頸動脈粥樣硬化斑塊無創性高分辨力磁共振成像研究進展
高鵬 楊斌 焦力群 張鴻祺 朱鳳水
·綜述·
頸動脈粥樣硬化斑塊無創性高分辨力磁共振成像研究進展
高鵬 楊斌 焦力群 張鴻祺 朱鳳水
頸動脈粥樣硬化性狹窄與腦卒中復發密切相關。目前頸動脈狹窄的治療方法主要包括藥物治療和外科手術(頸動脈支架成形術和頸動脈內膜切除術)。腦卒中預防在于識別頸動脈狹窄危險因素,篩查腦卒中復發高危患者,從而使其從藥物治療或外科手術中獲益,然而目前僅根據頸動脈狹窄程度制定治療方案,缺乏個體化治療。近年來,新型影像學技術如無創性高分辨力磁共振成像(HRMRI)等,可以檢測出頸動脈易損斑塊。與傳統數字減影血管造影術測量的頸動脈狹窄程度相比,無創性HRMRI可以根據頸動脈斑塊特征準確預測同側腦卒中風險,從而指導個體化治療。
頸動脈狹窄; 動脈粥樣硬化; 磁共振成像; 綜述
頸動脈狹窄程度和粥樣硬化斑塊穩定性均與腦卒中發生和復發密切相關。目前主要采用數字減影血管造影術(DSA)定量檢測頸動脈狹窄程度,而較少關注頸動脈斑塊穩定性。近年來,無創性高?分辨力磁共振成像(HRMRI)逐漸用于檢測頸動脈斑塊的穩定性。與DSA相比,HRMRI具有無創性、安全、費用相對較低和可重復性等優點,在DSA顯示血管狹窄的同時,HRMRI可以檢測斑塊穩定性,提供更敏感和客觀信息,具有較高的個體化預測價值,是一項極具潛力的影像學技術。本文擬對近年HRMRI檢測頸動脈斑塊穩定性研究進展進行綜述。
一、頸動脈狹窄相關臨床試驗的缺陷
根據美國心臟協會(AHA)/美國卒中協會(ASA)指南[1],頸動脈狹窄藥物治療和外科手術[包括頸動脈支架成形術(CAS)和頸動脈內膜切除術(CEA)]的治療決策主要依靠兩方面:(1)頸動脈狹窄程度,狹窄率<50%,輕度狹窄;50%~69%,中度狹窄;≥70%,重度狹窄。(2)是否存在臨床癥狀。結合上述兩方面,近20年涌現出大量頸動脈狹窄相關臨床試驗,例如,1991年的北美癥狀性頸動脈內膜切除術試驗(NASCET)顯示,對于頸動脈狹窄程度>70%患者,隨訪2年CEA組腦卒中復發率為9%,遠低于單純藥物組的26%[2]。2004年針對無癥狀性頸動脈狹窄患者的無癥狀性頸動脈外科手術試驗(ACST)顯示,當頸動脈狹窄程度>60%時,隨訪5年CEA組腦卒中復發率為6.4%,低于單純藥物組的11.8%;該項研究還顯示,對于>75歲的頸動脈狹窄程度>70%患者,隨訪5年腦卒中復發率和病死率顯著下降[3];2010年,ACST試驗10年長期隨訪結果發表于Lancet,CEA組腦卒中復發率為13.4%,低 于 單 純 藥 物 組 的 17.9%[4]。 Abbott 等[5]和Nicolaides等[6]報告的無癥狀性頸動脈狹窄患者單純藥物治療后同側腦卒中年復發率為0.6%~1.3%,低于ACST試驗的CEA組(5年腦卒中復發率為6.4%,腦卒中年復發率約1.3%[3])和無癥狀性頸動脈粥樣硬化研究(ACAS)的CEA組(5年腦卒中復發率為5.1%,腦卒中年復發率為1.0%[7])。因此,積極藥物治療仍是頸動脈狹窄的主要治療方法,主要表現為:(1)部分高危患者并不能從頸動脈支架成形術和頸動脈內膜切除術中獲益。(2)無論癥狀性(頸動脈狹窄程度<70%)或無癥狀性頸動脈狹窄患者,均無證據顯示頸動脈支架成形術和頸動脈內膜切除術療效優于單純藥物治療[8]。因此,僅根據頸動脈狹窄程度進行危險程度分層是遠遠不夠的,準確評價頸動脈狹窄程度和檢測斑塊穩定性以預測同側腦卒中風險的個體化分析具有潛在的臨床價值。
