過表達IDO大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞改善異位移植心臟存活①
賀繼剛 李貝貝 韓金秀 李宏遠 嚴 丹
(云南省第一人民醫院心臟大血管外科,昆明 650032)
過表達IDO大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞改善異位移植心臟存活①
賀繼剛 李貝貝 韓金秀 李宏遠 嚴 丹②
(云南省第一人民醫院心臟大血管外科,昆明 650032)
目的探討過表達IDO大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞(BMSC)改善大鼠腹腔異位移植心臟的存活機制。方法通過慢病毒載體GV308攜帶IDO基因轉染大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞構建過表達IDO大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞。建立大鼠腹腔異位移植心臟模型,經尾靜脈給予相應細胞處理:①利用超聲心動圖檢測移植心臟心功能變化。②采用小動物活體成像系統評估移植心臟局部熒光強度。③再取各組受體大鼠的脾臟,采用流式細胞技術檢測CD40、CD86、CD80、MHCⅡ、CD274、CD45RA、CD45RA+CD45RB、Treg細胞的表達情況。④取各組移植心臟,采用HE染色評估炎性細胞浸潤情況。⑤利用液相芯片檢測各組血清IL-1ɑ、IL-4、IL-1β、IL-2、IL-10、IFN-γ、IL-18、TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3因子的變化情況。結果①給予相應細胞處理,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs處理后2 d移植心臟的EF、FS較其余各組有提高。②采用小動物活體評估可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組移植心臟局部熒光強度最強。③給予干預措施后2 d可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組脾臟細胞CD40、CD86、CD80、MHCⅡ、CD45RA、CD45RA+CD45RB表達降低,而CD274、Treg細胞的表達增高。④采用液相芯片檢測各組提取血清可見在2 d時,過表達IDO-BMSCs組血清中IL-1α、IL-4、IL-1β、IL-2、IFN-γ、IL-18是降低的;IL-10、TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3表達量是升高的。HE染色證實過表達IDO-BMSCs組炎性細胞浸潤少于其他組。結論過表達IDO的BMSCs可以通過有效調節免疫DC、T細胞及細胞因子,從多個免疫層面改善移植心臟存活。
IDO;大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞;免疫抑制
20世紀以來,由于器官移植技術、移植免疫基礎研究以及各種免疫抑制劑的進展,器官移植已成為治療器官功能衰竭的有效治療手段。到2000年底,全球統計,共施行近80萬例次各種器官移植。但不可否認目前器官移植已經進入了一個尷尬的境地。一方面是隨著醫療生活水平改善,越來越多的器官終末期患者期盼器官移植。另一方面由于器官來源緊張及移植后的免疫排斥反應或免疫抑制藥物嚴重副作用使患者得不到有效治療、治療效果不佳、生活質量無法改善。而供體來源的緊張短期內無法有效緩解。本研究正是基于上述社會背景下,結合骨髓間充質干細胞免疫抑制調節特性聯合吲哚胺2,3-雙加氧酶(IDO),試圖尋找到一種有效改善心臟移植存活的生物免疫抑制方法。
1 材料與方法
1.1材料
1.1.1實驗動物 健康4周齡SPF級SD大鼠及Wistar大鼠各60只,均為雄性,由成都達碩實驗動物中心提供,動物許可證號為SCXK(川)2015-030。所有動物的喂養、觀察均按照GLP(非臨床研究管理規范)規定執行。
1.1.2主要試劑和儀器 TGFBMAG-64K-03試劑盒及RECYTMAG-65K-07試劑盒購自美國Merck millipore。 CD40-FITC、CD80-PE、CD86-PE、MH-CLASS Ⅱ-FITC、CD45RA-APC、CD3-FITC、CD4-APC、CD8a-PE、CD4-FITC、CD25-APC、FOXP3-PE、Foxp3 Staining Buffer 均購自eBioscience(美國);CD29、CD44、CD90、CD73、CD45、CD11b、CD34均購自BioLegend(美國);CD274-FITC購自Biorbyt(美國);CD45RA+CD45RB-FITC購自Thermo(美國);LS-C62680(ox62)FITC購自LSBio(美國);流式細胞儀BD Accuri C6 購自美國BD公司;MAGPIX檢測儀購自美國Luminex公司;小動物活體成像儀購自美國Caliper IVIS Lumina LT公司;心臟彩超儀購自美國PHILIPS EPIQ 7C。
1.2方法
1.2.1大鼠BMSC的分離、培養及鑒定 全骨髓培養大鼠BMSC,胰酶消化傳代至第7代。取生長至P7代BMSCs,待細胞融合達80%~90%時。制備單細胞懸液,采用流式細胞術檢測CD29、CD44、CD90、CD73、CD45、CD11b、CD34( CD29單抗5 μl做1∶ 20稀釋至100 μl,CD44單抗5 μl做1∶ 40稀釋至100 μl,CD90 5 μl作 1∶ 20稀釋至100 μl,CD73 5 μl 作1∶ 20稀釋至100 μl,CD45、CD11b、CD34單抗5 μl做1∶40稀釋至100 μl)。
