The impact of urological resection and reconstruction on patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery(CRS)and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy(HIPEC)
Gre Hwei Ching Tn,Nihols B.Shnnon,Clrme Shulyn Chi,Lui Shiong Lee,Khee Chee Soo,Meliss Ching Ching Teo,*
aDivision of Surgical Oncology,National Cancer Centre Singapore,Singapore
bDuke-NUS Medical School,Singapore
cDepartment of Urology,Singapore General Hospital,Singapore
KEYWORDS Cytoreductive surgery;Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy;Peritoneal carcinomatosis;Urological procedures;Urological reconstruction
Abstract Objective:Cytoreductive surgery(CRS)and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy(HIPEC)are increasingly being used to treat peritoneal malignancies.Urological resections and reconstruction(URR)are occasionally performed during the surgery.We aim to evaluate the impact of these procedures on peri-operative outcomes of CRS and HIPEC patients.Methods:A retrospective review of a prospectively maintained database of all patients who underwent CRS-HIPEC from April 2001 to February 2016 was performed.Outcomes between patients who had surgery involving,and not involving URR were compared.Primary outcomes were the rate of major complications and the duration of stay in the intensive care unit(ICU)and hospital.Secondary outcomes were that of overall survival(OS)and prognostic factors that would indicate a need for URR.Results:A total of 214 CRS-HIPEC were performed,21 of which involved a URR.Baseline clinical characteristics did not vary between the groups(URR vs.No URR).Urological resections comprised of 52%bladder resections,24%ureteric resections,and 24%involving both bladder and ureteric resections.All bladder defects were closed primarily while ureteric reconstructions consisted of two end-to-end anastomoses,one ureto-uretostomy, five direct implantations into the bladder and three boari flaps.URR were more frequently required in patients with colorectal peritoneal disease(p=0.029),but was not associated with previous pelvic surgery(76%vs.54%,p=0.065).Patients with URR did not suffer more serious complications(14%vs.24%,p=0.42).ICU(2.2 days vs.1.4 days,p=0.51)and hospital stays(18 days vs.25 days,p=0.094)were not significantly affected.Undergoing a URR did not affect OS(p=0.99),but was associated with increased operation time(570 min vs.490 min,p=0.046).Conclusion:While concomitant URR were associated with an increase in operation time,there were no significant differences in postoperative complications or OS.Patients with colorectal peritoneal metastases are more likely to require a URR compared to other primary tumours,and needs to be considered during pre-operative planning.
1.Introduction
Cytoreductive surgery(CRS)and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy(HIPEC)are used to treat selected patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal,ovarian,appendiceal,gastric,mesothelioma and primary peritoneal neoplasms[1-4].Urological resections and reconstruction(URR)are occasionally required during the CRS,due to disease involvement especially in patients with heavy pelvic disease volume,or secondary to inadvertent injury.Urological involvement during CRS and HIPEC has been reported in 7%-20%of published reports[5-11],although the impact on postoperative outcomes and longterm survival remains inconclusive.Studies have alternatively reported no differences in morbidity,operation time or overall survival(OS)[9],increased operation time without effect on morbidity or survival[8],increased risk of severe morbidity without an effect on survival[12]and increased operation time and risk of major complications,but with no effect on OS[11].
We aim to report on the experience of urological involvement and URR during CRS and HIPEC in a highvolume centre in South East Asia,and to evaluate the impact of these procedures on perioperative outcomes.
2.Patients and methods
A prospectively maintained,Institutional Review Board(IRB)approved database of all patients who underwent CRS-HIPEC for peritoneal-based malignancies at a single institution from April 2001 to February 2016,was retrospectively reviewed.Demographics including age,gender,race,and tumour type were included in the database and reported.
Primary outcomes were the rate of major complications and the duration of stay in the intensive care unit(ICU)and hospital.Secondary outcomes were that of OS and prognostic factors that would indicate a need for URR.
2.1.Patient selection
Patients considered for CRS-HIPEC had to be of Eastern Cooperative Group(ECOG)performance status 0 or 1,with no distant metastases.All patients were recommended for CRS-HIPEC after evaluation in a multidisciplinary tumour board.The extent of disease of the abdomen and pelvis was examined on computed tomography(CT)scans and the absence of extra-abdominal disease was determined either via CT scans of the thorax or positron emission tomography(PET)-CT scans.
