 bp;β-actin引物序列:上游:5′-CAGAGC TAGAACACGGCAGCG-3′,下游:5′-TGCGGCGATGG CTAGGCGTGA-3′,擴增片段長度463 bp。按照下列公式計算目的基因相對表達量:基因相對表達量=2-△Ct,△Ct=Ct(目的基因)- Ct(β-actin)。
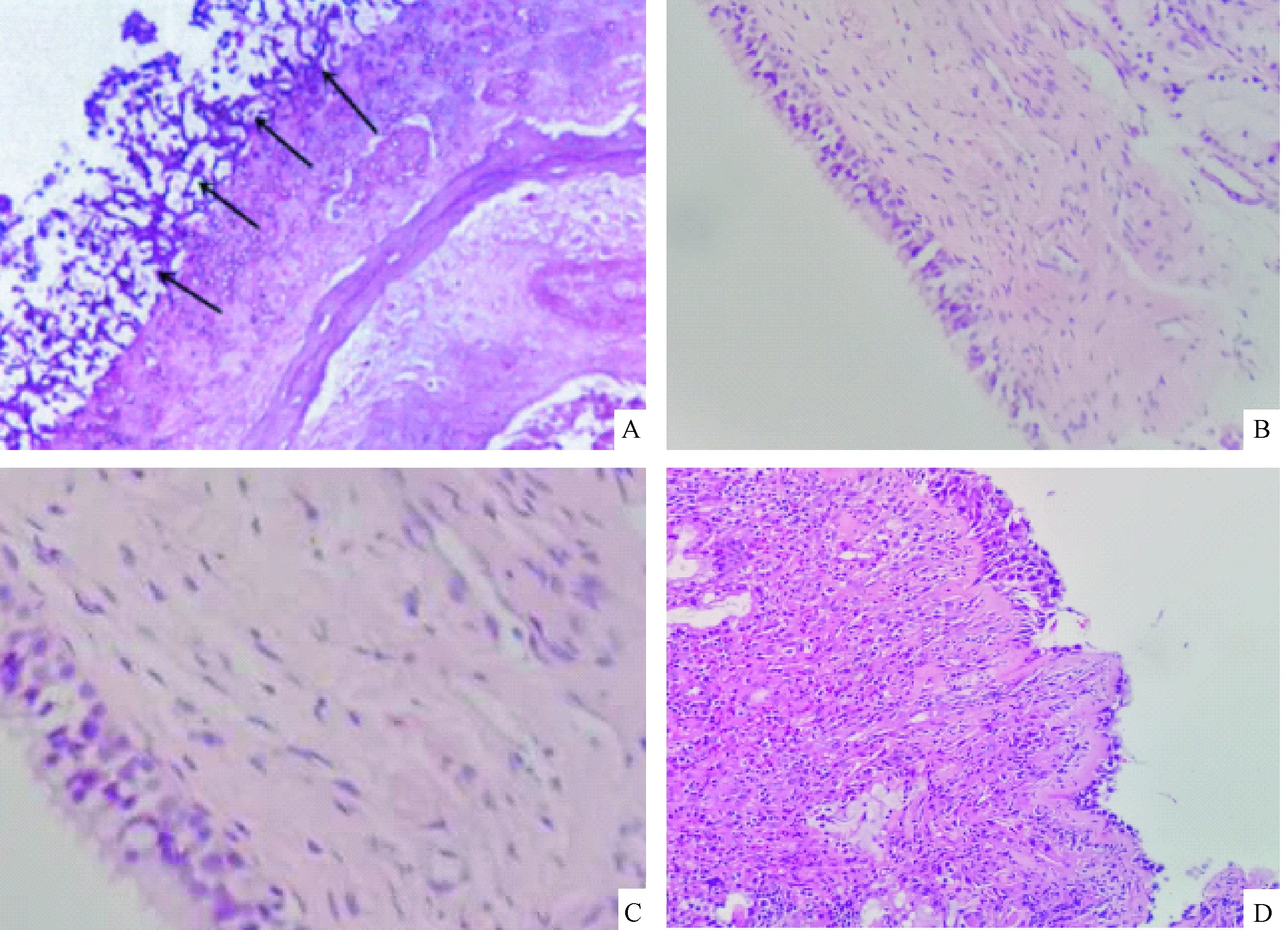
注:A:侵襲性FRS組 鼻竇黏膜組織內可見大量真菌(黑色箭頭所指處);B:對照組 上皮完整;C:免疫 抑制劑組 上皮細胞連續完整,少量淋巴細胞浸潤;D: FRS組 上皮不完整,伴有大量淋巴細胞浸潤。(SP法,×200)圖1 各組大鼠鼻竇黏膜組織的形態學改變Note. A. large number of fungi were found in the nasal mucosa of a rat from the invasive FRS group; B. Intact epithelium of a normal control rats; C. a rat from the Immunosuppressive group, showing intact epithelium with sparse lymphocyte infiltration; D. a rat from the FRS group, incomplete epithelium and extensive lymphocyte infiltration in the sinusoidal mucosa of a rat from the FRS group.Fig.1 Histological changes of sinusoidal mucosa in each group of rats
1.4 統計學方法
2 結果
2.1 病理檢查結果
大體觀察:對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組大鼠鼻腔黏膜正常;FRS組可見鼻腔內黏膜水腫,鼻腔出現大量分泌物,但是鼻竇組織未見破壞;侵襲性FRS組鼻腔內可見大量血性分泌物,鼻竇結構發生破壞,并伴有干酪樣壞死組織。PAS染色及顯微鏡觀察:侵襲性FRS組鼻腔組織存在大量真菌,鼻竇處有真菌侵犯血管,并伴有組織壞死、組織破壞,在壞死組織周圍能夠發現有嗜酸性細胞、中性粒細胞和淋巴細胞散在分布;對照組鼻腔上皮完整,未見有炎性浸潤;鼻塞組、鼻塞+免疫抑制劑鼻竇黏膜上皮連續完整,在上皮周圍可見少量淋巴細胞浸潤;FRS組上皮不完整,上皮周圍存在大量淋巴細胞浸潤,但鼻竇周圍未見真菌感染,周圍組織也未見侵入,見圖1。
2.2 各組大鼠血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較
