粗糙面上方三維目標復合散射的并行IPO方法研究
李娟 劉銳 郭立新 李科 柴水榮 孟肖
摘要:本文采用迭代物理光學法(IPO)研究二維粗糙面與上方三維目標的復合電磁散射,其中目標和粗糙面對入射波的一次散射均由物理光學法(PO)計算,二者之間耦合散射采用惠更斯原理和迭代策略求解。由于三維復合模型的電磁散射仿真將產生海量數據,本文采用基于消息傳遞接口(MPI)平臺的并行技術提高計算效率。最后利用基于MPI的并行IPO方法數值計算了二維粗糙面與其上方球、導彈等目標的復合散射,并與商用軟件、有限元-基爾霍夫法(FEM-KA)的結果進行了對比,結果表明在大多數散射角范圍內兩種方法的結果具有很好的一致性。
關鍵詞:粗糙面;目標;復合散射;IPO
中圖分類號:TN011文獻標識碼:ADOI:10.19452/j.issn1007-5453.2020.06.014
基金項目:航空科學基金(20172081009,20170181004);國家自然科學基金(61971338,41806210)
近些年來,隨著目標及其與粗糙面的復合電磁散射在雷達探測、目標識別、地物遙感等領域的廣泛應用[1-2],復合模型電磁散射的研究越來越受到國內外學者的關注。基于麥克斯韋方程的多種數值方法及其加速方法已被用來求解粗糙面與目標的復合散射,如矩量法(MOM)、多層快速多極子方法(MLFMM)[3]、前后向迭代結合譜積分加速法(FBM-SAA)和有限元法(FEM)[4]等算法已被用于計算粗糙面與其上、下方目標的復合電磁散射問題。
在以上的數值算法中,通常將目標和隨機粗糙面作為一個整體來建模,可以獲得較高的計算精度,但是它們通常以高內存需求及高耗時特性為代價。本文采用高頻算法迭代物理光學法(IPO)計算二維粗糙面與其上方三維目標的復合電磁散射,即目標散射和粗糙面散射均由PO計算,目標和粗糙面之間的耦合作用采用惠更斯原理和迭代策略進行求解。對于一維粗糙面與二維目標(上方、下方、半掩埋)復合電磁散射的IPO方法求解,作者已進行了大量的研究,詳見參考文獻[5]、參考文獻[6]。
