基于字典學習的土壤地球化學數據稀疏重構
吳琳 魏友華 洪姍
摘 ?要: 在土壤地球化學數據的勘察和采集過程中,因為各種客觀因素導致數據不完整,這會對后續的研究工作造成一定的影響,因此對數據進行重構是預處理階段最基本的步驟。基于土壤地球化學數據在自身或在變換域內的稀疏性,建立基于字典學習的土壤地球化學數據重構模型,將數據重構問題轉化為稀疏優化問題,可以減少數據重構后的平滑效果,在一定程度上保留土壤地球化學數據在異常區和背景區交界處的結構特征。最后將反距離插值法和稀疏重構算法重構后的數據進行對比,結果表明稀疏重構算法能有效地對土壤地球化學數據進行重構。
關鍵詞: 土壤地球化學; 稀疏優化; 數據重構; 字典學習; 正交匹配追蹤算法; 反距離插值法
中圖分類號: TN911.1?34 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼: A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文章編號: 1004?373X(2019)09?0018?04
Pedogeochemistry data sparse reconstruction based on dictionary learning
WU Lin, WEI Youhua, HONG Shan
(Geomathematics Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China)
Abstract: In the process of the exploration and collection of pedogeochemistry data, the data is incomplete due to various objective factors, which has the influence on the subsequent research to some extent. Therefore, the reconstruction of the data is the most fundamental step of pretreatment stage. On the basis of the sparsity of the pedogeochemistry data itself or in the transform domain, a pedogeochemistry data reconstruction model based on dictionary learning is established, which can convert the data reconstruction problem into sparse optimization problem, so as to reduce the smooth of reconstructed data, and reserve the structure feature of pedogeochemistry data at the junction of the abnormal area and background area to a certain extent. The data reconstructed by inverse distance interpolation method and sparse reconstruction algorithm is compared, which shows that the sparse reconstruction algorithm can reconstruct the pedogeochemistry data effectively.
Keywords: pedogeochemistry; sparse optimization; data reconstruction; dictionary learning; orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; inverse distance interpolation method
0 ?引 ?言
在實際的地球化學數據采集中,常常因為采集區域地理環境條件的限制,采集方式、環境噪音等客觀原因導致勘察收集到的數據不完整、不規則。而在地球化學數據異常圈定等各種處理中要求數據為標準的網格數據。另外,數據的不完整還導致信息的丟失,在后續的數據處理中會降低數據結果的可信度。因此,對實測數據的插值重構是地球化學數據處理的必要步驟。
地質學者們在地質數據插值過程中常用的方法為反距離加權插值法[1]、徑向基函數插值法[2]、克里金插值法[3]、分形插值法[4]等。這些傳統的插值方法均是將插值后的數據整體趨于平滑[5],會使土壤地球化學數據在背景區和異常區的交界處變得光滑,從而影響異常區域的波動。在此基礎上進行下一步研究會影響地質人員對數據的分析,同時也會影響實地勘測找礦工作。因為在插值前并沒有對實測數據進行降噪處理,所以使用傳統方法進行插值重構后,得到的數據是對實測數據的近似插值重構,仍然會受到各種噪音的影響。