二、易損斑塊定義
頸動脈斑塊性狀的判斷和易損斑塊的辨別,應借鑒“冠狀動脈易損斑塊”定義。“冠狀動脈易損斑塊”的定義最早由Virmani等[9]于2002年提出,他在尸檢中發現冠狀動脈粥樣硬化斑塊存在較大的富脂壞死核心(LRNC)和菲薄的纖維帽(FC),并確定其與心源性猝死有關。經臨床、病理學、分子生物學和影像學研究,一致認為典型易損斑塊的病理學特征為[7,10]:(1)較大的富脂壞死核心。(2)菲薄的纖維帽。(3)炎癥反應,如巨噬細胞浸潤。(4)斑塊裂隙(fissured plaque)。(5)斑塊表面鈣化結節。(6)斑塊內出血(IPH)。然而,上述“易損斑塊”定義僅限于病理學層面,實際工作中難以獲得活體斑塊,因此需要影像學技術以實現體外無創性斑塊成像。鑒于此,基于MRI的冠狀動脈和頸動脈易損斑塊成像技術和影像學分型應運而生[11]。1995年,AHA/ASA指南基于尸體解剖提出冠狀動脈粥樣硬化斑塊病理學分型,分為Ⅰ~Ⅷ型[12],并在此基礎上衍生出基于HRMRI的頸動脈易損斑塊影像學分型,亦分為Ⅰ~Ⅷ型(表1)[13]。
三、頸動脈斑塊無創性HRMRI在預測腦卒中風險方面優于單純DSA測量頸動脈狹窄程度
1.較大的富脂壞死核心和菲薄的纖維帽顯著增加腦卒中復發風險 (1)HRMRI可以識別和定量檢測頸動脈斑塊富脂壞死核心。既往大量研究顯示,富脂壞死核心體積較大和(或)纖維帽菲薄或破裂與近期腦卒中事件、同側動脈?動脈栓塞性缺血性卒中事件、頸動脈斑塊去穩定化、纖維帽破裂、斑塊內出 血 和 斑 塊 體 積 擴 大 顯 著 相 關[9,14?18]。 一 項 針 對 頸動脈狹窄程度50%~99%患者的橫斷面臨床研究顯示,HRMRI顯示的同側短暫性腦缺血發作(TIA)和(或)腦卒中與較大的富脂壞死核心和(或)菲薄或破裂的纖維帽顯著相關,而與頸動脈狹窄程度無關聯性[14]。(2)富脂壞死核心及其體積可以指導強化調脂治療,亦可以評價調脂治療效果[19]。Demarco等[14]的研究顯示,盡管頸動脈狹窄程度未達重度狹窄(≤70%),但HRMRI仍顯示易損斑塊,表現為較大的富脂壞死核心合并斑塊內出血、菲薄或破裂的纖維帽,考慮為腦卒中高危患者,與近期腦卒中風險具有相關性;盡管頸動脈狹窄程度達重度狹窄(>70%),但HRMRI仍顯示穩定斑塊,表現為富脂壞死核心體積較小、無斑塊內出血、纖維帽厚重,考慮為無癥狀性頸動脈狹窄。一項納入33例頸動脈狹窄患者的前瞻性臨床試驗顯示,經過3年強化調脂治療(阿托伐他汀10~80 mg/d+煙酸緩釋片2 g/d+考來維侖3.80 g/d),復查HRMRI顯示富脂壞死核心體積縮小,生物學時間效應表現為先出現斑塊脂質排空,再出現斑塊消融[19]。(3)HRMRI不單純依靠 DSA測量的頸動脈狹窄程度即可定性和定量檢測頸動脈斑塊富脂壞死核心,從而進行腦卒中危險程度分層,篩選出適宜進行強化調脂治療或外科手術的患者,以及評價治療效果。
2.斑塊內出血可以顯著增加腦卒中復發風險
