The relationship between academic adjustment and emotional intelligence among undergraduate students in Oman
Mohammad Qutishat, Aisha Al Shdefat
1Community and Mental Health Department, College of Nursing, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman; 2Maternal and Child Health Nursing, College of Nursing, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman.
Abstract Objective:A positive and successful transition into university is crucial.Transition to the college environment is a critical situation that can impact students holistically.The study aimed to examine the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic adjustment among undergraduate students in Oman.Methods: The study utilized a descriptive correlational and cross-sectional study design.The total sample was 339 based on defined inclusion criteria.The study used Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire and Academic Adjustment Scale to investigate the extents of the research phenomena among undergraduate students.Results: The average age of the participants was 21.5 years.The level of AD and EI was on medium.However, the findings revealed a strong positive relationship (r = 0.703) between emotional intelligence and academic adjustment among undergraduate students. Conclusion: Emotional intelligence may increase over time through the academic life.It can help students develop adequate social skills and bondings to satisfy academic demands and promote their social, moral, and cognitive abilities and adjustment.
Keywords: Emotional intelligence, Academic adjustment, Undergraduate students
Introduction
Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the individual's strength to sharply and steadily perceive, understand, direct, and react to feelings that can override thoughts, promote relationships, and influence behavior [1,2].EI acts as a background for understanding the association between cognition and emotions [3].People with high emotional intelligence can develop more successful social relationships that promote belongingness and well-being [4].
A positive and successful transition into university is crucial, as the students move to the college environment, they might find themselves under different challenges such as the psychological, academic, socio-cultural, and living demands [5], these challenges are the results of their schooling experiences.The personal attitudes they bring to the university [6].The result is that the changes in their emotional detachment and social role can cause further distress, anxiety, and depression [7], which can be varied among different students’ experiences and self- expected outcome [8].
Adjustment is an ongoing process in which the person changes his/her behavior to reach the harmonies in him/her self and environment [9].It is the process that the man maintains a balance between his demands and the circumstances that are required to satisfy these demands [10].Students’ adjustment refers to their unique ability and efforts to fulfill their academic and social needs [11,12], and to reconstruct their relations and social connections to the new academic life [13,14].
Being abroad from family and friends may affect students’ well-being and their academic achievements [15], it can promote the desire to achieve a sense of balance in their new educational environment leading them to work diligently to adjust to their academic lives, and college requirements [16].To our knowledge, few studies have been conducted, especially among college students concerning the relationship between EI and AD.Given the above, this study aimed to explore the relationships between EI and AD among undergraduate students.
Methods
Research Design
The authors keen to obtain ethical approval from the Research Ethics Committee of the College of Nursing at Sultan Qaboos University to conduct the study.The researchers used descriptive correlational analysis and cross-sectional study design to achieve the research purpose among SQU undergraduate students.The sample was detected by using the power analysis (with the following parameters confidence Level 95%, margin of error 5%, population proportion 50%, population size approximately 12000 students) to detect a total sample of 400 students; the sample consists of those students who met the eligibility criteria of being enrolled in the undergraduate program, completed their foundation programs.The study utilized a convenience sample; There were 339 participants after data cleaning.After obtaining approval from the Institutional Research Ethics Committee and Deans of Colleges, the investigator approached students to obtain written informed consent.The study design, purpose, methods, and potential benefits were appropriately explained, assuring their voluntary and confidential participation.The questionnaires were distributed over one month during the fall semester of 2019 by the research team at the Sultan Qaboos University during a designated time after lectures.Each student required approximately 15-20 min to complete the questionnaires.
Study instruments
A Self-assessment instrument was utilized as a tool measurement to investigate the extents of the research phenomena, and it consists of six sections:(1) demographical data (2) academic profile (3) Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire, and (4) Academic Adjustment Scale.
Brief emotional intelligence scale
A brief emotional intelligence scale is a revised version of Emotional intelligence scale created by [17], it consists of 10 items using a 5-point Likert scale anchored by one = “strongly disagree” to 5 = “strongly agree.” The score ranged between 10 to 50, whereas the lower score indicates lower emotional intelligence, the scale has good content validity and test-retest reliability [17].
Academic adjustment scale
The scale was created to a focus on local and sojourners students who are temporarily relocated to a new learning environment.It consists of three subscales:academic life-style, academic achievement, and academic motivation.The participants are requested to rate their responses on nine items using a 5-point Likert scale ranged from 1 = “Rarely applies to me” to 5 = “Always applies to me.” The score ranged from 9 to 45, whereas the lower score indicates lower academic adjustment; the scale has good content validity and test-retest reliability [18].
Statistical analysis
The authors used the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software at a 0.05 level of significance to analyze the data.
Results
The authors analyzed the responses of 339 participants who agreed to participate in the study and fit the inclusion criteria.Of those participates, 50.1% (n= 170) were female and 49.9% (n= 169) were male.As the survey was distributed primarily in the college classroom, respondents were asked to indicate their academic year.A majority (33.9%,n= 115) were in their fifth academic year, with many respondents falling in the 22-25 (59.7%,n= 172) age range.The majority of the students’ GPA ranged from B and C grades 48.1% (163) and 33% (112).
