大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)中基于能效最大化的資源聯(lián)合優(yōu)化算法
曹海燕,馮瑞瑞,方昕,王秀敏,許方敏
?
大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)中基于能效最大化的資源聯(lián)合優(yōu)化算法
曹海燕1,馮瑞瑞1,方昕1,王秀敏2,許方敏1
(1.杭州電子科技大學(xué)通信工程學(xué)院,浙江 杭州 310018;2.中國計量大學(xué)信息工程學(xué)院,浙江 杭州 310018)
針對信道條件未知的多小區(qū)大規(guī)模多輸入多輸出(MIMO)系統(tǒng),提出一種對導(dǎo)頻序列長度、導(dǎo)頻符號功率以及數(shù)據(jù)符號功率進(jìn)行聯(lián)合優(yōu)化的資源分配算法。采用最大比合并(MRC)接收,考慮電功率和導(dǎo)頻污染的影響,并對最大傳輸功率進(jìn)行約束從而建立起以能效(EE)最大化為目標(biāo)的非凸函數(shù)模型。根據(jù)分?jǐn)?shù)規(guī)劃的性質(zhì),首先將分?jǐn)?shù)形式轉(zhuǎn)化成減式形式,進(jìn)而分解成一系列凸函數(shù)之差(DC)的問題,最后采用交替優(yōu)化算法聯(lián)合調(diào)整3個變量從而達(dá)到能效最大化的目標(biāo)。仿真結(jié)果表明,隨著最大符號傳輸功率的增加,所提方案仍然能保持良好系統(tǒng)能效性能。
大規(guī)模MIMO;導(dǎo)頻序列;資源分配;聯(lián)合優(yōu)化;DC問題
1 引言
近年來隨著無線通信設(shè)備和多媒體業(yè)務(wù)要求的提高,無線通信網(wǎng)絡(luò)中的業(yè)務(wù)量急劇增加,大規(guī)模多輸入多輸出(multi-input multiple-output, MIMO)技術(shù)由于其具有空間分集的特點,可以大幅度提高系統(tǒng)吞吐量和傳輸可靠性,因此受到學(xué)術(shù)界和工業(yè)界的廣泛關(guān)注[1-4]。然而,大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)隨著天線數(shù)目的增加,能量消耗也隨之增加,因此如何提高大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)的能量效率(energy efficiency, EE)成為研究的熱點[5-15]。