腸易激綜合征患者5-羥色胺及5-羥色胺2B受體變化的研究
孫詠紅 張野 王宇
[摘要]目的 觀察腸易激綜合征(IBS)患者血漿和結腸黏膜5-羥色胺(5-HT)及5-HT2B受體的表達情況,并探討5-HT及5-HT2B受體在IBS發病機制中的作用。方法 選取2016年1月~2017年5月于大連市友誼醫院消化內科確診的48例腹瀉型IBS(IBS-D)及便秘型IBS(IBS-C)患者,其中IBS-D患者26例(IBS-D組),IBS-C患者22例(IBS-C組);另選取28例同期行結腸癌或結腸息肉篩查且結腸鏡檢查結果陰性者作為對照組。應用腹部癥狀評分量表對受試者進行評分,采用ELISA法檢測受試者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度。結腸鏡下獲取升結腸處結腸黏膜標本,采用逆轉錄PCR檢測5-HT mRNA及5-HT2B受體mRNA的表達水平,并分析血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體水平與腹部癥狀評分的相關性。結果 IBS-D及IBS-C組患者的腹部癥狀評分高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);IBS-D及IBS-C組患者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);IBS-D及IBS-C組患者結腸黏膜組織5-HT及5-HT2B受體mRNA表達量高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Spearman分析結果顯示,IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.82、0.79,P<0.05);IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.78、0.76,P<0.05);對照組血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分無相關性(P>0.05)。結論 5-HT及5-HT2B在IBS患者中顯著升高,且血漿5-HT及5-HT2B與IBS患者的腹部癥狀評分成正相關,提示5-HT及5-HT2B受體可能參與了IBS患者腹痛的發生。
[關鍵詞]腸易激綜合征;5-羥色胺;5-羥色胺2B受體;結腸組織;腹痛
[Abstract] Objective To observe the changes of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and 5-HT2B receptor in the patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). And to explore the role of 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor in the pathogenesis of IBS. Methods From January 2016 to may 2017, 48 patients with diarrhea type IBS (IBS-D) and constipation type IBS (IBS-C) were selected from the Department of Gastroenterology, Dalian Friendship Hospital, including 26 cases of IBS-D patients (IBS-D group), 22 cases of IBS-C patients (IBS-C group). In addition, those undergoing colonoscopy for polyps or cancer surveillance with negative results were included in the control group (28 cases). The abdominal symptom scale was used to score the subjects, and the Plasma 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor concentrations were detected by ELISA. Specimens were obtained from the ascending colon during the colonoscopy, and the expression level of 5-HT mRNA and 5-HT2B receptor mRNA in colonic mucosa were detected by reverse transcription PCR. The relationship between 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor levels and abdominal symptoms were calculated. Results The scores of abdominal symptoms in IBS-D and IBS-C groups were higher than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The plasma concentrations of 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor in IBS-D and IBS-C groups were higher than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The expression of 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor mRNA in colonic mucosa of IBS-D and IBS-C group were higher than those of control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Spearman analysis showed that the expression of plasma 5-HT in IBS-D and IBS-C group were positively correlated with abdominal symptom score (r=0.82, 0.79; P<0.05). The plasma 5-HT2B receptor expression in IBS-D and IBS-C groups were positively correlated with abdominal symptom scores (r=0.78, 0.76; P<0.05). There was no correlation between the expression of 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptor and abdominal symptom score in the control group (P>0.05). Conclusion T5-HT and 5-HT2B are significantly increased in IBS patients, and plasma 5-HT and 5-HT2B are positively correlated with the abdominal symptom score of IBS patients, suggesting that 5-HT and 5-HT2B receptors may be involved in the occurrence of abdominal pain in IBS patients.