粗糙面和目標之間的耦合過程需要考慮電磁波在粗糙面與目標上任意兩個面片間的傳播與散射,對該過程的仿真極其耗時。為進一步提高計算效率,本文采用基于MPI平臺的并行技術[7]對IPO方法進行加速,實現對二維粗糙面與上方三維目標復合散射的快速計算。
1復合散射IPO方法求解機理
圖1是利用IPO方法對粗糙面與目標復合電磁散射進行求解的物理機理,圖1(a)表示粗糙面與目標表面的直接散射,圖1(b)~圖1(d)表示粗糙面和目標之間的耦合散射。具體求解過程為:首先假設目標(或粗糙面)不存在時,通過PO方法求得粗糙面(或目標)表面上直接散射的等效感應電磁流;然后以直接感應電磁流激發的散射場為基礎,采用惠更斯原理獲得粗糙面和目標上的一次耦合等效電磁流,依次通過迭代策略獲得二次、三次、四次等高階耦合等效電磁流,直到目標和粗糙面上的感應電磁流達到穩定后,迭代結束。以下分別給出直接感應電磁流和耦合感應電磁流的求解過程。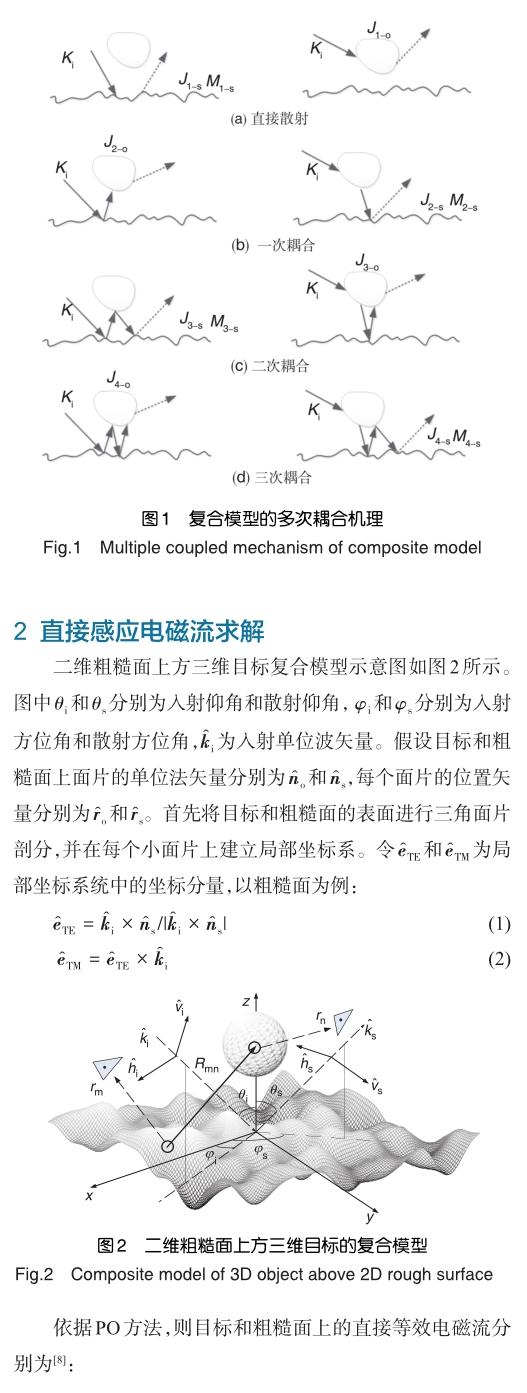


5 MPI并行技術
粗糙面與目標之間的耦合過程需要考慮電磁波在粗糙面與目標上任意兩個面片間的傳播與散射,對該過程的仿真極其耗時,這里采用基于MPI平臺的并行技術[7]加速粗糙面與目標之間的耦合過程。與目標相比,粗糙面表面包含大量的三角面片,將粗糙面表面面片劃分到不同的區域,每個區域對應一個進程與目標同時進行耦合(見圖3),最后將不同區域粗糙面表面的耦合電磁流收集起來,再進行下一階耦合散射求解。
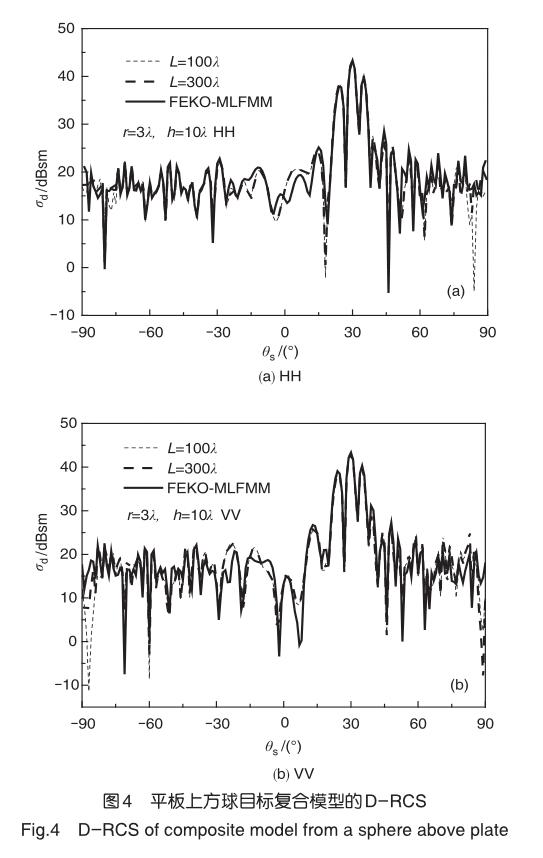
6數值結果與討論

7結論
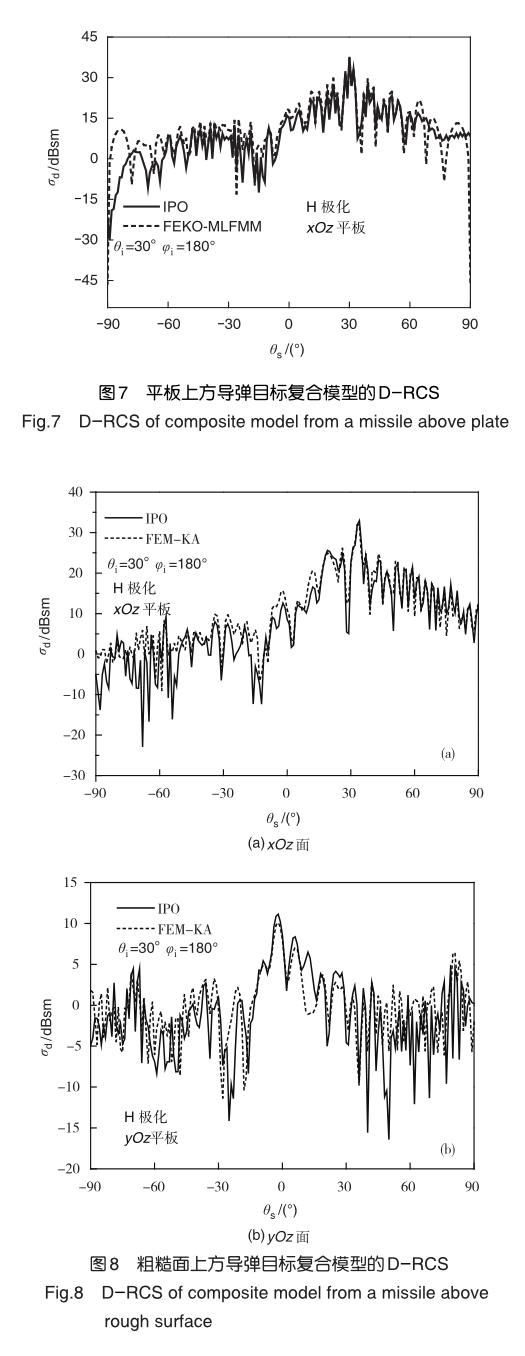
本文采用基于MPI平臺的并行IPO方法求解了二維粗糙面上方三維目標的復合電磁散射。給出了IPO方法中粗糙面與目標之間的多次耦合散射機理,粗糙面與目標表面直接電磁流的計算公式以及耦合電磁流的計算公式。數值結果詳細呈現了并行IPO方法求解平板、粗糙面與球體、戰斧式導彈目標復合模型的遠區差場雷達散射截面,并與商業軟件以及FEM-KA的結果進行了對比,驗證了本文算法的有效性。