酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的神經網絡研究
堵錫華,吳瓊,陳艷,馮惠
徐州工程學院 化學化工學院, 徐州 221018
酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的神經網絡研究
堵錫華*,吳瓊,陳艷,馮惠
徐州工程學院 化學化工學院, 徐州 221018
酚類化合物(BP)是重要的工業原料或中間體,但工業廢水含有的酚類化合物會對環境造成污染。為建立酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的QSPR(quantitative structure-property relationship)預測模型,分析了23種酚的分子結構與臭氧氧化速率之間的相關關系,計算了這些酚的分子連接性指數和分子形狀指數,優化篩選了連接性指數的1χ和2χ、分子形狀指數的K1和K2共4種參數,將其作為BP神經網絡的輸入層變量,臭氧氧化速率作為輸出層變量,采用4:2:1的網絡結構,獲得了令人滿意的QSPR神經網絡預測模型,模型總相關系數r為0.976,計算得到的臭氧氧化速率的預測值與實驗值較為吻合,平均殘差僅為0.05;為檢驗結構參數建立模型的普適性,同樣方法建立對酚類化合物的辛醇-水分配系數的預測模型,模型總相關系數r達到0.993,辛醇-水分配系數的預測值與實驗值吻合度較為理想,結果表明,本法建構的神經網絡模型具有良好的穩健性和預測能力。
酚類化合物;臭氧氧化;分子連接性指數;分子形狀指數;神經網絡
Received6 January 2017accepted20 February 2017
Abstract: Phenolic compounds were important industrial raw materials or intermediates, but industrial wastewater containing phenolic compounds was polluted to the environment. In order to establish QSPR (quantitative structure-property relationship) model of ozonation rate of phenolic compounds, the relationship between molecular structure and the ozonation rate of 23 kinds of phenolic compounds was analyzed. Moreover, the molecular connectivity indices and molecule shape indices of these compounds were calculated.1χand2χ of the molecular connectivity indices, K1and K2of the molecule shape indices were optimized. The four parameters were used as input variables of neural network and the ozonation rate was used as output variable, and the 4:2:1 network structure was adopted and BP neural network method was used to establish a satisfying QSPR prediction model. The total correlation coefficient r was 0.976. The predicted values and experimental values were very close, and the mean error was 0.05. In order to test the generality of our method, a QSPR model of octanol-water partition coefficient lgp of phenolic compounds was established using the same method. The total correlation coefficient r was 0.993. The predicted values of lgp agree with the experimental values. The results showed that the neural network model had good stability and predictive ability.