The reliability of both questionnaires was assessed and showed a Cronbach’s α of 0.930 and 0.877.The mean score of EI among college students was 32.05.Moreover, the mean score of AD was 27.6.Our results show no statistical differences between study variables such as age, marital status, living arrangement, the academic year with both EI and AD.However, the results also highlight significant gender differences in EI among study participants (p= 0.040).Also, it shows a significant correlation between EI, AD, and students’ GPA (Table 1).To understand further whether the students’ AD (the dependent variable) could be predicted by their EI experiences (the independent variable), a linear regression was calculated; however, a significant correlation was found [F (8.290) = 18.167,p= 0.000], with an R2of .495 (Table 2).
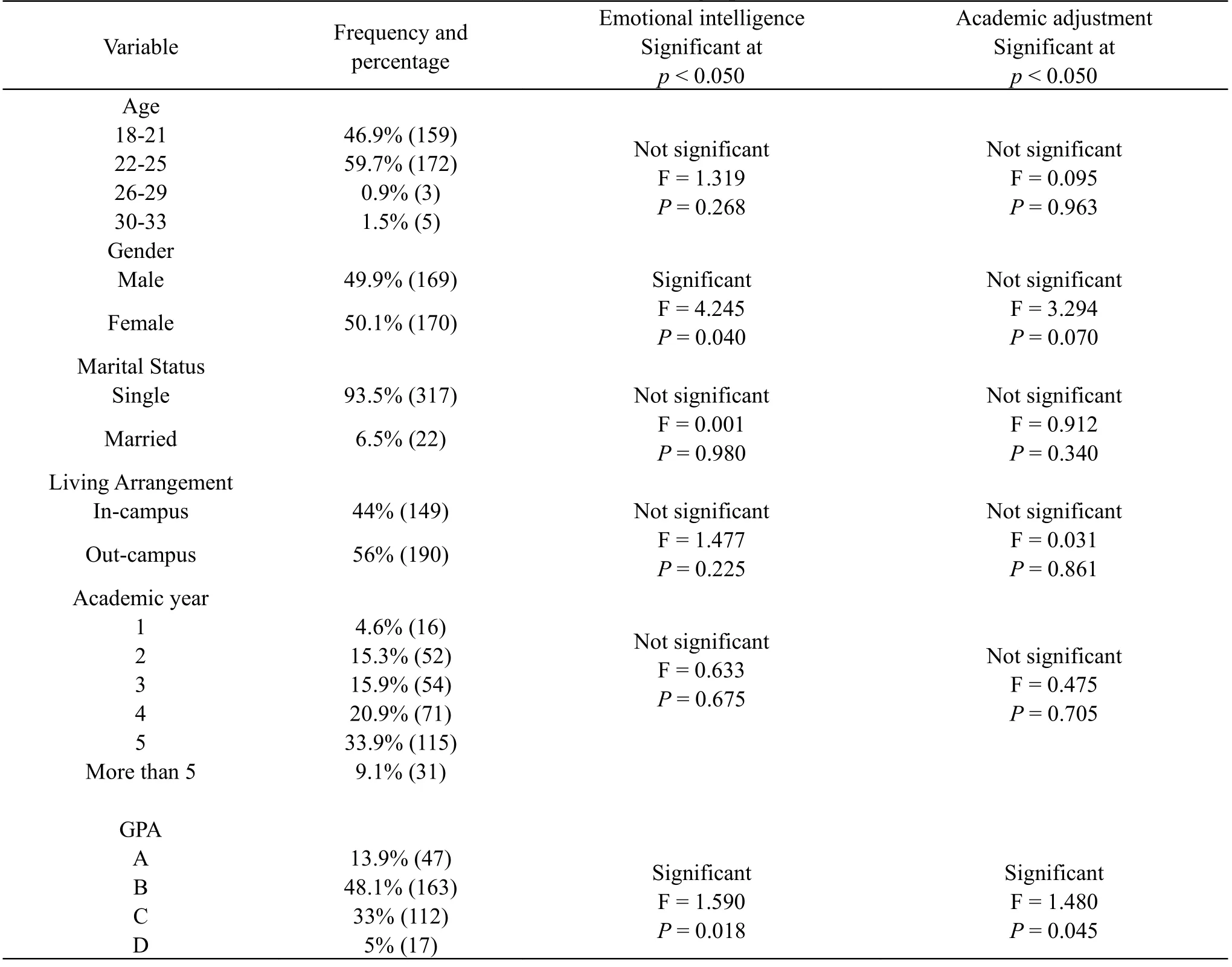
Table 1:Distribution of EI, and AD based on students’ demographical characteristics
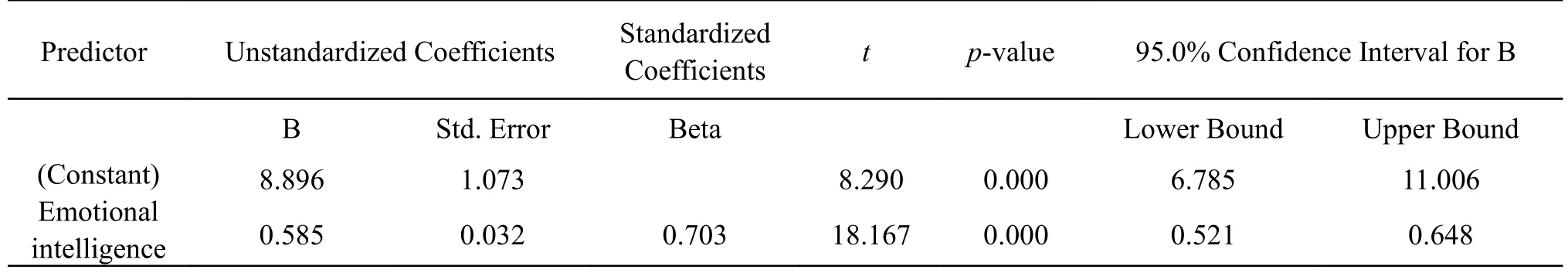
Table 2:Result of the linear regression analysis.