本文研究了二維粗糙面與單個三維目標的復合電磁散射,粗糙面與上方多個目標的復合電磁散射的IPO方法研究將作為下一步的研究重點。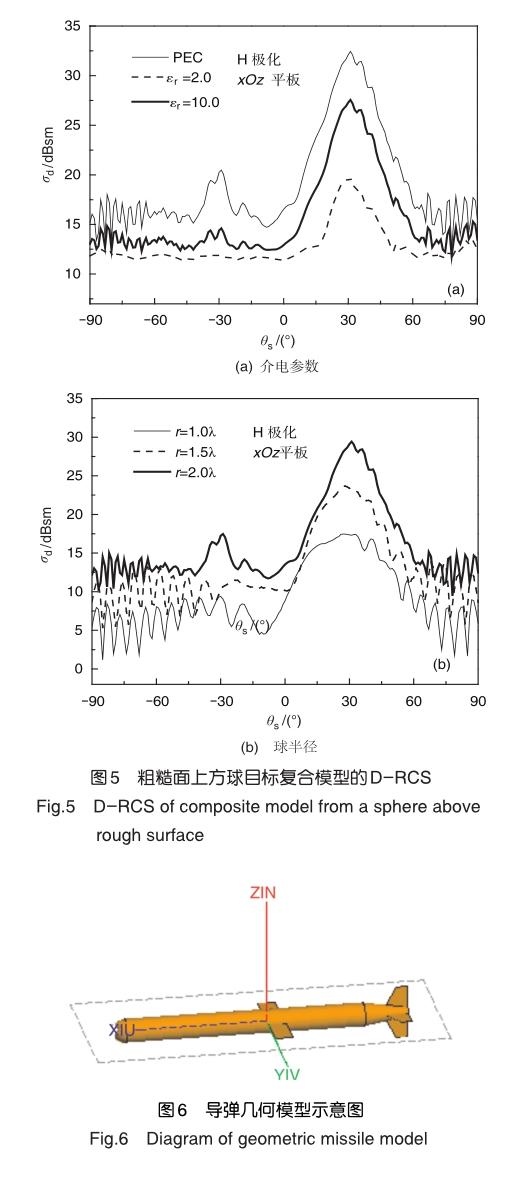
參考文獻
[1]郭鵬,白亮,武夢潔,等.基于FEKO的雷達散射截面實時計算[J].航空科學技術, 2013(6): 72-76. Guo Peng, Bai Liang, Wu Mengjie, et al. Real-time RCS caculation based on FEKO[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2013(6): 72-76. (in Chinese)
[2]劉偉,張穎,李可可,等.覆蓋泡沫動態海面散射回波多普勒譜頻移及展寬特征[J].航空科學技術, 2018, 29(8): 70-74. Liu Wei, Zhang Ying, Li Keke, et al. Doppler spectral frequency shift and widening characteristics of scattered echoesfromdynamicfoam-seasurface[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology,2018,29(8):70-74. (in Chinese)
[3]Geng N,Sullivan A,Carin L. Multilevel fast-multipole algorithm for scattering from conducting targets above or embedded in a lossy half space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing,2000,38(4):1561-1573.