參考文獻(xiàn)[6]研究了單小區(qū)大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)上下行鏈路的能量效率模型,并且通過凸理論分析了系統(tǒng)參數(shù)之間的相互作用。參考文獻(xiàn)[7]研究了大規(guī)模MIMO混合預(yù)編碼下的能效優(yōu)化問題,并通過迭代算法得出了最優(yōu)的射頻鏈路數(shù)。參考文獻(xiàn)[8]針對大規(guī)模多輸入多輸出正交頻分復(fù)用(MIMO-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing, MIMO-OFDM)系統(tǒng),設(shè)計了包括功率分配、數(shù)據(jù)速率分配、天線分配和子載波分配的聯(lián)合資源分配方案,但是這些研究都是在假設(shè)信道狀態(tài)信息(channel status information, CSI)完全已知的情況下進(jìn)行的。而實際的通信系統(tǒng)要想獲知CSI需要利用導(dǎo)頻序列進(jìn)行信道估計。參考文獻(xiàn)[10]針對迫零(zero forcing, ZF)預(yù)編碼的分布式MIMO系統(tǒng),研究了能效為目標(biāo)的功率分配問題,并且考慮了信道估計。典型的大規(guī)模MIMO上行傳輸系統(tǒng)包含兩個階段:上行導(dǎo)頻和數(shù)據(jù)傳輸。參考文獻(xiàn)[11,12]在對大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)進(jìn)行研究時,假設(shè)上行導(dǎo)頻和數(shù)據(jù)傳輸兩個階段消耗相同的符號功率。然而這種等功率分配方案在低功率情況下會造成“平方效應(yīng)”,當(dāng)傳輸功率下降時,系統(tǒng)的容量會雙倍地降低。參考文獻(xiàn)[12,13]研究了大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)的能效資源分配問題,但是沒有考慮實際的電功率消耗,而是將其直接忽略或者用一個常數(shù)值來代替。