(1)斑塊內出血發生機制是頸動脈斑塊內富脂壞死核心的紅細胞滲出和鐵離子沉積。上述兩個過程促進炎癥反應,導致斑塊去穩定化[10,20]。一項前瞻性臨床試驗顯示,頸動脈斑塊內出血與斑塊進展相關[21]。既往由于臨床檢查方法有限,不能動態觀察斑塊內出血的發生與發展過程;現有的無創性頸動脈斑塊成像技術可以同時觀察斑塊進展和頸動脈粥樣硬化自然病程。(2)斑塊內出血與斑塊體積擴大和同側動脈?動脈栓塞性缺血性卒中事件相關。Takaya等[17]納入98例無癥狀性中至重度頸動脈狹窄患者,HRMRI顯示43例(43.88%)存在斑塊內出血,經過38.20個月隨訪,6例(6.12%)發生同側缺血性卒中且均存在斑塊內出血。Altaf等[22]納入64例癥狀性頸動脈狹窄患者(狹窄程度30%~69%),39例(60.94%)基線HRMRI顯示存在斑塊內出血,經28個月隨訪,14例(21.88%)發生同側缺血性卒中,其中13例(20.31%)存在斑塊內出血。Meta分析顯示,基線HRMRI顯示存在斑塊內出血的頸動脈狹窄患者發生同側腦卒中風險是無斑塊內出血患者的 5.60 倍[23]。
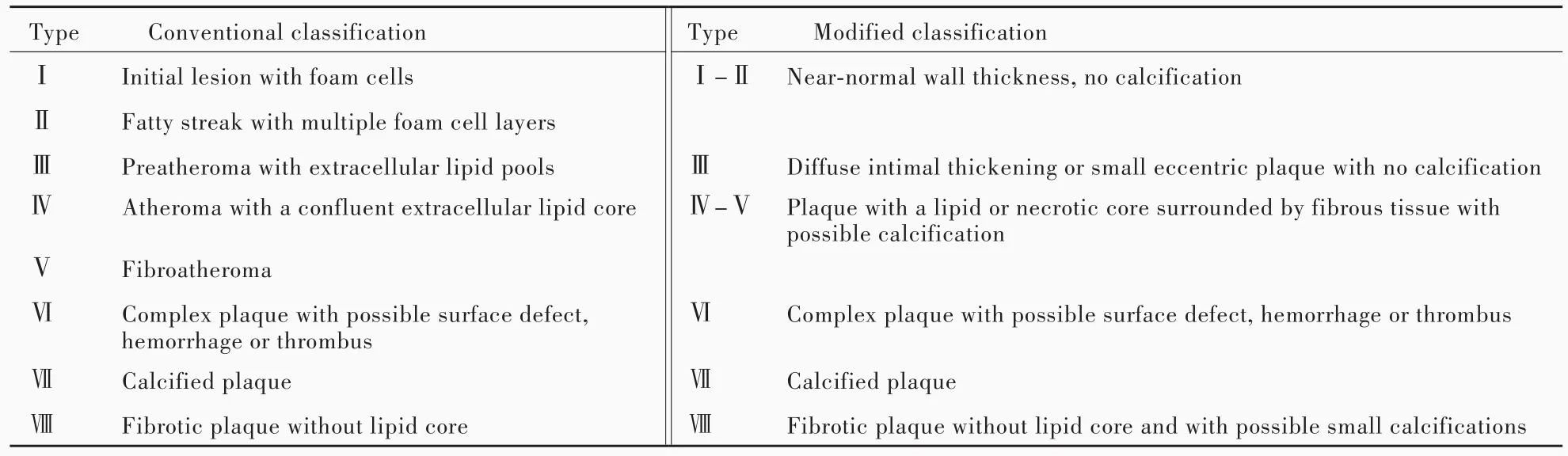
表1 基于HRMRI的頸動脈易損斑塊影像學分型[13]Table 1. Conventional and modified classification of carotid vulnerable plaque based on HRMRI[13]
3.頸動脈斑塊性狀的性別差異及其與同側腦卒中風險的關系 Ota等[24]納入131例頸動脈狹窄患者(狹窄程度≥50%),男性不穩定型斑塊特征高于女性,表現為男性頸動脈斑塊富脂壞死核心、纖維帽菲薄或破裂、斑塊內出血發生率均高于女性,男性易損斑塊發生率亦高于女性,可以部分解釋頸動脈內膜切除術在預防男性無癥狀性頸動脈狹窄相關腦卒中方面優于女性。另一項研究顯示,頸動脈斑塊性狀的性別差異不僅限于中至重度頸動脈狹窄患者,亦存在于輕度頸動脈狹窄患者(狹窄程度<50%)[25]。因此,頸動脈狹窄的治療策略應同時考慮易損斑塊特征和性別因素。
四、展望
1.頸動脈斑塊HRMRI技術 未來頸動脈斑塊HRMRI技術有待改進和提高成像質量、縮短成像時間。2013年出現的非對比血管造影和出血成像(SNAP),將檢查時間縮短至4~5分鐘,可以檢測到斑塊內出血[26]。2012年出現的多對比三維梯度回波序列,可以提高成像質量,提供良好的信噪比(SNR)[27]。共識普遍認為,綜合 3 項 HRMRI序列(如SNAP、3D?T1WI和增強3D?T1WI)掃描4分鐘,即可獲得頸動脈易損斑塊的所有特征,包括富脂壞死核心、纖維帽和斑塊內出血。若這一技術實現,快速多對比頸動脈斑塊成像可以列入常規影像學檢查。此外,提高成像質量還有賴于專用的頸動脈斑塊線圈。第1代4通道線圈通常置于頸部中間,可以提供高信噪比圖像,掃描范圍覆蓋10~12 cm區域;第2代頸部線圈采用高密度設計(6~8通道線圈),全面提高信噪比,亦可以增加掃描范圍(覆蓋16~18 cm區域),第1和2代線圈均已通過美國食品與藥品管理局(FDA)審批,并已廣泛應用于臨床;第3代線圈為頸部高度集成線圈,系神經血管專用,掃描范圍下至主動脈弓,上至Willis環和腦組織。如果將第3代線圈與新研發的HRMRI序列相結合,可以在45分鐘內完成主動脈弓、頸動脈、腦組織和Willis環成像,極大地擴展頸動脈斑塊成像的臨床應用。目前,HRMRI技術自動識別頸動脈斑塊成分的可行性已經完成[28],有助于臨床醫師對頸動脈斑塊的認識和理解。
