2013—2017年度淮河流域菏澤市牡丹區(qū)食管癌早診早治項(xiàng)目開展情況及實(shí)施效果分析
李保全
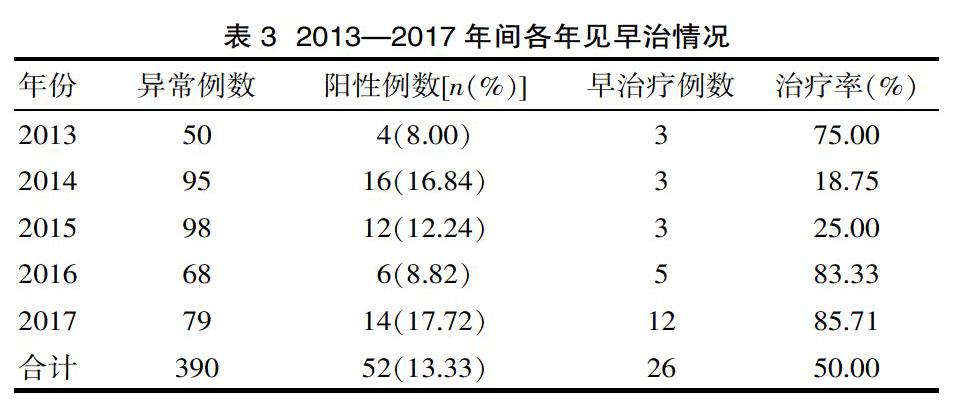

[摘要] 目的 分析該市2013—2017年度我市淮河流域牡丹區(qū)食管癌早診早治療的項(xiàng)目開展情況與實(shí)施效果的分析。方法 分析淮河流域牡丹區(qū)2013—2017年早診早治項(xiàng)目實(shí)施以來每年食管癌的檢出率、早診率、早治率。結(jié)果 2013—2017年間接受內(nèi)鏡檢查者中共檢測出癌52例(1.04%)2013年共檢測出5例(0.498%),2014年檢測出16例(1.589%)。2015年檢測出11例(1.09%),2016年檢測出7例(0.69%),2017年檢測出13例(1.30%);2013年檢出患者中早期治療早治率(75.00%),2014年早期治療早治率(18.75%);2015年早期治療率(25.00%);2016年早期治療率(83.33%),2017早期治療率(85.71%),該文中52例腫瘤患者男性檢出40例(76.92%)遠(yuǎn)高于女性檢出率12例(23.08%)。結(jié)論 中淮河流域菏澤市牡丹區(qū)各鄉(xiāng)鎮(zhèn)參與篩查40~69歲人群中參與內(nèi)鏡檢查人數(shù)相對(duì)較少,參與胃鏡檢查人群發(fā)病率相對(duì)較低,男性患者的發(fā)病率遠(yuǎn)高于女性,但在發(fā)現(xiàn)病癥后患者參與治療率相對(duì)較低。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 食管癌;早診;早治;實(shí)施效果
[中圖分類號(hào)] R735 [文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼] A [文章編號(hào)] 1672-5654(2019)09(a)-0186-04
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the development and implementation of the early diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer in the Mudan area of the Huaihe River Basin in our city from 2013 to 2017. Methods The detection rate, early diagnosis rate and early treatment rate of esophageal cancer were analyzed every year since the implementation of the early diagnosis and treatment project in the Mudan District of the Huaihe River Basin from 2013 to 2017. Results 52 cases (1.04%)by endoscopy from 2013 to 2017, In 2013, 5 cases(0.498%) were detected, and in 2014, 16 cases (1.589%) were detected. In 2015, 11 cases(1.09%) were detected, 7 cases(0.69%) were detected in 2016, and 13 cases(1.30%) were detected in 2017. The early treatment rate of early detection in 2013(75.00%), The early treatment rate of early treatment in 2014(18.75%); early treatment rate in 2015(25.00%); early treatment rate in 2016 (83.33%), early treatment rate in 2017 (85.71%), 52 cases of cancer patients detected 40 cases(76.92%) was much higher than the female detection rate of 12 cases (23.08%). Conclusion The towns and villages in the Mudan District of Heze City, participated in the screening of 40 to 69 years old. The number of people participating in endoscopy was relatively small. The incidence of participation in gastroscopy was relatively low. The incidence of male patients was much higher than that of females. The rate of patient participation in the treatment was relatively low after the illness was discovered.
[Key words] Esophageal cancer; Early diagnosis; Early treatment; Implementation effect
惡性腫瘤是現(xiàn)今臨床中威脅人類健康安全的嚴(yán)重疾病之一[1]。在我國消化道腫瘤的發(fā)病率與死亡率在全球各國家中位居首位[2]。大多數(shù)患者在發(fā)現(xiàn)患病后多數(shù)都已進(jìn)入中晚期,期治療效果不佳,預(yù)后較差[3]。食管癌在消化道惡性腫瘤中屬于較為常見的疾病之一,該病的發(fā)病率在全球位列惡性腫瘤疾病的第8位,我國食管癌的發(fā)病率位居世界第4位,該病位居我國惡性腫瘤導(dǎo)致死亡的第6位[4]。根據(jù)研究結(jié)果報(bào)道,食管癌的發(fā)病率在我國城市與農(nóng)村地區(qū)仍屬于偏高的比例。所以,臨床中眾多學(xué)者認(rèn)為對(duì)于食管癌患者而言提升該病的早發(fā)現(xiàn),早治療是提高患者生產(chǎn)時(shí)間及生存率的關(guān)鍵[5-6]。……

