High tumor mutation burden indicates a poor prognosis in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
INTRODUCTION
TMB was an independent risk predictor for ICC. Furthermore, independent prognostic factors of ICC included CA19-9, chronic viral hepatitis, tumor resection and disease progression (metastatic diseasesolitary liver tumor). The clinical characteristics and TMB data of some cases had missing. which increased the analysis error in our study.Using a single data source also increases statistical error. Further larger–cohort studies are necessary to confirm the predictive value of TMB in the prognosis of ICC patients.
Gastroenterology and hepatology
Therefore, in this study, we used the ICC database from the Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center to investigate the impact of TMB on the prognosis of ICC patients in combination with other clinical features, confirming that TMB was an independent prognostic factor for ICC patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data collection and processing
Data of 412 ICC patients from the MSK Cancer Center cohort (MSK cohort:http://www.cbioportal.org/study/summary?id=ihch_msk_2021) were included[18].TMB was calculated as the total number of somatic, non-silent, protein-coding mutations divided by the coding region captured in each MSK-IMPACT panel (341 genes, 0.98 Mb; 410 genes, 1.06 Mb; 468 genes, 1.22 Mb). Ethics approval and patient consent were waived by the MSKCC Institutional Review Board and the need for informed consent has been waived by the MSKCC IRB per 45 CFR 46.116 and 45 CFR 164.512, since our data were retrieved from a public database. Clinicopathological information, including age, gender, BMI, TMB, CA19-9, chronic viral hepatitis, tumor resection, tumor grade, disease progression and smoking status, were all reviewed retrospectively.
Cox regression analysis and survival analysis
Cox regression analysis was performed to examine the correlation between TMB and patient’s overall survival (OS). According to the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, patients were divided into either the high (TMB > 3.1 mut/Mb) or low TMB (TMB ≤ 3.1 mut/Mb) group. Kaplan-Meier method was used to construct the survival curves of patients. The time dependent specificity and sensitivity of survival were analyzed by deploying timeROC and survival in the R package. The log-rank test was used to examine the differences between the curves,and avalue < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The nomogram model and calibration curve were also analyzed using the rms package in R.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS version 25.0 (IBM Corp.) software.The Kaplan-Meier curve was analyzed using the survival package in R version 3.6.3,and the time dependent ROC curve was analyzed using the timeROC package,wherein the picture was generated by the ggplot2 package in R version 3.6.3. All reportedvalues were two-tailed, and≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analyses in this study.
RESULTS
Overview of the MSK-IMPACT cohort
In this study, the MSK-IMPACT cohort included a total of 412 ICC patients who were mainly compared using TMB as an independent prognostic factor. Most patients in this cohort were examined using the 341- (IMPACT341) and 410-gene (IMPACT410)panels. In comparison to the latest 468-gene panel (IMPACT468), the unsequenced genes in the earlier versions were assumed to be wild-type or non-mutated. Clinical data in this study included age (< 65, ≥ 65), gender (male, female), BMI (< 28, ≥ 28),TMB (≤ 3.1, > 3.1), CA19-9 (< 40 U/mL, ≥ 40 U/mL), chronic viral diseases (negative,positive), tumor resection (resected, unresected), tumor grade (well differentiated,moderately differentiated, poorly differentiated), disease progression (solitary liver tumor, multifocal liver disease, metastatic disease), and smoking status (never smoked, former smoker, current smoker). Baseline clinicopathological features of the study cohort are summarized in Table 1 (median age: 63 years, range: 18-88; 46.1% of patients were females; median: TMB 2.5 mut/MB, range: 0-51.6).