2.頸動脈斑塊HRMRI的前瞻性多中心研究未來研究最核心的問題在于,頸動脈斑塊HRMRI能否替代傳統DSA測量的頸動脈狹窄程度以指導臨床決策、改進治療效果。可以設想,頸動脈易損斑塊HRMRI可以同時指導藥物治療和外科手術。(1)HRMRI可以檢出頸動脈易損斑塊的富脂壞死核心,從而指導臨床醫師進行積極藥物治療;此外,還可以根據頸動脈斑塊HRMRI設計前瞻性多中心隨機對照臨床試驗,將存在富脂壞死核心的頸動脈狹窄患者隨機分為標準藥物治療組和積極藥物治療組,除將短暫性腦缺血發作和(或)腦卒中作為終點事件外,也將富脂壞死核心體積變化作為終點事件或頸動脈粥樣硬化療效判定指標。(2)對于近期發生癥狀性頸動脈狹窄的患者,HRMRI可以進行腦卒中危險程度分層,篩選出適宜早期外科手術(頸動脈支架成形術或頸動脈內膜切除術)的患者。由此可見,即使輕至中度頸動脈狹窄患者,如果HRMRI檢出斑塊內出血,同側短暫性腦缺血發作和(或)腦卒中風險明顯增加;早期外科手術(頸動脈支架成形術或頸動脈內膜切除術)可以有效預防腦卒中復發,尚待前瞻性多中心隨機對照臨床試驗的驗證。
綜上所述,腦卒中預防的關鍵在于早期識別危險因素。過去幾十年,全世界在危險因素控制方面取得長足進步,如高血壓、冠心病、糖尿病、高脂血癥等均得到有效控制。未來腦卒中預防的重點在于識別個體化危險因素。國際上多個單中心臨床試驗業已證實基于HRMRI的頸動脈易損斑塊成像技術較傳統的頸動脈超聲或DSA能夠更準確預測腦卒中復發風險[17,29?30]。我們也寄希望于國際上的前瞻性臨床試驗以驗證頸動脈易損斑塊與同側動脈?動脈栓塞性缺血性卒中事件的相關性。未來有望根據頸動脈易損斑塊的HRMRI,提供個體化藥物治療和外科手術方案。
[1]Kernan WN,Ovbiagele B,Black HR,Bravata DM,Chimowitz MI,Ezekowitz MD,Fang MC,Fisher M,Furie KL,Heck DV,Johnston SC,Kasner SE,Kittner SJ,Mitchell PH,Rich MW,RichardsonD,Schwamm LH,WilsonJA;AmericanHeart Association Stroke Council,Councilon Cardiovascularand Stroke Nursing,Council on Clinical Cardiology,Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease.Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack:a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association.Stroke,2014,45:2160?2236.
