微塑料對水生生物的生態毒理效應研究進展
楊秉倬 黃河
摘要:隨著塑料的大量生產和使用,由此而產生的塑料污染問題逐漸引起了人們的關注。各種塑料制品被當做廢物隨意遺棄到環境后,在各種環境因素的作用下會變為塑料微粒,隨地表徑流進入水環境,最終進入大海,如果不對其進行管理和控制,將貽害無窮。為系統性地了解微塑料對水生生物的影響,本文概述了微塑料在水環境中的環境行為,歸納了微塑料在水生生物中的生物累積及毒性機制,從其對水生動物行為、生長發育、免疫及基因遺傳等方面的影響綜述了微塑料的生態毒性效應,并概述了微塑料對其他有毒污染物的生態毒理效應的影響。最后,對未來微塑料生態毒理效應的研究方向進行了展望,以期對微塑料的環境危害研究提供更多理論參考。
關鍵詞:微塑料;水生生物;生物累積;毒理效應
中圖分類號:X503.22 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:2095-672X(2019)09-0-05
DOI:10.16647/j.cnki.cn15-1369/X.2019.09.074
Research progress on the ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms
Yang Bingzhuo,Huang He
(School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering , Yangtze University,Jingzhou Hubei 434023,China)
Abstract: With the increasing production and use of plastics, the problem of plastic pollution has gradually attracted peoples attention. After being discarded as waste into the environment, plastic products will become particle matter under natural environmental factors, enter the water environment with surface runoff, and eventually enter the sea. If not managed and controlled, the consequences will be endless. In order to understand the effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms systematically, the environmental behavior of microplastics in water environment was outlined, the bioaccumulation and toxicity mechanisms of microplastics in aquatic organisms were generalized, the behavior, growth, immune and genetic aspects of the aquatic animals were reviewed and the combined toxicity of microplastics and other pollutants was summarized in this paper. Finally, the direction of the research on the ecotoxicological effects of microplastics was prospected, so as to provide more theoretical references for the further research on the harmful effects of microplastics in the environment.