1.2.2慢病毒載體及基因開啟技術構建過表達IDO大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞 ①將已構建成功的IDO基因插入慢病毒包裝質粒GV308中,構建GV308-IDO重組慢病毒包裝質粒。②將構建成功的GV308-IDO重組慢病毒包裝質粒轉染入大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞并加入基因開啟劑DOX(強力霉素)。③轉染成功后利用Q-PCR方法檢測轉染48 h IDO基因量的表達。
1.2.3大鼠腹腔異位移植心臟模型建立 ①取供體(Wistar大鼠)心臟開腹后將50 U/L的4℃冰肝素鹽水5 ml經下腔靜脈注射,2 min后剪開腹主動脈及下腔靜脈充分放血,剪開胸腔放入鹽水冰削,結扎下腔、左右上腔后剪斷升主動脈,游離肺動脈后剪斷肺動脈,結扎心臟后的肺靜脈。取下心臟。②供體心臟吻合到受體(SD大鼠)腹腔主動脈及下腔靜脈,將受體開腹后,分離腹主動脈及下腔靜脈,套3-0絲線,阻斷下腔靜脈及腹主動脈,剪開腹主動脈及下腔靜脈,采用連續單點吻合方法將供體心臟的主動脈及肺動脈與受體心臟的腹主動脈及下腔靜脈吻合。
1.2.4采用心臟彩超評估移植心臟心功能變化和采用小動物活體成像評估移植心臟熒光強度 收集過表達IDO-BMSCs、空載體-BMSCs、BMSCs細胞懸液。每106細胞中加入5 μl Dir(2.5 mmol/L)。在37℃培養40 min。利用PBS洗脫3次后應用。經尾靜脈注射到大鼠腹腔異位移植心臟術后3 d的模型中,每只400 μl,106個細胞。并將建模未處理組及正常大鼠給予喂養DOX(0.25 mg/L)作為對照組1及對照組3。另外一組建模未處理的大鼠按40 mg/kg的標準喂養嗎替麥考,作為對照組2。注射后分別喂養2 d,進行心臟彩超評估移植心臟心功能和小動物活體成像。
1.2.5體內流式檢測 ①完成小動物活體成像后,取其大鼠脾臟組織,制備成單細胞懸液。取100 μl細胞懸液分裝到1.5 ml EP管中,加相應抗體,避光孵育15 min。每支100 μl的細胞懸液加相應抗體量為CD40 0.5 mg/ml 1 μl、 CD86 0.2 mg/ml 0.8 μl、CD80 0.2 mg/ml 1.4 μl、 MHCⅡ 0.5 mg/ml 2 μl、CD274 0.5 mg/ml 1 μl、CD45RA 0.2 mg/ml 0.5 μl、CD45RA+CD45RB 0.1 mg/ml 1.4 μl、OX62 0.1 mg/ml 8 μl、CD3 0.5 mg/ml 0.5 μl、CD4 0.2 mg/ml 1 μl、CD8 0.2 mg/ml 0.5 μl。②Treg細胞染色步驟:取100 μl細胞懸液到離心管中,加細胞表面抗原CD4 0.5 mg/ml 0.5 μl和CD25 0.2 mg/ml 0.5 μl,避光孵育20 min。加1 ml Foxp3 Fixation/Permeabilization工作液,渦旋,室溫避光孵育40 min。加2 ml 1×Permeabilization緩沖液,1 000 r/min離心5 min,棄上清。用100 μl Permeabilization緩沖液重懸細胞,1 000 r/min離心5 min棄上清使剩余體積約為100 μl。加3 μl細胞內染色抗體0.2 mg/ml Foxp3,室溫避光孵育40 min。加 2 ml 1×Permeabilization緩沖液,1 000 r/min離心5 min,棄上清。加300 μl PBS重懸細胞后,采用BD Accuri C6流式細胞儀進行檢測。
1.2.6液相檢測 待小動物活體成像后,取其新鮮全血,制備成血清用于液相檢測,按RECYTMAG-65K-07試劑盒及TGFBMAG-64K-03試劑盒檢測說明書完成細胞因子濃度監測。
1.2.7心臟石蠟切片與HE染色 將心臟組織切成約1 cm×1 cm×1 cm放入包埋盒中,固定心臟組織并進行脫水,浸蠟,包埋,連續切片,貼片,烤片。切片進行常規脫蠟、水化;伊紅染色15 s;中性樹膠封片,顯微鏡下觀察顯色結果并拍照。
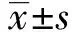
2 結果
2.1大鼠BMSC流式細胞儀鑒定結果 結果顯示超過90%大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞表達CD29、CD44、CD90、CD73。但不表達CD45、CD11b、CD34。
2.2慢病毒轉染大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞并加入DOX(強力霉素) 慢病毒轉染大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞加入DOX后48 h RT-PCR結果可見過表達組IDO表達量為62 906.27±4.36;對照組的表達量為0.05±0.02,見圖1。
2.3大鼠腹腔異位移植模型建立 異位心臟移植48 h,心臟彩超結果,見圖2。
2.4采用心臟彩超評估移植心臟心功能改變 大鼠腹腔異位心臟移植模型建立3 d,經大鼠尾靜脈給予各組BMSCs,采用心臟彩超評估移植心臟心功能改變,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組其射血分數前后差值為18.367±1.32較其余各組高。環比收縮前后差值為14.5±1.26較其余各組仍有較大改善,見圖3。
