3,5-二烷基-1,2,4-三唑衍生物構筑的兩個Cu4I4簇配合物的合成、結構和熒光性質
閆娟枝盧麗萍
3,5-二烷基-1,2,4-三唑衍生物構筑的兩個Cu4I4簇配合物的合成、結構和熒光性質
閆娟枝1,2盧麗萍*,1
(1山西大學分子科學研究所,太原030006)
(2太原學院,太原030032)
以3,5-二甲(丙)基-4-氨基-1,2,4-三唑為配體,與CuI在H2O/MeCN混合溶劑熱合成了2個構型不同的Cu4I4超分子化合物{[Cu2(aadmtrz)I2]·CH3CN}n(1)和[Cu2(dptrz)I]n(2)(aadmtrz=4-((1-氨乙基)-氨基)-3,5-二甲基-1,2,4-三唑,dptrz=3,5-二丙基-1,2,4-三唑),并進行了元素分析,紅外,X射線粉末衍射及單晶衍射等表征。2個配合物中Cu4I4構型不同,配合物1中,Cu4I4簇連結成一個8環椅式-椅式結構,通過配體連接成(4,4)二維菱形格子結構;而配合物2中,Cu4I4簇呈畸變的立方烷結構,構成了含有19.5%孔隙率三維孔洞聚合物,其結構可簡化為(3,4)-連接的拓樸結構。同時,在常溫下研究了2個配合物的固體熒光性質。
亞銅碘配合物;1,2,4-三唑;晶體結構;熒光性質
Cuprous halide complexes have been of great interest for their various structure,unique topologies[1-3], as well as attractive properties such as luminescence[4-5], pores[6]and high reactivity in numerous organic and biochemical reactions[7-8].(CuxXy)x-y(X=halide)[9]have richeraggregatesofdifferentgeometries:Cu2X2,Cu3X3,Cu3X7,Cu3X8,Cu4X4,Cu4X11,Cu4X9,Cu6X6[10-14], and so on.Neutral cuprous halide clusters show Cu2X2, Cu4X4,and Cu6X6.These aggregates can be linked by organic ligands to form cuprous halide coordination polymers.IthasbeenreportedN-donorligands such as pyrazine,bipyridyl[11],imidazole,triazole[13,15], tetrazole[9],benzotriazole[16].To date,a large number of cuprous halide complexes containing triazole ligands have been reported[17-19].What we are interested in is thatcuprousiodidewith4-aminotriazoleshows diversities of Cucoordination geometry and new 4-aminotriazoleligandsareself-assembledbythe condensation reaction or the reductive deaminization[20]. Herein,we report the syntheses and crystal structures of two Cu4I4aggregates complexes{[Cu2(aadmtrz)I2]· CH3CN}n(1)and[Cu2(dptrz)I]n(2),and illustrate that the length of alkyl side chains of 4-aminotriazole has a certain extent influence on the product formations, structuresandtopologies.Thecomplexeswere characterized by X-ray single crystal analysis and studied by various spectroscopic techniques.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and methods
All reagents were purchased commercially and used without further purification.Ligands dmatrz and dpatrz were synthesized according to the literature[21]. Elemental analyses(C,H,and N)were performed on an Elementar Vario ELⅢanalyzer.FTIR spectra were recorded from KBr pellets in the range of 4 000~400 cm-1on a Bruker Tensor 27 spectrometer.PXRD data were collected in a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation(λ=0.154 059 8 nm)at 30 kV and 15 mA over the 2θ range of 5°~50°.The simulated patterns of 1 and 2 were derived from free Mercury Version 2.2 software.Luminescence spectra were recorded on a CARY Eclipse(Varian, USA)fluorescencespectrophotometeratroom temperature.
1.2 Synthesis of complex{[Cu2(aadmtrz)I2]· CH3CN}n(1)
A mixture containing CuI(0.10 g,0.53 mmol), dmatrz(0.056 g,0.50 mmol),CH3CN(1 mL)and H2O (5 mL)was sealed in a 23 mL of Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel,which was heated at 150℃for 4 days, and cooled to room temperature.Light-green block crystals of 1 were obtained,and picked out,washed with CH3CN/H2O(1∶5,V/V)and dried in air.Yield: 47.5%.Anal.Calcd.for C8H14Cu2I2N6(%):C,16.71;H, 2.45;N,14.61.Found(%):C,16.68;H,2.51;N,14.62. IR(cm-1):3 315(s),3 216(m),3 004(w),2 968(w), 2 914(w),1 622(s),1 543(s),1 427(s),1 373(m), 1 266(m),1 043(m),990(m),891(s),758(s),742(m).