Keywords: Microplastics;Aquatic organisms;Bioaccumulation;Toxicological effect
塑料來源廣泛,種類繁多,已廣泛應用于社會生產以及人類生活的各個方面,與此同時由塑料產生的環境污染問題也逐漸受到了關注。微塑料(Microplastic)這個概念由Tompson于2004年首次提出,并將其定義為粒徑小于5mm的塑料粒子[1]。微塑料化學性質穩定、難以降解,可在環境中存在數百年至上千年。環境中的微塑料根據組分可分為聚乙烯(PE) 、聚丙烯(PP)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、聚酰胺(PA)等[2]。Galgani等人[3]根據粒徑大小將微塑料分為小型微塑料(粒徑小于1mm)和大型微塑料(粒徑在1-5mm之間);根據來源也可將微塑料分為兩類:一類是初生微塑料,其成品就是塑料微粒,例如日化用品中含有的微塑料及在運輸過程中泄露進入環境的塑料微珠;另一類是次生微塑料,也就是體積較大的塑料垃圾進入自然環境后,經過長時間的物理、化學或生物作用,塑料碎片的結構逐漸被破壞,最終降解后的塑料微粒[4]。
水環境是最易受污染的系統之一,微塑料等多種污染物可通過污水排放、地表徑流或大氣沉降等最終歸于河、湖和海洋中。水體微塑料污染是一個全球范圍內的問題,無論是深海水域、淡水環境還是陸地環境中,甚至在赤道[5]和極地[6]研究人員均檢測到了它的存在。最新研究發現,人口稀少的馬爾代夫Faafu環礁海水中也檢測到了平均豐度為0.32±0.15粒/m3的微塑料,該地沉積物中微塑料平均豐度也達到了22.8±10.5粒/m3[7];印度尼西亞被認為是世界上第二大海洋塑料碎片來源地,對其11個海灘站采集的樣品進行分析,發現樣品中含有多種微塑料,其中包括PP(54.0 ± 13.0%)、PE(17.3 ± 8.3%)、PS(10.4 ± 9.1%)等[8]。為詳細了解微塑料的性質和毒性機理,達到保護環境和人類健康的目的,本文概述了微塑料在水環境中的環境行為,歸納了微塑料在水環境中的生物累積,從其對水生動物行為、生長發育、免疫及基因遺傳等方面的影響綜述了微塑料的生態毒性效應,并概述了微塑料與其他污染物的聯合毒性效應。
1 微塑料在水環境中的行為
根據相關研究可以得知,微塑料在水環境中的行為大致包括遷移、沉降、堆積等物理行為;降解、氧化等化學行為以及攝入、富集等生物行為[9]。首先,風的驅動對微塑料的遷移起著不可忽視的作用,Kukulka等[10]提出對上層海洋塑料含量的準確估計必須考慮到風力的影響,可以說大多數微塑料的遷移都是風作用后的結果。雖然微塑料密度比海水低,但是由于菌落的定植、浮游植物的附著以及有機碎片和金屬的聚集等作用,漂浮的塑料碎片最終會沉到海底,甚至有學者[11]認為深海沉積物中很有可能大多是微塑料的沉淀。在堆積方面,在北大西洋等非開放的海域中,由于亞熱帶洋流及環流運動形成了微塑料的高污染堆積區[12]。可見水體微塑料污染具有長期持久性,一旦形成微塑料堆積,其解決難度比較大,污染比較嚴重。
塑料碎片的降解主要通過機械侵蝕、光誘導降解和細菌或真菌的生物降解的組合來完成[13]。降解后的微塑料大多數具有脆性、毛邊或裂紋等物理特征,降解到一定粒徑即會釋放在海洋環境中從而對水環境及水生生物的生存與健康造成威脅[14]。不同類型微塑料的降解速度會有所不同,比如PE就比PP更耐化學風化,PE更易降解[15]。綜合各方面的資料發現:微塑料正以一種潛移默化的形式對水體環境產生影響,而且當前水環境中微塑料污染范圍已極為廣泛。
2 微塑料在水生生物中的累積
近些年微塑料研究多關注其采集[16-17]、分離與提取[18-19]及鑒定[20-21],生物累積和食物鏈遷移研究相對來說還是較少的。通過研究微塑料在生物體內不同器官和組織的富集及轉移來探討微塑料對生物體的毒性效應,對今后科學地評價微塑料的環境風險具有重要意義。
2.1 生物富集部位
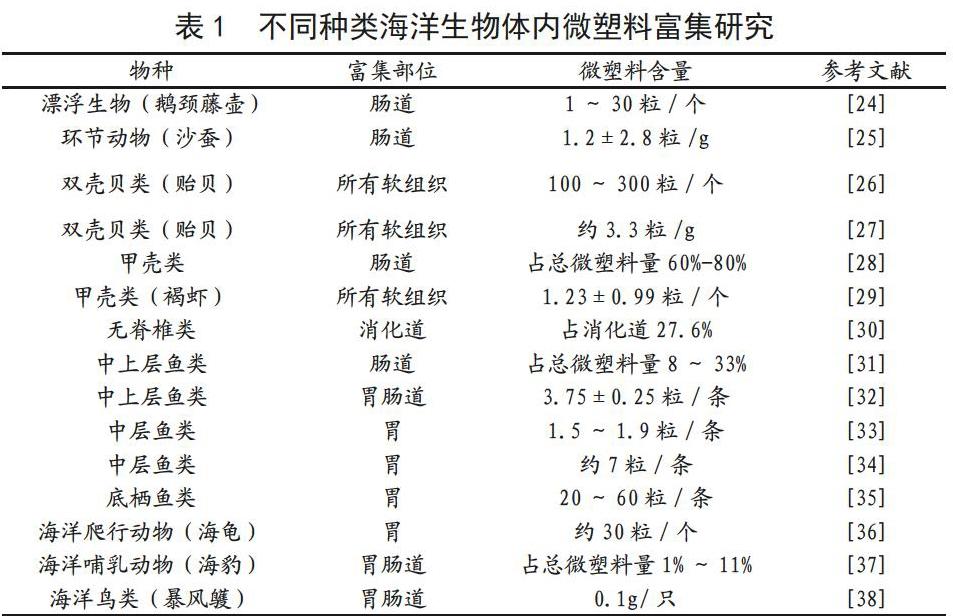