Keywords: phenolic compound;ozonation;molecular connectivity index;molecule shape index;neural network
酚類化合物在工業上被廣泛用作酚醛樹脂、高分子材料、合成纖維、防腐劑、殺蟲劑、香料、染料等生產原料或中間體[1],工業生產產生的廢水由于含有酚類污染物,容易造成對環境的破壞[2-3],因此世界上許多國家將部分酚類化合物列為優先控制的環境污染物[4],越來越多的研究工作者對其對環境的影響也越發關注,開展了卓有成效的研究[5-7]。在這些研究中,對酚類化合物的生物毒性[8-9]、電化學腐蝕性[10]、色譜保留特性[11]等較為常見,對水體中酚類化合物臭氧氧化降解研究雖然較少,但已逐漸引起科研人員的重視[12]。為此,在前人研究[13-14]工作基礎上,本文采用人工神經網絡(Artificial Neural Network,ANN)方法建立了酚類化合物臭氧氧化降解的QSPR構效關系模型,通過酚類化合物分子結構參數與其臭氧氧化速率之間的關系,分析了對臭氧氧化速率的影響因素。本研究可為酚類化合物的環境降解處理提供理論上的指導。
1 分子連接性和形狀指數的計算和優化篩選(Calculation and optimization of molecular connectivity index and shape index)


表1 lgk與結構參數的最佳變量子集回歸結果Table 1 The results of structure parameters and lgk with best subsets regression
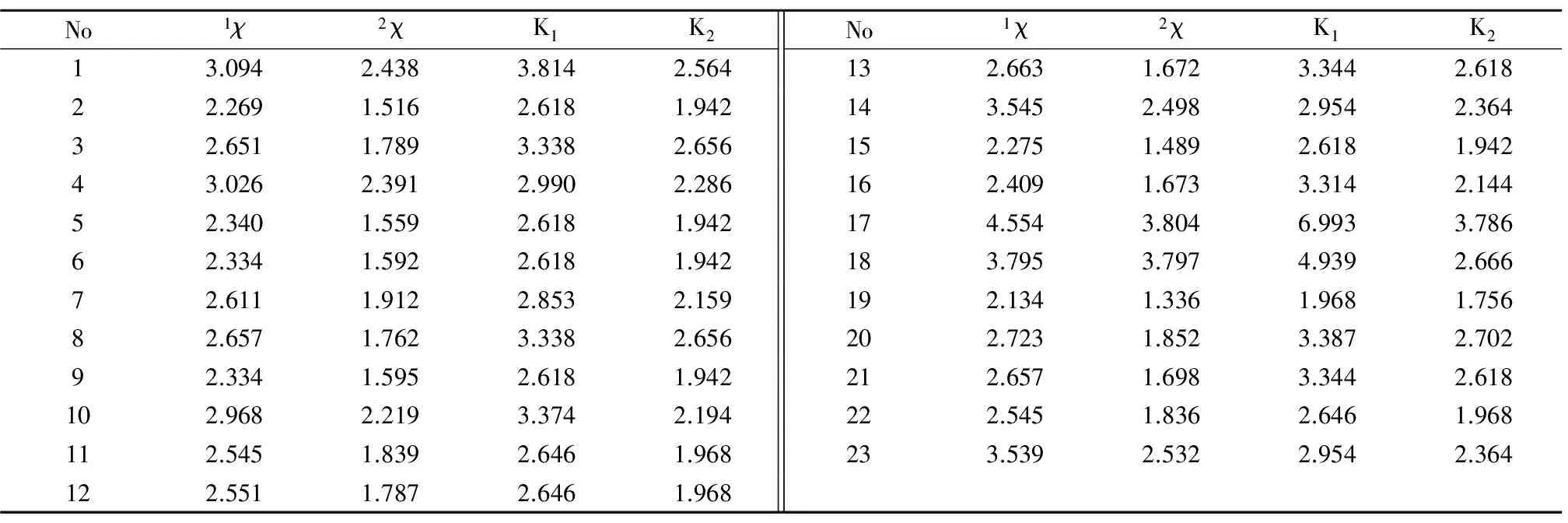
表2 酚類化合物的結構參數Table 2 Structural parameters of phenolic compound
優化篩選的分子連接性指數1χ和2χ揭示分子中原子的連接特性,分別代表分子二價和三價的路徑指數;分子形狀指數K1和K2揭示形狀特征,K1反映分子的環性,K2反映原子的空間密度。
2 多元回歸模型的構建(Construction of multiple regression model)
考察文獻[15]中列出的23種酚類化合物的臭氧氧化速率lgk,與優化篩選出的分子連接性指數和分子形狀指數中的4種1χ、2χ、K1、K2進行相關性分析,得到回歸方程為:
lgk =1.6101χ-1.7482χ+0.899 K1-1.598 K2+3.993
(1)

式(1)中n為樣本數。可以看出,該方程的決定系數r2為0.807,相關性并不理想,根據式(1)得到的lgk預測值與實驗值的平均殘差為0.09。
3 神經網絡模型的構建(Construction of neural network model)
為建立準確預測酚類化合物臭氧氧化降解的QSPR模型,在多元回歸分析基礎上,采用人工神經網絡(ANN)方法對酚類化合物的臭氧氧化速率lgk進一步進行研究,以篩選得到的4種結構參數作為神經網絡法的輸入層神經元數,酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率lgk作為輸出層神經元數,按照許祿等[19]建議的規則:
2.2> n/M ≥1.4
(2)
式(2)中:n為樣本數,M為神經網絡的總權重。M的計算式為:
M =(I+1)H+(H+1)Q
(3)