[Key words] Irritable bowel syndrome;5-hydroxytryptamine;5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor;Colon tissues; Abdominal pain
腸易激綜合征(IBS)是一種以反復發作的腹痛或腹部不適,伴有糞便性狀及排便習慣改變為主的慢性功能性腸道疾病[1-2],是消化科的常見病、慢性病,嚴重影響患者的生活質量。其病因和發病機制尚不清楚,其中,內臟敏感性增高是IBS患者腹痛或腹部不適發生的最主要病因[3-4],也是IBS患者反復就診的最重要的因素。
5-羥色胺(5-hydroxytryptamine,5-HT),又名血清素,是腦-腸軸中重要的神經遞質。哺乳動物體內95%的5-HT來源于胃腸道,大部分外周5-HT受體分布于腸道,5-HT與腸道和腸神經元細胞表面的5-HT受體結合,產生調控腸道運動、感覺和分泌的作用[5-9]。IBS患者血漿中5-HT及其代謝產物表達較正常人顯著增高[10-11],但5-HT與IBS患者腹痛的相關性研究,目前鮮有報道。5-HT2B受體廣泛分布于外周組織中,5-HT與5-HT2B受體結合可以促進人離體結腸組織的收縮[12]。5-HT2B受體拮抗劑則可以劑量依賴性地降低IBS大鼠的內臟高敏感[13],提示5-HT2B受體可能參與了IBS的內臟高敏感。目前,關于5-HT2B受體在IBS患者血清和結腸黏膜中的表達尚缺少報道。本研究通過檢測腸IBS患者血漿和結腸黏膜5-HT及5-HT2B受體的表達情況,探討其與IBS患者腹痛的相關性,現報道如下。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料
選取2016年1月~2017年5月于大連市友誼醫院消化內科確診的48例腹瀉型IBS(IBS-D)及便秘型IBS(IBS-C)患者,其中IBS-D患者26例(IBS-D組),IBS-C患者22例(IBS-C組);另選取28例同期行結腸癌或結腸息肉篩查且結腸鏡檢查結果陰性者作為對照組。IBS-D組中,男12例,女14例;年齡29~70歲,平均(52.3±10.8)歲。IBS-C組中,男9例,女13例;年齡30~72歲,平均(52.9±10.3)歲。對照組中,男12例,女16例;年齡28~70歲,平均(52.1±11.1)歲。三組的一般資料比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。本研究已經醫院醫學倫理委員會審核批準,所有研究對象均簽署知情同意書。
1.2方法
抽取受試者的靜脈血,經12 000 r/min,4℃,超速離心10 min,取上清液置于-80°C冰箱內保存;采用ELISA試劑盒檢測血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體的濃度;結腸鏡檢查時各取升結腸黏膜標本2塊,置于-80°C冰箱內,采用逆轉錄PCR檢測5-HT及5-HT2B受體mRNA的表達情況。
1.3觀察指標及評價標準
記錄受試者的腹部癥狀評分、血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度、結腸黏膜5-HT及5-HT2B受體的mRNA表達情況。
采用腹部癥狀評分量表進行腹部癥狀評分。根據最近2周內受試者腹痛、腹部不適癥狀對其日常生活的影響,進行量化評分[14]:0分,無任何影響;1分,輕度影響(不影響日常活動);2分,有相應影響(影響了日常活動);3分,嚴重影響(顯著影響了日常活動);4分,非常嚴重(對日常活動嚴重妨礙)。
1.4統計學方法
采用SPSS 19.0統計學軟件對數據進行分析,符合正態分布的計量資料以均數±標準差(x±s)表示,組間兩兩比較采用t檢驗,不符合正態分布的轉換為正態分布,再行統計學分析;計數資料以率(%)表示,采用χ2檢驗,相關性采用Spearman等級相關性分析,以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2結果
2.1三組腹部癥狀評分的比較