微塑料的粒徑一般在5 mm以內,容易被海洋環境中的浮游動物、底棲生物、魚類等誤食, 從而危害其生長。例如,Rummel等人[22]從海里捕獲的底層魚類(鱈魚和比目魚)和中上層魚類(鯡魚和鯖魚)內檢測到粒徑大小在200μm-2.2mm之間的PE和PP等微塑料。Alomar等人[23]通過檢測地中海附近海域的上百條鋸尾鯊發現,其體內富集有5mm左右的PP和PA等塑料。微塑料在不同種類海洋生物體內的富集研究已成為其生態效應研究的熱點之一,部分相關研究內容如表1所示。
由表1可以看出:微塑料進入生物體后不能及時被代謝,可以富集在水生動物的胃腸道組織中以及甲殼類和雙殼類動物的所有軟組織中。不同組織器官中微塑料的富集程度不同,其中胃腸道是主要的富集部位。微塑料富集劑量已經破壞了生態系統的平衡與協調,達到污染水平程度,對生物個體的生理健康造成威脅。
2.2 微塑料的水生食物鏈遷移
微塑料進入水環境后可能被浮游生物所誤食,并通過食物鏈從低營養級轉移到高營養生物體內。Setala等[39]將攝有標記的PS微粒的浮游動物提供給糠蝦作為食物,3小時后顯微鏡下觀察到糠蝦腸道中存在PS微粒。Mattsson等[40]研究微塑料食物鏈效應時也選擇了PS,他們發現PS被大型溞攝食后能夠通過食物鏈轉移到鯉魚體內并富集,嚴重影響了鯉魚的行為和新陳代謝。值得注意的是,微塑料可能已經進入人類的食物鏈體系。有文獻報道,對供人類食用的大西洋鱈魚進行抽樣調查,結果在2.4%的大西洋鱈魚消化道中檢測到了微塑料[41]。
環境遷移和生物放大作用會加劇微塑料的潛在危害,影響人類健康和整個生態系統的協調,所以更深層的研究微塑料環境遷移和生物放大作用迫在眉睫。微塑料隨著食物網在更高營養級生物體內具有怎樣的生物放大效應及富集效應,以及沿著食物鏈進入人體后產生怎樣的危害還需要進一步研究[42]。
3 微塑料對水生生物的毒性效應
微塑料被小型動物甚至一些稍大型動物誤食后無法被消化, 可能堵塞腸道,產生長時間的虛假飽腹感,影響正常的食物攝取,體內能量儲備減少[43],機體生長所需能量來源補充不足[44],最終導致生物體的饑餓和死亡[45]。微塑料進入生物體內產生的一系列生態毒理學效應可以概括為六個方面:行為毒性、生長發育毒性、致死效應、生殖毒性、免疫毒性和基因與遺傳毒性。
3.1 行為毒性
微塑料在短時間內低濃度下的暴露不會使生物體致死,但會影響其行為活動。Chen等[46]觀察到微塑料可以改變斑馬魚幼魚的游動行為,這是微塑料使斑馬魚zfrho視覺基因表達出現上調的結果。微塑料的暴露還會嚴重擾亂生物體的攝食行為:PS的存在能夠降低紫貽貝的濾食效率[47];歐洲鱸魚暴露在一定濃度的90μm PS顆粒的環境下,孵化會被抑制,生長速度降低,捕食能力和逃避天敵的先天行為也發生了明顯改變[48]。
3.2 生長發育毒性
微塑料會影響生物體的正常生長發育。在急性暴露條件下,橙線雀幼魚的生長速度隨2mm粒徑的PET濃度的升高而降低[49]。經 10~45 μm PE暴露5 d后,超過30%的海膽幼蟲的胃內檢測到了微塑料,并發現攝入的微塑料越多海膽的體形變得越小,體重越輕[50]。原生微塑料對胚胎發育具有毒性作用,研究表明,與空白對照組相比微塑料的暴露使海膽胚胎的異常發育率從52.0%增加至84.6%[51]。
3.3 致死效應
微塑料的暴露最終可導致生物體存活率下降。Au等[52]的試驗發現:端足類美洲鉤蝦暴露在PE和PP中顯示出明顯的劑量-效應關系,隨著微塑料暴露劑量的上升,鉤蝦的死亡率也呈現出逐漸升高的趨勢。Mazurais等[53]發現歐洲鱸魚幼魚在粒徑為10~45μm PE暴露下,隨暴露劑量的增加其死亡率從30%增加至44%。
3.4 生殖毒性
微塑料可導致水生生物胚胎發育受阻、孵化率下降、發育畸形等。Sussarellu等[54]將牡蠣暴露于2μm和6μm的PS顆粒環境兩個月后發現,與對照組相比,PS使牡蠣產生卵細胞的數量和大小、精子的運動速度等指標均有所降低,該研究表明PS微塑料顆粒會干擾牡蠣的攝食和繁殖,影響產卵量和后代幼體的發育。
3.5 免疫毒性