[2]Barnett HM,Taylor DW,Haynes RB,Sackett DL,Peerless SJ,Ferguson GG,Fox AJ,Rankin RN,Hachinski VC,Wiebers DO,Eliasziw M; North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators.Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high?grade carotid stenosis.N Engl J Med,1991,325:445?453.
[3]Halliday A,Mansfield A,Marro J,Peto C,Peto R,Potter J,Thomas D;MRC Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial(ACST)Collaborative Group.Prevention of disabling and fatal strokes by successful carotid endarterectomy in patients without recent neurologicalsymptoms:randomised controlled trial.Lancet,2004,363:1491?1502.
[4]Halliday A,Harrison M,Hayter E,Kong X,Mansfield A,Marro J,Pan H,Peto R,Potter J,Rahimi K,Rau A,Robertson S,StreiflerJ,ThomasD;Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial(ACST)Collaborative Group.10?year stroke prevention after successfulcarotid endarterectomy forasymptomatic stenosis(ACST?1):a multicentre randomised trial.Lancet,2010,376:1074?1084.
[5]Abbott AL,Chambers BR,Stork JL,Levi CR,Bladin CF,Donnan GA.Embolic signals and prediction of ipsilateral stroke or transient ischemic attack in asymptomatic carotid stenosis:a multicenter prospective cohort study.Stroke,2005,36:1128?1133.
[6]Nicolaides AN,Kakkos SK,Griffin M,Sabetai M,Dhanjil S,Tegos T,Thomas DJ,Giannoukas A,Geroulakos G,Georgiou N,Francis S,Ioannidou E,DoréCJ;Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis and Risk of Stroke(ACSRS)Study Group.Severity of asymptomatic carotid stenosis and risk of ipsilateral hemispheric ischaemic events:results from the ACSRS study.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2005,30:275?284.
[7]NaghaviM,Libby P,Falk E,CasscellsSW,Litovsky S,Rumberger J,Badimon JJ,Stefanadis C,Moreno P,Pasterkamp G,Fayad Z,Stone PH,Waxman S,Raggi P,Madjid M,Zarrabi A,Burke A,Yuan C,Fitzgerald PJ,Siscovick DS,de Korte CL,Aikawa M,Airaksinen KE,Assmann G,Becker CR,Chesebro JH,Farb A,Galis ZS,Jackson C,Jang IK,Koenig W,Lodder RA,March K,Demirovic J,Navab M,Priori SG,Rekhter MD,Bahr R,Grundy SM,Mehran R,Colombo A,Boerwinkle E,Ballantyne C,Insull W Jr,Schwartz RS,Vogel R,Serruys PW,Hansson GK,Faxon DP,Kaul S,Drexler H,Greenland P,MullerJE,VirmaniR,RidkerPM,ZipesDP,Shah PK,Willerson JT.From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient:a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies.PartⅡ.Circulation,2003,108:1772?1778.
[8]Abbott AL.Medical(nonsurgical)intervention alone is now best for prevention of stroke associated with asymptomatic severe carotid stenosis:results of a systematic review and analysis.Stroke,2009,40:E573?583.
[9]VirmaniR,BurkeAP,KolodgieFD,Farb A.Vulnerable plaque:the pathology of unstable coronary lesions.J Interv Cardiol,2002,15:439?446.
[10]NaghaviM,Libby P,Falk E,CasscellsSW,Litovsky S,Rumberger J,Badimon JJ,Stefanadis C,Moreno P,Pasterkamp G,Fayad Z,Stone PH,Waxman S,Raggi P,Madjid M,Zarrabi A,Burke A,Yuan C,Fitzgerald PJ,Siscovick DS,de Korte CL,Aikawa M,Juhani Airaksinen KE,Assmann G,Becker CR,Chesebro JH,Farb A,Galis ZS,Jackson C,Jang IK,Koenig W,LodderRA,MarchK,DemirovicJ,NavabM,PrioriSG,Rekhter MD,Bahr R,Grundy SM,Mehran R,Colombo A,Boerwinkle E,Ballantyne C,Insull W Jr,Schwartz RS,Vogel R,Serruys PW,Hansson GK,Faxon DP,Kaul S,Drexler H,Greenland P,Muller JE,Virmani R,Ridker PM,Zipes DP,Shah PK,Willerson JT.From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient:a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies.PartⅠ.Circulation,2003,108:1664?1672.