參考文獻(xiàn)[14,15]提出了實際的電功率消耗模型,其中,參考文獻(xiàn)[14]研究了功率消耗參數(shù)對EE的影響,參考文獻(xiàn)[15]則提出了針對MIMO-OFDM系統(tǒng)的能效資源分配算法。然而參考文獻(xiàn)[12-15]都沒有考慮實際情況中的導(dǎo)頻復(fù)用問題,進(jìn)而忽略了系統(tǒng)的導(dǎo)頻污染。參考文獻(xiàn)[16]針對采用下行導(dǎo)頻的多小區(qū)MIMO系統(tǒng),研究了導(dǎo)頻污染對EE的影響,但是沒有研究導(dǎo)頻符號功率以及數(shù)據(jù)符號功率對EE的影響。參考文獻(xiàn)[17]針對多小區(qū)MIMO系統(tǒng)的資源分配問題,考慮了不同的導(dǎo)頻功率和數(shù)據(jù)功率分配,但是將功率約束的不等式條件簡化成了等式,從而得出一個固定的導(dǎo)頻長度。參考文獻(xiàn)[18]針對導(dǎo)頻復(fù)用的多小區(qū)MIMO系統(tǒng),研究了包含基站天線數(shù)、導(dǎo)頻符號和數(shù)據(jù)符號的資源分配,但同樣忽略了導(dǎo)頻長度對EE的影響。
基于以上分析,本文針對多小區(qū)大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)的能效資源分配問題進(jìn)行研究。不同于已有研究中將導(dǎo)頻和數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行等功率分配,將導(dǎo)頻長度設(shè)為定值的情況,本文提出了對導(dǎo)頻符號功率、數(shù)據(jù)符號功率以及導(dǎo)頻序列長度進(jìn)行聯(lián)合優(yōu)化的迭代算法,并與傳統(tǒng)資源分配算法進(jìn)行了比較。仿真結(jié)果表明,所提方案相比于已有的等功率分配方案,在符號傳輸功率限制較大的情況下仍然能保持良好的能效性能。
2 系統(tǒng)模型與問題描述
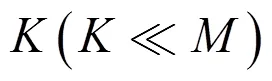
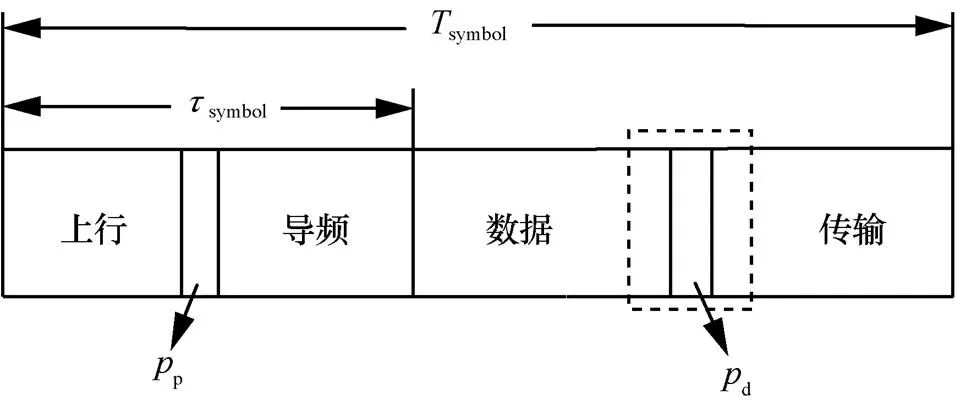
圖1 連續(xù)時間間隔內(nèi)的數(shù)據(jù)傳輸過程
2.1 上行導(dǎo)頻
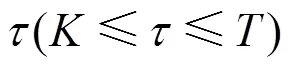