微塑料還會產生免疫毒性。比如,粒徑小于 80μm 的HDPE可在貽貝消化系統中富集,出現血流粒細胞增多和溶酶體膜不穩定等現象,引發機體免疫系統的炎癥反應[55]。Pedà等[56]利用組織病理學分析了PVC碎片暴露對歐洲鱸魚的影響,研究結果表明,PVC的暴露會引起鱸魚腸道末端明顯的炎癥反應,且隨著暴露時間的增加,腸道末端的病變程度呈現出由中度逐漸到重度的趨勢。
3.6 基因與遺傳毒性
從細胞和基因角度看,微塑料具有一定的毒性作用。比如,經過兩個月的慢性飲食暴露后,青鳉魚出現內分泌功能受損和Chg H、Vtg I基因表達明顯下調的現象,且精原細胞和精母細胞異常增殖,其遺傳信息的表達受到影響[57]。還有研究發現PS微塑料會導致紫貽貝上千個基因表達出現異常以及增加突變可能[58]。
4 微塑料與其他物質復合作用下的生態毒理效應
由于微塑料具有比表面積大、疏水性強等特點,使其具有富集持久性有機污染物和重金屬的能力,成為污染物的載體。微塑料類型、粒徑大小、暴露劑量等因素同樣是影響復合作用的重要因素,此外不同配比方式、作用對象、觀察指標等因素也會導致不同的聯合作用結果。進入生物體后,微塑料所吸附的污染物可能隨之釋放出來,釋放之后的復合作用大多是相加或協同作用。Teuten等[59]實驗證明,向含有菲的沉積物中分別加入PE、PP、PVC這三種微塑料均可顯著提高海蚯蚓組織中菲的濃度,從而增強了毒性作用。Karami等人[60]進一步探討了LDPE與菲聯合作用的毒性機制,暴露96h后發現LDPE改變了菲對非洲鯰魚幼魚肝組織的變化程度、總蛋白含量、血漿膽固醇濃度和肝糖原的轉錄水平的影響程度。Oliveira等人[61]采用1-5μm PE微球和多環芳烴芘研究其對鰕虎魚幼魚的生理影響,試驗發現PE增加了魚膽汁中芘代謝物的濃度,并且二者混合物顯著降低了鰕虎魚的乙酰膽堿酯酶 (AChE)和異檸檬酸脫氫酶(IDH)的活性, 從而可能會增加天然魚類種群的死亡率。此外,有學者利用組織學觀察到日本青鳉魚攝食結合有多環芳烴、多氯聯苯和多溴聯苯醚的PE顆粒后,吸附污染物出現了轉移,引起青鳉魚誘發肝臟應激,出現肝糖原耗竭、脂肪空泡化、細胞壞死和病變等現象[62]。目前微塑料和其他物質的拮抗作用尚未有文獻報道,綜上所述,微塑料對水體環境及生物的損害只注重其本身的研究是片面的,吸附有毒污染物的塑料微粒的生態效應影響更大。
5 研究展望
進入水環境的微塑料通過遷移和富集后,最終以自身毒性以及吸附重金屬或持久性有機物等化學物質造成永久性的危害。而微塑料危害程度與其本身粒徑大小、暴露劑量、表面污染情況、暴露時間以及生物體性質等呈顯著相關性。基于此,對于未來開展微塑料對水生生物的生態毒理效應研究提出以下見解:
(1)微塑料對水生生物的毒害是一個復雜且漫長的過程,微塑料與重金屬或持久性有機物等其他化學污染物的聯合毒害作用更是復雜。然而現有的研究均局限于短期的、暴露濃度比實際環境濃度高出幾個數量級的室內實驗條件,這有悖于現實意義。在未來的研究中,真實環境條件下不同種類和粒徑的微塑料與其他污染物質的長期混合作用及其毒理機制仍然是需要攻克的重要內容。同時,提升微塑料源解析技術和實現塑料降解速度的一定程度的調控,有利于微塑料污染的源頭控制。
(2)微塑料粒徑小、比表面積大、疏水性強的特性使其往往吸附并富集其他物質,研究微塑料生態效應時應注重微塑料與有毒物質的多重作用,盡管Razanajatovo等人[63]采用PE對磺胺甲惡唑、丙泊酚和舍曲林在水中的吸附解析性能進行了研究并得到相關吸附率順次,但微塑料的吸附能力、吸附過程、吸附行為等吸附及解吸機理研究仍存在很大的研究空白。
(3)至今關于微塑料對生物 LC50值研究報道甚少,為了進一步研究并預測生物體對環境中微塑料的響應和變化,應開展急性毒理試驗、亞急性毒理試驗、慢性毒理試驗的綜合研究,分析建立生物體(考慮多個生命階段)隨時間變化而產生的各種病變的數據庫,通過對低營養級生物到高營養級生物的食物鏈效應研究來探索微塑料最終對人類構成的威脅程度,為微塑料的生態毒理效應研究及風險評估提供更多依據。
參考文獻
[1]Thompson R C, Olsen Y, Mitchell R P, et al. Lost at sea: where is all the plastic ? [J].Science,2004,304(5672):838.