2.5采用小動物活體成像評估移植心臟熒光強度 大鼠心臟移植模型建立3 d后給予注射過表達IDO-BMSCs、空載體-BMSCs、BMSCs后2 d完成小動物活體成像,給予注射各組干細胞后,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組平均熒光強度為8.224±1.56,較其余各組熒光強度高,見圖4。

圖1 慢病毒轉染大鼠骨髓間充質干細胞后48 h IDO-PCRFig.1 Result of IDO-PCR that 48 hours after using lentiviral vector transfect rats bone marrow mesenchymal stem cellsNote:RT-PCR results showed that in the rats bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and comparison of NC(Negative control group),OE(overexpressing IDO group) expression level of IDO gene was 62 906.27 times of NC (P<0.05).

圖2 腹腔異位移植心臟48 h后復查心臟彩超結果Fig.2 After rat abdominal heterotopic heart transplan-tation model established 48 h that color Doppler examination resultNote:The white arrow points to the formation of the thrombus;The black arrow points to the transplanted heart.

圖3 大鼠移植模型建立3 d后給予IDO-BMSCs、空載體-BMSCs、BMSCs處理后2 d移植心臟心功能Fig.3 Using color Doppler examination assessment of transplanted cardiac function after intervention 2 daysNote:EF and FS were significantly improved in the transplant heart after 3 days of rat abdominal heterotopic heart transplantation model intervention by IDO-BMSCs 2 days, and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).

圖4 給予干預措施2 d后完成移植心臟局部熒光強度評價Fig.4 Assessing cardiac local average fluorescence intensity after intervention 2 daysNote:The group of IDO-BMSCs the cardiac local average fluorescence intensity was the strongest,and there were significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).
2.6采用流式細胞術檢測受體大鼠脾臟細胞免疫抗原分子變化 提取給予干預措施(IDO-BMSCs、空載體-BMSCs、BMSCs、嗎替麥考)2 d后受體大鼠脾臟細胞完成CD40、CD86、CD80、MHCⅡ、CD274、CD45RA、CD45RA+CD45RB、Treg表達檢測,將未給予干預措施組(未處理組)及正常大鼠的脾臟細胞作為對照:可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組CD40表達為3.24±0.23;CD86表達為9.24±0.74;CD80表達為8.54±0.26;MHCⅡ表達為24.76±0.36;CD45RA表達為47.23±1.27;CD45RB+CD45RA表達為26.15±1.46其表達較其余組低。過表達IDO-BMSCs組CD247表達為10.37±1.42;Treg細胞表達為6.54±2.35,其表達較其余組高,如圖5。

圖5 給予干預措施2 d后流式檢測脾臟細胞抗原分子表達Fig.5 Using flow cytometry detection of splenic cell antigen molecules expression after intervention 2 daysNote:Overexpression IDO-BMSCs group CD40,CD86,CD80,MHCⅡ,CD45RA,CD45RA+CD45RB expression are the lowest,and no significant difference compared with the normal group(P>0.05),and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).Overexpressing IDO-BMSCs group CD274 expression was the highest,and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).Overexpressing IDO-BMSCs group Treg expression was the highest,and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).