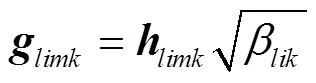
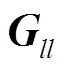
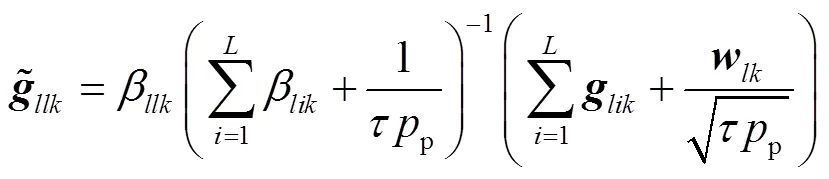
2.2 數(shù)據(jù)傳輸
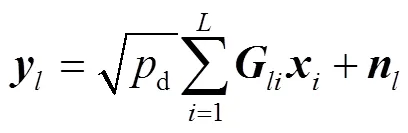
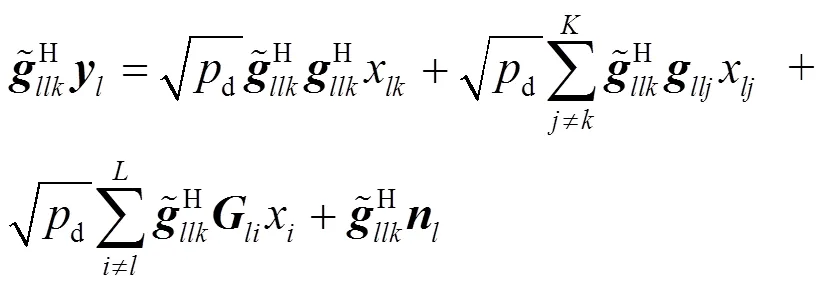
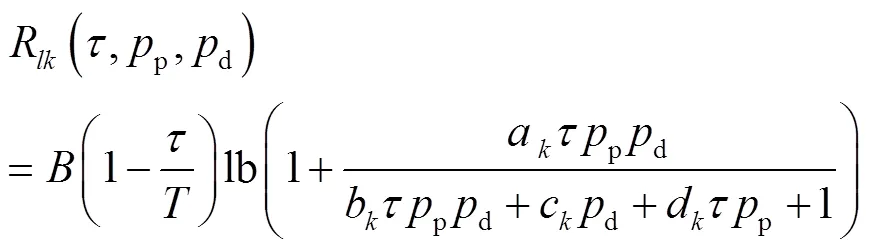
2.3 功率消耗模型
大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)中的功率消耗可分為3個方面[18]。
(1)用戶端的功率放大
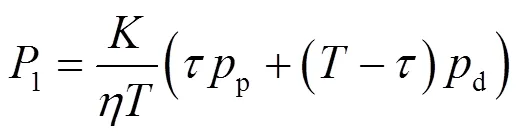
(2)BS和用戶端電功率消耗
可以歸類為4個主要的方面:信號的處理和收發(fā)、信道估計、線性檢測和信道的編碼和解碼,即:
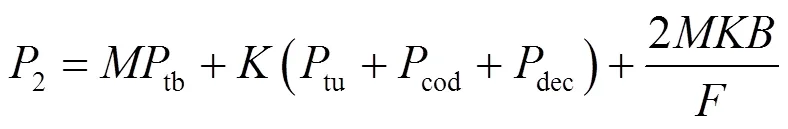
(3)其他特定功率消耗
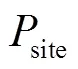
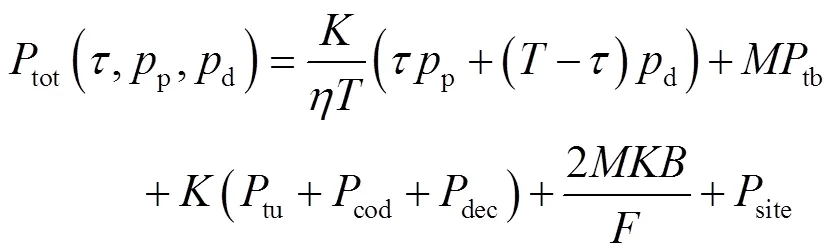
3 最大化EE資源分配算法
3.1 目標(biāo)問題
利用式(5)和式(10),第個小區(qū)上行傳輸系統(tǒng)的 EE計算式為:
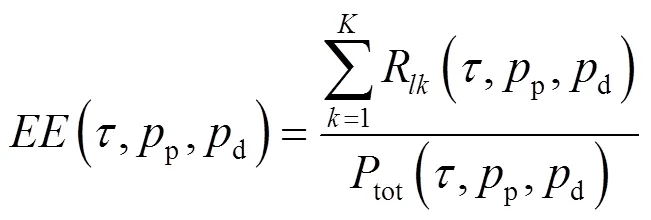
實際通信系統(tǒng)中,實現(xiàn)EE最大化目標(biāo)的同時還需要考慮實際的功率限制和導(dǎo)頻序列長度。基于以上分析,最終的目標(biāo)問題為:
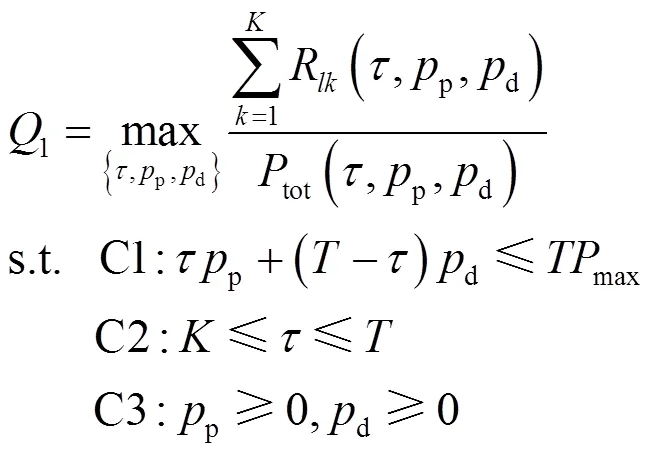
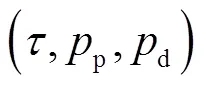
基于分?jǐn)?shù)規(guī)劃的性質(zhì),目標(biāo)函數(shù)中的非線性分?jǐn)?shù)規(guī)劃問題可以轉(zhuǎn)化成成等價的減式形式[20]:
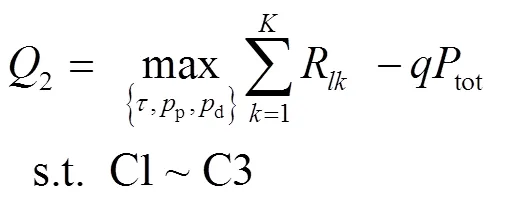

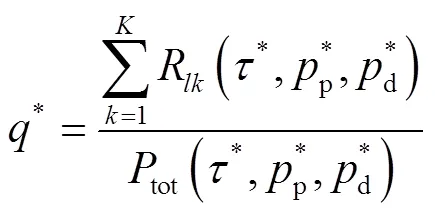
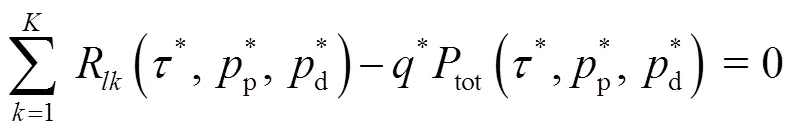
