PBL教學法在醫學留學生心律失常教學中的應用分析
李耀東 湯寶鵬 周賢惠
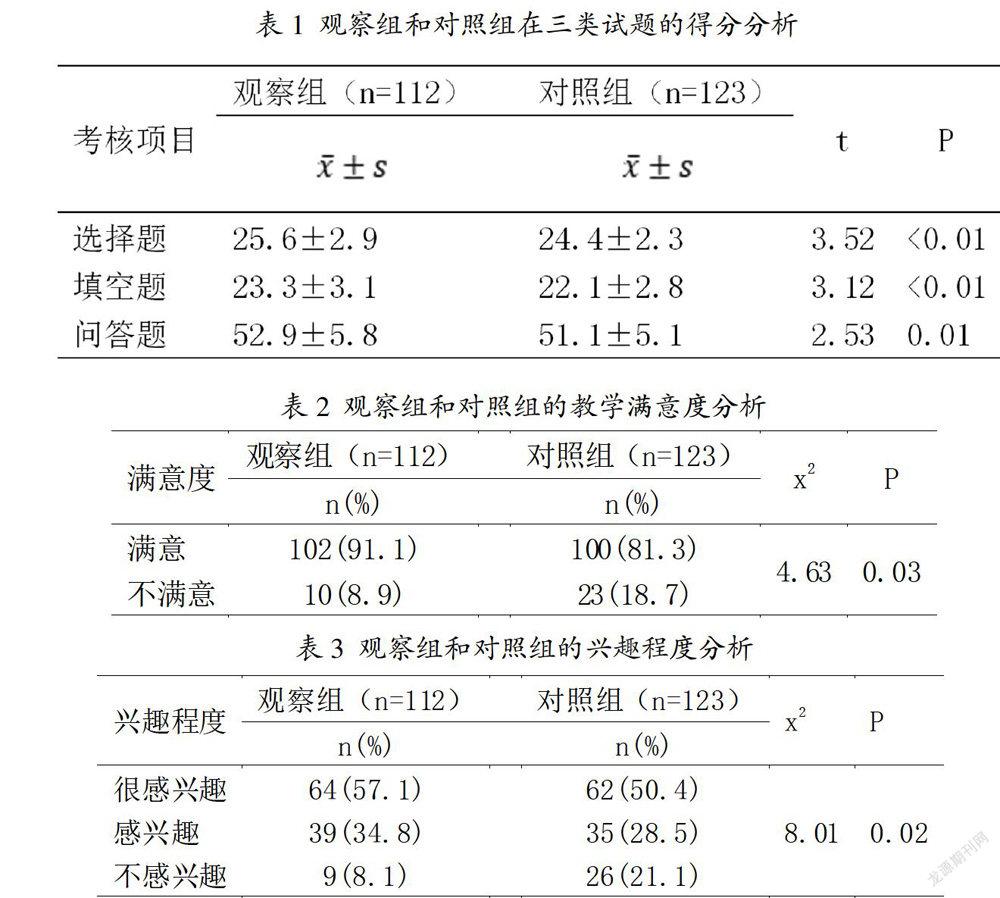
摘? 要:目的:調查針對醫學留學生在心血管內科的心律失常教學部分采用以問題為基礎教學法(Problem based learning, PBL)的教學效果。方法:選取進行心血管內科心律失常章節教學的新疆醫科大學臨床專業2015-2016級留學生,隨機分為兩組,對觀察組研究對象采用PBL進行教學,對照組研究對象采用傳統的教學法。結果:一個學期后,觀察組研究對象成績考核的選擇題、填空題、問答題平均得分均顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組研究對象對教學的滿意度也顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組研究對象在很感興趣和感興趣的比例要高于對照組。結論:采用PBL有利于提升對醫學留學生心律失常知識的教學效果。
關鍵詞:心血管內科;PBL;教學方法
中圖分類號:G642 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:2096-000X(2019)07-0090-03
Abstract: Objective: To investigate the teaching effectiveness of Problems based learning for medical students abroad in the teaching of arrhythmia in cardiovascular knowledge. Methods: 2015-2016 clinical students abroad of Xinjiang Medical University were selected and divided into two groups randomly. The subjects in the observation group were taught by PBL. The traditional teaching method was used in the control group. Results: After one semester, the average scores of choice questions, fill in questions and essay questions in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). The satisfaction degree of the subjects in the observation group was also significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). The proportion of very interested and interested subjects in the observation group was higher than that in the control group. Conclusion: The adoption of PBL is beneficial to improve the teaching effectiveness of arrhythmia knowledge for medical students abroad.
Keywords: cardiovascular medicine; PBL; teaching method
傳統教學法是教師講解、學生被動接受的“注入式”教育。在醫學學習過程中,對于成長在不同教育環境下的留學生而言,很難適應這種教學方法;尤其是在進行內容冗雜、抽象的心律失常知識學習時,這種教學方法難以激起留學生的學習興趣,學生的主動性受到了抑制,教學效果頗微。以問題為導向的教學方法(Problem based learning, PBL)是目前世界上比較流行的教學方法。PBL是20世紀60年代末由美國神經病學教授Barrows首創、最初主要用于醫學教育的教學方法[1]。荷蘭、比利時和瑞典等歐洲國家也先后開始嘗試這種教學模式。此外,PBL在美國也取得了較為迅速的發展,截止1991年,已有100所以上的美國醫學院全部或部分采用了PBL[2]。PBL應用到我國醫學教育的探索最早可追溯至上世紀80年代中期,而目前PBL已成為我國醫學教育改革的方向之一。……

