機(jī)器人小車焊接構(gòu)架變形預(yù)測(cè)和分析
張金玉 門志輝 劉靖楠 李婭娜


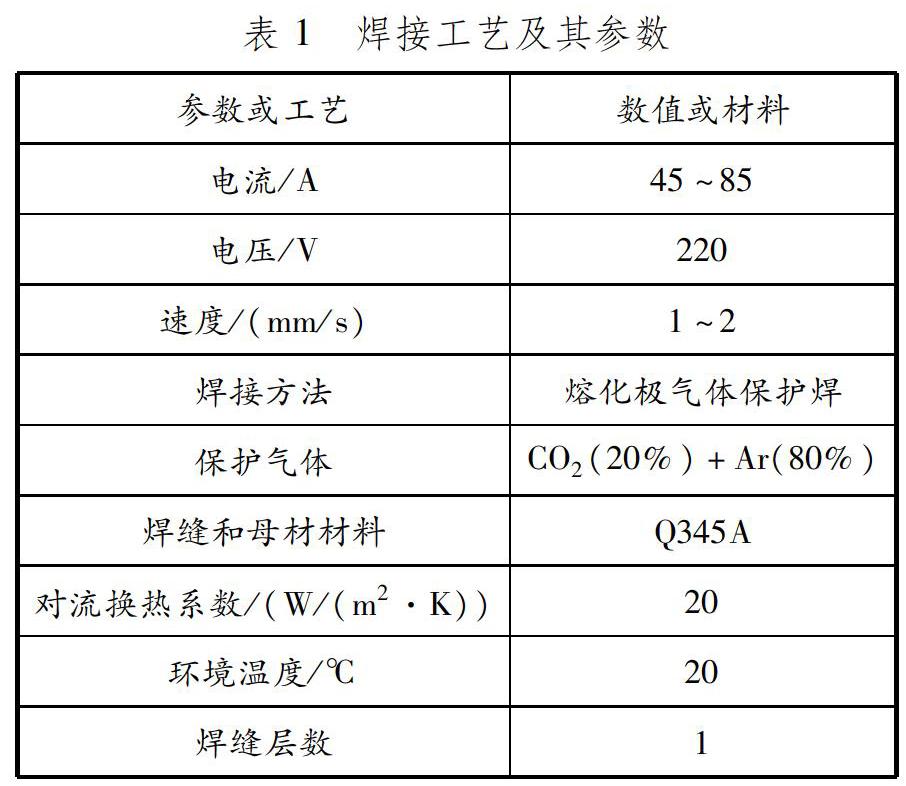
摘要: 為探究焊接變形對(duì)機(jī)器人小車碰撞性能和使用壽命的影響,基于熱彈塑性固有應(yīng)變法,利用仿真軟件VIRFAC對(duì)機(jī)器人小車焊接構(gòu)架變形進(jìn)行數(shù)值模擬。通過(guò)熱源校核,模擬4種典型接頭的熱源分布,建立固有應(yīng)變數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù),分析具有282條焊縫的機(jī)器人小車整體變形規(guī)律。結(jié)果表明:機(jī)器人小車焊接構(gòu)架的最大變形為2.962 mm,位于頂層邊框位置。研究結(jié)果為機(jī)器人小車的焊接設(shè)計(jì)、強(qiáng)度和穩(wěn)定性分析提供支持。
關(guān)鍵詞: 焊接; 構(gòu)架; 熱彈塑性; 固有應(yīng)變; 熱源校核; 變形
中圖分類號(hào): TG404; TB115.1 ? 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼: B
Abstract: To study the influence of welding deformation on the collision performance and the service life of the robot vehicle, based on the thermo-elasto-plasticity inherent strain method, the deformation of the robot vehicle welding frame is simulated in software VIRFAC. By checking with heat source, the heat source distributions of four typical joints are simulated, the inherent strain database is established, and the overall deformation rule of the robot vehicle with 282 welding seams is analyzed. The results show that the maximum deformation of the welding frame of the robot vehicle is 2.962 mm, which is located at the top of the frame. The research results can support the welding design, strength and stability analysis of the robot vehicle.
Key words: welding; frame; thermo-elasto-plasticity; inherent strain; heat source checking; deformation
0 引 言
焊接變形涉及傳熱學(xué)、電磁學(xué)、材料冶金學(xué)、固體力學(xué)和流體力學(xué)等,是多學(xué)科融合的復(fù)雜現(xiàn)象。[1]作為機(jī)械加工常用的連接方式之一,焊接在機(jī)器人小車構(gòu)架的生產(chǎn)和制造中有重要的作用。焊接加工時(shí)往往出現(xiàn)殘余變形,殘余變形的大小直接影響機(jī)器人小車焊接構(gòu)架的性能和使用壽命。焊接構(gòu)架是機(jī)器人小車的關(guān)鍵承載部件之一,其安全性和可靠性至關(guān)重要。在機(jī)器人小車焊接構(gòu)架的設(shè)計(jì)階段,合理完善的焊接變形預(yù)測(cè)和分析需要可靠、適用的焊接變形數(shù)據(jù)支撐。
近年來(lái),計(jì)算機(jī)技術(shù)快速發(fā)展,對(duì)焊接變形的數(shù)值仿真計(jì)算有很大地促進(jìn)作用,數(shù)值模擬成為結(jié)構(gòu)焊接殘余應(yīng)力和焊接變形預(yù)測(cè)的有效方法之一。常用的數(shù)值模擬方法有熱彈塑性有限元法和固有應(yīng)變法。張立平等[2]利用熱彈塑性有限元法分析厚……