2.2.CRS and HIPEC
CRS-HIPEC proceeded according to previously published techniques[13].The extent of disease was documented according to the peritoneal cancer index(PCI)[14].Complete cytoreduction was attempted whenever possible,and the extentofcytoreductionwasrecordedbythecompletenessof cytoreduction(CC)score[15].Chemotherapywasinfusedvia a hyperthermia pump(Belmont)into a closed abdomen at a target temperature of 41-42°C for 60 min.The chemotherapeutic agent used was determined by a medical oncologist on the basis of malignancy type.
2.3.Urological procedures
Operative reports were individually reviewed to determine if preoperative ureteric stenting or a urological procedure was performed during the CRS.Urological procedures were defined as any resection or reconstruction of the genitourinary tract during the same anaesthetic as the CRS-HIPEC procedure.Ureteric stents were placed routinely after all ureteric reconstructions,and typically removed in the outpatient setting via a flexible cystoscopy between 4 and 6 weeks from the time of the CRS-HIPEC.
No distinction was made between urological organs removedduetoinvolvementwithtumouroriatrogenicinjury.
Complicationswere categorized according to the Clavien-Dindo classification,with majorcomplications defined as Clavien III and IV[16].OS was defined as time from date of CRS-HIPEC to date of death from any cause.Survival was censored on date of death or last follow-up.
For the purposes of comparison,patients were divided into two groups based upon whether or not a urological procedure was included.Thirteen patients underwent more than one CRS-HIPEC procedure during the study period.Data were analysed at the CRS-HIPEC level in order to increase the generalizability of results to include patients who undergo multiple procedures.In these instances,listed patient characteristics are representative of the patient’s state at the time of each included operation.
2.4.Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as mean±SD(normally distributed data)and categorical data as proportions throughout the article.Clinical variables and surgical outcomes were compared across groups as follows:Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test(if a group contained five or less samples)for comparison between categorical variables reported as number and percentage in each group.Independent sample t-test or ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc testing(when the comparison included more than one degree of freedom)for continuous variables,reported as mean±SD orusingMann-WhitneyU testforordinalvariables reporting median and interquartile range(IQR).p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Median OS was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared via the log-rank test.All statistical analyses were performed using R 3.2.3[17].
3.Results
3.1.Baseline characteristics of study population
Between April 2001 through to February 2016,201 patients underwent a total of 214 CRS-HIPEC.Twelve patients underwent CRS-HIPEC twice and one patient had CRS-HIPEC thrice.One hundred and eight(50%)of the HIPEC used mitomycin C,88(41%)used cisplatin,seven(3%)used oxaliplatin,and for nine(4%)patients the HIPEC regime was not recorded.Twenty-one of 214(10%)CRS-HIPEC procedures included a URR(Table 1),of which five(24%)were due to an iatrogenic injury.
Urological resections comprised of 52%partial bladder resections,24%ureteric resections,and 24%involving both.All bladder defects were closed primarily while ureteric reconstructions consisted of two end-to-end anastomoses,one ureto-uretostomy, five direct implantation and three boari flaps.
The median follow-up of all patients was 18 months(IQR 6-27 months).
Operations were grouped according to whether or not a URR was performed concurrently.Baseline clinical features are summarised in Table 2 and did not defer between the groups.
3.1.1.Preoperative factors
Operations involving URR were more common in patients with colorectal peritoneal disease than other primary tumours(p=0.029).Concomittent URR also appeared to be required more frequently in patients who had undergone previous pelvic surgery,but this association was not statistically significant(76%vs.54%,p=0.065).There was no significant association between URR and previous abdominal-only surgery(14%vs.24%,p=0.42).Therewere no differences seen in the other baseline preoperative characteristics.

Table 1 Types of urological resections and reconstructions performed(n=21).
3.1.2.Intraoperative factors
Concomitant URR was associated with an increase in operation time(570 min vs.490 min,p=0.046).Patients with upper abdominal disease who required subdiaphragmatic peritoneal stripping were less likely to require a URR during the CRS-HIPEC(p<0.01).There was no difference in PCI score,CC score,or estimated blood loss between the two groups(p=0.54,0.94 and 0.62,respectively).
3.1.3.Ureteric stenting
Preoperative ureteral stenting to aid in ureteral identi fication was performed in 26%of patients and done at each surgeon’s discretion.The rate of preoperative stenting was higher in the URR group(52%vs.23%,p<0.01),of note there was a strong association between stenting and previous pelvic surgery(87%of stented had previous pelvic surgery versus 50%of non-stented,p<0.01).