Prognostic impact of TMB in ICC patients
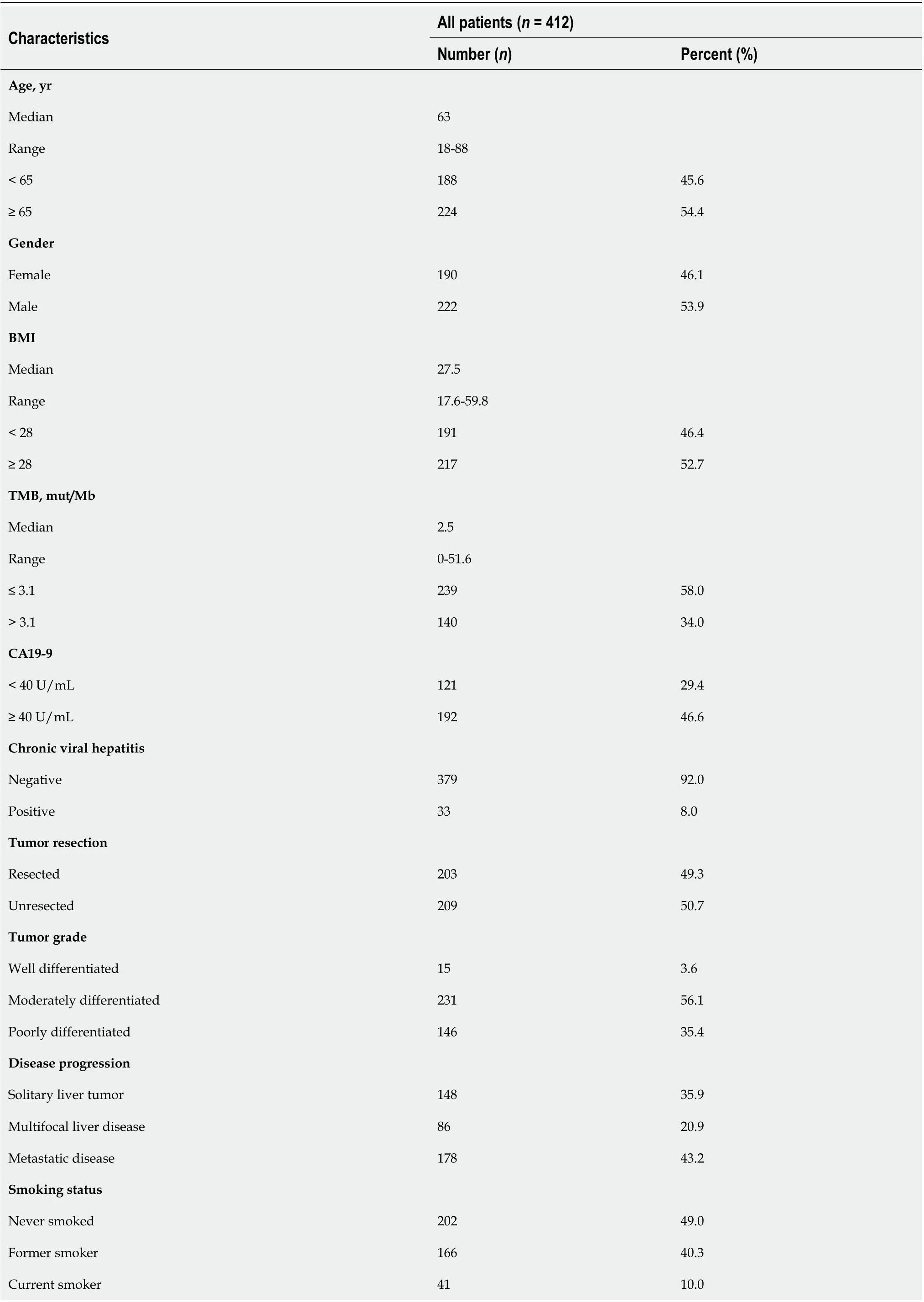
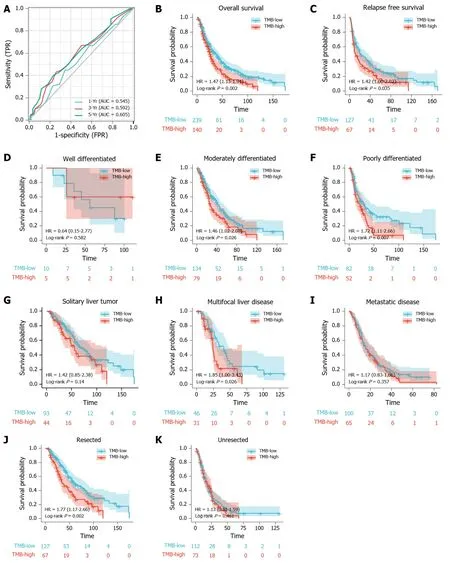
First, we analyzed the utility of TMB in prognosis, calculating a median TMB of 2.5 mut/Mb (range: 0-51.6 mut/Mb). To analyzed the predictive performance of TMB relating to OS, we generated a time-dependent ROC curve which showed the area under the curve (AUC) for TMB involving 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival was 0.545, 0.592,and 0.605, respectively (Figure 1A). Afterwards, we used the 1-, 3-, and 5-year ROC curve analysis with the corresponding maximum Youden index to calculate the TMB threshold values. As a result, when the TMB cut-off value was 3.1, the maximal AUC value was achieved (1-year sensitivity: 0.448, specificity: 0.656; 3-year sensitivity: 0.430,specificity: 0.742; 5-year sensitivity: 0.402, specificity: 0.767). Therefore, we defined 3.1 mut/Mb as the cut-off value. Patients with a TMB > 3.1 mut/Mb were clarified as the high group (= 140), and patients with a TMB ≤ 3.1 mut/Mb were clarified as the low group (= 239).