IBS-D組患者的腹部癥狀評分為(2.3±0.8)分,IBS-C組患者的腹部癥狀評分為(2.2±0.7)分,對照組的腹部癥狀評分為(0.3±0.2)分。IBS-D及IBS-C組患者的腹部癥狀評分高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。IBS-D組患者的腹部癥狀評分與IBS-C組,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
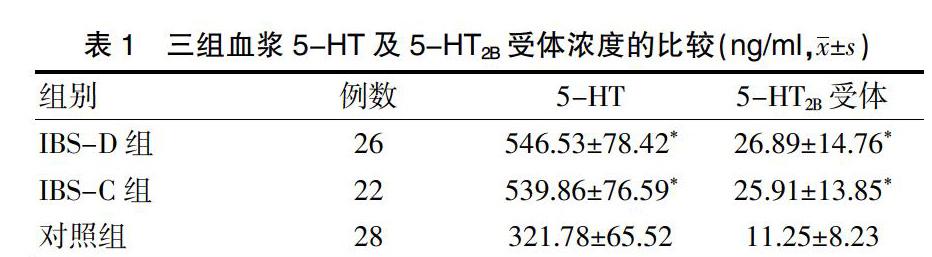
2.2三組血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度的比較
IBS-D及IBS-C組患者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);IBS-D組患者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度與IBS-C組比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)(表1)。
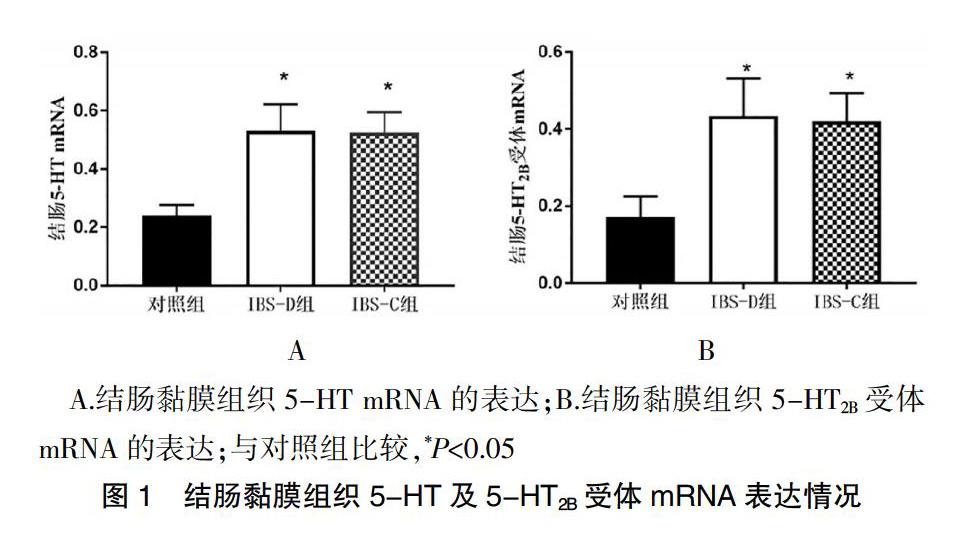
2.3三組結腸黏膜5-HT及5-HT2B受體mRNA表達情況的比較
IBS-D及IBS-C組患者結腸黏膜組織5-HT及5-HT2B受體mRNA表達量高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);IBS-D組患者的結腸黏膜組織5-HT及5-HT2B受體mRNA表達量與IBS-C組比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)(圖1)。
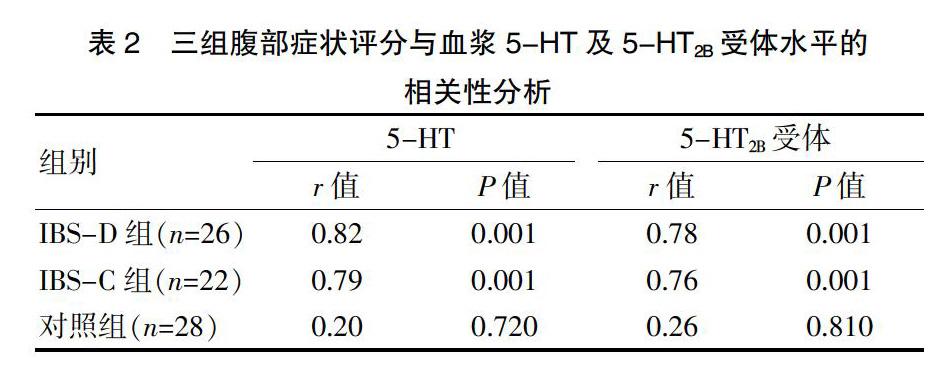
2.4三組腹部癥狀評分與血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體水平的相關性分析
Spearman分析結果顯示,IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.82、0.79,P<0.05);對照組血漿5-HT的表達量與腹部癥狀評分無相關性(P>0.05)。IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.78、0.76,P<0.05);對照組血漿5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分無相關性(P>0.05)(表2)。
3討論
IBS的病因和發病機制仍不清楚,傳統觀念認為胃腸動力障礙和內臟敏感性增高等是引起IBS發病的關鍵因素[15-18]。近年來發現了與IBS發病相關的新的病理生理學改變依據,如腦腸軸功能失調、肥大細胞的激活并釋放活性物質等[19]。其中,內臟敏感性增高被認為是IBS最主要的病理生理學基礎,也是IBS患者腹痛發生的最主要的病理生理學基礎[20]。
5-HT作為神經遞質,廣泛分布在周圍組織和中樞神經系統中。大部分5-HT受體分布于腸道,5-HT與腸道的5-HT受體結合,產生調控腸道運動、感覺和分泌的作用。5-HT與5-HT2B受體結合可以發揮收縮結腸的作用,5-HT含量或功能異常可能引起IBS患者的臨床癥狀。IBS患者可出現5-HT含量異常,而5-HT信號系統的異常則可以引起腸道分泌,感覺和運動功能的改變,進而導致IBS臨床癥狀的發生[21]。既往研究報道,IBS-D和IBS-C患者的血漿5-HT水平較健康者顯著增高[22],而Sen等[23]的研究顯示,IBS-D患者血漿5-HT水平較健康者明顯升高,而IBS-C患者血漿5-HT與健康者比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。本研究結果顯示,IBS-D及IBS-C組患者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),與上述研究結果一致。但本研究中,IBS-D患者的血漿5-HT及5-HT2B受體濃度與IBS-C患者比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),可能與研究樣本量相對較少有關,后期可擴大樣本量進行驗證。