式(3)中:I、H、Q分別為神經網絡中輸入層、隱含層和輸出層的神經元數(即變量數)。這里的輸入層變量(即結構參數)I = 4;輸出層變量(即酚臭氧氧化速率lgk)Q = 1;按式(3)計算H只能取2,故神經網絡結構采用4:2:1方式。為避免過擬合、過訓練,將23個酚類化合物分子樣本分為3組: 訓練集(在每5個數據組中取第1、3、5個數據,依次類推)、測試集(數據組的第2個)和驗證集(數據組的第4個),由此構建得到神經網絡模型的總相關系數r=0.976,決定系數R2=0.9526,其他分別為: 訓練集決定系數R2=0.9506、測試集決定系數R2=0.9643、驗證集決定系數R2=0.9545;利用該神經網絡預測模型計算得到的酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的預測值(Pre.)列于表3中,該預測值(Pre.)與實驗值(Exp.)吻合度較為理想,兩者的平均殘差(Err.)為0.05,與多元回歸方法所得殘差0.09的結果相比,神經網絡法預測臭氧氧化速率的誤差明顯要小。楊靜等[15]分別用遺傳-偏最小二乘算法(GA-PLS)、遺傳-人工神經網絡法(GA-ANN)2種方法,也采用4個變量建模,得到的23個酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率預測值與實驗值的平均殘差分別為0.28和0.15,顯然本法的預測能力優于文獻,預測精度明顯高于文獻。本法預測值與實驗值的關系見圖1。
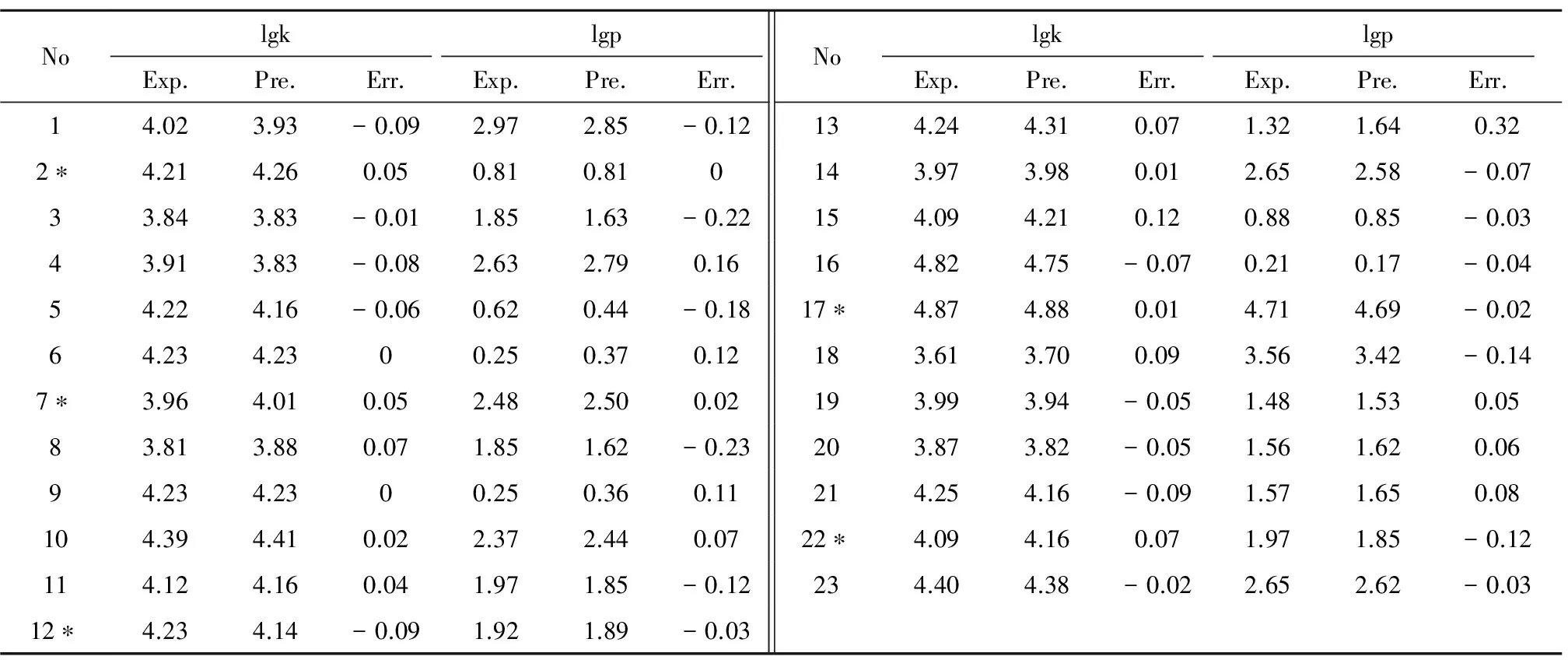
表3 酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的預測Table 3 Prediction of ozonation rates of phenolic compound
從表3可以看出,利用訓練集分子建構的模型對另外的測試集分子(標記有*的分子)進行預測,得到的平均殘差為0.054,與所有分子預測結果的平均殘差吻合,說明本法建構的預測模型有良好的魯棒性和預測能力。預測模型的權重和偏置見表4。對臭氧氧化速率lgk研究中,測試集的預測值與實驗值平均誤差為0.05,驗證集的預測值與實驗值平均誤差為0.03,與訓練集的平均誤差0.06及總平均誤差0.05基本吻合,說明不存在過訓練、過擬合現象。
4 普適性檢驗(Test of universality)
為檢驗利用結構參數構建模型的普適性,將上述4種結構參數與文獻[15]列出的辛醇-水分配系數(取對數值lgp)進行神經網絡建模,網絡結構、樣本分組等條件均與對lgk分析相同,所得模型的總相關系數r=0.993,各組相關系數為: 訓練集r=0.989、測試集r=0.999、驗證集r=0.997,可以看出結構參數與辛醇-水分配系數之間呈優級的非線性相關關系,利用模型得到的預測值Pre.與文獻值Exp.的平均殘差為0.10,吻合度較好,相關數據也列入表3中,預測值與實驗值的關系見圖2。
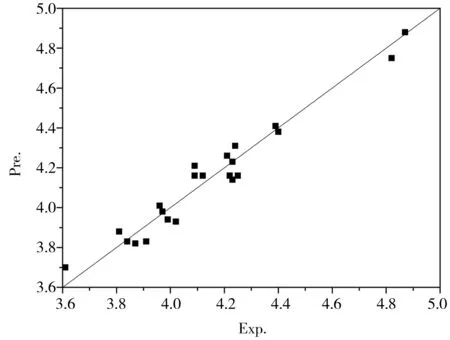
圖1 lgk的實驗值與預測值關系Fig. 1 Relationship between literal and calculated lgk
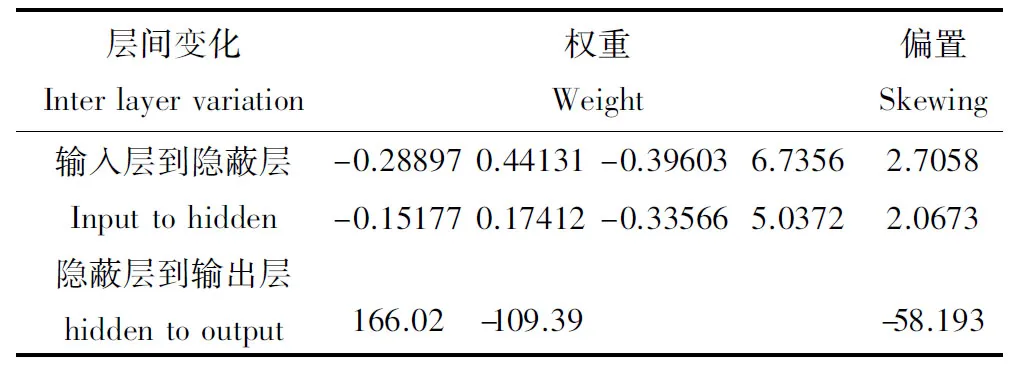
表4 BP-ANN模型的權重和偏置Table 4 Weights and bias of BP-ANN model

圖2 lgp的實驗值與預測值關系Fig. 2 Relationship between literal and calculated lgp
5 Jackknifed法檢驗(Jackknifed test)
為檢驗模型中分子的離域性,這里用Jackknifed法對模型(1)采用逐一剔除法檢驗,從23個酚類化合物分子中依次剔除1個,用余下的酚類化合物分子進行回歸分析,這樣就有23個決定系數值,對這些值作控制圖(見圖3)。
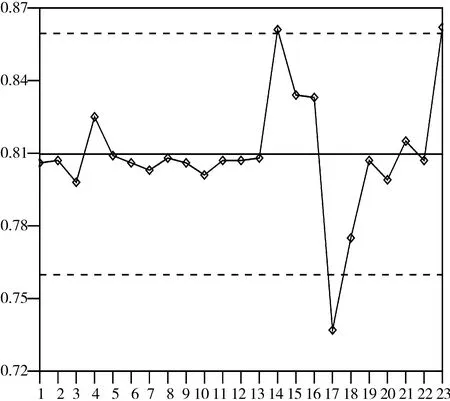
圖3 Jackknifed決定系數的檢驗Fig. 3 Inspection of Jackknifed determination coefficient
從檢驗的決定系數控制圖可以看出,只有去除17號分子時,模型的決定系數低至0.737,游離于可控區域之外,說明該分子的存在對模型的影響較大。
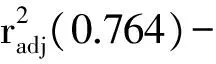

圖4 Jackknifed決定系數R2的雷達圖Fig. 4 Radar map of determination coefficient R2 of Jackknifed
6 結果與討論(Results and discussion)