3.2 求解Q2
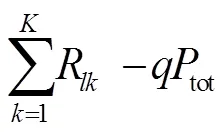
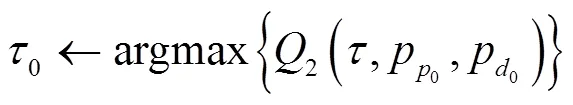
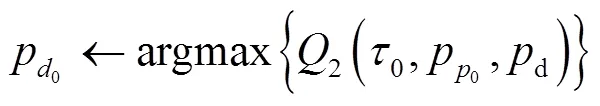
步驟5 循環(huán)至收斂
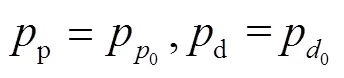
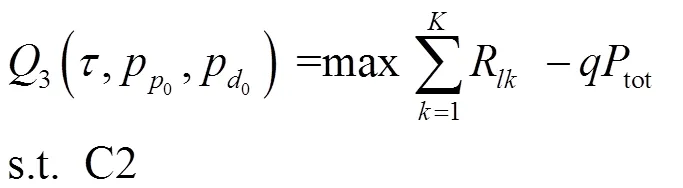
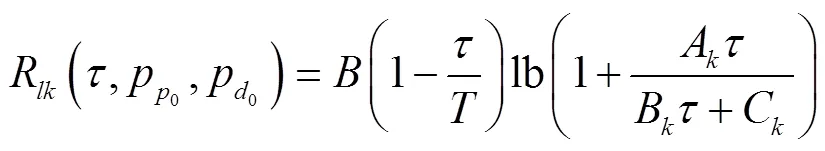
將式(15)進(jìn)一步轉(zhuǎn)化:
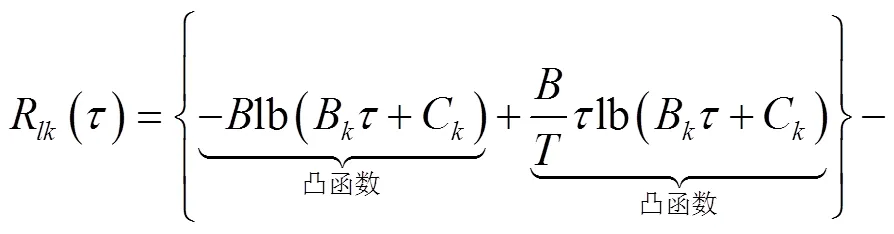
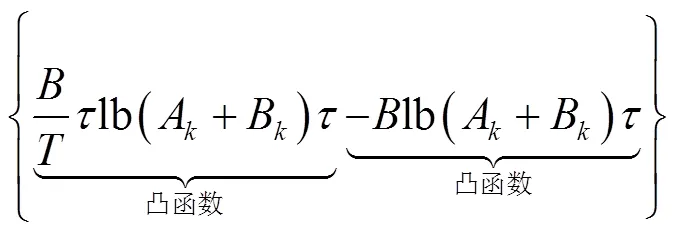
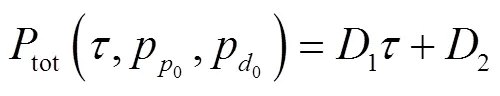
3.3 EE最大化的資源分配算法
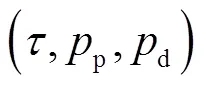
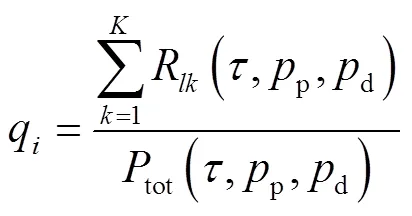
步驟6 返回步驟2
步驟7 endwhile
4 仿真結(jié)果
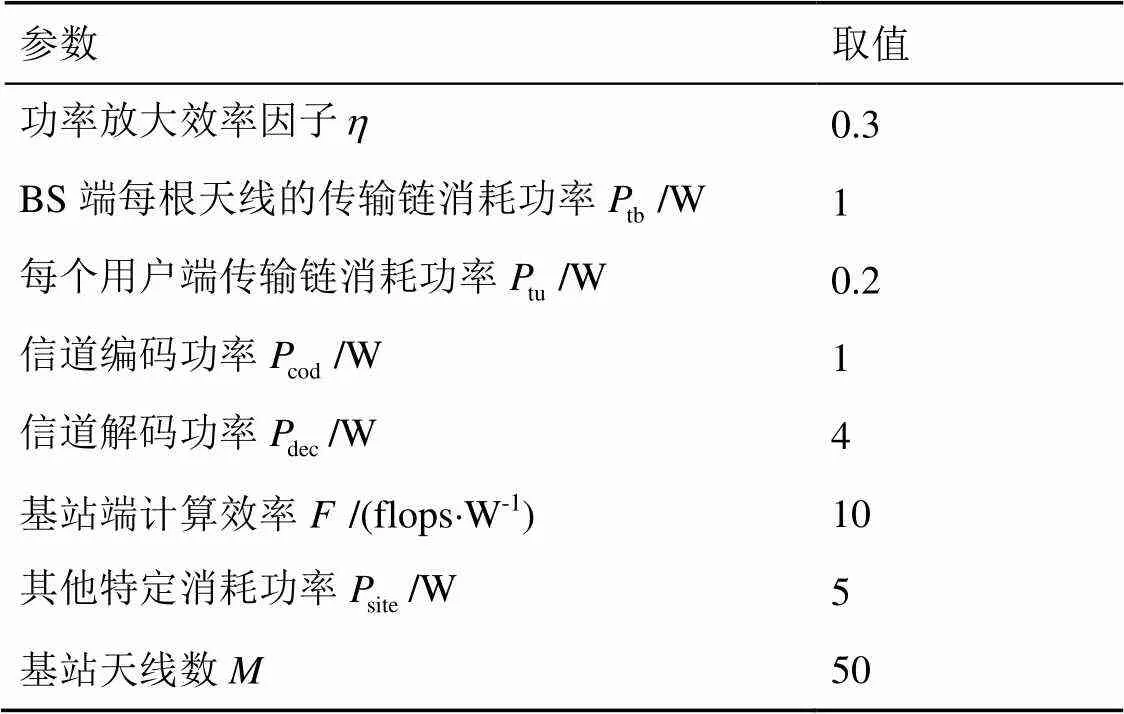
表1 系統(tǒng)參數(shù)值
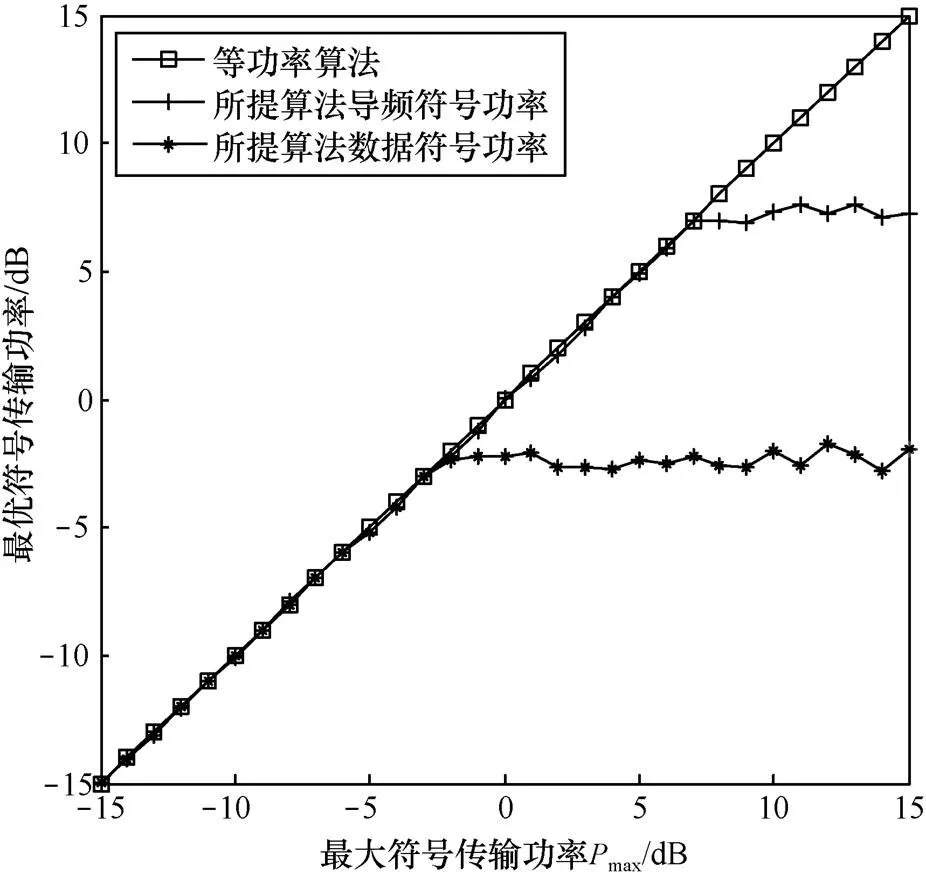
圖2 導(dǎo)頻、數(shù)據(jù)符號功率隨Pmax的變化情況
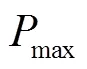
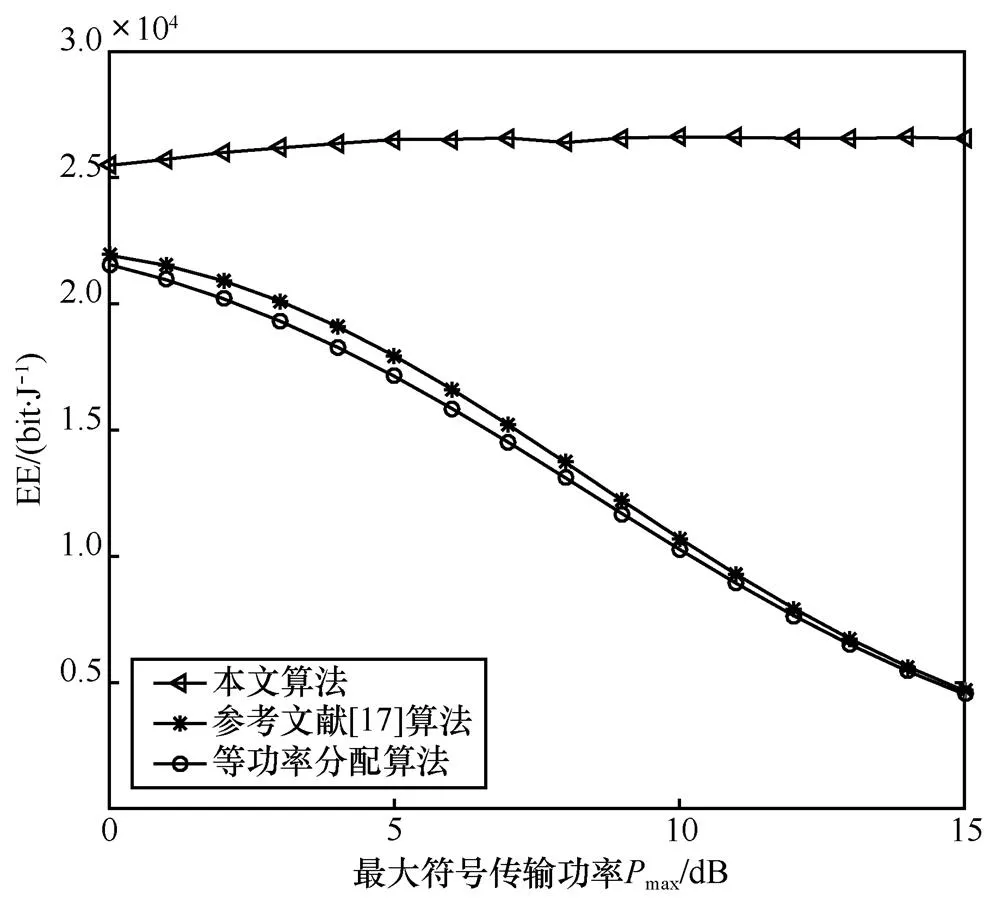
圖3 EE隨Pmax的變化情況
5 結(jié)束語
本文研究了多小區(qū)大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)能效資源分配問題,提出了一種對導(dǎo)頻符號和數(shù)據(jù)符號功率以及導(dǎo)頻長度進(jìn)行聯(lián)合優(yōu)化的迭代算法。其主要思想是將變量進(jìn)行交替優(yōu)化,實現(xiàn)未知 CSI 下的導(dǎo)頻和功率分配,相比于大多數(shù)已知 CSI 下的研究,本文的研究內(nèi)容更接近現(xiàn)實環(huán)境。后續(xù)的研究將進(jìn)一步考慮其他因素對 EE 的綜合影響。