1.3 Synthesis of complex[Cu2(dptrz)I]n(2)
The same synthetic procedure as that for 1 was used except that dmatrz was replaced with dpatrz (0.084 g,0.50 mmol),giving pale-green octahedral crystals 2 in 25.8%yield.Anal.Calcd.for C8H14Cu2N3I(%):C,23.65;H,3.47;N,10.34,Found(%):C, 23.58;H,3.44;N,10.32%.IR(cm-1):3 318(s),3 255 (m),3 198(s),2 970(s),2 927(m),2 880(m),2 052(s), 1 621(s),1 544(s),1 460(m),1 390(m),1 343(w), 1293(w),1210(w),1072(w),946(m),889(w),715(m).
1.4 X-ray crystallography
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for complexes 1 and 2 were collected in Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility(BSRF)beamline 3W1A which mounted with a MARCCD-165 detector(λ=0.072 00 nm)with storage ring working at 2.5 GeV.In the process,the crystals were protected by liquid nitrogen at 100(2)K.Data were collected by the MARCCD and processed using HKL 2000[22].Absorption corrections were applied by using the multi-scan program SCALEPACK[22].All the structures were solved by the direct methods and refined by the full-matrix leastsquares technique using the SHELXL-2014[23]with all non-hydrogen atoms refined anisotropically.Hydrogen atoms attached to C and N atoms wereadded theoretically and treated as riding on the concerned atoms.The final cycle of full-matrix least-squares refinement was based on observed reflections and variable parameters.Further crystallographic data and structural refinement details are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and bond angles are given in Table 2.