考察酚類化合物的分子結構與其臭氧氧化速率的大小可以看出,當酚的苯環上連接的基團數越多時,分子體積越大,被臭氧氧化的速率也越大;當取代基數目相同時,基團的性質對速率有一定的影響,基團的吸電子能力越強,氧化速率越慢;分子連接性指數和分子形狀指數蘊含了分子的連接特性和空間密度等特性,在一定程度上與氧化速率的變化規律一致,通過與神經網絡方法結合,可進一步提高所建模型的預測能力:
(1)神經網絡對多元回歸分析具有一定的糾錯能力,能很好地反映出分子連接性指數結合分子形狀指數與酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率之間具有良好的非線性關系,模型具有良好的穩健性和較強的預測能力,預測平均殘差僅為0.05。
(2)優化篩選的指數與酚類化合物的其他性質也具有良好的非線性關系,具有普適性。將幾種指數與辛醇-水分配系數建立模型的預測平均殘差只有0.10,故可用于辛醇-水分配系數的數據挖掘。一般而言,辛醇-水分配系數值越大,進入生物體體內的有機物分子數目會越多,毒性會越強,故通過預測酚類化合物的辛醇-水分配系數,可揭示該類化合物對環境生物毒性的影響,評價其對環境的危險性。
[1] 崔秀君, 王志欣, 袁星, 等. 支持向量機用于酚類化合物毒性的QSAR研究[J]. 計算機與應用化學, 2008, 25(3): 298-302
Cui X J,Wang Z X,Yuan X,et al. Application support vector machine to QSAR study of toxicity of substituted phenols [J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2008, 25(3): 298-302 (in Chinese)
[2] 廖立敏,卿東紅,李建鳳,等. 烴基酚類化合物結構與毒性關系研究[J]. 環境化學, 2011, 30(2): 495-499
Liao L M,Qing D H,Li J F,et al. Quantitative structure-toxicity relationship study of alkylphenols[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(2): 495-499 (in Chinese)
[3] Altenburger R, Backhaus T, Boedeker W, et al. Predictability of the toxicity of multiple chemical mixtures to Vibrio fischeri: Mixtures composed of similarly acting chemicals [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2000, 19(9): 2341-2347
[4] 周文明,傅德黔,孫宗光. 中國水中優先控制污染物黑名單的確定[J]. 環境科學研究, 1991, 4(6): 9-12
Zhou W M, Fu D Q, Sun Z G. Determination of black list of China’s priority pollutants in water [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 1991, 4(6): 9-12 (in Chinese)
[5] 鄧金鋒, 黃占斌, 郭相坤. 酚類化合物分子連接性指數與毒性[J]. 環境污染與防治, 2007, 29(5): 340-342
Deng J F, Huang Z B, Guo X K. Correlation of toxicity and molecular connectivity index of hydroxybenzenes [J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2007, 29(5): 340-342 (in Chinese)