Following TMB classification, the Kaplan-Meier plotter of survival analysis showed that high TMB patients had a poor OS (HR = 1.47,= 0.002; Figure 1B) and RFS (HR =1.42,= 0.035; Figure 1C), as compared to low TMB patients. We then performed subgroup analysis of prognosis to assess the impact of TMB in different clinical subsets(Table 2). For tumor grade, high TMB patients had poor OS in moderately differentiated (HR = 1.46,= 0.026; Figure 1E) and poorly differentiated subsets (HR = 1.72,= 0.007; Figure 1F). In contrast, no definite results can be obtained in well differentiated subsets due to the small sample size (HR = 0.64,= 0.582; Figure 1D).
For disease progression, high TMB indicated poor OS in patients with multifocal liver disease (HR = 1.85,= 0.026; Figure 1H). However, no significant differences in survival between the high TMB and low TMB groups were found in patients with solitary liver tumor (HR = 1.42,= 0.140; Figure 1G) and metastatic disease (HR =1.17,= 0.357; Figure 1I).
For tumor resection, high TMB indicated a shorter OS in patients who underwent tumor resection (HR = 1.77,= 0.002; Figure 1J). Conversely, no differences in prognosis were observed between the high TMB and low TMB groups in patients without tumor resection (HR = 1.13,= 0.461; Figure 1K).
Construction of multivariate survival model
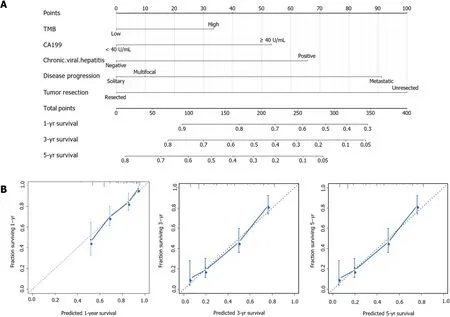
Finally, we would like to screen the independent prognostic factors and establish a prognostic model of ICC patients. Multivariate Cox regression analysis to was used to analyze the associations between OS and specific factors, including age, sex, and TMB.As a result, TMB was identified as an independent risk predictor for ICC patients [HR= 1.43 (1.05-1.96),= 0.0240]. Additionally, independent prognostic factors of ICC included CA19-9 [HR = 1.78 (1.28-2.46),= 0.0005], chronic viral hepatitis [HR = 1.72(1.01-2.95),= 0.0468], tumor resection [HR = 2.58 (1.72-3.88),< 0.0001], and disease progression [metastatic diseasesolitary liver tumor HR = 2.55 (1.55-4.20),= 0.0002](Table 3). Following this, we constructed a predictive nomogram based on the Cox regression coefficients of selected variables, and the predictive accuracy of every nomogram was evaluated using calibration plots (Figure 2A). The total score for ICC patients can be calculated to predict the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates, which would help clinicians assess the risk level of ICC patients in clinical practice. Notably, the calibration curve indicated that the observed and predicted values were consistent in predicting OS (Figure 2B).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we investigated the role of TMB in predicting survival among patients with ICC. First, the clinical and mutation data of the 412 ICC patients were obtained from the MSK public database. Next, the best cut-off TMB value was determined using time-dependent ROC curve. Combined with other clinical features, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to establish a risk model for prognosis prediction, showing that elevated TMB was associated with poor OS and RFS. In addition to TMB, CA19-9, chronic viral hepatitis, tumor resection, and disease progression (metastatic diseasesolitary liver tumor) were also found to be independent predictors of OS in ICC patients. Based on these risk factors, a reliablenomogram model was then constructed, demonstrating a satisfactory performance in predicting OS in ICC patients. Therefore, this study provided an effective indicator for the clinical prognostic evaluation of ICC patients, as well as contributed to the screening of high-risk ICC patients and the provision of individualized treatment.