通過對血漿5-HT的表達水平與腹部癥狀評分的相關性進行分析,結果顯示,IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.82、0.79,P<0.05);對照組血漿5-HT的表達量與腹部癥狀評分無相關性(P>0.05),提示5-HT可能參與了IBS腹痛/腹部不適癥狀的發生。5-HT2B受體在人結腸組織中存在表達,5-HT與5-HT2B受體結合發揮收縮結腸的作用[24]。相關研究顯示,RS-127445作為5-HT2B受體拮抗劑,抑制小鼠的腸道蠕動,抑制大鼠的排便,提示5-HT2B受體可能參與了生理狀態下結腸的運動,且RS-127445可以降低IBS大鼠的內臟高敏性[26]。該研究提示5-HT2B受體可能參與了IBS內臟高敏感的發生。本研究結果顯示,IBS-D和IBS-C組患者血漿5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分成正相關(r=0.78、0.76,P<0.05);對照組血漿5-HT2B受體的表達量與腹部癥狀評分無相關性(P>0.05),提示5-HT2B受體可能參與了IBS腹痛/腹部不適癥狀的發生。
綜上所述,IBS患者不僅存在5-HT的高表達,5-HT2B受體也存在高表達,IBS患者高表達的5-HT可能通過結合5-HT2B受體,參與IBS患者腹痛癥狀的發生,后期可擴大樣本量進一步驗證,以期為IBS的發病機制及臨床治療提供新的靶點。
[參考文獻]
[1]Wiley JW,Chang L.Functional bowel disorders[J].Gastroenterology,2018,155(10):1-4.
[2]El-Salhy M,Hatlebakk JG,Hausken T.Diet in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS):interaction with gut microbiota and gut hormones[J].Nutrients,2019,11(9):152-161.
[3]Li Y,Yang T,Yao Q,et al.Metformin prevents colonic barrier dysfunction by inhibiting mast cell activation in maternal separation-induced IBS-like rats[J].Neurogastroenterol Motil,2019,31(12):e13556.
[4]Ng QX,Soh A,Loke W,et al.The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)[J].J Inflamm Res,2018,11(9):345-349.
[5]He Q,Li M,Wang X,et al.A simple,efficient and rapid HPLC-UV method for the detection of 5-HT in RIN-14B cell extract and cell culture medium[J].BMC Chem,2019,13(7):76-82.
[6]Ago Y,Tanabe W,Higuchi M,et al.(R)-ketamine induces a greater increase in prefrontal 5-HT release than (S)-ketamine and ketamine metabolites via an AMPA receptor-independent mechanism[J].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2019,22(10):665-674.