[6] Suksomtip M,Ukrisdawithid S,Bhusawang P,et al. Phenolic compound content, antioxidant and radical-scavenging properties of methanplic extracts from the seed coat of certain thai tamarind cultivars [J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 2010, 34(5): 916-931
[7] Kamalraj S, Ramesh S, Muthumary J. A novel antibacterial and antifungal phenolic compound from the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis mangiferae [J]. Natural Product Research, 2013, 27(16): 1445-1453
[8] 莫凌云,劉樹深,劉海玲. 苯酚與苯胺衍生物對發光菌的聯合毒性[J]. 中國環境科學, 2008, 28(4): 334-339
Mo L Y,Liu S S,Liu H L. Joint toxicity of selected phenolic and aniline derivatives to photobacterium [J]. China Environmental Science, 2008, 28(4): 334-339 (in Chinese)
[9] 于瑞蓮, 林喜燕, 胡恭任. 酚類化合物對發光菌的聯合毒性[J]. 華僑大學學報:自然科學版, 2009, 30(5): 549-552
Yu R L, Lin X Y, Hu G R. The joint toxicity of phenols to Photobacterium phosphoreum [J]. Journal of Huaqiao University: Natural Science, 2009, 30(5): 549-552 (in Chinese)
[10] 沈藝程, 龔翠然, 王飛, 等. 苯酚及其衍生物的電化學聚合及耐蝕性能[J]. 腐蝕與防護, 2006, 27(12): 637-639
Shen Y C, Gong C R, Wang F, et al. Electropolymerizationg and corrosion resistance of phenol and its derivatives [J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2006, 27(12): 637-639 (in Chinese)
[11] 王岳松, 張軍, 林樂明. 苯酚和苯胺類衍生物的結構與薄層色譜保留值關系的研究[J]. 色譜, 1999, 17(1): 18-20
Wang Y S, Zhang J, Lin L M. The relationship between thin-layer chromatographic retention values and molecular structures of phenol and aniline derivatives[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 1999, 17(1): 18-20 (in Chinese)
[12] Liu H, Tan J, Yu H X, et al. Determination of the apparent reaction rate constants for ozone degradation of substituted phenols and QSPR/QSAR analysis[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2010, 4(3): 507-512
[13] 堵錫華. 用新的路徑定位指數和神經網絡研究多溴聯苯醚理化性質[J]. 化工學報, 2014, 65(4): 1169-1178
Du X H. Physicochemical property of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by new path location index and neural network [J]. CIESC Journal,2014,65(4): 1169-1178 (in Chinese)