[11]Saam T,Hatsukami TS,Takaya N,Chu B,Underhill H,Kerwin WS,Cai J,Ferguson MS,Yuan C.The vulnerable,or high?risk,atherosclerotic plaque: noninvasive MR imaging for characterization and assessment.Radiology,2007,244:64?77.
[12]Stary HC,Chandler AB,Dinsmore RE,Fuster V,Glagov S,Insull W Jr,Rosenfeld ME,Schwartz CJ,Wagner WD,Wissler RW.A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis:a report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis,American Heart Association.Circulation,1995,92:1355?1374.
[13]Cai JM,Hatsukami TS,Ferguson MS,Small R,Polissar NL,Yuan C.Classification of human carotid atherosclerotic lesions with in vivo multicontrast magnetic resonance imaging.Circulation,2002,106:1368?1373.
[14]Demarco JK,OtaH,Underhill HR,ZhuDC,ReevesMJ,Potchen MJ,Majid A,Collar A,Talsma JA,Potru S,Oikawa M,Dong L,Zhao X,Yarnykh VL,Yuan C.MR carotid plaque imaging and contrast?enhanced MR angiographyidentifies lesions associated with recent ipsilateral thromboembolic symptoms:an in vivo study at 3T.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2010,31:1395?1402.
[15]Hatsukami TS,Ross R,Polissar NL,Yuan C.Visualization of fibrous cap thickness and rupture in human atherosclerotic carotid plaque in vivo with high?resolution magnetic resonance imaging.Circulation,2000,102:959?964.
[16]Cai J,Hatsukami TS,Ferguson MS,Kerwin WS,Saam T,Chu B,Takaya N,PolissarNL,Yuan C.In vivo quantitative measurement of intact fibrous cap and lipid?rich necrotic core size in atherosclerotic carotid plaque:comparison of high?resolution,contrast?enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and histology.Circulation,2005,112:3437?3444.
[17]Takaya N,Yuan C,Chu B,Saam T,Underhill H,Cai J,Tran N,Polissar NL,Isaac C,Ferguson MS,Garden GA,Cramer SC,Maravilla KR, Hashimoto B, Hatsukami TS.Association between carotid plaque characteristics and subsequent ischemic cerebrovascular events:a prospective assessment with MRI?initial results.Stroke,2006,37:818?823.
[18]Underhill HR,Hatsukami TS,Cai J,Yu W,DeMarco JK,Polissar NL,Ota H,Zhao X,Dong L,Oikawa M,Yuan C.A noninvasive imaging approach to assess plaque severity:the carotid atherosclerosis score.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2010,31:1068?1075.
[19]Zhao XQ,Dong L,Hatsukami T,Phan BA,Chu B,Moore A,Lane T,Neradilek MB,Polissar N,Monick D,Lee C,Underhill H,Yuan C.MR imaging of carotid plaque composition during lipid?lowering therapy a prospective assessment of effect and time course.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging,2011,4:977?986.
[20]Kolodgie FD,Gold HK,Burke AP,Fowler DR,Kruth HS,Weber DK,Farb A,Guerrero LJ,Hayase M,Kutys R,Narula J, Finn AV, Virmani R. Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma.N Engl J Med,2003,349:2316?2325.
[21]Takaya N,Yuan C,Chu B,Saam T,Polissar NL,Jarvik GP,Isaac C,McDonough J,Natiello C,Small R,Ferguson MS,Hatsukami TS.Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques:a high?resolution magnetic resonance imaging study.Circulation,2005,111:2768?2775.
[22]Altaf N,Daniels L,Morgan PS,Auer D,MacSweeney ST,Moody AR,Gladman JR.Detection of intraplaque hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging in symptomatic patients with mild to moderate carotid stenosis predicts recurrent neurological events.J Vasc Surg,2008,47:337?342.