各組大鼠血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較差異有顯著性(P< 0.05),FRS組血清IL-6、TNF-α顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組和侵襲性FRS組(P< 0.05),對照組血清IL-6、TNF-α又顯著高于免疫抑制劑組和侵襲性FRS組,免疫抑制劑組、侵襲性FRS組間血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較差異無顯著性(P> 0.05),見表1。
2.3 各組大鼠組織Maspin、IKKα蛋白表達水平比較
FRS組、侵襲性FRS組Maspin蛋白表達水平顯著低于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,FRS組、侵襲性FRS組IKKα蛋白表達水平顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組(P< 0.05);其中侵襲性FRS組Maspin蛋白表達顯著低于FRS組,IKKα蛋白表達顯著高于FRS組,見表2。
2.4 各組大鼠組織Maspin、IKKα mRNA表達水平比較
實時熒光定量PCR分析顯示FRS組、侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA表達水平顯著低于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,IKKα mRNA表達水平顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組(P< 0.05);其中侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA表達顯著低于FRS組,IKKα mRNA表達顯著高于FRS組(P< 0.05),見表3。
表1 各組大鼠血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平比較Tab.1 Comparison of the serum expression of IL-6 and TNF-α in the groups of rats
注:與免疫抑制劑組比較,aP< 0.05;與FRS組比較,bP< 0.05;與侵襲性FRS組比較,cP< 0.05。
Note. Compared with the immunosuppressive group,aP< 0.05; Compared with the FRS group,bP< 0.05; Compared with the invasive FRS group,cP< 0.05.
表2 各組大鼠組織Maspin、IKKα蛋白表達水平比較Tab.2 Comparison of the expression of Maspin and IKKα protein in each group
注:與FRS組比較,aP< 0.05;與侵襲性FRS組比較,bP< 0.05。
Note. Compared with the FRS group,aP< 0.05; Compared with the invasive FRS group,bP< 0.05.
