PEAR1基因多態性對長期服用阿司匹林腦梗死患者復發的影響
李建設 孟 軻 趙劍婷 馬玉龍 車振勇
新鄉市中心醫院,河南 新鄉 453000
·論著科研之窗·
PEAR1基因多態性對長期服用阿司匹林腦梗死患者復發的影響
李建設 孟 軻 趙劍婷 馬玉龍 車振勇
新鄉市中心醫院,河南 新鄉 453000
目的探討血小板內皮聚集受體1(platelet endothelial aggregation receptor 1,PEAR1)基因多態性與腦梗死患者長期服用阿司匹林復發的相關性。方法對114例初發腦梗死后長期(≥1 a) 服用阿司匹林的患者,根據入組時是否腦梗死復發分為復發組(21例)與無復發組(93例),使用PEAR1基因芯片檢測系統對2組患者的PEAR1基因型進行檢測。結果114例患者PEAR1檢出GG、GA、AA三種基因型,其中野生型GG占50.9%,突變型GA占42.1%,AA占7.0%;復發組野生型GG頻率明顯低于無復發組(23.8% vs.57.0%,P<0.01),復發組純合突變型AA的頻率明顯高于無復發組(28.6% vs.2.1%,P<0.01);2組GA頻率無明顯差異(47.6% vs.40.9%,P>0.05)。復發組年齡、吸煙、LDL- C、糖尿病比例明顯偏高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Logistic回歸分析顯示,PEAR1基因變異與腦梗死復發顯著相關(P=0.006)。結論PEAR1基因變異與長期服用阿司匹林腦梗死卒中復發相關,PEAR1基因純合突變增加腦梗死復發的風險。
阿司匹林;腦梗死;基因多態性;PEAR1
腦梗死已成為威脅人類生命健康的重要疾病,阿司匹林是一種常用的抗血小板聚集藥物,能有效減少缺血性腦卒中事件,在腦梗死二級預防中占重要地位,但部分腦梗死患者長期規律服用阿司匹林的仍有腦梗死復發,阿司匹林療效存在個體差異,即部分患者服用過程中會出現阿司匹林抵抗,其療效減弱,基因多態性是其重要原因之一[1- 2]。血小板內皮聚集受體1(platelet endothelial aggregation receptor 1,PEAR1)參與誘導血小板激活過程,PEAR1基因變異可影響血小板的聚集功能[3],可能導致阿司匹林抵抗[2,4]。本文通過檢測PEAR1的基因多態性,探討其與長期服用阿司匹林腦梗死復發的相關性。
1 資料與方法
1.1研究對象2015- 01-2015- 12新鄉市中心醫院神經內科門診及住院患者114例,男65例,女49例,年齡(59.1±15.7)歲。1 a前確診初發非心源性腦梗死,服用阿司匹林(100 mg/d)1 a以上,所有患者知情同意,并簽署知情同意書。腦梗死復發標準:出現新的腦梗死癥狀體征,且由腦MRI或CT證實。排除標準:服用阿司匹林1 a內復發腦梗死,阿司匹林劑量不足100 mg/d,服用阿司匹林依從性差的(平均每周停藥時間≥2 d);心房纖顫;合并短暫性腦缺血發作、腦靜脈竇血栓、顱內感染、腦瘤、凝血功能障礙、血液病及嚴重心肝腎功能不全者;聯合應用其他抗血小板聚集藥物者。
1.2方法
1.2.1 分組及樣本收集:根據入組時是否腦梗死復發分為腦梗死復發組和無復發組。于早晨用EDTA抗凝管采集空腹外周靜脈血2 mL,保存于4 ℃冰箱內。
1.2.2 PEAR1基因型檢測:采用熒光染色原位雜交技術。用1×NH4Cl預處理液處理血樣,離心、制備白細胞懸液、加入PEAR1基因(rs12041331G>A)耀金分試劑106(北京華夏時代基因科技發展有限公司),將樣本置入TL998A熒光檢測儀(西安天隆科技有限公司生產),其結果由天隆700軟件分析和自動判讀,給出PEAR1 基因SNP信息。以上步驟嚴格按試劑盒和檢驗儀器標準操作規程操作。
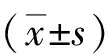
2 結果
2.1腦梗死單因素分析腦梗死復發組與無復發組患者男性比例、高血壓、飲酒、TC、TG、HDL- C比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);而在年齡、吸煙、LDL- C、糖尿病、PEAR1基因變異方面,腦梗死復發組較無復發組明顯偏高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表1。

表1 腦梗死復發單因素分析