在圖像處理領域,文獻[6]提到降噪的同時會損失原始圖像的紋理特征,因此提出基于稀疏表示的圖像降噪算法,在降噪后可有效保留原始圖像的結構信息。在土壤地球化學數據中,異常區與背景區之間的差異就類似于這種結構信息,在降噪時也需要保留這種結構信息。文獻[7]在對地球化學數據的研究中指出,地球化學數據具有稀疏性,無噪聲的土壤地球化學數據可以通過字典稀疏表示,與實際數據之間的逼近殘差就是噪聲,這樣的降噪也不會使曲線光滑。
根據以上研究,本文嘗試將稀疏表示應用在土壤地球化學數據重構中。對重構后的土壤地球化學數據進行異常圈定,再與反距離插值重構數據的異常圈定結果以及實際結果進行比較,最終數值實驗模擬表明,該算法適用于土壤地球化學數據重構。
1 ?土壤地球化學數據稀疏重構模型
根據文獻[8]提到的壓縮感知理論的核心思想以及文獻[7]指出的地球化學數據具有稀疏性可知,地球化學數據可以表示為:
式(5)是NP難問題,很難直接求解出該問題的精確解。本文采用貪婪算法中的正交匹配追蹤(Orthogonal Matching Pursuit,OMP)算法[10]近似求解這個問題。在實際應用中該算法的迭代過程如下:
2) 更新索引集[Vt=Vt-1?λt],記錄找到的傳感矩陣中的重建原子集合[At=At-1,aλt]。
3) 由最小二乘法得到[θt=arg miny-Atθ2];更新殘差[rt=y-Atθt],并且令[t=t+1]。
4) 判斷是否滿足[t>K],若滿足,則停止迭代; 若不滿足,則執行步驟1)。
最后得到變換系數[Θ],這一過程又被稱為稀疏編碼。
為了更加精確地重構出數據,則要求設計出高效的觀測矩陣和選擇最能稀疏表達數據[X]的稀疏變換矩陣[Ψ]。本文只考慮稀疏變換矩陣[Ψ]。該矩陣要根據具體數據的特征來選擇,適合于某一類數據的稀疏變換,不一定適合于另一類數據。因此選擇K?SVD算法對稀疏變換矩陣[Ψ]進行自適應學習[11?12],從而達到能夠適合于不同地區的土壤地球化學數據重構。
K?SVD每次更新一個原子(即變換矩陣的一列)及其對應的稀疏系數,并且需要將實際勘察數據分塊。假設按照某種方式將數據分為[L]塊,依次對稀疏變換矩陣第[ll=1,2,…,L]列進行更新:
1) 找出所有滿足[wl=jθjl≠0]的數據小塊[Yj];
2) 對每個下標[j∈wl],計算殘差[elj=Yj-m≠lΦψmθmj];
3) 計算殘差矩陣[El],其列為[eliji,j∈wl];
4) 對[El]進行奇異值分解得[El=UΔVT]。則[U]的第一列將作為字典更新后的第[l]列,同時更新[αliji,j∈wl]為[Δ1,1]乘以[V]的第一列。
每次迭代后會得到更新的稀疏變換矩陣[Ψ],直到達到最優的[Ψ]或達到設定的迭代次數。再重復稀疏編碼和變換矩陣更新過程,最后得到重構的數據塊,對其平均得到最終的重構數據[9]。
2 ?數值實驗
為檢驗本文提出的基于字典學習的稀疏重構模型的效果,將其應用到實際土壤地球化學數據的插值重構中。在本文中,選擇常用的高斯矩陣作為測量矩陣[13],選擇DCT變換矩陣作為訓練變換矩陣的初始矩陣[14]。根據土壤地球化學數據只有實際勘察數據這一特點,本文只能根據含噪數據對變換矩陣進行訓練。
首先將數據對進行分塊(本文中的塊大小為[4×4]),把分塊后的矩陣按列排列,則[M=16,N=25],變換矩陣的原子數[15][K=600]。采用本文的算法得到重構后的數據,對其平均即可得到最終的重構數據。
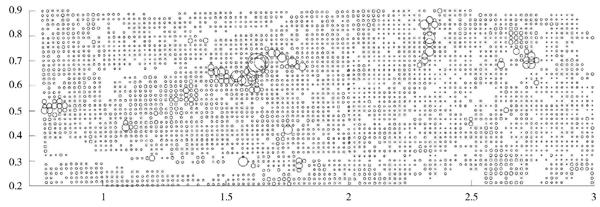
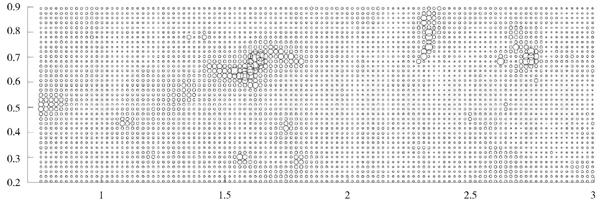
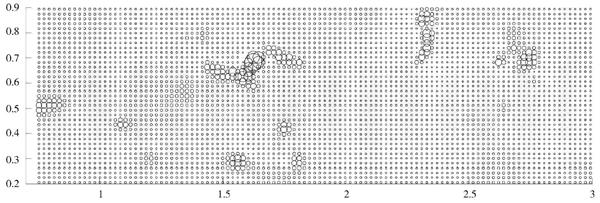
圖1是原始缺失數據的散點圖,圖2為使用反距離插值法得到的數據散點圖,圖3為使用本文提出的稀疏重構模型得到的數據散點圖。其中,圖中圓圈越大表示元素含量越高;圓圈越小表示元素含量越低。
從圖1~圖3中可以看出,兩種重構數據與原始數據的值分布比較一致。圖2中,反距離插值重構數據在圈較大區域內,其元素含量比原始數據的值低,且增長緩慢,即較為嚴重地破壞了異常區與背景區交界處的結構;而根據稀疏重構算法重構后的數據在圈較大區域內與原始數據的元素含量值保持一致,與圖2相比,減弱了對異常區與背景區交界處結構的破壞,能更好地保留土壤數據的原始結構和有用信息的完整性。
圖1 原始數據散點圖

圖2 反距離插值數據的散點圖

圖3 稀疏重構數據的散點圖

3 ?結 ?論
本文根據土壤地球化學數據本身或在變換域的稀疏性,將數據重構問題轉化為優化問題,可對土壤地球化學數據進行很好的重構,并且重構后的數據符合原始數據的特點,從而保留了異常區和背景區交界處的數據結構等有用信息,在一定程度上有利于后期處理土壤地球化學數據。
參考文獻
[1] 樊子德,李佳霖,鄧敏.顧及多因素影響的自適應反距離加權插值方法[J].武漢大學學報(信息科學版),2016,41(6):842?847.