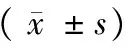
表3 各組大鼠組織Maspin、IKKα mRNA表達水平比較Tab.2 Comparison of the expression of Maspin and IKKα mRNA in each group
注:與FRS組比較,aP< 0.05;與侵襲性FRS組比較,bP< 0.05。
Note. Compared with the FRS group,aP< 0.05; Compared with the invasive FRS group,bP< 0.05.
3 討論
真菌性鼻竇炎分為侵襲性和非侵襲性兩種,其中侵襲性鼻竇炎患者預后較差,當侵犯至顱內時甚至導致患者死亡。關于FRS的發病機制目前仍不完全清楚,有研究顯示免疫功能低下是導致FRS的主要誘因[7,8]。王立朋等[9]報道稱免疫正常的宿主存在的上皮細胞層和吞噬細胞能夠對真菌的侵襲起到良好的防御能力,吞噬細胞在殺滅真菌孢子時會產生大量細胞因子,而細胞因子又會進一步誘導和激活淋巴細胞、中性粒細胞等,從而增強宿主對真菌的抵抗能力。然而對于存在免疫缺陷的患者,吞噬細胞的活性及細胞因子產生能力均有所降低,導致宿主正常的防御屏障不足以抵抗真菌的感染,使得真菌孢子與呼吸道上皮細胞粘連,而這一過程常提示發展結局為侵襲性FRS[10]。本研究顯示FRS組血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平最高,FRS組血清IL-6、TNF-α表達水平最高,說明免疫抑制導致的炎性細胞和抗炎細胞失衡是侵襲性FRS發病的主要原因之一。
侵襲性FRS的免疫應答反應有賴于免疫細胞表面受體對真菌的識別,并通過釋放細胞因子、趨化因子等殺滅真菌[11]。正常情況下宿主對真菌的免疫應答反應需要跨膜受體的級聯反應,國外研究[12]證實Toll樣受體(Toll-like receptor,TLR)介導的核因子κB(nuclear Factor κB,NF-κB)信號通路信號途徑異常會導致抗炎和促炎因子表達失衡,從而誘導腫瘤細胞發生侵襲、轉移。IKKα是調控NK-κB信號途徑的關鍵蛋白,在另一項研究中發現,細胞因子能夠誘導宿主內源性IKKα表達異常升高,從而結合并抑制Maspin啟動子,導致Maspin表達下調[13]。Maspin能夠促進細胞與細胞外基質發生黏附作用,進而抑制細胞發生遷移。張芳等[14]發現絲氨酸蛋白酶抑制劑能夠與抗真菌藥起到協同治療作用,該研究進而發現絲氨酸蛋白酶是促進真菌發生侵襲的關鍵酶,因而作為乳腺絲氨酸蛋白酶的抑制劑:Maspin蛋白可能在真菌侵襲中發揮著類似的作用。
本研究顯示FRS組、侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA和蛋白表達水平顯著低于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,IKKα mRNA和蛋白表達水平顯著高于對照組、鼻塞組、免疫抑制劑組,提示Maspin在FRS的發病中起到重要作用,這一過程可能與腫瘤細胞的侵襲、轉移過程類似。進一步研究發現侵襲性FRS組Maspin mRNA和蛋白表達顯著低于FRS組,IKKα mRNA和蛋白表達顯著高于FRS組,說明IKKα、Maspin共同參與了真菌的侵襲。兩者的參與過程可能是炎性因子激活IKKα表達,從而下調Maspin表達水平,導致真菌從呼吸道上皮細胞中發生脫落,進而向周圍組織侵襲[15-17]。Luo等[18]報道稱在免疫功能正常的宿主中IKKα活化未下調Maspin表達,推測IKKα雖然能夠下調Maspin表達,但是這種調節水平可能并不存在直接線性關系,在接下來的研究中也將就此進行深入研究。
綜上所述,IKKα活化后下調Maspin表達是導致FRS發病的主要原因,這一過程可能也是侵襲性FRS分子作用機制之一。
[1] Ragab A, Samaka RM, Salem M. Impact of fungal load on diagnosis and outcome of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis [J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(1): 93-101.
