吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍與單用亞甲藍在乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢中的對比研究
衡瑞娟 齊攀 馮躍慶 周勇 楊留勤
(1.新鄉醫學院 河南 新鄉 453003; 2.新鄉市中心醫院 頭頸乳腺科 河南 新鄉 453000;3.新鄉市中心醫院 放療科 河南 新鄉 453000)
·論著·
吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍與單用亞甲藍在乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢中的對比研究
衡瑞娟1齊攀2馮躍慶2周勇2楊留勤3
(1.新鄉醫學院 河南 新鄉 453003; 2.新鄉市中心醫院 頭頸乳腺科 河南 新鄉 453000;3.新鄉市中心醫院 放療科 河南 新鄉 453000)
目的研究吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍與單用亞甲藍在乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢(SLNB)中的對比應用價值。方法選取2015年1月至2016年8月新鄉市中心醫院頭頸乳腺外科收治的120例乳腺癌患者,用兩種方法行SLNB行前瞻性研究。聯合組46例應用吲哚菁綠熒光法聯合亞甲藍法,亞甲藍組74例單用亞甲藍法,兩組患者SLNB后常規行腋窩淋巴結清掃(ALND)。結果聯合組SLNB的檢出率、準確率、前哨淋巴結檢出平均數高于亞甲藍組,假陰性率低于亞甲藍組,兩組間的檢出率、前哨淋巴結檢出平均數差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩組間的準確率及假陰性率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論在乳腺癌SLNB中,吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍法與單用亞甲藍法相比,前者可提高SLNB的檢出率、準確率及前哨淋巴結檢出平均數,降低假陰性率。
乳腺癌;前哨淋巴結活檢;吲哚菁綠;亞甲藍
前哨淋巴結(sentinel lymph node,SLN)是原發腫瘤發生淋巴轉移的第一站淋巴結[1],SLNB(sentinel lymph node biopsy,SLNB)是早期乳腺癌腋窩淋巴結分期的標準手術[2]。乳腺癌SLNB常用的示蹤劑主要有藍染料、核素、熒光劑等。國內最常用的藍染料是亞甲藍,藍染法檢出成功率低,假陰性率高,并且少數患者可出現過敏反應;核素法操作復雜,價格昂貴。近年來吲哚菁綠成為乳腺癌SLNB示蹤劑的研究熱點。本研究對新鄉市中心醫院頭頸乳腺外科收治的乳腺癌患者用兩種方法行SLNB,分析吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍在乳腺癌SLNB中的應用價值。
1 資料與方法
1.1臨床資料選取2015年1月至2016年8月新鄉市中心醫院頭頸乳腺外科收治的符合納入標準及排除標準的乳腺癌患者120例,行SLNB后均行腋窩淋巴結清掃(axillary lymph node dissection,ALND)進行前瞻性研究,所有患者均為女性,聯合組46例應用吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍行SLNB,亞甲藍組74例單用亞甲藍行SLNB。入組標準:①臨床上顯示腋窩淋巴結陰性;②術前乳腺腫瘤空心針穿刺或術中冰凍病理證實為原發性乳腺癌;③腫瘤最大直徑≤50 mm,無遠處轉移;④患者及家屬同意并簽知情同意書。排除標準:①新輔助化療后;②有乳房或腋窩手術或放射史;③病理學證實腋窩淋巴結陽性;④炎性乳腺癌;⑤對示蹤劑過敏。兩組患者的年齡、腫瘤大小、位置、病理類型、組織分級、ER、PR之間差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2材料及儀器注射用吲哚菁綠(遼寧天醫生物制藥股份有限責任公司),滅菌注射用水(遂成藥業股份有限公司),亞甲藍注射液(濟川藥業集團有限公司),紅外熒光定位觀察相機(濱松光子學商貿有限公司)。
1.3治療方法
1.3.1聯合組示蹤SLN 患者平臥位,全麻成功后,擺好體位,消毒鋪巾,術前10~15 min于患側乳暈區皮下注射亞甲藍,配制1 mg/ml吲哚菁綠注射液,術前5 min于患側乳暈區皮內注射吲哚菁綠注射液1 ml,用無菌紗布按摩5 min,關閉手術燈,用熒光定位探頭觀察淋巴管道引流情況,觀察到熒光劑由乳暈區流向腋窩方向,在淋巴管道消失的位置上2 cm處行弧形切口,切開皮膚及皮下組織,用熒光定位探頭定位SLN位置,取出所有高亮的淋巴結,并沿藍染的淋巴管仔細尋找所有的藍染淋巴結,將取出的SLN送術中快速冰凍及常規病理檢查,SLNB后均行ALND并送常規病理檢查。
1.3.2亞甲藍組示蹤SLN 患者平臥位,全麻成功后,擺好體位,消毒鋪巾,于患側乳暈區皮下注射2~4 ml亞甲藍,用無菌紗布按摩,10~15 min后在胸大肌外側緣行約3 cm切口,切開皮膚及皮下組織,檢出所有藍染淋巴管的第一個藍染淋巴結,切除后送快速冰凍活檢及常規病理學檢查,SLNB后均行ALND并送常規病理檢查。
1.4SLNB評價標準檢出率=成功檢出SLN例數/SLNB總例數×100%;準確率=(SLN真陰性例數+真陽性例數)/SLNB總例數×100%;假陰性率=SLN假陰性例數/腋窩非前哨淋巴結轉移例數×100%。
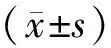
2 結果
聯合組SLNB檢出率為97.8%(45/46),共檢出138枚,平均(3.1±0.9)枚/例,準確率為95.6%(43/45),聯合組的假陰性率為5.9%(1/17)。亞甲藍組SLNB檢出率為83.5%(64/74),共檢出136枚,平均(2.1±0.7)枚/例,準確率為90.6%(58/64),假陰性率為12.5%(3/24)。聯合組SLNB的檢出率、準確率及SLN平均數均高于亞甲藍組,聯合組的假陰性率低于亞甲藍組,兩組間的檢出率、SLN平均數差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩組間的準確率及假陰性率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
3 討論
目前乳腺癌SLNB的方法有藍染法、核素法、熒光法及聯合法。國內藍染法常用的示蹤劑是亞甲藍,操作簡單,價格低廉,但其檢出成功率偏低,假陰性率偏高,需要較長的學習曲線。核素法檢出率高,假陰性率低,但術前準備復雜,花費高,存在放射性污染。Niebling等[3]對88篇行SLNB的結果進行了系統性分析,藍染法平均檢出率為85%,本研究中亞甲藍組SLNB的檢出率為86.5%,與文獻報道一致。美國臨床腫瘤學會指南推薦應用核素與藍染料聯合法[4]。但因核素存在放射性污染、價格昂貴等問題,國內應用較少。2005年Kitai等[5]在乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢中第1次應用吲哚菁綠熒光導航技術,其檢出率達94%,SLN平均數為2.8枚。Murawa等[6]研究顯示單用吲哚菁綠的檢出率及假陰性率分別為97%、8%,SLNB結果優于單用核素法。