[23]Saam T,Hetterich H,Hoffmann V,Yuan C,Dichgans M,Poppert H,Koeppel T,Hoffmann U,Reiser MF,Bamberg F.Meta?analysis and systematic review of the predictive value of carotid plaque hemorrhage on cerebrovascular events by magnetic resonance imaging.J Am Coll Cardiol,2013,62:1081?1091.
[24]Ota H,Reeves MJ,Zhu DC,Majid A,Collar A,Yuan C,DeMarco JK.Sex differences in patients with asymptomatic carotid atherosclerotic plaque:in vivo 3.0?T magnetic resonance study.Stroke,2010,41:1630?1635.
[25]Ota H,Reeves MJ,Zhu DC,Majid A,Collar A,Yuan C,Demarco JK.Sex differences of high?risk carotid atherosclerotic plaque with less than 50%stenosis in asymptomatic patients:an in vivo 3T MRI study.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2013,34:1049?1055.
[26]Wang J,B?rnert P,Zhao H,Hippe DS,Zhao X,Balu N,FergusonMS,Hatsukami TS,Xu J,Yuan C,KerwinWS.Simultaneous noncontrast angiography and intraplaque hemorrhage(SNAP)imaging for carotid atherosclerotic disease evaluation.Magn Reson Med,2013,69:337?345.
[27]Liu W,Balu N,Sun J,Zhao X,Chen H,Yuan C,Zhao H,Xu J,Wang G,Kerwin WS.Segmentation of carotid plaque using multicontrast 3D gradient echo MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging,2012,35:812?819.
[28]LiuF,XuD,FergusonMS,ChuB,Saam T,TakayaN,HatsukamiTS,Yuan C,Kerwin WS.Automated in vivo segmentation of carotid plaque MRI with Morphology?Enhanced probability maps.Magn Reson Med,2006,55:659?668.
[29]Kwee RM,van Oostenbrugge RJ,Mess WH,Prins MH,van der Geest RJ,ter Berg JW,Franke CL,Korten AG,Meems BJ,van Engelshoven JM,Wildberger JE,Kooi ME.MRI of carotid atherosclerosis to identify TIA and stroke patients who are at risk of a recurrence.J Magn Reson Imaging,2013,37:1189?1194.
[30]Turc G,Oppenheim C,Naggara O,Eker OF,Calvet D,Lacour JC,Crozier S,Guegan ?Massardier E,Hénon H,Neau JP,Toussaint JF,Mas JL,Méder JF,Touzé E;HIRISC Study Investigators. Relationships between recent intraplaque hemorrhage and stroke risk factors in patients with carotid stenosis:the HIRISC study.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2012,32:492?499.
Research progress of noninvasive high?resolution magnetic resonance imaging in carotid atherosclerotic plaque
GAO Peng,YANG Bin,JIAO Li?qun,ZHANG Hong?qi,ZHU Feng?shui
Department of Neurosurgery,Xuanwu Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100053,China
Carotid atherosclerotic stenosis is closely related to recurrent ischemic stroke.Currently,therapies for carotid artery stenosis are mainly intensive medication or surgery,including carotid artery stenting(CAS)and carotid endarterectomy(CEA).The prevention of stroke lies in identifying risk factors for carotid artery stenosis,screening patients with high risk of recurrent stroke,so as to benefit from medication or surgery.However,therapeutic schedule is formulated only according to the degrees of carotid artery stenosis,and there lacks of individualized treatment. Recently,new imaging modalities,such as noninvasive high?resolution MRI(HRMRI)could detect the vulnerability of carotid atherosclerotic plaque.Compared with the degree of carotid artery stenosis measured by conventional DSA,noninvasive HRMRI can precisely predict the risk of ipsilateral stroke according to plaque morphology,so as to guide individualized treatment.
Carotid stenosis; Atherosclerosis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Review
ZHU Feng?shui(Email:zhufengshui@sina.com)
This study was supported by the NationalKey Research and DevelopmentProgram (No.2016YFC1301700)and Beijing Municipal Scientific and Technological New Star Plan Program (No.2010B052).
10.3969/j.issn.1672?6731.2017.05.012
國家重點研發計劃項目(項目編號:2016YFC1301700);北京市科技新星計劃項目(項目編號:2010B052)
100053 北京,首都醫科大學宣武醫院神經外科
朱鳳水(Email:zhufengshui@sina.com)
2017?05?02)