[14] Du X H,Zhuang W C,Shi X Q,et al. Research on thermodynamic properties of polybrominated diphenylamine by neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 28(1): 59-64
[15] 楊靜, 王建兵, 王亞華, 等. 酚類物質臭氧氧化降解的定量構效關系[J]. 環境化學, 2015, 34(10): 1932-1939
Yang J, Wang J B, Wang Y H, et al. Quantitative structure-activity relationship for the ozonation of phenols [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(10): 1932-1939 (in Chinese)
[16] 張婷, 梁逸曾, 趙晨曦, 等. 基于分子結構預測氣相色譜程序升溫保留指數[J]. 分析化學, 2006, 34(11): 1607-1610
Zhang T, Liang Y Z, Zhao C X, et al. Prediction of temperature-programmed retention indices from molecule structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2006, 34(11): 1607-1610 (in Chinese)
[17] Kier L B, Hall L H. Molecular Connectivity in Structure-Activity Analysis[M]. England: Research Studies Press, 1986: 69-75
[18] Kier L B. A shape index from molecular graphs [J]. Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships, 1985, 4(3): 109-116
[19] 許祿,邵學廣. 化學計量學方法[M]. 北京:科學出版社,2004: 441
Xu L,Shao X G. Methods of Chemometrics [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 441 (in Chinese)
◆
ResearchonOzonationRatesofPhenolicCompoundbyNeuralNetworkMethod
Du Xihua*,Wu Qiong,Chen Yan, Feng Hui
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xuzhou Institute of Technology, Xuzhou 221018,China
10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170106003
2017-01-06錄用日期2017-02-20
1673-5897(2017)3-675-06
X132
A
國家自然科學基金項目(No.21472071)
堵錫華(1963—),男,教授,研究方向為環境污染物構效學研究,E-mail: 12dxh@sina.com
堵錫華, 吳瓊, 陳艷, 等. 酚類化合物臭氧氧化速率的神經網絡研究[J]. 生態毒理學報,2017, 12(3): 675-680
Du X H,Wu Q,Chen Y, et al. Research on ozonation rates of phenolic compound by neural network method [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(3): 675-680 (in Chinese)