Discussion
The authors in the current study find a significant difference in EI across participants’ genders (p= 0.040); also, it is showing a significant correlation between EI, AD, and students’ GPA.Indeed.Females possess higher emotional intelligence compared to males, the mean females’ emotional intelligence score was 33.07, while males scored 31.02, which indeed, is congruent with other reports [19,20].Our results also highlight that students with a high GPA demonstrate high EI and AD scores, which is supported previously in many studies [21].The existing evidence from previous studies indicated that the development of emotional skills could enhance the academic performance of undergraduates [22]
To our knowledge, few studies have been conducted, especially among college students concerning the relationship between EI and AD, the majority of them possess to examine the relationship between EI and academic success or academic performance [9,22].However.Our result finds that EI is strongly and significantly correlated to AD; Regression analyses indicate that higher levels of EI predicting a higher level of AD.
Literature concerning emotional perception among undergraduate students reported that emotional intelligence might increase over time through academic life [23].Students with high EI can develop a broad range of social skills and impulsivity control that are incredibly essential for social bonding [24].It can satisfy students’ academic needs, distinguish their abilities, improve their decisions making skills, and configure their moral and personal values [25], it also can enhance the quality of their social interactions, social behavior, social adjustment, and academic achievement [26].
An explanation of our findings can refer to the students’ desire to be continuously connected to their supported system through the social media platforms, in which they can post their updates consistently and observe others openly [27].Social media use is related to an increase in an individual’s cognitive and affective empathy over time.It promotes a student’s ability to understand their feeling and share it with peers [28].Several studies indicated that college students spend more time on their smartphones due to positive social rewards and feedback that they can gain toward their academic achievement, interests, and social life [26].Students use social media to update themselves with current educational affairs, express academic problems, share a similar academic issue, and to express academic challenges to school counselor [29].
For example, Facebook has a positive impact on students' language, intellectual, and moral behavior.It can positively help them to improve their knowledge, creativity, and technical skills [30].Social media use indicators such as the amount, the frequency, or the intensity of overall use are significantly associated with psychosocial outcomes and well-being [31].Although Off-campus connections through social media platforms with family members and childhood friends may facilitate the transition to college shortly to the university admission, on-campus social relationships are also found to be much valued for successful college adjustment and good college life [31].
The study shows some limitations; first, the examined relationship has been investigated through the only quantitative research methodology.Therefore, expanded information and explanation can be gathered by applying a mixed-method research methodology.Second, collecting data was only from one Omani national university, which may limit our generalization; therefore, future studies should investigate more students in different universities across all Oman governorates.Third, some critical demographic variables such as parental education, parental income, nature of family, cultural values, students personality were ignored in this study which may play a significant role in predicting the examined relationship; Future studies should address these variables to explore the relationship between EI and AD effectively.
Conclusion
The researchers found no statistical differences between study variables such as age, marital status, living arrangement, and academic year with EI and AD.However, the results also highlight significant gender differences in EI among study participants.Also, it is showing a significant correlation between EI, AD, and students’ GPA.The main findings reveal that there is a strong positive relationship between emotional intelligence and academic adjustment among undergraduate students.
Students with high EI can develop a variety of social skills and social bonding through social media platforms due to positive social rewards and feedback that they can gain toward their academic achievement, interests, and social life.Social media can link students’ EI and AD.Both social connections in and out-campus are required to satisfy their needs, distinguish their abilities, improve their decision skills, and configure their moral and personal values.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Real experience among undergraduate nursing students in learning the course of geriatric nursing:a qualitative study
- Validity and reliability of the complementary and integrative health assessment for practitioners scale:CIHAPTR
- An investigation on hand hygiene cognition status and influencing factors of nursing workers in a third-grade a hospital during COVID-19 epidemic
- Analysis on the status quo and influencing factors of fear of disease progress in 120 patients’spouse after bladder cancer surgery

