遺傳算法在水平軸洋流機葉片優化設計中的應用
余萬 李春 楊陽

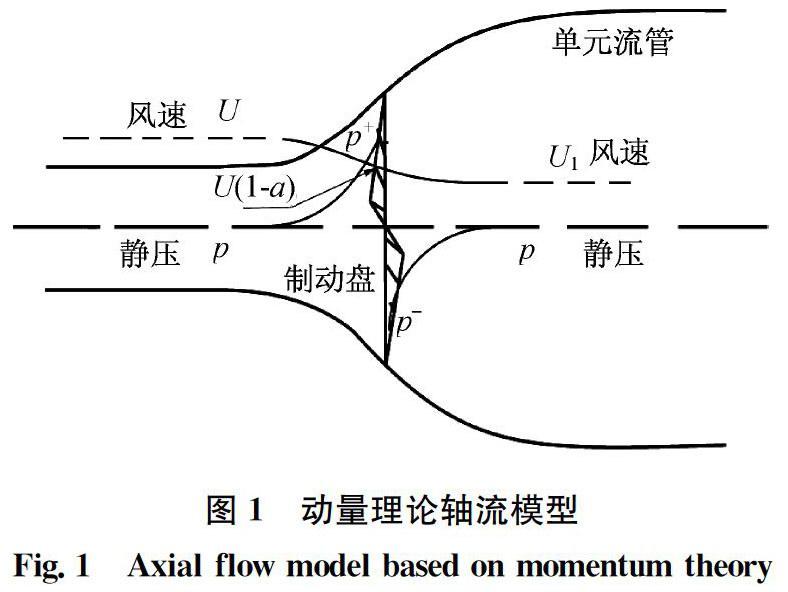
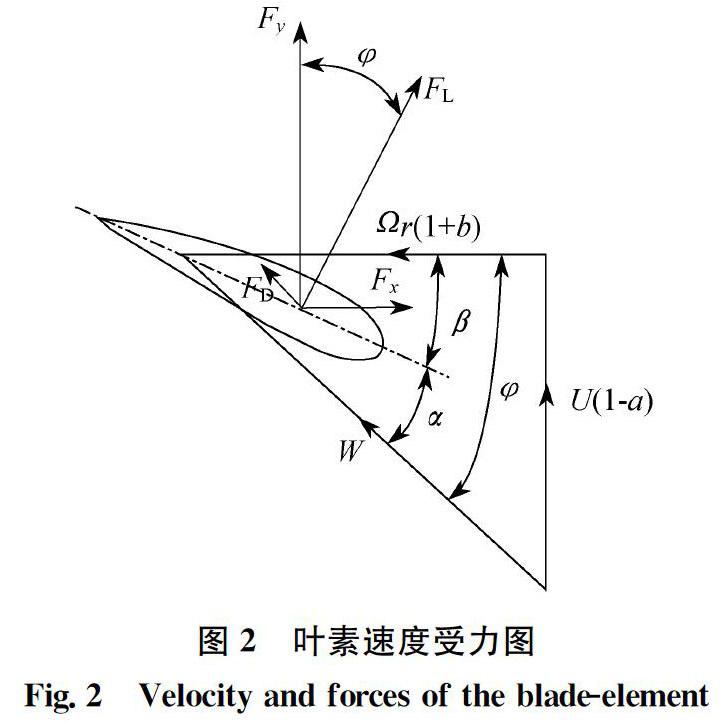
摘 要: 水平軸洋流機是捕獲洋流能的主要設備,其葉片外形直接影響捕能效率。通過Bezier參數化曲線描述定速定槳距洋流機的葉片弦長和扭角分布規律,采用葉素動量理論計算其水動特性。以額定流速下能量利用系數系數最大為目標,基于遺傳算法建立了葉片外形優化模型。同時,為了避免因汽蝕導致功率輸出不穩定的現象,在優化過程中以汽蝕作為約束條件,與經典設計方法Wilson理論設計葉片進行了比較。結果表明:優化葉片在葉根處的扭角更小,具有更佳的抗扭性能;葉根和葉尖處弦長均更小,節省了材料;在設計流速范圍內,優化葉片在低流速下效率更高,平均提高了4.6%,具有更好的啟動性能。
關鍵詞: 洋流機; 葉片; 汽蝕; 遺傳算法; 優化
中圖分類號: TK 83 文獻標志碼: A
Application of Genetic Algorithm to the Optimization
Design of Horizontal Axis Tidal Turbine Blade
YU Wan, LI Chun, YANG Yang
(School of Energy and Power Engineering/Shanghai Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow and Heat Transfer
in Power Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China)
Abstract: Horizontal axis tidal turbine is the key equipment to capture energy of the current.The blade shape can directly affect the capture efficiency.In this paper,the distribution of chord length and twist angle for tidal turbine blade with fixed speed and pitch was described by Bezier parametric curves.Bladeelement momentum theory was applied to calculate its hydraulic dynamic characteristics.With the goal of maximizing the power coefficient at the constant flow velocity,the optimization model of blade shape was built based on genetic algorithm.Meanwhile,in order to avoid the instability of power output caused by cavitation,the cavitation resistance was used as constraints in the optimization model.Compared with the classical Wilson theory of blade design,the results showed that the torsional angle has reduced in the hub of the optimized blade and the better torsion properties was achieved.The root and tip chord length of the blade decreased,which could save materials.Within the range of designed flow rate,higher efficiency was achieved for the optimized blade under low flow rate.The efficiency increased by 4.6% on average.The better startup performance was achieved as well.
Keywords: tidal turbine; blade; cavitation; genetic algorithm; optimization
在全球氣候變暖的背景下,隨著能源短缺和經濟高速發展,可再生能源發電技術更需進一步的飛躍,不僅要求處理溫室效應而且要求保護自然環境以及與自然環境和諧共存。世界各國可持續發展的主要方向轉向開發和利用綠色可再生能源。潮流能作為一種對環境幾乎不會產生污染的可再生能源,蘊藏量豐富,而且具備相對成熟的利用技術,開發潛力極為巨大[1-2]。
葉片的性能直接影響著洋流機的性能,也是洋流機捕獲洋流能的唯一部件,其制造成本也占整個發電機組的百分之二十左右[2]。葉片設計是洋流能利用效率的優劣和洋流機運行安全以及發電機組成本控制的關鍵因素。目前在國內外洋流機葉片設計大多數是采用了風力機的葉片設計方法[3],其中最為常用方法是與相關的約束模型結合的葉素動量理論,如Wilson模型[4-5]和Glauert模型[6]。其中,Wilson在Glauert研究的基礎上考慮了升阻比和葉尖損失的影響提出的以單葉素截面輸出最大功率為設計目標的葉片設計方法應用最為廣泛[8-9]。該設計方法速度快,僅考慮了單個葉素的氣動性能而忽略了葉素之間的相互影響。
洋流機工作環境和水泵相似,因此需要考慮洋流機葉片的汽蝕問題。汽蝕現象是在流體流動過程中,當某一局部區域的壓力不大于水溫相對應的汽化壓力時,流體就會在該局部區域發生汽化[9-10]。汽化壓力被定義為液體發生汽化時的壓力,和液體種類、溫度有關[11]。汽化產生的氣泡順流進入高壓區發生破裂,引發周圍液體高頻碰撞從而導致材料受到破壞[12-13]。