圖6 給予干預措施后2 d提取受體大鼠血清檢測細胞因子表達Fig.6 Detection of cytokine expression in serum of recipient rats after intervention 2 daysNote:Overexpress IDO-BMSCs group the expression of IL-1α,IL-4,IL-1β,IL-2,IFN-γ,IL-18 were reduced,and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05),but IL-10 were rised and had significant difference between the other groups(P<0.05).
2.7采用液相芯片檢測受體大鼠血清體液免疫分子變化 取腹腔異位移植術后2 d受體大鼠血清,使用RECYTMAG-65K-07試劑盒檢測IL-1ɑ、IL-4、IL-1β、IL-2、IL-10、IFN-γ、IL-18及使用TGFBMAG-64K-03試劑盒檢測TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組IL-1ɑ、IL-4、IL-1β、IL-2、IFN-γ、IL-18表達分別為(78.341±2.45、3.455±0.24、134.563±7.21、45.761±4.81、38.273±1.67、178.346±2.34)較其余組低但較正常組對照組高。IL-10的表達為(1 003.245±3.56 )較其余組表達增高,見圖6。

圖8 大鼠心臟移植模型建立3 d后給予干預措施2 d后HE染色結果Fig.8 After 3 days of rat abdominal heterotopic heart transplantation model, and after intervention 2 days,result of HE stainingNote:A.Overexpressing IDO-BMSCs group;B.Empty vector-BMSCs group;C.BMSCs group;D.Mycophenolate mofetil;E.Untreated model group;F.Normal heart.Untreated model group the infiltration of inflammatory cells were higher than others, but overexpressing IDO-BMSCs the infiltration of inflammatory cells are lesser than others.

圖7 給予干預措施后2 d提取受體大鼠血清檢測細胞因子表達Fig.7 Detection of TGFβ1,TGFβ2,TGFβ3 expression in serum of recipoient rats after intervantion 2 daysNote:Overexpressing IDO-BMSCs group the expression of TGFβ1,TGFβ2,TGFβ3 were rised, and there was significant difference between the other groups (P<0.05).
2.8采用液相芯片檢測受體大鼠血清TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3的變化 給予干預措施后2 d提取受體大鼠血清,檢測TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3的量,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3表達量為(80 006.982±4.23、0.321±0.12、7.346±1.12)較其余各組表達量高,見圖7。
2.9HE染色結果 大鼠心臟移植模型建立3 d后,給予注射相應BMSCs細胞后2 d取其腹腔心臟,制備石蠟切片,完成HE染色(圖8A~F)。可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組其炎癥細胞浸潤較正常組多但較其余組少。
3 討論
20世紀以來,由于器官移植技術、移植免疫基礎研究以及各種免疫抑制劑的進展,器官移植已成為臨床治療器官功能衰竭的有效治療手段。但不可否認的是免疫排斥一直是阻礙器官移植進一步發展的瓶頸。本實驗正是基于上述社會背景下,結合最新免疫調節研究結果,試圖尋找到一種有效的生物免疫抑制方法。
MSCs具有免疫調節功能,目前認為其可能涉及以下途徑:①MSCs持續不斷表達低水平的MHCⅠ分子但不表達MHCⅡ及協同刺激分子,包括CD80、CD86或者CD40[1]。因此,MSCs將不會激活異種或異體淋巴細胞而其本身缺乏免疫原性。②MSCs能夠抑制T、B淋巴細胞的激活和增生,部分是通過將細胞抑制于G0/G1細胞周期階段[2,3]。MSCs也可能通過可溶性細胞因子(如:IL-6、M-CSF)干涉樹突細胞的分化、成熟及功能[4]。③MSCs能夠通過釋放抗炎及抗凋亡分子修飾損傷組織的微環境并且保護損傷組織[5,6]。但目前MSCs臨床應用免疫排斥仍不成熟,歸根還是由于其調節免疫耐受的效果不確切。