3.2.Perioperative outcomes
There was no difference in perioperative complication rate(49%vs.43%,p=0.28),or rate of major complications(24%vs.14%,p=0.42)between the patients without a URR andthosewhounderwentURR.Therewasalsonodifferencein average length of ICU stay(2.2±5.5 days vs.1.4±1.4 days,p=0.51)or total hospital stay(18±14 days vs.25±39 days,p=0.094).In the long term,there were no leaks or stenoses reported.
3.3.OS
There was no difference in OS after operations involving concomitant URR or no URR,median survival was 67 vs.70 months,respectively(p=0.99,Fig.1).
4.Discussion
In this retrospective review,we examined concomitant urological procedures during CRS and HIPEC,performed at one of the largest Asian institutions with more than 10 years of experience.Out of 214 CRS-HIPEC,9.8%of casesrequired a URR.This rate of URR is similar to other reports from western centres performing CRS-HIPEC[1-6].We found that the majority of the resections involved resection of the bladder(52%),with subsequent reconstruction by primary closure.When resections involved the ureter(48%),the commonest reconstruction was direct implantation(45%),followed by a boari flap(27%).No patients required a nephrectomy,radical cystectomy or ileal conduit.
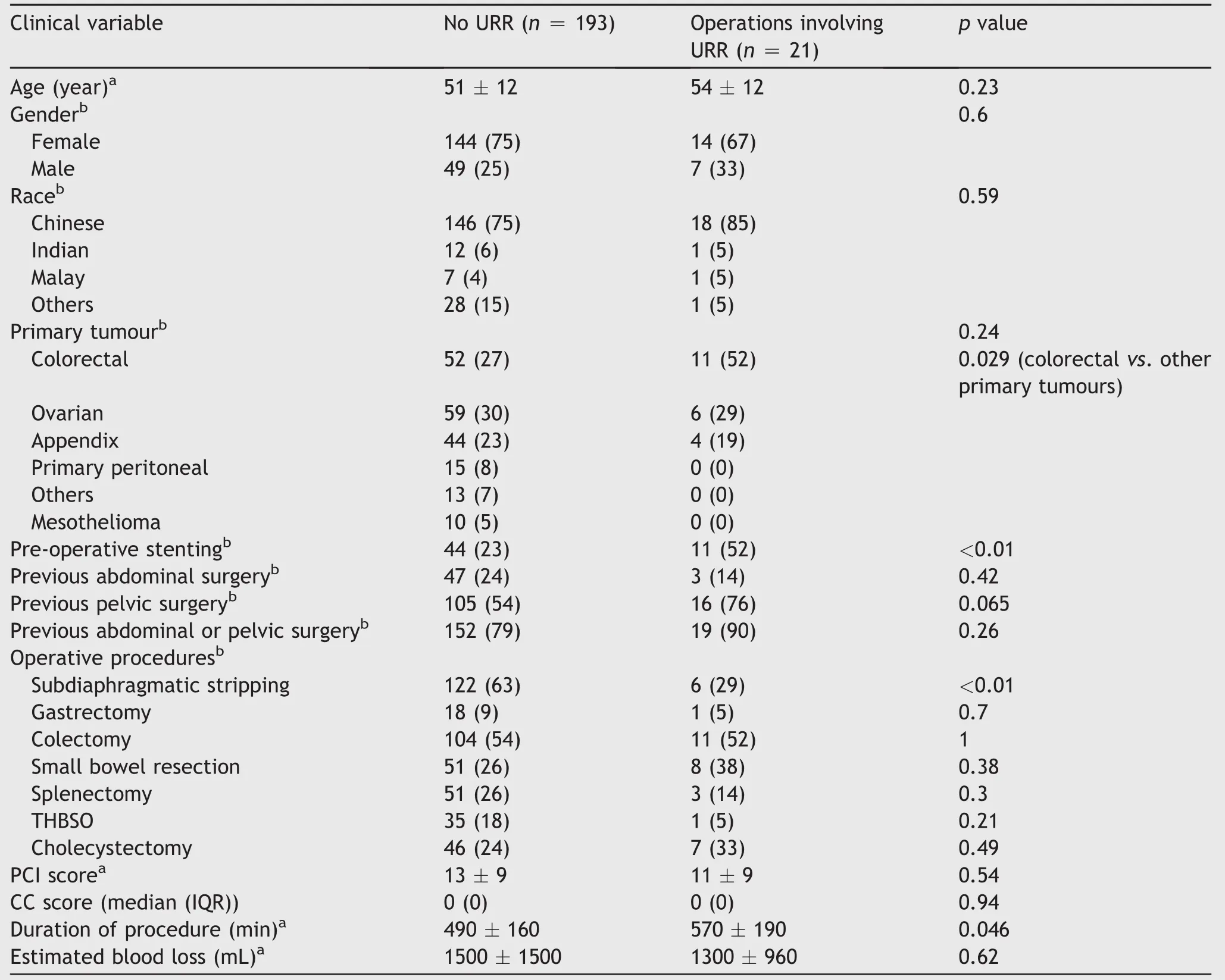
Table 2 Baseline characteristics of study population.