2.2 PEAR1基因變異與腦梗死復發的多因素回歸分析以腦梗死復發與否為因變量,把單因素分析中P<0.05的危險因素作為自變量納入Logistic回歸模型,調整年齡、吸煙、糖尿病、PEAR1基因變異、LDL- C等混雜因素,PEAR1基因變異與腦梗死復發呈顯著正相關(OR=5.17,95%CI=2.363~8.864,P=0.006)。見表2。

表2 PEAR1基因變異與腦梗死復發的多因素回歸分析
2.3 PEAR1基因的多態性及與腦梗死復發的關系114例患者PEAR1檢出野生型GG、雜合突變型GA、純合突變型AA三種基因型,其中GG占50.9%,GA占42.1%,AA占7.0%。腦梗死復發組野生GG基因型頻率23.8%,顯著低于腦梗死無復發組的57.0%,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01);腦梗死復發組突變純合AA基因型頻率28.6%,顯著高于腦梗死無復發組的2.1%,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01);2組突變雜合型GA頻率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表3。

表3 2組患者PEAR1基因型頻率分布
3 討論
PEAR1基因是一種近年新發現的與血小板聚集密切相關的基因,在血小板和內皮細胞均有高度的表達,其編碼一種跨膜蛋白,在胞外有多個酪氨酸和脯氨酸殘基,在胞內有5個脯氨酸殘基和1個NPXY922區域,均為磷酸化酪氨酸的結合位點[5- 6]。該基因可通過調控PI3K/PTEN(磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/四硝酸戊赤蘚醇)通路,影響血小板的功能[7]。有研究證實,PEAR1具有激活血小板、降低血小板祖細胞增值,進而影響血小板聚集反應功能,與冠心病、腦梗死等血管病密切相關[8]。
目前,PEAR1的研究多集中在單核苷酸多態性(SNP),針對的位點有rs12041331、rs1256688、rs9550270、rs11264579、rs4661012、rs3737224、rs1273215等。其中rs12041331在對血小板聚集功能的影響研究較多[9- 10]。Faraday 等[11]研究發現,PEAR1(rs12041331)基因內含子1的變異增加PEAR1蛋白的表達,與多種血小板聚集激動劑觸發的血小板聚集相關,還可能有其他潛在的功能變異。Lewis等[8]在227例經皮穿刺冠脈介入治療(PCI)的冠心病患者研究表明,PEAR1(rs12041331)基因多態性與服用阿司匹林單抗或阿司匹林、氯吡格雷雙抗治療的反應顯著相關(P=7.66×10- 9),其中高加索裔和非裔美國人PEAR1(rs12041331)基因AA突變型患者的心血管事件發生率和病死率均高于GG野生型患者(P=0.035)。
本研究單因素分析顯示,腦梗死復發組與無復發組比較,在年齡、吸煙、LDL- C、糖尿病、PEAR1基因變異方面差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),對這些因素進行多因素回歸分析,PEAR1基因變異與腦梗死復發呈顯著正相關(P=0.006)。114例患者PEAR1檢出野生型GG(50.9%)、雜合突變型GA(42.1%)、純合突變型AA(7.8%)三種基因型。腦梗死復發組野生GG基因型頻率顯著低于腦梗死無復發組(P<0.01);腦梗死復發組突變純合AA基因型頻率顯著高于腦梗死無復發組(P<0.01);2組突變雜合型GA頻率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。以上結果符合PEAR1野生型GG患者對阿司匹林抗血小板聚集敏感,AA基因型患者不敏感的結論。進一步證實PEAR1基因多態性對血小板聚集功能有明顯影響,其機制尚不明確。有學者認為,相對于未服用阿司匹林的血小板聚集,服用阿司匹林的PEAR1基因多態性對血小板聚集功能的顯著影響可能是上調了COX1的表達,或是通過不同于COX1的途徑促進血小板的聚集[12];PEAR1基因變異加強了膠原誘導的血小板聚集功能[8]。
本研究顯示,REAR1的基因多態性與長期服用阿司匹林腦梗死復發密切相關,即PEAR1基因純合突變增加腦梗死復發的風險,而其機制尚不明確,在這方面需要更多的研究。
[1] 范崇桂,付國惠,閃海峽.阿司匹林抵抗與缺血性腦卒中復發的相關性[J].中國老年學雜志,2014,34(8):2 050- 2 051.