[2] Thurtell MJ, Chiu AL, Goold LA, et al. Neuro-ophthalmology of invasive fungal sinusitis: 14 Consecutive patients and a review of the literature [J].Clin Experiment Ophthalmol, 2013, 41(6): 567-576.
[3] Hatten KM, Loevner LA, Palmer JN, et al. Isolated sinonasal posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder: A clinical and radiographic invasive fungal sinusitis look-a-like [J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2012, 74(6): 339-342.
[4] 吳峰, 吳立連, 朱立新, 等. 真菌性鼻-鼻竇炎發病相關的危險因子和臨床表現探討 [J].臨床與病理雜志, 2015, 35(10): 1794-1798.
[5] Sharma G, Mirza S, Parshad R, et al. Clinical significance of Maspin promoter methylation and loss of its protein expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma: correlation with VEGF-A and MTA1 expression [J]. Tumour Biol, 2011, 32(1): 23-32.
[6] Maier HJ, Schips TG, Wietelmann A, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific IκB kinase (IKK)/NF-κB activation induces reversible inflammatory cardiomyopathy and heart Failure [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109(29): 11794-11799.
[7] 梁曉, 張允嶺, 王新祥, 等. 清熱活血組分對急性腦梗死火毒證大鼠NF-κB炎癥信號通路調控作用研究?[ J].北京中醫藥大學學報, 2015, 38(6): 377-382.
[8] Petrova RD, Mahajna J, Wasser SP, et al. Marasmius oreades substances block NF-κB activity through interference with IKK activation pathway [J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2009, 36(4): 737-744.
[9] 王立朋, 秦榛, 夏云, 等. 侵襲性曲霉菌感染的診斷方法及臨床應用 [J]. 中國老年學雜志, 2015, 35(2): 523-525.
[10] LeBlanc RE, Meriden Z, Sutton DA, et al. Cunninghamella echinulata causing fatally invasive fungal sinusitis [J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 2013, 76(4): 506-509.
[11] Maschio M, Mengarelli A, Girmenia C, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia as unusual isolated symptom of fungal paranasal sinusitis in patients with haematological malignancies [J]. Neurol Sci, 2012, 33(3): 647-652.
[12] Kerekes J, Kaspari M, Stevenson B, et al. Nutrient enrichment increased species richness of leaf litter fungal assemblages in a tropical forest [J]. Mol Ecol, 2013, 22(10): 2827-2838.
[13] 龐俊, 湛海倫, 劉偉鵬, 等. 腫瘤RNA轉染DCs與同源CIKs共培養調控Akt/NF-κB細胞生存信號通道的實驗研究 [J]. 中國現代醫學雜志, 2010, 20(18): 2729-2732.
[14] 張芳, 安云芳, 趙長青, 等. 煙曲霉菌誘導大鼠呼吸道上皮細胞IKKα調控maspin蛋白表達的初步研究 [J]. 中華耳鼻咽喉頭頸外科雜志, 2013, 48(1): 48-53.
[15] Ordonez ME, Farraye FA, Di Palma JA. Endemic fungal infections in inflammatory bowel disease associated with anti-TNF antibody therapy [J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2013, 19(11): 2490-2500.
[16] Fei M, Bhatia S, Oriss TB, et al. TNF-α from inflammatory dendritic cells (DCs) regulates lung IL-17A/IL-5 levels and neutrophilia versus eosinophilia during persistent fungal infection [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108(13): 5360-5355.
[17] Boveland SD, Moore PA, Mysore J, et al. Immunohistochemical study of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9,macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases-1 and -2 in normal, purulonecrotic and fungal infected equine corneas [J].Vet Ophthalmol, 2010, 13(2): 81-90.
[18] Luo JL, Tan W, Ricono JM, et al. Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKα controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin [J]. Nature, 2007, 446(7136): 690-694.