IDO主要通過三條途徑完成免疫調節:①通過產生犬尿氨酸(KYN)[其是芳基羥化物(AhR)受體的一個天然配體]。IDO催化分解色氨酸并產生毒性代謝產物犬尿氨酸,其被淋巴細胞攝取可以阻止細胞進入G1期,而凋亡[6]。犬尿氨酸途徑,包括(犬尿氨酸、3OH-犬尿氨酸),可以誘導Tregs產生或抑制DCs[7,8]。治療上,應用天然及合成的犬尿氨酸產物可以促進免疫耐受,保護移植器官,減少由于病原感染而引起的組織損傷[9]。②通過消耗色氨酸以觸發細胞敏感轉錄信號途徑。色氨酸的消耗可以經由分子應激反應途徑,諸如:GCN2激酶和在哺乳動物中對色氨酸缺失反應的帕雷霉素樣受體(mTOR)兩者的激活可以發揮免疫調節作用。任何氨基酸的缺失都可以激活GCN2激酶而導致下游目標的磷酸化,真核細胞啟動因子(eIF)-2α的磷酸化可以阻斷大多數mRNA物種核糖體的轉錄,但是它可以選擇性增強少量轉錄因子轉錄[10]。色氨酸的缺失也可影響到營養敏感性mTOR途徑[11]。mTOR激活后可通過IDO、精氨酸酶、色氨酸羥化酶和其他酶抑制炎性位點色氨酸的分解代謝而影響Tregs細胞和效應性T細胞的功能[11]。③在DCs上表達的IDO可以直接作為細胞間信號分子[12]。IDO信號分子的功能是不依賴IDO酶的活性的。它主要是通過IDO和Src同族的第2域(SHP-1/SHP-2)與磷酸酯酶相接觸,觸發IDO的免疫調節域發揮作用。有研究表明,IDO-SHP復合體是維持TGF-β對老鼠血漿DCs發揮作用的關鍵因素[13]。
本實驗正是在上述研究基礎上通過建立大鼠異位心臟移植模型,采用心臟彩超、小動物活體成像、流式細胞、液相芯片、HE染色技術證實:①大鼠異位心臟移植模型建立后,給予相應細胞處理,可見過表達IDO-BMSCs處理后2 d移植心臟的EF、FS較其余各組有所提高。②進一步采用小動物活體評估也可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組移植心臟局部熒光強度最強。③給予干預措施后2 d可見過表達IDO-BMSCs組脾臟細胞CD40、CD86、CD80、MHCⅡ、CD45RA、CD45RA+CD45RB表達降低,而CD274、Treg細胞的表達增高。④采用液相芯片檢測各組提取血清可見,2 d時過表達IDO-BMSCs組血清中IL-1ɑ、IL-4、IL-1β、IL-2、IFNγ、IL-18是降低的。IL-10、TGFβ1、TGFβ2、TGFβ3表達量是升高的。HE染色證實過表達IDO-BMSCs組炎性細胞浸潤少于其他組。
綜上所述,過表達IDO的BMSCs可以通過有效調節免疫DC、T細胞及細胞因子。從多個免疫層面改善移植心臟存活。
[1] G?therstr?m C.Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience [J].Placenta,2007,262(5):509.
[2] Jones S,Horwood N,Cope A,etal.The antiproliferative effect of mesenchymal stem cells is a fundamental property shared by all stromal cells [J].J Immunol,2007,179(5):2824.
[3] Corcione A,Benvenuto F,Ferretti E,etal.Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions [J].Blood,2006,107(1):367-372.
[4] Djouad F,Charbonnier LM,Bouffi C,etal.Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism [J].Stem Cells,2007,25(8):2025-2032.
[5] Meirelles LS,Fontes AM,Covas DT,etal.Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells [J].Cytokine Growth Factor Rev,2009,20(5-6):419-427.
[6] Terness P, Bauer TM, Rose L,etal.Inhibition of allogeneic T cell proliferation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells: mediation of suppression by tryptophan metabolites[J].J Exp Med,2002,196(4):447-457.
[7] Belladonna ML,Grohmann U,Guidetti P,etal.Kynurenine pathway enzymes in dendritic cells initiate tolerogenesis in the absence of functional IDO[J].J Immunol,2006,177(1):130-137.