本研究將吲哚菁綠與亞甲藍聯合應用在乳腺癌前哨淋巴結活檢中,可兼顧兩種示蹤劑的優點,相互彌補,在近紅外熒光系統的引導下清楚地顯示淋巴引流情況,外科醫生能夠直觀地觀察到淋巴管走向及準確定位皮膚切口,準確定位SLN,降低了尋找SLN的盲目性,減少組織損傷,縮短學習曲線。若因吲哚菁綠泄露污染手術野而影響手術操作,可以沿著藍染淋巴管尋找SLN,提高SLNB檢出率,降低假陰性率。聯合組SLN平均數高于亞甲藍組。聯合組的假陰性率低于亞甲藍組。有研究顯示SLN檢出個數與假陰性率成反比,適當地增加SLN個數可降低SLNB假陰性率[7],這可能是聯合組的假陰性率較低的原因之一。兩組間的準確率及假陰性率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),有可能與樣本量太少有關,因此需要日后進一步研究。
綜上,在乳腺癌SLNB中,熒光劑吲哚菁綠聯合亞甲藍優于單用亞甲藍,兩者聯合能夠提高SLNB檢出率、準確率、SLN平均數,降低假陰性率,是一種很有前景的SLNB示蹤法。
[1] Cabanas R M. An approach for the treatment of penile carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 1977,39(2):456-466.
[2] Moncayo V M, Aarsvold J N, Grant S F, et al. Status of sentinel lymph node for breast cancer[J]. Semin Nucl Med,2013,43(4):281-293.
[3] Niebling M G, Pleijhuis R G, Bastiaannet E, et al. A systematic review and meta-analyses of sentinel lymph node identification in breast cancer and melanoma, a plea for tracer mapping[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol,2016,42(4):466-473.
[4] Lyman G H, Temin S, Edge S B, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol,2014,32(13):1365-1383.
[5] Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M, et al. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer, 2005, 12(3): 211-215.
[6] Murawa D, Hirche C, Dresel S, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer guided by indocyanine green fluorescence[J].Br J Surg,2009,96(11):1289-1294.
[7] Benson J R, della Rovere G Q. Management of the axilla in women with breast cancer[J]. Lancet Oncol,2007,8(4):331-348.
Comparisonstudyofindocyaninegreenjointmethylenebluewithmethylenebluealoneforsentinellymphnodebiopsyinpatientswithbreastcancer
Heng Ruijuan1, Qi Pan2, Feng Yueqing2, Zhou Yong2, Yang Liuqin3
(1.XinxiangMedicalUniversity,Xinxiang453003,China; 2.DepartmentofHeadandNeckBreastSurgery,theCentralHospitalofXinxiangCity,Xinxiang453000,China; 3.DepartmentofRadiotherapy,theCentralHospitalofXinxiangCity,Xinxiang453000,China)
ObjectiveTo discuss the comparable value of indocyanine green joint methylene blue with methylene blue alone for sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in patients with breast cancer.MethodsOne hundred and twenty eligible patients with breast cancer who
SLNB in Department of Head and Neck Breast Surgery, the Central Hospital of Xinxiang City from January of 2015 to August of 2016 were selected, they were randomized the combination group (46 patients with the method of indocyanine green and methylene blue) and the methylene blue group(74 patients with the methylene blue method). All patients underwent axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) after SLNB.ResultsThe detection rate, accuracy, the average number of SLN in the combination group were higher than the methylene blue group, the false negative rate of the former was lower than the latter, the differences of the detection rate, the average number of SLN between the two groups were statistically significant(P<0.05), the accuracy and false negative rate of the former was lower than the latter, differences of the accuracy and false-negative rate between the two groups had no statistical significance(P>0.05).ConclusionCompared indocyanine green joint methylene blue with methylene blue for SLNB in breast cancer, the former can obviously improve the detection rate, accuracy and the average number of SLN, reduce the false-negative rate.
breast cancer;sentinel lymph node biopsy;indocyanine green;methylene blue
R 737.9doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2017.17.001
2016-12-14)
國家自然科學基金(81572939)。
楊留勤,E-mail: yangliuqin8888@163.com。