CCDC:1437794,1;1437795,2.

Table1 Crystallographic data and structure refinement for 1 and 2
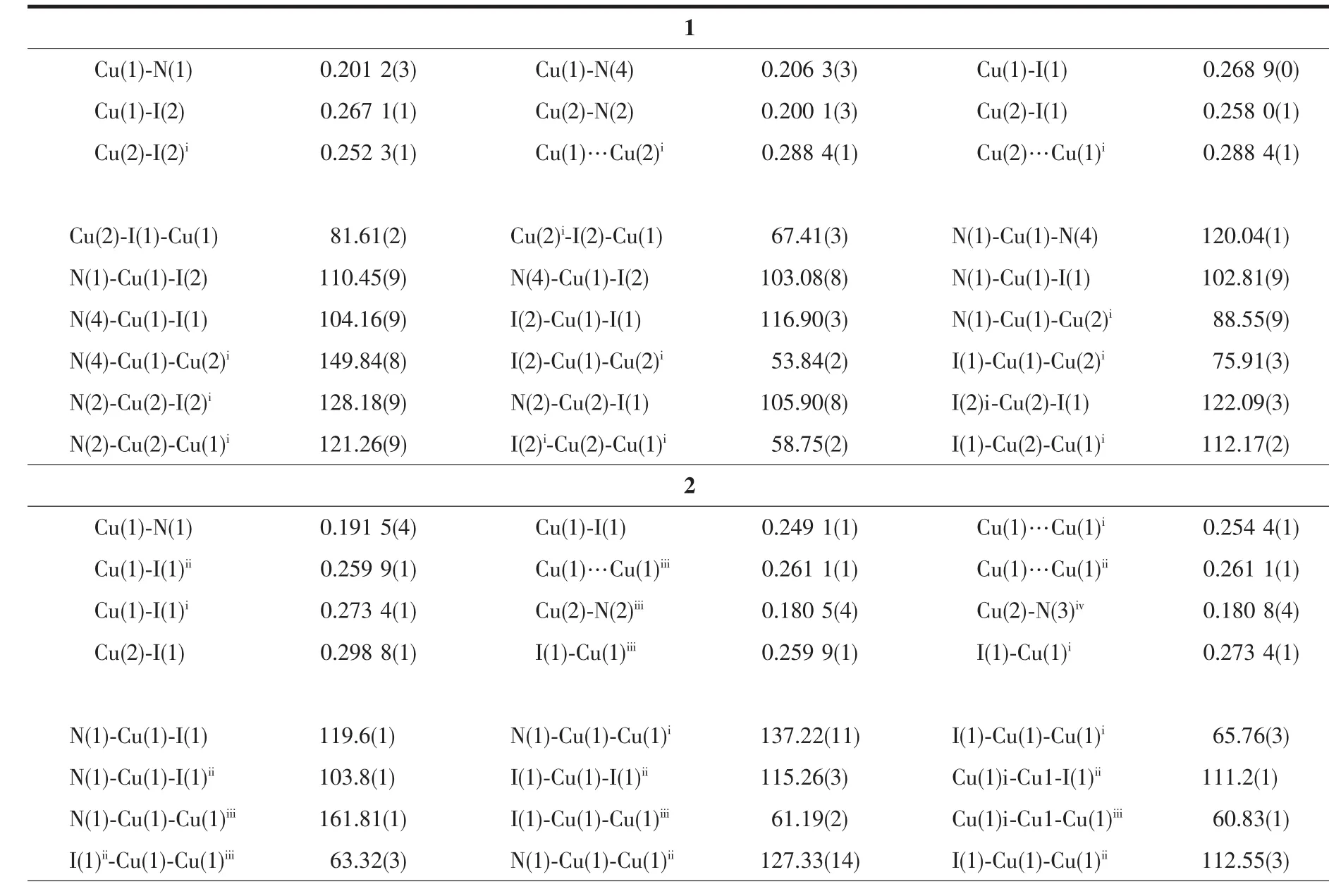
Table2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)of complexes 1 and 2
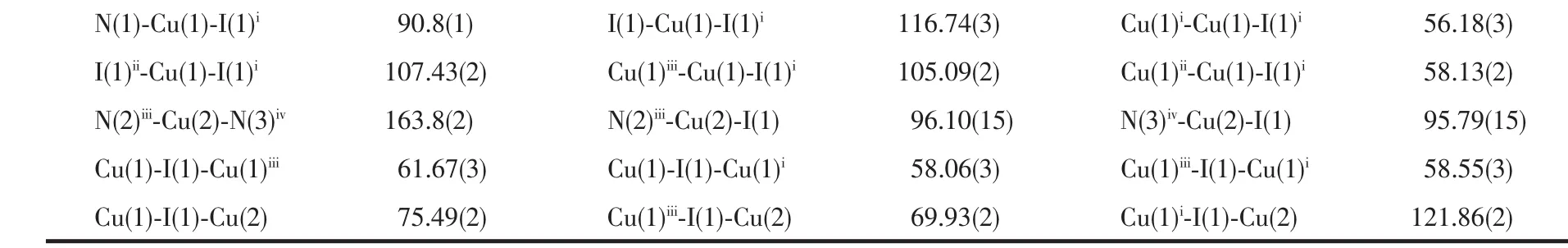
Continued Table 2
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Syntheses of the complexes
The aadmtrz ligand in complex 1 is in situ prepared from the condensation reaction of acetonitrile and 3,5-dimethyl-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole.This condensation reaction is observed between amino compounds and nitrile compounds under solvothermal conditions. The formation mechanism of in situ alkylation is suggested as follows:under high temperature and autogenous pressure,the hydrolysis breaks CH3CN molecules into CH3CONH2;the nucleophilic substitution reaction of dmatrz and CH3CONH2can generate aadmtrz,which attacks the nitrogen atom of dmatrz to form the 1-aminoethylidene group.The ligand in complex 2,dptrz,is from the reductive deaminization of the 3,5-propyl-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole ligand.The cuprous iodide in both reactions serves not only as the metal catalyst for the other triazole ligands,but also as the source of the cuprous-iodide aggregates.