[2] 彭文星,馮頻頻,石秀錦,等.阿司匹林抵抗的基因多態性及個體化治療[J].中國藥房,2016,27(23):3 172- 3 174.
[3] Kim Y,Suktitipat B,Yanek LR,et al.Targeted Deep Resequencing Identifies Coding Variants in the PEAR1 Gene That Play a Role in Platelet Aggregation[J].Plos One,2013,8(5):e64 179.
[4] 邵淵,丁紅,徐運.基因多態性與抗血小板藥物個體化治療研究[J].中國卒中雜志,2014,9(4):309- 316.
[5] Yao Y,Tang XF,Zhang JH,et al.Association of PEAR1 genetic variants with platelet reactivity in response to dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel in the Chinese patient population after percutaneous coronary intervention[J].Thromb Res,2016,141:28- 34.
[6] 梁杰,傅應云.血小板內皮聚集受體- 1基因與肺血栓栓塞癥關系的研究進展[J].廣東醫學,2016,37(4):623- 626.
[7] Kauskot A,Vandenbriele C,Louwette S,et al.PEAR1 attenuates megakaryopoiesis via control of the PI3K/PTEN pathway[J].Blood,2013,121(25):5 208- 5 217.
[8] Lewis JP,Ryan K,O'Connell JR,et al.Genetic Varia- tion in PEAR1 is Associated with Platelet Aggregation and Cardiovascular Outcomes[J].Circ:Cardiovascr Genet,2013,6(2):184- 192.
[9] Würtz M,Nissen PH,Grove EL,et al.Genetic Determinants of On- Aspirin Platelet Reactivity:Focus on the Influence of PEAR1[J].Plos One,2014,9(10):e111 816.
[10] Backman JD,Yerges- Armstrong LM,Horenstein RB,et al.Prospective Evaluation of Genetic Variation in Platelet Endothelial Aggregation Receptor 1 Reveals Aspirin- Dependent Effects on Platelet Aggregation Pathways[J].Clin Transl Sci,2017,10(2):102- 109.
[11] Faraday N,Yanek LR,Yang XP,et al.Identification of a specific intronic PEAR1 gene variant associated with greater platelet aggregability and protein expression[J].Blood,2011,118(12):3 367- 3 375.
[12] Herrera- Galeano JE,Becker DM,Wilson AF,et al.A Novel Variant in the Platelet Endothelial Aggregation Receptor- 1 Gene Is Associated With Increased Platelet Aggregability[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2008,28(8):1 484- 1 490.
TheeffectsofPEAR1genepolymorphismsonrecurrenceofstrokeinlong-termtakingaspirinpatientswithcerebralinfarction
LIJianshe,MENGKe,ZHAOJianting,MAYulong,CHEZhenyong
TheCentralHospitalofXinxiang,Xinxiang453000,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the relationship between PEAR1 gene polymorphisms and the recurrence of stroke in long- term taking aspirin patients with cerebral infarction.Methods114 long- term (≥1 year) taking aspirin patients after the first attack of cerebral infarction were recruited and divided into two groups according to whether the stroke recurred or not.The genotypes of PEAR1 were detected with PEAR1 gene chip.ResultsIn the 114 patients,three genotypes of PEAR1 were detected:wild type GG,Mutant heterozygous GA and Mutant homozygote AA,the frequencies were 50.9%,42.1% and 7.0%,respectively.The GG genotype frequency of the stroke recurred group was significantly lower than that of the non- stroke recurred group (23.8% vs.57.0%,P<0.01),and the AA genotype frequency of the stroke recurred group was significantly higher than that of the non- stroke recurred group ( (28.6% vs.2.1%,P<0.01).The GA genotype frequency was not significant difference between the 2 groups (47.6% vs.40.9%,P>0.05).There were significant differences in age,smoking,LDL and diabetes (P<0.05).It was identified that genetic variants of PEAR1 were associated with the recurrence of stroke by multiple logistic regression analysis (P=0.006).ConclusionThe genetic variants of PEAR1were associated with the recurrence of stroke in long- term taking aspirin patients after the first attack of cerebral infarction,mutant homozygote AA of PEAR1 increased the risk of stroke recurrence.
Aspirin;Cerebral infarction;Gene polymorphisms;PEAR1
10.3969/j.issn.1673- 5110.2017.20.006
李建設(1972—),碩士,副主任醫師。研究方向:腦血管病。Email:ljsh204001@163.com
R743.33
A
1673- 5110(2017)20- 0026- 04
(收稿2017- 05- 19)
關慧