We found that CRS-HIPEC for colorectal peritoneal metastases were more likely to involve a URR compared to other primary tumours(p=0.029).This could be explained by the more invasive nature of colorectal peritoneal metastases compared to other malignancies like pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendical tumours[17].Patients who had disease involving the upper abdomen and required subdiaphragmatic stripping were also less likely to require a URR(p<0.01).These findings emphasise the important role that disease biology and distribution play in planning for CRS-HIPEC cases.
Similar to a recent report,we found that having a concomitant URR during CRS-HIPEC was associated with a longer operation time.However,unlike the Pittsburgh group[11],we did not find a difference in length of ICU stay or hospital stay(p=0.51 and 0.094 respectively).This may be due to the relatively small number of URR procedures in our CRS-HIPEC cohort.In addition,there was no difference in perioperative complication rate(p=0.28),rate of major complications(p=0.42),or blood loss(p=0.62)during the combined procedure.Few western centres have reported increase in major complications amongst patients who undergo URR during CRS-HIPEC[11,12],but the difference has been postulated to be due to an increase in urinary-tract specific complications related to the URR themselves[11].
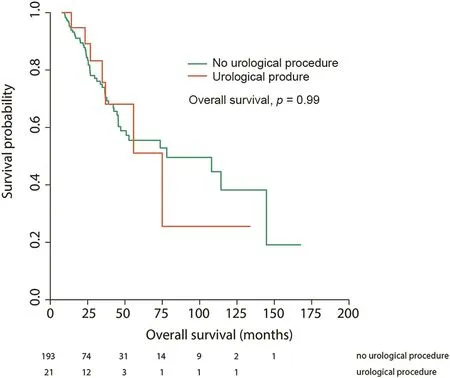
Figure 1 Overall survival following cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy,stratified by concomitant urological procedure.
As a secondary outcome,we also looked at OS,and found no difference between operations involving concomitant URR or no URR,with a median survival of 67 vs.70 months,respectively(p=0.99).This is important,as it highlights the fact that peritoneal disease involving the urinary tract,does not necessarily relate to a more aggressive disease biology[5],and should not deter surgeons from performing CRS-HIPEC where indicated.
As with all retrospective reviews,there were inherent limitations on the data and the presence of a selection bias.In addition,despite having similar rates of URR compared to other published series,our small numbers of URR did not allow for us to perform separate subset analyses to determine if there were any significant differences between URR performed for tumour involvement or iatrogenic injury.Lastly,as this study looked at URR performed in a single institution,the results may not be applicable to all other institutions.
5.Conclusion
Concomitant URR were performed in 9.8%of CRS and HIPEC cases.They can be safely carried out in patients undergoing CRS and HIPEC but does involve a longer operating time.Patients with colorectal peritoneal metastases are more likely to require a URR compared to other primary tumours,and this information should be included during patient consultation.
Conflicts of interest
All the above authors have participated in the research design,analysing of data and writing of the paper.The authors have reviewed the manuscript and approved it for submission.All authors declare no conflict of interest or receive any funding for research.
 Asian Journal of Urology2018年3期
Asian Journal of Urology2018年3期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- The treatment of complex female urethral pathology
- The choice of surgical approach in the treatment of vesico-vaginal fistulae
- Contemporary diagnostics and treatment options for female stress urinary incontinence
- The aging bladder insights from animal models
- Functional and reconstructive urology(part two)
- “Thumb’s off” for acrometastasis of renal cell carcinoma:Is there a role for acrometastasectomy in the era of targeted therapy?