2.2 Structure description
2.2.1 Structure of{[Cu2(aadmtrz)I2]·CH3CN}n(1)
Complex 1 is a 2D coordination polymer with the monoclinic space group P21/c,and the asymmetric unit consists of two crystallographically independent cuprous ions,one aadmtrz group,two iodides,one CH3CN solvent molecule.As shown in Fig.1a,its monomer is composed of a Cu4I4cluster and two tridentate aadmtrz molecules.The Cuatoms are precisely coplanar,thusformingaparallelogram. Cu(1)showstetrahedralcoordination geometries [CuN2I2]by two I ions(I(1),I(2))and two nitrogen atoms(N(1),N(4))from the different addmtrz ligands. The distance of Cu(1)-N(1)(0.201 2(3)nm)is longer than that of Cu(1)-N(4)(0.206 3(3)nm),meanwhile the distance of Cu(1)-I(1)(0.268 9(1)nm)is also longer than that of Cu(1)-I(2)(0.267 1(1)nm).Cu(2)is in a slightly distorted[CuNI2]triangular planar site with one μ2-I(1)andtwo nitrogen atoms from different aadmtrz groups(N(2)iii,N(3)iv,Symmetry codes:iiiy+1/4, -x+7/4,-z+3/4;iv-x+3/2,-y+3/2,-z+1/2).The distances of Cu(2)-N(0.180 5(4)and 0.180 8(4)nm)are shorter than those of Cu(1)-N,and the distances of Cu(2)-I(0.257 8(1)and 0.252 2(1)nm)are shorter than that of Cu(1)-I(0.268 9(1)nm).The Cu(1)…Cu(2) interactions(0.288 4(1)nm)are crucial to build the Cu4I4aggregates.The parallelogram Cu4I4unit(Fig.1b) has an inversion center and is formed by four iodine atoms bridges four copper atoms in the μ2-bridging modes,generating an 8-membered ring that has the chair-chair conformation of cyclooctane.This chairchairconformationissimilartothosesimilarcomplexes such as[Cu2I2(aadtz)]n[20].

Scheme 1Syntheses of ligands of 1 and 2

Fig.1 (a)ORTEP drawing of 1 with 30%thermal ellipsoids;(b)Basic building block of Cu4I4cluster
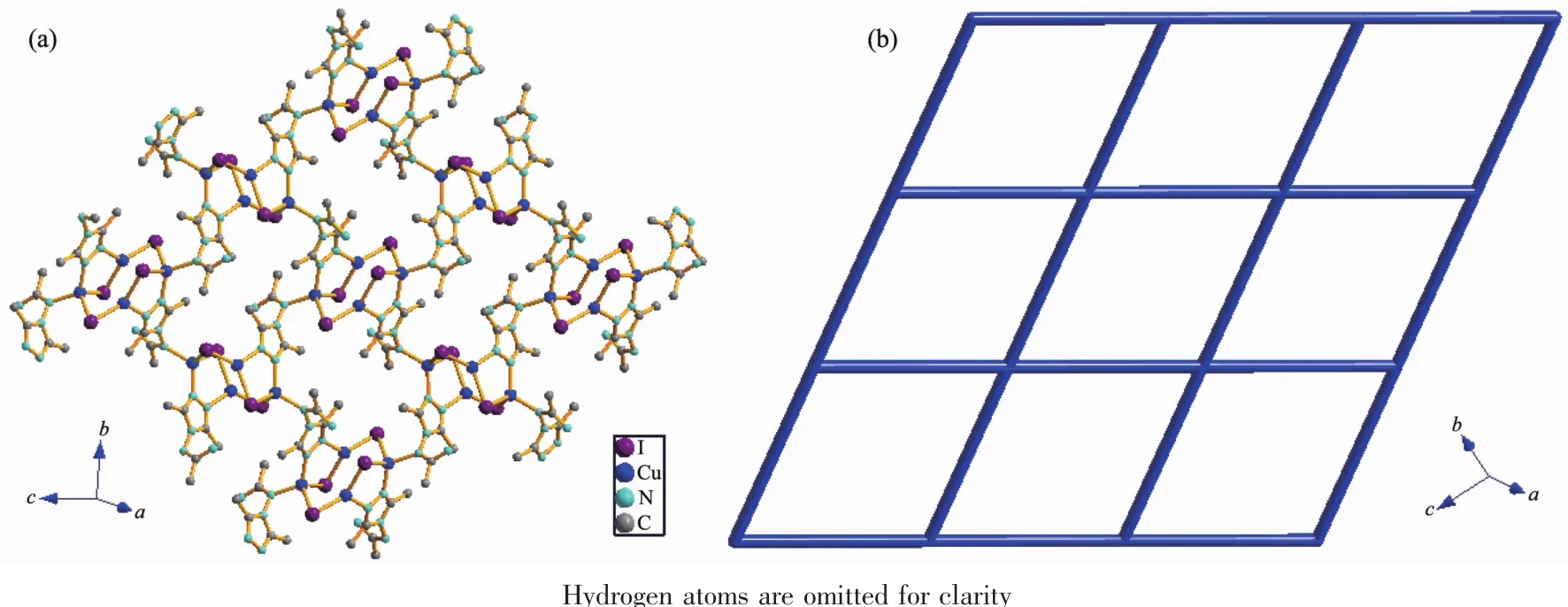
Fig.2 (a)View of the 2D network in 1;(b)Topological representation of the 4-connected network in 1