[2]Vandermeersch G, Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen C R, et al. A critical view on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms[J].Environmental Research, 2015,143:46-55.
[3]Galgani F, Hanke G, Werner S, et al. Marine litter within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive[J].ICES Journal of Marine Science,2013, 70(06):1055-1064.
[4]Syberg K, Khan F R, Selck H, et al. Microplastics: addressing ecological risk through lessons learned[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2015,34(05):945-953.
[5]Ivar d S J A , Costa M F , Barletta, Mário, et al. Pelagic microplastics around an archipelago of the Equatorial Atlantic[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 75(1-2):305-309.
[6]Obbard R W, Sadri S, Wong Y Q, et al. Global warming releases microplastic legacy frozen in Arctic Sea ice[J]. Earths Future,2014, 2(06):315-320.
[7]Saliu F, Montano S, Garavaglia M G, et al. Microplastic and charred microplastic in the Faafu Atoll,Maldives[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018,136:464-471.
[8]Syakti A D, Hidayati N V, Jaya Y V, et al. Simultaneous grading of microplastic size sampling in the Small Islands of Bintan water, Indonesia[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,137:593-600.
[9]Wang J D, Tan Z, Peng J P, et al. The behaviors of microplastics in the marine environment[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2016, 113:7-17.
[10]Kukulka T, Proskurowski G S. Morét-Ferguson, et al. The effect of wind mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant plastic debris[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(07):7601.
[11]Woodall L C, Sanchez-Vidal A, Canals M, et al. The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2014, 1(04):140317.
[12]Law K L, Moret-Ferguson S, Maximenko N A,et al. Plastic Accumulation in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre[J].Science, 2010, 329(5996):1185-1188.
[13]Moore C J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat[J].Environmental Research, 2008,108(02):131–139.
[14]Roy P K, Hakkarainen M, Varma I K, et al. Degradable polyethylene:fantasy or reality[J].Environmental Science& Technology. 2011,45(10):4217-4227.
[15]Zbyszewski M, Corcoran P L. Distribution and Degradation of Fresh Water Plastic Particles Along the Beaches of Lake Huron, Canada[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution,2011, 220(1-4):365-372.
[16]Nuelle M T, Dekiff J H, Remy D, Fries,E.A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014,184(01): 161–169.
[17]Green D S, Kregting L, Boots B, et al. A comparison of sampling methods for seawater microplastics and a first report of the microplastic litter in coastal waters of Ascension and Falkland Islands[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,137:695-701.
[18]Wenfeng W, Jun W. Investigation of microplastics in aquatic environments: An overview of the methods used, from field sampling to laboratory analysis[J],Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2018,8:1-33.
[19]Wagner J, Wang Z, Ghosal S, et al. Novel method for the extraction and identification of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish gut matrices [J].Anal Methods-UK,2017,9(09): 1479-1490.
[33]Digka N, Tsangaris C, Torre M, et al. Microplastics in mussels and fish from the Northen Ionian Sea[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,135:30-40.
[34]Romeo T, Pietro B, Pedà C, et al. First evidence of presence of plastic debris in stomach of large pelagic fish in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 95(01):358-361.
[35]Ramos J A A. Barletta M, Costa Monica F. Ingestion of nylon threads by Gerreidae while using a tropical estuary as foraging grounds[J]. Aquatic Biology, 2012,17(01):29-34.
[36]Tourinho P S, Sul J A I D, Fillmann G.Is marine debris ingestion still a problem for the coastal marine biota of southern Brazil? [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2010,60(03):396-401.
[37]Rebolledo E L B, Van Franeker J A, Jansen O E, et al. Plastic ingestion by harbour seals(Phoca vitulina)in The Netherlands[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2013,67(1/2):200-202.