[7]Chen B,Li J,Xie Y,et al.Cang-ai volatile oil improves depressive-like behaviors and regulates DA and 5-HT metabolism in the brains of CUMS-induced rats[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2019,244(10):112-119.
[8]Cartolano MC,Gancel HN,Lonthair J,et al.Pulsatile urea excretion in Gulf toadfish:the role of circulating serotonin and additional 5-HT receptor subtypes[J].J Comp Physiol B,2019,189(5):537-548.
[9]Sengupta A,Holmes A.A discrete dorsal raphe to basal amygdala 5-HT circuit calibrates aversive memory[J].Neuron,2019,103(10):489-505.
[10]Lin LD,Chang L.Using the rome Ⅳ criteria to help manage the complex IBS patient[J].Am J Gastroenterol,2018,113(8):453-456.
[11]Ng QX,Soh A,Loke W,et al.The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)[J].J Inflamm Res,2018,11(10):345-349.
[12]Borman RA,Tilford NS,Harmer DW,et al.5-HT(2B) receptors play a key role in mediating the excitatory effects of 5-HT in human colon in vitro[J].Br J Pharmacol,2002, 135(8):1144-1151.
[13]Bassil AK,Taylor CM,Bolton VJ,et al.Inhibition of colonic motility and defecation by RS-127445 suggests an involvement of the 5-HT2B receptor in rodent large bowel physiology[J].Br J Pharmacol,2009,158(7):252-258.
[14]Long Y,Huang Z,Deng Y,et al.Prevalence and risk factors for functional bowel disorders in south China:a population based study using the Rome Ⅲ criteria[J].Neurogastroenterol Motil,2017,29(9):173-179.
[15]Schiller LR.Chronic diarrhea evaluation in the elderly:IBS or something else?[J].Curr Gastroenterol Rep,2019,21(2):45-52.
[16]Shakya AK,Naik RR,Almasri IM,et al.Role and function of adenosine and its receptors in inflammation,neuroinflammation,IBS,autoimmune inflammatory disorders,rheu-matoid arthritis and psoriasis[J].Curr Pharm Des,2019,25(26):2875-2891.
[17]Lackner JM,Jaccard J.Cognitive-behavioural therapy for IBS comes home:mapping a route for efficacy and efficiency in the digital age[J].Gut,2019,68(12):1541-1542.
[18]Husein DM,Naim HY.Impaired cell surface expression and digestive function of sucrase-isomaltase gene variants are associated with reduced efficacy of low FODMAPs diet in patients with IBS-D[J].Gut,2019,52(6):1261-1265.
[19]Xiong L,Gong X,Siah KT,et al.Rome foundation asian working team report:real world treatment experience of Asian patients with functional bowel disorders[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2017,32(11):1450-1456.
[20]Camilleri M,Boeckxstaens G.Dietary and pharmacological treatment of abdominal pain in IBS[J].Gut ,2017,66(12):966-974.
[21]Kim JE,Koh EK,Song SH,et al.Effects of five candidate laxatives derived from Liriope platyphylla on the 5-HT receptor signaling pathway in three cell types present in the transverse colon[J].Mol Med Rep,2017,15(8):431-441.
[22]詹麗杏,許國銘,李兆申,等.腸易激綜合征患者活動期和緩解期血漿5-HT、5-HIAA的變化[J].第二軍醫大學學報,2003,24(2):61-65.
[23]Sen F,Pinarbasi B,Issever H,et al.Postprandial platelet-poor plasma 5-hydroxytryptamine concentrations during diarrhea and constipation periods of alternatingtype irritable bowel syndrome patients[J].Turk J Gastroenterol,2011, 22(9):270-278.
[24]Borman RA,Tilford NS,Harmer DW,et al.5-HT(2B) receptors play a key role in mediating the excitatory effects of 5-HT in human colon in vitro[J].Br J Pharmacol,2002, 135(10):1144-1151.
[25]O′ Mahony SM,Bulmer DC,Coelho AM,et al.5-HT2B receptors modulate visceral hypersensitivity in a stress-sensitive animal model of brain-gut axis dysfunction[J].Neurogastroenterol Motil,2010,22(5):573-578.
(收稿日期:2019-08-27? 本文編輯:閆? 佩)