[1] ALKHATEEB A, NAM Y H, ZHANG J, et al. Massive MIMO combining with switches[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2016, 5(3):232-235.
[2] SHINJO S, NAKATANI K, KAMIOKA J, et al. Highly integrated RF frontend module for high SHF wide-band massive MIMO in 5G, and switching-mode amplifiers beyond 4G[C]// 2017 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test (VLSI-DAT), April 16, 2017, Taiwan, China. New Jersey: IEEE Press, 2017.
[3] YAZDAN A, PARK J, PARK S, et al. Energy-efficient massive MIMO: wireless-powered communication, multiuser MIMO with hybrid precoding, and cloud radio access network with variable-resolution ADC[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2017, 18(5):18-30.
[4] ZAPPONE A, ALFANO G, BUZZI S, et al. Energy-efficient non-cooperative resource allocation in multi-cell OFDMA systems with multiple base station antennas[C]//Online Conference on Green Communications, Sept 26-29, 2011, New York, USA. New Jersey: IEEE Press, 2011:82-87.
[5] XU W, LI S, WANG S, et al. Joint parameter selection for massive MIMO: an energy-efficient perspective[J]. IEEE Access, 2016(4): 3719-3731.
[6] BJ?RNSON E, SANGUINETTI L, HOYDIS J, et al. Optimal design of energy-efficient multi-user MIMO systems: is massive MIMO the answer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 14(6):3059-3075.
[7] ZI R, GE X, THOMPSON J, et al. energy efficiency optimization of 5G radio frequency chain systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(4):758-771.
[8] NG D W K, LO E S, SCHOBER R. Energy-efficient resource allocation in OFDMA systems with large numbers of base station antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(9):3292-3304.
[9] MIAO G. Energy-efficient uplink multi-user MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 12(5): 2302-2313.
[10] LONG D N, DUONG T Q, NGO H Q, et al. Energy efficiency in cell-free massive MIMO with zero-forcing precoding design[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, PP(99):1.
[11] MARZETTA T L. Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(11):3590-3600.