In this complex,each aadmtrz ligand bridges two Cuatoms on the longer side of the Cu parallelogram through N(1)and N(2)nitrogen donors,while 4-substituent N(4)and N(5)atoms link an adjacent Cu4I4unit to form a 2D network(Fig.2a).The overall structure of 1 can thus be simplified as a 2D(4,4) rhombic-grid network with 4-connecting node of the Cu4I4aggregates(Fig.2b).The coplanar sheets of 1 are further built into a 3D supramolecular architecture through the hydrogen bonding interactions(Table 3).
Furthermore,complex1isdifferentfrom previously reported[Cu4I4(C4H8N4)4][15]with the similar reaction,where the ligand 3,5-dimethyl-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole took part in the compound directly.This case isdifferentfrom3,5-diethyl-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole compounds[20],where may attribute to the shorter-CH2in the 3,5-position of 1,2,4-triazole.
2.2.2 Structure of[Cu2(dptrz)I]n(2)
Complex2 showsan interesting 3Dporous structure with the tetragonal space group I41/a.As shown in Fig.3a,the asymmetric unit of complex 2 contains two crystallographically independent Cuions,one dptrz ligand,one iodide anions.Each Cu(1) or I(1)links three neighboring I(1)or Cu(1)to form a distorted Cu4I4cubane unit(Fig.3b),which is similar to those reported Cu4I4tetramer units[24-25].Each Cu(1) is tetrahedrally coordinated[CuNI3]by three I ions and a nitrogen from the bridging dptrz ligand.The distances of Cu(1)-I,Cu(1)-N and Cu…Cu are 0.249 1(1)~0.273 4(1),0.191 4(4)and 0.254 4(1)~0.261 1(1)nm, respectively,which are shorter than those of isostructural complex[Cu2(dtz)I][20],due to the longer-CH2group in the ligand of 2.Furthermore,these values are comparable to those found in other cubane-like Cu4I4L4complexes(L=nitrogen-containing ligand)[26].Cu(2)is in a slightly distorted[CuN2I]triangular planar site with one μ3-I(1)and two nitrogen atoms from different dptrz groups(N(2)iii,N(3)iv,Symmetry codes:iiiy+1/4,-x+7/4,-z+3/4;iv-x+3/2,-y+3/2,-z +1/2).The distances of Cu(2)-N(0.180 5(4),0.180 8(4) nm)are shorter than those of Cu(1)-N,and the distance of Cu(2)-I is 0.298 7(7)nm,which is longer than that of Cu(1)-I.The angle of N(2)iii-Cu(2)-N(3)ivis 163.7(1)°.