Recently, TMB has become a novel predictive biomarker with the potential to predict the therapeutic effect of ICIs and screen suitable patients for immunotherapy[19]. At present, the research on TMB has mainly focused on its ability to predict the efficacy of ICIs, with numerous studies showing its association with the survival rate of cancer patients. In particular, Xie[20] found that papillary thyroid carcinoma patients with high TMB reported a worse prognosis. A study by Zhang[21] also indicated that low TMB resulted in a better prognosis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Similarly, a study of 318 ICC patients showed that high TMB indicated a worse prognosis [HR = 1.500 (1.085-2.073)][22]. In the present study,the data of 412 ICC patients published by the MSK Cancer Center in March 2021 were used to determine the utility of TMB in prognosis prediction. Notably, the original researchers investigated the relationship between the mutation gene, clinical characteristics, and the prognosis of ICC patients; however, they did not explore the role of TMB in prognosis. Analyzing the aforementioned data, we found that ICC patients with high TMB had a poor OS and RFS, which was consistent with the findings of previous studies.
Clinically, CEA and CA19-9 levels are commonly used prognostic indicators in ICC[23,24]. However, their prognostic thresholds vary widely across different reports,with a lack of a large meta-analysis to consolidate these values[25]. Moreover, some studies have reported on other prognostic indicators associated with poor prognosis in ICC patients, including elevated C-reactive protein, circulating osteopontin, as well as KRAS and TP53 mutations in tumor tissues[26-29]. With the wide application of immunotherapy, TMB has also become a common clinical index. In order to detect TMB, common mutations in ICC patients were detected, which reflected the overall mutation of tumor tissue. Therefore, TMB is a convenient and crucial prognostic value in clinical practice.
Medical nomograms use biologic and clinical variables, including tumor grade and patient age, to graphically depict a statistical prognostic model that generates a probability of a clinical event for a given individual, such as cancer recurrence or death. Furthermore, nomograms are user-friendly, can incorporate continuous variables and relevant disease determinants into prognosis, and are superior to clinician judgment in estimating disease course[30,31]. In this study, we constructed apredictive nomogram according to the Cox regression coefficients of selected variables to help clinicians evaluate the prognostic risk of ICC patients, calculate their survival rate, and make correct clinical decisions. Particularly, TMB and CA19-9 were combined to construct a nomogram model to predict the prognosis of ICC patients,which was helpful for its clinical application. To ensure the accuracy of this nomogram model, we used a calibration plot, as it allowed us to determine how close the nomogram estimated risk was to the observed risk.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, we explored the prognostic role of TMB in ICC patients. Multivariate analysis indicated that TMB and CA19-9 were among the identified independent prognostic factors in ICC. Although our study confirmed the prognostic value of TMB,our study had several limitations. First, the clinical characteristics and TMB data of the cases analyzed in this study were all extracted from the MSK Cancer Center, of which some cases had missing data. As a result, this increased the analysis error in our study.Second, using a single data source also increases statistical error. Thus, further larger.cohort studies are necessary to confirm the predictive value of TMB in the prognosis of ICC patients. For the benefit of future studies, we will continue to collect the clinical data of ICC patients and consolidate our conclusions by expanding the present study’s sample size.
Grade C (Good): 0
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is malignancies of the biliary duct system and constitutes approximately 10%-20% of all primary liver cancers. Tumor mutation burden (TMB) is a useful biomarker across many cancer types for the identification of patients who will benefit from immunotherapy. This study collected the ICC database from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center to investigate the impact of TMB on the prognosis of ICC patients.
The prognosis of ICC patients is very poor. Previous studies suggest that TMB can used to be a prognostic factor in many types of cancer. It is critical to analyze the prognostic value of TMB in ICC to help individual clinical treatment.