[12] NGO H Q, LARSSON E G, MARZETTA T L. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(4): 1436-1449.
[13] HU Y, JI B, HUANG Y, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in uplink multiuser massive MIMO systems[J]. International Journal of Antennas & Propagation, 2015, 2015(4):1-9.
[14] MOHAMMED S K. Impact of transceiver power consumption on the energy efficiency of zero-forcing detector in massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2014, 62(11):3874-3890.
[15] ZHANG J, JIANG Y, LI P, et al. Energy efficient power allocation in massive MIMO systems based on standard interference function[C]// IEEE VTC-Spring, May 15, 2016, Nanjing, China. New Jersey: IEEE Press, 2016.
[16] NGO H Q, LARSSON E G, MARZETTA T L. Massive MU-MIMO downlink TDD systems with linear precoding and downlink pilots[J]. Communication, Control & Computing, 2013:293-298.
[17] NGO H Q, MATTHAIOU M, LARSSON E G. Massive MIMO with optimal power and training duration allocation[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2014, 3(6):605-608.
[18] PRASAD K N R S V, BHARGAVA V K. Resource optimization for energy efficiency in multi-cell massive MIMO with MRC detectors[C]//2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW), April 3-6, 2016, Doha, Qatar. New Jersey: IEEE Press, 2016: 121-126.
[19] Ericsson. Ericsson energy and Carbon report [R/OL]. (2013-06-19) [2017-04-06]. http://www.ericsson.com.
[20] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7):492-498.
[21] BEZDEK J C, HATHAWAY R J. Convergence of alternating optimization[J]. Neural Parallel & Scientific Computations, 2003, 11(4):351-368.
[22] AN L T H, TAO P D. The DC (difference of convex functions) programming and DCA revisited with DC models of real world nonconvex optimization problems[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2005, 133(1-4):23-46.
A joint optimization algorithm based on energy efficiency maximization for massive MIMO systems
CAO Haiyan1, FENG Ruirui1, FANG Xin1, WANG Xiumin2, XU Fangmin1
1. Telecommunication Engineering School, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China2. Information Engineering School, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
For the massive multi-cell multi-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication uplink system with unknown channel status information, a resource allocation algorithm which jointly optimizes the pilot sequence length, pilot symbol power and data symbol power was proposed. With the maximum ratio combining (MRC) receiver, the influence of circuit power was considered, pilot contamination and the constraint of maximum transmission power, and a nonconvex function modeled with the goal of maximizing energy efficiency (EE) was established. Firstly, the fractional form was transformed into an equivalent subtractive form by using the properties of fractional programming and then decomposed into a series of DC problems, finally, by using an iterative optimization algorithm, the three variables were alternately adjusted with maximizing the energy efficiency. Simulation results show that with the increasing of the maximum symbol transmission power, the proposed scheme can still have the great EE performance for the massive MIMO systems.
massive MIMO, pilot sequence, resource allocation, joint optimize, DC problem
TN911.22
A
10.11959/j.issn.1000?0801.2017317
2017?08?07;
2017?09?21
國家自然科學(xué)基金資助項目(No.61501158,No.61379027);浙江省教育廳科學(xué)基金資助項目(No.LY14F010019,No.LQ15F01004)
: The National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.61501158, No.61379027), Education Department Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (No.LY14F010019, No.LQ15F01004)
曹海燕(1975?),女,博士,杭州電子科技大學(xué)通信工程學(xué)院副教授、碩士生導(dǎo)師,主要研究方向為無線通信系統(tǒng)的信道編碼、信號檢測和LTE物理層標(biāo)準(zhǔn)等。

馮瑞瑞(1993?),女,杭州電子科技大學(xué)通信工程學(xué)院碩士生,主要研究方向為無線通信、大規(guī)模MIMO系統(tǒng)的能效資源分配。
方昕(1975?),女,博士,杭州電子科技大學(xué)通信工程學(xué)院副教授、碩士生導(dǎo)師,主要研究方向為4G/5G物理層算法。
王秀敏(1963?),女,中國計量大學(xué)信息工程學(xué)院教授、碩士生導(dǎo)師,主要研究方向為電路與系統(tǒng)、信號處理。
許方敏(1980?),女,博士,杭州電子科技大學(xué)通信工程學(xué)院講師,主要研究方向為先進(jìn)移動通信系統(tǒng)及其關(guān)鍵技術(shù)。