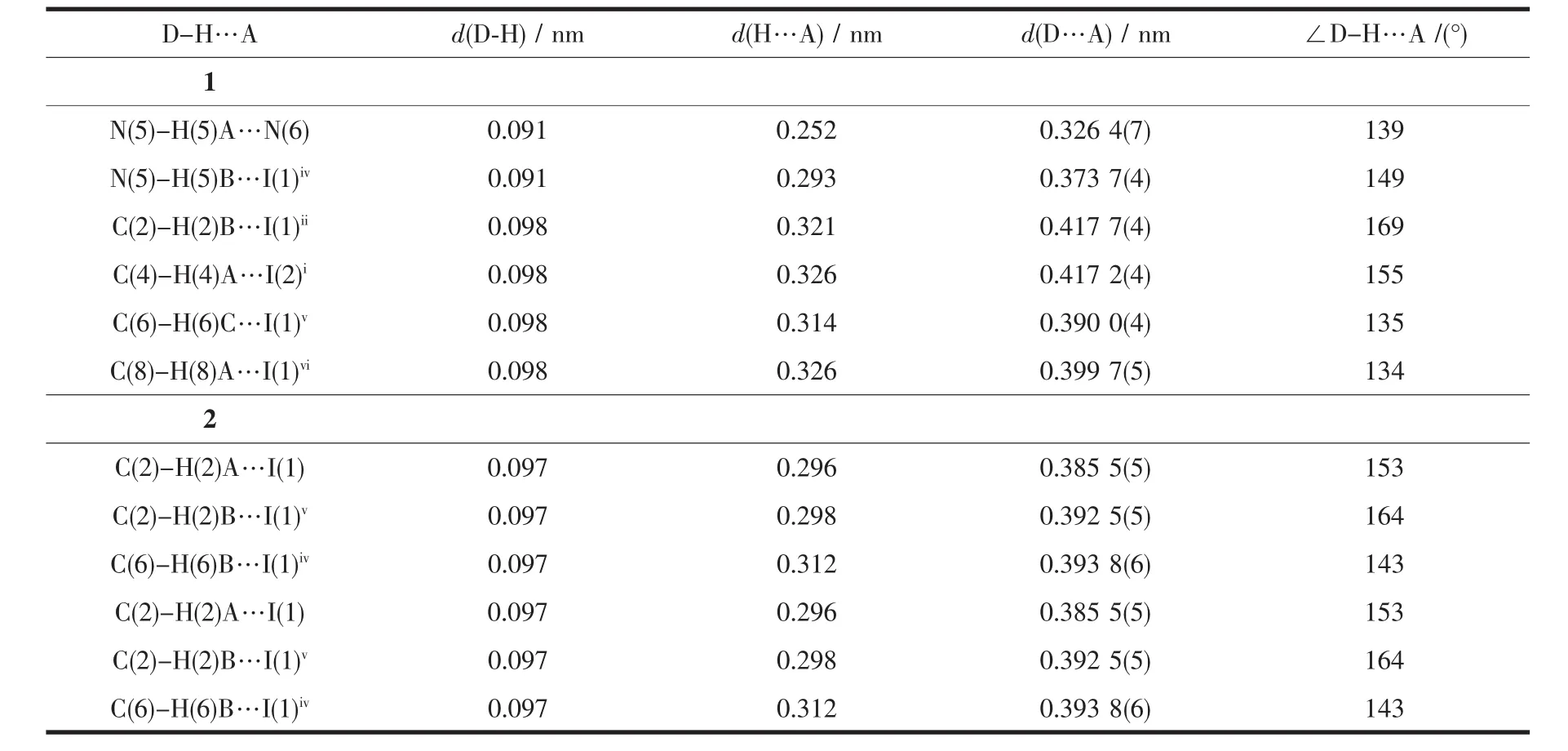
Table3 Hydrogen bonds geometry for 1 and 2
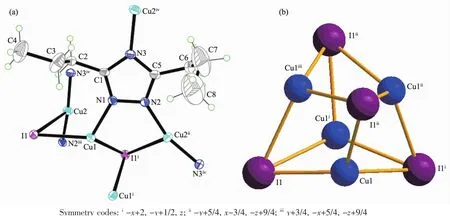
Fig.3 (a)ORTEP drawing of 2 with 30%thermal ellipsoids;(b)Basic building block of Cu4I4cluster
Cu(2)atoms are bridged by μ1,2-dptrz ligands forming single-stranded helices,with the helices being left-and right-handed along the fourfold axis(Cu4I4unitlocatesonthefourfoldinversionaxes), respectively(Fig.4a).Each helical chain along the c axis is further linked through Cu(1)of the Cu4I4unit, forming a non-interpenetrating 3D framework(Fig.4b). Topologically,when the Cu4I4SBU are depicted as four-connecting nodes,and dptrz ligands are regarded as three-connecting nodes,complex 2 can be defined as a(3,4)-connected framework,which is similar to the isostructural[Cu2I(dtz)]n[20].Interesting,PLATON calculations[27]show that the potential solvent area volume of 2 is estimated to be 0.982 3 nm3,19.5%of the unit cell volume(5.039 6 nm3),which may hold10H2Omolecules.Thismayindicatethatthe construction of the cage-like motifs is accomplished by the-(CH2)nspacers of 3,5-dialkyl-1,2,4-triazole.
