云南省氣溫和降水變化特性研究
張楠
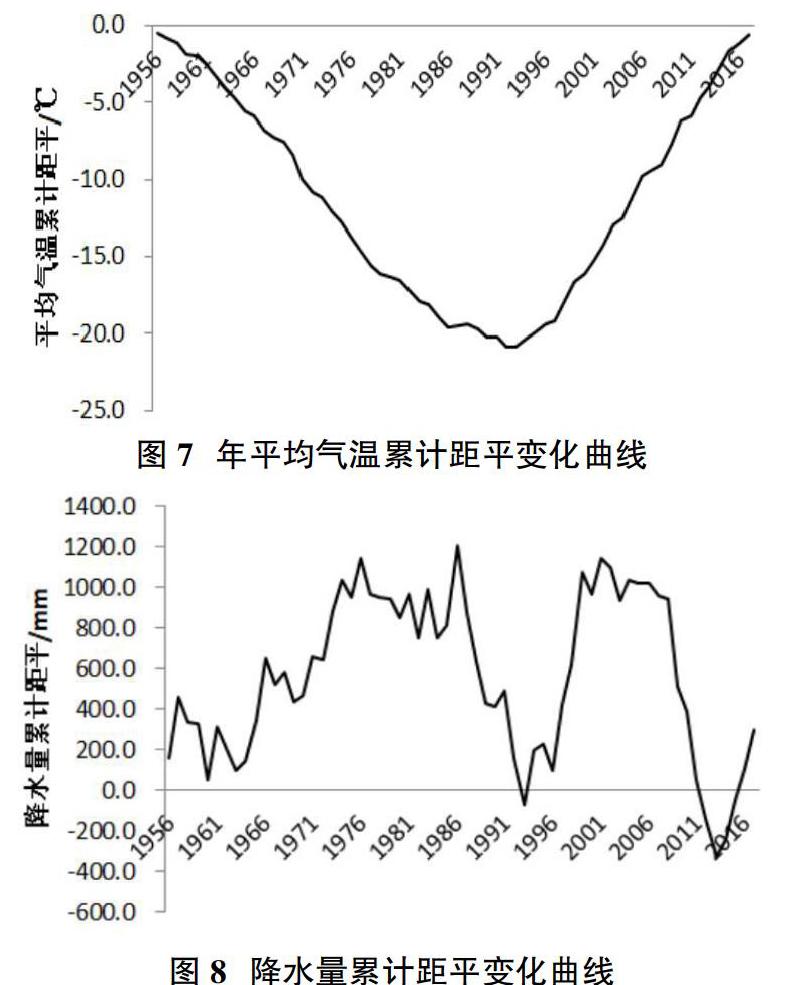
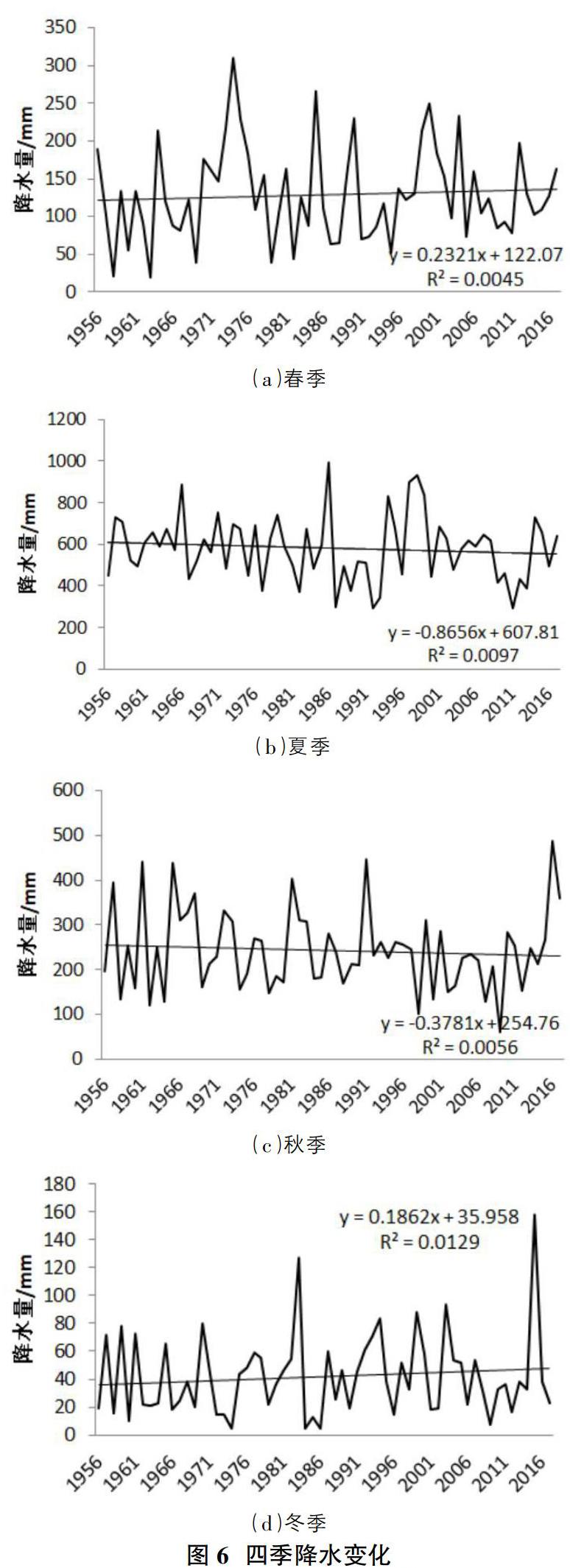
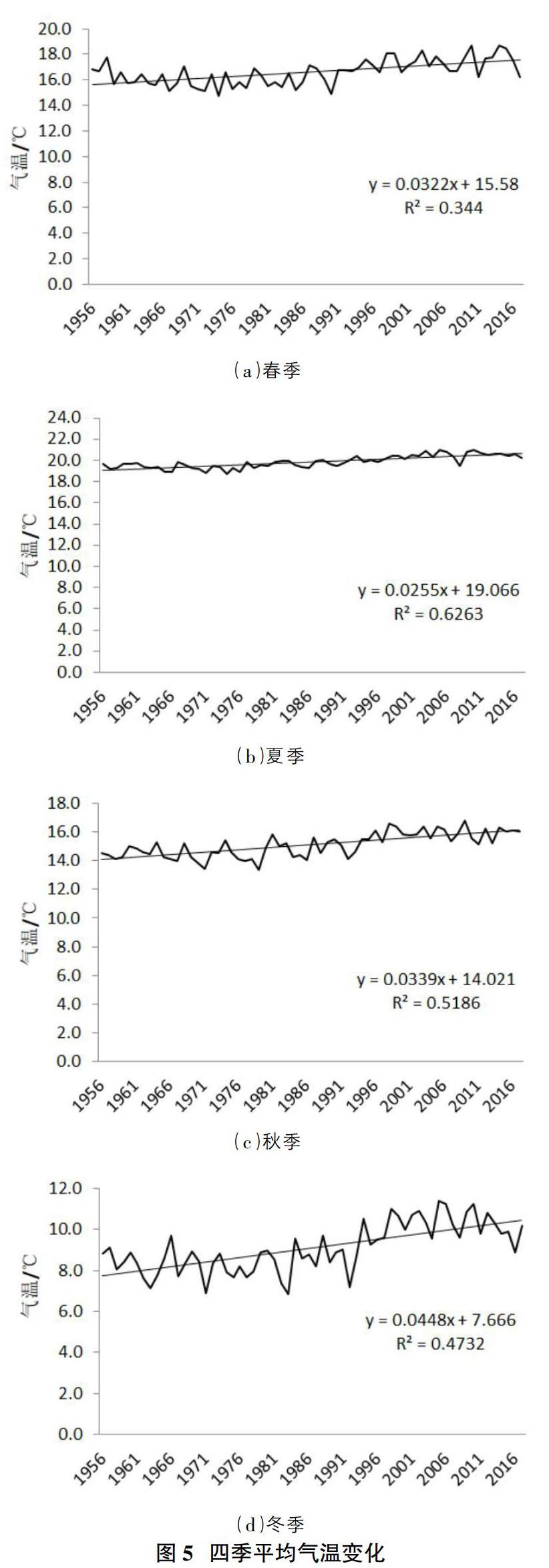
摘要:利用云南國家9個氣象站觀測1956-2017年的氣溫和降水資料,采用線性回歸分析,趨勢線分析、累積距平統計量與信噪比檢驗方法,對62年來的氣溫和降水變化進行特性分析。結果表明:云南省年平均氣溫呈現逐年增加的趨勢,降水量都出現逐年減小的趨勢,不考慮量綱差異,其降低速率具有反向相關性,大致年平均氣溫每升高1℃,年降水量減少24.2mm。四季氣溫均呈現穩步上升趨勢,其中夏季氣溫升高最為顯著,四季降水量變化表現為春、冬兩季降水量有所增加,夏、秋兩季降水量有所減小。
Abstract: The temperature and precipitation data from 1956 to 2017 were observed at 9 national weather stations in Yunnan province, and the characteristics of temperature and precipitation changes over 62 years were analyzed by using linear regression analysis, trend line analysis, cumulative anomaly statistics and signal-to-noise ratio test methods. The results show that the annual average temperature in Yunnan province shows a trend of increasing year by year, and the precipitation shows a trend of decreasing year by year. Regardless of dimensional differences, the decreasing