Expression and significance of Maspin and IKKα in sinusoidal mucosa ofrats with fungal rhinosinusitis
LI Qin, XIE Qiong*
(Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University ofScience & Technology, Hubei Jingzhou 434020, China)
Objective To investigate the expression and significance of Maspin and IKKα in nasosinusoidal mucosa of rats with fungal rhinosinusitis (FRS). Methods A total of 40 SD rats were used to establish the FRS model, and randomly divided into nasal obstruction group, FRS group, immunosuppressive group and invasive FRS group, 10 rats in each group. Another 10 normal rats were used as control group. Mice in the control group were fed with normal diet. In the nasal obstruction group, the mice had only hemostatic cotton stuffed in the nasal cavity and injection of 0.9% NaCl in the abdominal and nasal cavities. In the FRS group, the mice were injectedAspergillusfumigatusspore suspension into the nasal cavity and 0.9% NaCl i.p. The mice of the immunosuppressive group were given cyclophosphamide i.p. and 0.9% NaCl injection into the nasal cavity. The invasive FRS group was injected with cyclophosphamide i.p. andAspergillusfumigatusspore suspension into the nasal cavity. The serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The expression of Maspin and IKKα in nasosinusoidal mucosa was detected by immunohistochemical staining. The expression of Maspin mRNA and IKKα mRNA in the nasosinusoidal mucosa was detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR. Results The serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in different groups were significantly different (P< 0.05). The level of IL-6 in the FRS group was (69.3 ± 10.9) ng/L, significantly higher than those in the control group, nasal obstruction group, immunosuppressive group and invasive FRS group [ (45.2 ± 7.1)ng/L, (46.4 ± 6.7) ng/L, (21.3 ± 4.5) ng/L, and (20.9 ± 4.3 ng/L)] (P< 0.05). The level of TNF-α in the FRS group was (30.4 ± 4.8) ng/L, significantly higher than those in the control group, nasal obstruction group, immunosuppressive group and invasive FRS group [(14.8 ± 2.7) ng/L, (13.9 ± 1.4) ng/L, (7.9 ± 0.6) ng/L, and (7.8 ± 0.4 ng/L)] (P< 0.05). The levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the control group were significantly higher than those in the immunosuppressive group and invasive FRS group (P< 0.05). There was no significant difference between the immunosuppressive group and the invasive group (P> 0.05). Theresult of immunohistochemical staining showed that the protein expression of Maspin in the FRS group and invasive FRS group was significantly lower than that in the control group, nasal obstruction group and immunosuppressive group, while the expression of IKKα protein was significantly higher than that of control group, nasal obstruction group and immunosuppressive group (P< 0.05). The protein expression of Maspin in the invasive FRS group was significantly lower than that in the FRS group, by contrast, the expression of IKKα protein was significantly higher (P< 0.05). The PCRresult revealed that the expression levels of Maspin and IKKα mRNA were (0.217 ± 0.013) and (0.193 ± 0.012), significantly lower than that in the control, obstruction and immunosuppressive groups [(0.309 ± 0.021), (0.302 ± 0.017), and (0.293 ± 0.02)] (P< 0.05), while the expressions level of IKKα mRNA were significantly higher [(0.319 ± 0.043), (0.384 ± 0.048) vs (0.169 ± 0.015), (0.171 ± 0.018), and (0.175 ± 0.019)] (P< 0.05). Conclusions Down-regulation of Maspin expression after IKKα activation is the main cause of the onset of FRS, which may also be one of the mechanisms of invasive FRS.
Fungal rhinosinusitis, FRS; Invasive fungal rhinosinusitis; Mammary serine proteinase inhibitor, Maspin; IκB kinase α, IKKα; Invasion; Cytokines
李琴(1982-),女,主治醫師。Email: liqinyixue@163.com
謝瓊(1969-),女,主任醫師。Email: 1279566754@qq.com
研究報告
R-33
A
1671-7856(2017) 07-0075-06
10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856. 2017.07.014
2016-11-21