FAN Zide, LI Jialin, DENG Min. An adaptive inverse?distance weighting spatial interpolation method with the conside?ration of multiple factors [J]. Geomatics & Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(6): 842?847.
[2] ZOU Youlong, HU Falong, ZHOU Cancan, et al. Analysis of radial basis function interpolation approach [J]. Applied geophysics, 2013, 10(4): 397?410.
[3] 陳琳,任春穎,王宗明,等.基于克里金插值的耕地表層土壤有機質空間預測[J].干旱區研究,2017,34(4):798?805.
CHEN Lin, REN Chunying, WANG Zongming, et al. Prediction of spatial distribution of topsoil organic matter content in cultivated land using Kriging methods [J]. Arid zone research, 2017, 34(4): 798?805.
[4] PARSA M, MAGHSOUDI A, YOUSEFI M, et al. Multifractal interpolation and spectrum?area fractal modeling of stream sediment geochemical data: implications for mapping exploration targets [J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 128: 5?15.
[5] 朱鈺,王偉,章傳銀,等.流動重力空間插值方法比較[J].測繪通報,2017(10):12?17.
ZHU Yu, WANG Wei, ZHANG Chuanyin, et al. Comparison on mobile gravity among different spatial interpolation methods [J]. Bulletin of surveying & mapping, 2017(10): 12?17.
[6] HAN Jin, JING Yue, ZHANG Yue, et al. Local sparse structure denoising for low?light?level image [J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2015, 24(12): 5177?5192.
[7] FELISA G, CIRIELLO V, ANTONELLINI M, et al. Data?driven models of groundwater salinization in coastal plains [J]. Journal of hydrology, 2015, 531: 187?197.
[8] 馬堅偉,徐杰,鮑躍全,等.壓縮感知及其應用:從稀疏約束到低秩約束優化[J].信號處理,2012,28(5):609?623.
MA Jianwei, XU Jie, BAO Yuequan, et al. Compressive sen?sing and its application: from sparse to low?rank regularized optimization [J]. Signal processing, 2012, 28(5): 609?623.
[9] ELAD M, AHARON M. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries [J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2006, 15(12): 3736?3745.
[10] 馬小薇.基于壓縮感知的OMP圖像重構算法改進[J].電子科技,2015,28(4):51?53.
MA Xiaowei. Improvement of OMP image reconstruction algorithm based on compressed sensing [J]. Electronic science & technology, 2015, 28(4): 51?53.
[11] 劉翠響,馬玉雙,王寶珠,等.過完備字典稀疏表示下的RAMP重構算法[J].計算機工程與應用,2018,54(14):199?202.
LIU Cuixiang, MA Yushuang, WANG Baozhu, et al. RAMP reconstruction algorithm based on overcomplete dictionary sparse representation [J]. Computer engineering and applications, 2018, 54(14): 199?202.
[12] 吳建寧,徐海東,王玨.基于過完備字典稀疏表示的多通道腦電信號壓縮感知聯合重構[J].電子與信息學報,2016,38(7):1666?1673.
WU Jianning, XU Haidong, WANG Jue. A new joint reconstruction algorithm of compressed sensing for multichannel EEG signals based on over?complete dictionary approach [J]. Journal of electronics & information technology, 2016, 38(7): 1666?1673.
[13] 黨骙,馬林華,田雨,等.[m]序列壓縮感知測量矩陣構造[J].西安電子科技大學學報,2015,42(2):186?192.
DANG Kui, MA Linhua, TIAN Yu, et al. Construction of the compressive sensing measurement matrix based on [m] sequences [J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2015, 42(2): 186?192.
[14] 王強,李佳,沈毅.壓縮感知中確定性測量矩陣構造算法綜述[J].電子學報,2013,41(10):2041?2050.
WANG Qiang, LI Jia, SHEN Yi. A survey on deterministic measurement matrix construction algorithms in compressive sensing [J]. Acta electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(10): 2041?2050.
[15] 練秋生,張偉.基于圖像塊分類稀疏表示的超分辨率重構算法[J].電子學報,2012,40(5):920?925.
LIAN Qiusheng, ZHANG Wei. Image super?resolution algorithms based on sparse representation of classified image patches [J]. Acta electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(5): 920?925.