[8] Zaher SS,Germain C,Fu H .etal.3-hydroxykynurenine suppresses CD4+T-cell proliferation,induces T-regulatory-cell development,and prolongs corneal allograft survival[J].Invest J Vis Sci,2011,52(5):2640-2648.
[9] Kilberg MS,Shan J,Su N.ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid limitation[J].J Metab,2009,20(9):436-443.
[10] Powell JD,Pollizzi KN,Heikamp EB.etal.Regulation of immune responses by mTOR[J].Annu J Rev Immunol,2012,30(5):39-68.
[11] Dalton DK,Noelle RJ.The roles of mast cells in anticancer immunity[J].Cancer Immunol J,2012,61(9):1511-1520.
[12] Cobbold SP,Adams E,Farquhar CA,etal.Infectious tolerance via the consumption of essential amino acids and mTOR signaling[J]. J Acad Sci USA,2009,106(29):12055-12060.
[13] Pallotta MT,Orabona C,Volpi C,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a signaling protein in long-term tolerance by dendritic cells[J].J Nat Immunol,2011,12(9):870-878.
[收稿2017-05-28]
(編輯 倪 鵬)
ImprovedsurvivalofheterotopichearttransplantoverexpressingIDOratbonemesenchymalstemcells
HEJi-Gang,LIBei-Bei,HANJin-Xiu,LIHong-Yuan,YANDan.
CardiovascularSurgery,theFirstPeople′sHospitalofYunnanProvince,Kunming650032,China
Objective:To explores the improvement in survival mechanism of a rat model of enterocoelia heterotopic heart transplant with rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells(BMSCs) IDO-overexpressing.MethodsIDO-overexpressing rat BMSCs were produced through transfection of rat BMSCs with IDO gene carried by the lentiviral vector GV308.A rat model of enterocoelia heterotopic heart transplantation was established.This rat model
a cell treatment via its tail veins,as follows:①Echocardiography was employed to detect the functional changes in the transplanted heart.②The fluorescence intensity of the different parts of the transplanted heart was evaluated using a body imaging system for small living animals.③Receptors rat spleens cells were obtained and used for a flow cytometric detection of the expression levels of CD40,CD86,CD80,MHCⅡ,CD274,CD45RA,CD45RA+CD45RB,and Treg cells.④A transplanted heart was obtained after injection to evaluate inflammatory cell infiltration through HE staining.⑤Liquid phase chips were used to detect changes in the serum factors IL-1ɑ,IL-4,IL-1β,IL-2,IL-10,IFN-γ,IL-18,TGFβ1,TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 in after injection cells.Results①After the rat heterotopic heart transplantation model and the corresponding cell treatment were established,after over-expressed IDO-BMSCs treatment 2 days the EF and FS were higher in the transplanted heart than other groups.②The fluorescence intensity of the parts of the transplanted heart was highest in the IDO-BMSC overexpression group as revealed by small animal living body evaluation.③Two days after the interventions,spleen cells in the over-expressed IDO-BMSCs group showed reduced expression levels of CD40,CD86,CD80,MHCⅡ,CD45RA,CD45RA+CD45RB and increased expression levels of CD274 and Treg cells as revealed by flow cytometry.④Liquid phase chips were used to examine the serum obtained from each group 2 days after the intervention,and the results showed that the expression levels of IL-1α,IL-4,IL-1β,IL-2,IFN-γ and IL-18 in the IDO-BMSC overexpression group decrease.By contrast,the expression levels of IL-10,TGFβ1,TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 increase.HE staining results demonstrate that inflammatory cell infiltration was lower in IDO-BMSC overexpression group than in other groups.ConclusionIDO-overexpressing BMSCs improve the survival of a transplanted heart through effective adjustment of immune DC and T cells,as well as cell factors.
IDO;Rat bone mesenchymal stem cell;Immunosuppression
①本文為國家自然科學基金(81460073)、云南省科技廳-昆明醫科大學應用基礎研究聯合專項(2014FB089)、云南省教育廳科學研究基金(2015Z051)、中國博士后科學基金(2015M582764XB)、成都醫學院2015年度科研項目(CYZ15-18)和云南省醫學后備人才(H-201607)項目。
②通訊作者,E-mail:jiganghe999@163.com。
R392.4
A
1000-484X(2017)10-1447-06
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.10.002
賀繼剛(1980年-),男,副主任醫師,碩士生導師,主要從事干細胞在終末重癥心臟疾病中的應用研究。