“打。”夏國忠見部隊的行動已經日軍被發現了,立即向戰士們發出了戰斗的命令。隨著他的命令聲,“呯”的一聲槍響,跟在夏國忠身邊的神槍手瞄準那盞探照燈開了槍,隨著槍聲響起,燈光一下滅了,眼前頓時漆黑一片。
This study aims to investigate the prognostic value of TMB in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma ICC. In particular, we sought to confirm that TMB is an independent prognostic factor of ICC and construct a nomogram model to predict the prognosis of ICC patients, which was helpful for its clinical application.
This study is a retrospective cohort study of ICC patients. This is a study of large sample to investigate the prognostic value of TMB and other clinical characters in ICC.
2.3.3 解吸時間 從圖4可見,AB-8大孔樹脂吸附花青素后,在pH 1.0的70%乙醇溶液中解吸,解吸率隨時間延長呈上升趨勢。解吸2 h后,解吸率為74.3%。其后,隨時間延長,解吸率升高幅度較小,解吸12 h后,解吸率僅為79%。因此,考慮時間成本及花青素的穩定性,解吸時間以2 h為宜。
實踐教學是培養學生創新精神、創新能力和實踐能力的重要環節,在創新創業人才培養中占有重要的地位。傳統的實踐教學強調專項技能或單學科訓練,學生往往被動參與實踐訓練,很大程度上限制了自身創新思維的訓練和實踐能力的提高。有些高校在實踐教學改革方面下了很大功夫,但由于實踐條件尚不夠完善,實踐平臺數量少,實踐教學與工程實踐聯系較少,學生缺少實際訓練和創新實踐的機會,實踐教學效果不佳。實踐環節涉及大量實驗操作和數據處理,部分學生缺乏科學嚴謹、細致認真的態度,不能按照國家標準和行業規范操作,不重視實驗結果的準確可靠性,影響了工匠精神的養成。
Cholangiocarcinomas are malignancies of the biliary duct system, classified as being either intrahepatic or extrahepatic in origin. Particularly, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) constitutes approximately 10%-20% of all primary liver cancers[1].Despite its increasing incidence rate worldwide, the etiology of ICC remains unclear[2]. Moreover, although surgery is the only potentially curative treatment for ICC,more than two-thirds of patients have been found to be unsuitable for surgery at the time of diagnosis, and more than 60% of patients who underwent surgery reported relapse of disease[3]. A previous study also showed that the 5-year survival rate and median survival time of patients with ICC (hereinafter, ICC patients) who underwent curative resection was approximately 30% and 28 mo, respectively[4]. Besides surgical resection, the standard treatment for ICC includes gemcitabine-based chemotherapy,liver transplantation, and local treatment, such as transarterial chemoembolization[5].Of the several prognostic factors of ICC, radical resection (R0), number of tumors(single or multiple), vascular invasion, and lymph node metastasis have all been recognized as the most important independent prognostic predictors for ICC patients[6].
These findings suggest that TMB was an independent prognostic biomarker in patients with ICC. Moreover, patients with ICC with high TMB had poor overall survival and relapse free survival as compared to those with low TMB.
從企業內部情況來看,大部分文獻[11-12]都指出國有糧食企業依然背負沉重的歷史包袱,政企尚未真正分開,內部組織結構、經營方式、管理模式落后[13];內部控制制度不健全、監管失控[14];產權制度落后,不適應市場環境[15-17]。童應[18]指出了國有糧企職工主觀的問題,職工固步自封的消極情緒、難有作為的畏難情緒、安于現狀的自滿情緒導致國有糧食企業管理難度大。
We will continue to collect the clinical data of ICC patients and consolidate our conclusions by expanding the present study’s sample size.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Mycoplasma hominis meningitis after operative neurosurgery: A case report and review of literature
- Recurrence of sigmoid colon cancer–derived anal metastasis: A case report and review of literature
- New method to remove tibial intramedullary nail through original suprapatellar incision: A case report
- Metastasis to the thyroid gland from primary breast cancer presenting as diffuse goiter: A case report and review of literature
- Gastric submucosal lesion caused by an embedded fish bone: A case report
- Epibulbar osseous choristoma: Two case reports