[38]Franeker J A V, Blaize C, Danielsen J, et al. Monitoring plastic ingestion by the northern fulmar Fulmarus glacialis in the North Sea[J].Environmental Pollution,2011, 159(10):2609-2615.
[39]Setala O, Fleming-lehtinen V, Lehtiniemi M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web[J].Environmental Pollution, 2014, 185: 77-83.
[40]Mattsson K, Ekvall M T, Hansson L A, et al. Altered Behavior, Physiology, and Metabolism in Fish Exposed to Polystyrene Nanoparticles[J].Environmental Science&Technology,2015, 49(01):553-561.
[41]Liboiron M, Liboiron F, Wells E, et al. Low plastic ingestion rate in Atlantic cod(Gadus morhua)from Newfoundland destined for human consumption collected through citizen science methods[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,113(1-2):428-437.
[42]Lusher A L, Mchugh M, Thompson R C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 67(1-2):94-99.
[43]Watts A J, Lewis C, Goodhead R M, et al. Uptake and retention of microplastics by the shore crab Carcinus maenas[J].Environmental Science&Technology,2014,48(15):8823-8830.
[44]José G B Derraik.The Pollution of the Marine Environment by Plastic Debris:A Review[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2002,44(09):842-852.
[45]Lee K W, Shim W J, Kwon O Y, et al. Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicas [J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2013,47(19): 11278-11283.
[46]Chen Q, Gundlach M, Yang S, et al. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017,584-585:1022-1031.
[47]Wegner A, Besseling E, Foekema E M, et al. Effects of nanopolystyrene on the feeding behavior of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.)[J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 2012,31(11):2490-2497.
[48]Lonnstedt O M, Eklov P. Environmentally relevant concentrations of microplastic particles influence larval fish ecology[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290):1213-1216.
[49]Critchell K, Hoogenboom M O, Patterson H M, et al. Effects of microplastic exposure on the body condition and behaviour of planktivorous reef fish (Acanthochromis polyacanthus)[J]. Plos One, 2018, 102(102):178-190.
[50]Kaposi K L, Mos B, Kelaher B P, et al. Ingestion of microplastic has limited impact on a marine larva[J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2014,48(3):1638-1645.
[51]Nobre C R, Santana M F M, Maluf A, et al. Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 92(1-2): 99-104.
[52]Au S Y, Bruce T F, Bridges W C, et al. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2015, 34(11):2564-2572.
[53]Mazurais D, Ernande B, Quazuguel P, et al. Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae[J].Marine Environmental Research, 2015, 112:78-85.
[54]Sussarellu R, Suquet M, Thomas Y, et al. Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2016,113(09):2430-2435.
[55]Moos N V, Burkhardt-Holm P, Angela K?hler. Uptake and Effects of Microplastics on Cells and Tissue of the Blue Mussel Mytilus edulis L after an Experimental Exposure[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(20):11327-11335.
[56]Pedà C, Caccamo L, Fossi M C, et al. Intestinal alterations in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus,1758) exposed to microplastics: Preliminary results[J].Environmental Pollution,2016, 212:251-256.
[57]Rochman C M, Kurobe T, Flores I, et al. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment[J].Science of The Total Environment,2014, 493:656-661.
[58]Browne M A, Dissanayake A, Galloway T S, et al. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus edulis(L.)[J].Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 42(13):5026-5031.
[59]Teuten E L, Rowland S J, Galloway T S, et al. Potential for Plastics to Transport Hydrophobic Contaminants[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(22):7759-7764.
[60]Karami A, Romano N, Galloway T, et al.Virgin microplastics cause toxicity and modulate the impacts of phenanthrene on biomarker responses in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus)[J].Environmental research,2016,151:58-70.
[61]Oliveira M, Ribeiro A, Hylland K, et al. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles(0+group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps(Teleostei,Gobiidae)[J].Ecological Indicators,2013,34:641-647.
[62]Rochman C M, Hoh E, Kurobe T, et al. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 47(03):1646-1654
[63]Razanajatovo R M, Ding J, Zhang S, et al. Sorption and desorption of selected pharmaceuticals by polyethylene microplastics[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,136:516-523.
收稿日期:2019-08-19
基金項目:湖北省新農村發展研究院(長江大學)開放基金
作者簡介:楊秉倬(1994-),女,碩士研究生,研究方向為生態毒理學。
通訊作者:黃河,男,副教授,研究方向為污染物在環境中的環境行為和毒性效應。