[4]Ozgun O,Mustafa K. Monte carlo-based characteristic basis finite-element method(MC-CBFEM)for numerical analysis of scattering from objects on/above rough sea surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing,2012,50(3):769-783.
[5]Li J,Guo L X,Chai S R,et al. Electromagnetic scattering from a PEC object above a dielectric rough sea surface by a hybrid PO-PO method [J]. Waves Random Complex Media,2015,25(1):60-74.
[6]Li K,Guo L X,Li J,et al. A fast and efficient method for the composite scattering of a coated object above 3D random rough surfaces [J]. IEEEAccess,2018,6(1):56192-56199.
[7]張玉.電磁場并行計算[M] .西安:西安電子科技大學出版社, 2006. Zhang Yu. Parallel computation in electromagnetics [M]. Xian: Xidian University Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[8]Tsang L,Kong J A,Ding K H. Scattering of electromagnetic waves,theories and applications [M]. New York,NY,USA:Wiley,2000.
[9]李科.時域有限差分法和物理光學法在粗糙面與目標復合電磁散射中的應用[D].西安:西安電子科技大學,2019.Li Ke. Application of finite difference time domain method and physical optics method in composite EM scattering from rough surface and target[D]. Xian: Xidian University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[10]Johnson J T. A numerical study of scattering from an object above a rough surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,2002,50(10):1361-1367.
[11]Jakobus U,Tonder J V,Illenseer F. Overview of recent extensions in Feko with regard to the MLFMM and cable coupling[C] // International Itg Conference onAntennas,2007.
[12]He H J,Guo L X. A multihybrid FE-BI-KA technique for 3-D electromagnetic scattering from a coated object above a conductiveroughsurface[J].IEEEGeoscienceRemote Sensing Letters,2016,13(12):2009-2013.
(責任編輯王為)
作者簡介
李娟(1984-)女,博士,副教授。主要研究方向:隨機介質中目標電磁散射、計算電磁學。
Tel:13991206571E-mail:juanli@xidian.edu.cn
劉銳(1988-)男,博士,高級工程師。主要研究方向:雷達信號處理。
Tel: 18921505600E-mail: skywordlr@126.com
郭立新(1968-)男,博士,教授。主要研究方向:隨機介質中波傳播與散射。
Tel: 029-88201450E-mail: lxguo@xidian.edu.cn
李科(1987-)男,博士,講師。主要研究方向:地面環境及其與目標復合電磁散射。
Tel: 029-88201450E-mail: xidian_keli@163.com
柴水榮(1989-)男,博士,講師。主要研究方向:陸海交界區域電磁散射。
Tel: 029-88201450E-mail: srchai@xidian.edu.cn
孟肖(1989-)女,博士,講師。主要研究方向:高海情下海面及其與目標復合電磁散射。
Tel: 029-88201450E-mail: mengxxidian@126.com
Investigation on Composite Scattering from 3D Object Above Rough Surface by Parallel IPO Method
Li Juan1,*,Liu Rui2,Guo Lixin1,Li Ke1,Chai Shuirong1,Meng Xiao1
1. Xidian University,Xian 710071,China
2. AVIC Leihua Electronic Technology Research Institute,Wuxi 214063,China
Abstract: In this paper, the composite scattering from a 3D object above 2D rough surface is investigated by the iterative physical optics (IPO). In present method both the scatterings of object and underlying rough surface are calculated by the PO method. And the mutual couplings between them are solved by the equivalence principle and iterative strategy. The geometry model of rough surface and object are meshed by triangular patches, which lead to enormous data for 3D composite model. The message-passing-interface (MPI)-based parallel technology is used to improve calculative efficiency. The composite scattering from an object (sphere, missile) above 2D rough surface is calculated and compared with the results by commercial software and hybrid FEM-KA method. The results indicate that the two methods match very well for most observed angles.
Key Words: rough surface; object; composite scattering; IPO