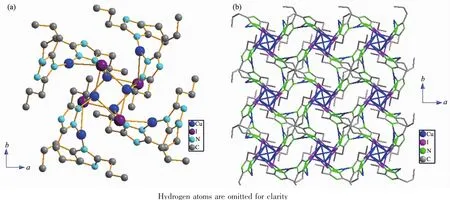
Fig.4 (a)Local coordination environment around the Cu4I4cluster in 2;(b)View of a 3D framework in 2
2.3 PXRD analysis
As shown in Fig.5,the experiment PXRD patterns for 1 and 2 are in agreement with the simulated ones fromthesingle-crystalX-raydata.Theresult indicates that the growth of crystals of both complexes is well-proportioned and consistent.The structures are representative of the bulk materials.
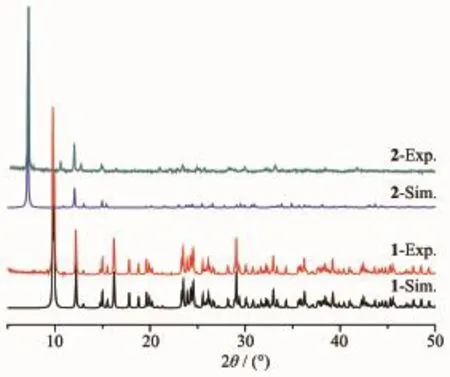
Fig.5 PXRD patterns of complexes 1 and 2
2.4 Luminescence properties
The emission spectra for 1 and 2 and the ligands dmatrz,dpatrz in the solid state at room temperature areshowninFig.6.Theemissionpeaksof luminescence of ligands dmatrz,dpatrz are the same at 419 nm.It can be observed that complex 1 and 2 exhibit green emission bands at 498,493 nm upon excitation at 266,254 nm,respectively.The emission spectra for both complexes may be assigned,in character,to iodide(X)-to-ligand charge transfer(XLCT).
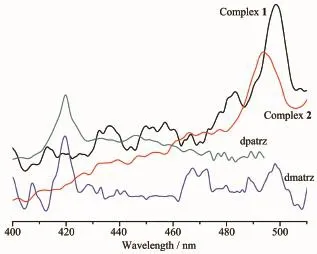
Fig.6 Emission spectra of the ligands dmatrz,dpatrz, and complexes 1~2
3 Conclusions
In summary,two cuprous halide coordination polymers containing Cu4I4clusters layers as structural motifs have been successfully synthesized,which are further linked by 1,2,4-triazole to form extended 2D 4-connected grid frameworks(1)and 3D(3,4)-connected (2)frameworks with 19.5%porosity.The Cu4I4cluster in complex 1 is an inorganic 8-membered ring with a chair-chair conformation,while the one in complex 2 is a distorted cubane.The large spacers of alkyl side chainsof4-aminotriazolemayaccomplishedthe construction of the cage-like motifs.This provides a method to design the porous metal-organic frameworks(PMOFs).Both complexes exhibit similar green photoluminescence at room temperature in the solid state.
Acknowledgements:The authors thank Dr.GAO Zeng-Qiang at line 3W1A of BSRF for his help in the single-crystal X-ray diffraction data collection and reduction.