rate is inversely correlated, and the approximate annual average temperature decreases by 24.2mm for every 1℃ increase. The temperature in all four seasons showed a steady trend of rise, among which the temperature in summer was the most significant. The change of precipitation in the four seasons showed that the precipitation in spring and winter increased, while the precipitation in summer and autumn decreased.
關鍵詞:氣溫;降水;季節變化;年際變化
Key words: temperature;precipitation;seasonal changes;interannual variability
中圖分類號:P333 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文章編號:1006-4311(2020)25-0241-04
1 ?研究背景
云南省地處中國南部,屬青藏高原南延部分,平均海拔2000米左右。地形上常常以元江谷地和云嶺山脈中的寬谷為界,將其劃分成東、西兩大地形區。東部稱為滇東、滇中高原,地形波狀起伏,表現為起伏和緩的低山和渾圓丘陵,巖溶廣泛發育。西部為橫斷山脈縱谷區,高山深谷相間,相對高差較大,地勢險峻。云南地處低緯高原,地形地貌復雜,氣候類型多變,雨量較為充沛,但是每年都會出現不同程度的干旱,這種濕潤地區的臨時干旱特點對農業及工業有很大的影響[1-4]。同時隨著全球氣候變暖及極端天氣的增多,探究云南省的氣溫和降水量是否有與全球氣候變暖趨勢一致這一問題,對社會生產和經濟建設都有著及其重要的意義。
本文以來自空間離散分布的氣象臺站的氣候數據資料,研究了云南地區氣候條件隨時間發生的變化。……