Supporting information is available at http://www.wjhxxb.cn
[1]Graham P M,Pike R D,Sabat M.et al.Inorg.Chem.,2000, 39:5121-5132
[2]Zhang Z Y,Deng Z P,Zhang X F,et al.CrystEngComm, 2014,16:359-368
[3]Murdock C R,Jenkins D M.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2014,136: 10983-10988
[4]Roesch P,Nitsch J,Lutz M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53: 9855-9859
[5]SUN Xiao-Mei(孫曉美),NING Wei-Hua(寧為華),LIU Jian-Lan(劉建蘭),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(無機化學學報),2013,29(10):2171-2182
[6]Denysenko D,Grzywa M,Jelic J,et al.Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2014,53:5832-5836
[7]Li S L,Zhang X M.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53:8376-8383
[8]Liu Z,Qayyum M F,Wu C,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2011, 133:3700-3703
[9]Jiang D P,Yao R X,Ji F,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2013, 2013:556-562
[10]Lee J Y,Kim H J,Jung J H,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2008, 130:13838-13839
[11]Lu J Y,Cabrera B R,Wang R J,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1999, 38:4608-4611
[12]Hou J J,Li S L,Li C R,et al.Dalton Trans.,2010,39:2701-2707
[13]Wu T,Li M,Li D,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2008,8:568-574
[14]DeBord J R D,Lu Y J,Warren C J,et al.Chem.Commun., 1997,15:1365-1366
[15]Zhao Z G,Wu X Y,Zhang Q S,et al.Chin.J.Struct.Chem., 2010,29(2):245-249
[16]Hu M C,Wang Y,Zhai Q G,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2009,48: 1449-1468
[17]ZHANG Jun-Jun(張俊珺),YANG Nian-Fa(陽年發),ZHANG Chun-Hua(張春華),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(無機化學學報),2010,26(3):533-536
[18]Ouellette W,Jones S,Zubieta J.CrystEngComm,2011,13: 4457-4485
[19]Yan J Z,Lu L P,Su F,et al.Chin.J.Struct.Chem.,2015, 34(3):401-407
[20]Zhao Z G,Yu R M,Wu X Y,et al.CrystEngComm,2009, 11:2494-2499
[21]Robert M H,James A G.J.Org.Chem.,1953,18:872-877
[22]Otwinowski Z,Minor W.Methods in Enzymology:Vol.276. Carter Jr C W,Sweet R M Ed.San Diego:Academic Press, 1997:307-326
[23]Sheldrick G M.Acta Crystallogr.Sect.A,2015,71:3-8
[24]Zhai Q G,Lu C Z,Chen S M,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2006,9:819-822
[25]Harvey P D,Knorr M M.Rapid Commun.,2010,31:808-826
[26]Zhang D Q,Ding L,Xu W,et al.Chem.Lett.,2001:242-243
[27]Spek A L.J.Appl.Crystallogr.,2003,36:7-13
Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Luminescence Properties of Two Cu4I4Coordination Polymers Based on 3,5-Dialkyl-1,2,4-triazole
YAN Juan-Zhi1,2LU Li-Ping*,1
(1Institute of Molecular Science,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China)
(2Taiyuan University,Taiyuan 030032,China)
Two Cu4I4coordination polymers,{[Cu2(aadmtrz)I2]·CH3CN}n(1)and[Cu2(dptrz)I]n(2)(aadmtrz=4-((1-aminoethylidene)-amino)-3,5-dimethyl-1,2,4-triazole,dptrz=3,5-dipropyl-1,2,4-triazole),have been synthesized by the solvothermal reactions of CuI and 3,5-dialkyl-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole ligands in mixed H2O/MeCN solution and characterized using elemental analysis,IR,PXRD and single-crystal X-ray diffraction.The structures of the Cu4I4units in the polymers are different.The Cu4I4cluster in complex 1 is an inorganic 8-membered ring with a chairchair conformation,while the one in complex 2 is a distorted cube.Complex 1 exhibits 2D 4,4-connected rhombic-grid.Complex 2 is a(3,4)-connected framework with 19.5%porosity.In addition,the luminescent properties of the complexes in the solid state were also investigated.CCDC:1437794,1;1437795,2.
copperiodide;1,2,4-triazole;crystal structures;luminescence
O614.121
A
1001-4861(2017)09-1697-08
10.11862/CJIC.2017.165
2017-04-08。收修改稿日期:2017-05-15。
國家自然科學基金(No.21571118)和山西省回國留學人員科研資助項目(No.2013-026)資助。*
。E-mail:luliping@sxu.edu.cn;會員登記號:S06N7852M1605(閆娟枝)。

