Management of retroperitoneal sarcoma involving the iliac artery: Single-center surgical experience
INTRODUCTION
Retroperitoneal sarcomas (RPSs) are malignant tumors originating from mesenchymal tissue and are exceedingly rare entities, among which liposarcoma is the most common type, followed by leiomyosarcoma[1]. Solitary fibroma and invasive fibroma are uncommon RPS subtypes that may arise in any location, including the retroperitoneum. Surgical excision remains the main treatment for primary tumors and is also recommended for recurrent tumors[2]. Specifically, tumors in the unique anatomic location of the retroperitoneum, which involves important blood vessels and organs,require the concerted efforts of a multidisciplinary team (MDT) during surgical treatment. Studies have shown that the success and radical resection rates were higher and the local relapse rate was lower for patients treated by professional MDTs than for those treated in nonprofessional centers[3]. High-throughput MDT centers are key to ensuring the effectiveness of medical services and the desired patient outcomes.
RPSs, especially recurrent lesions, are more likely to invade blood vessels, and resection of these major vessels is necessary for complete oncological clearance. The most frequently involved vessels for RPS are iliac vessels. Dissociation and reconstruction of iliac vessels are critical for the success of surgery. Vascular surgeons play an indispensable role in surgery in cases of aggressive tumors and in treating complications during surgery[4]. Artificial vascular reconstruction is most often performed between the common or external iliac artery and the femoral artery. The majority of artificial vessels used in the clinic are composed of polytetrafluoroethylene(PTFE), and satisfactory clinical results have been obtained[5,6]. Recanalization and monitoring of reconstructed blood vessels and anticoagulation after operation are indispensable during the postoperative recovery period[7].
隨著云計算的發展和企業集約化、一體化、集中化的發展,云工作流引擎成為企業建立私有云工作流引擎的發展必然,給企業帶來更多的經濟效益,包括硬件的成本得以降低、硬件資源的使用率大幅提升、平臺維護人員大幅減少、數據的管理和管控更加集中;同時,云工作流引擎可帶來系統的高可用、可擴展性和自動伸縮等能力。但是,云工作流引擎是分布式系統,會提高部署和管理的復雜性,從而對開發者提出更高的要求。
June 9, 2021
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical information
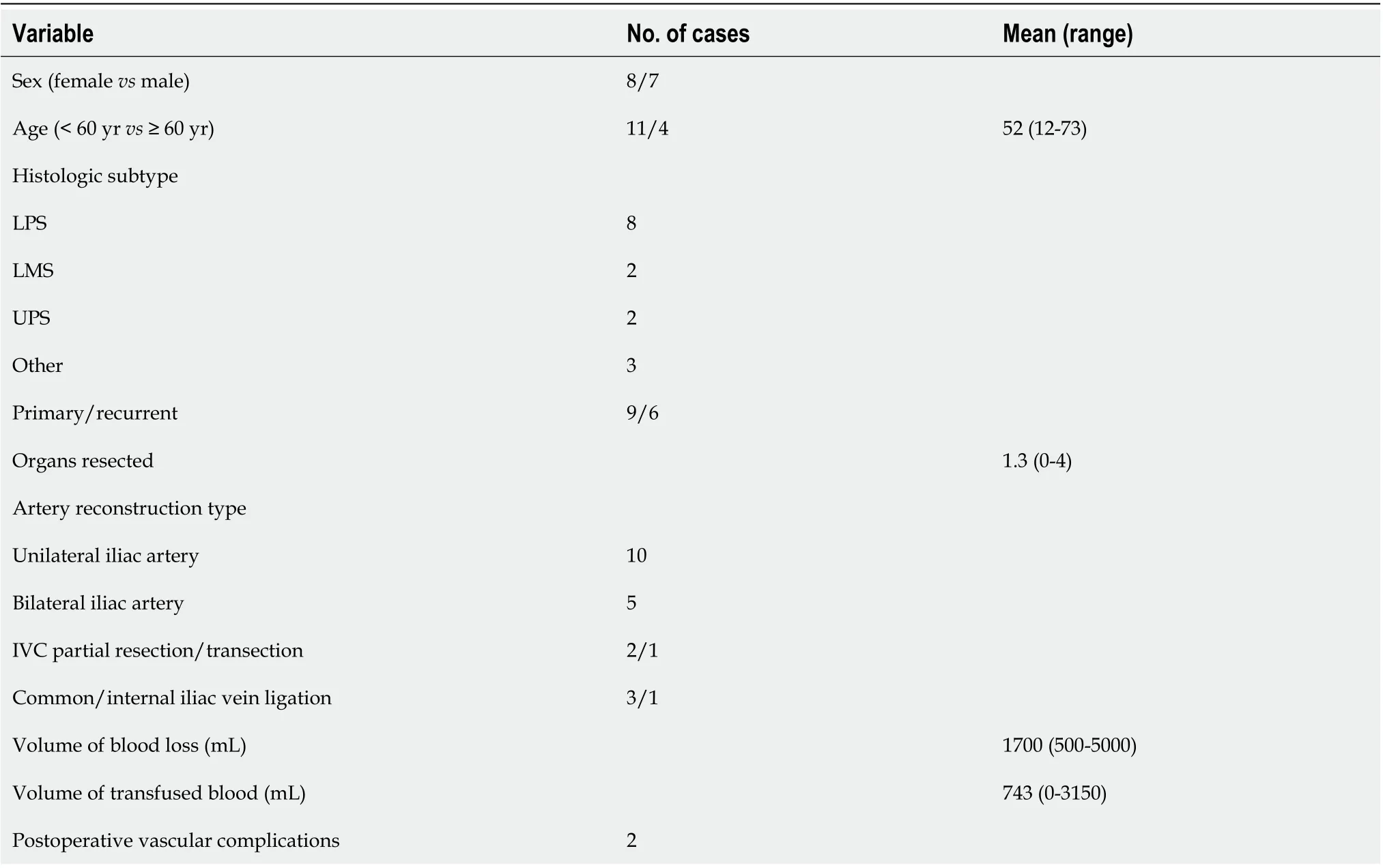
From July 2004 to June 2020, a total of 15 patients aged 12 to 73 years underwent RPS resection combined with iliac artery reconstruction. Patient data were retrospectively gathered in a retroperitoneal tumor database and analyzed. Clinical manifestations included abdominal pain (3 cases) and abdominal mass (5 cases). The other seven tumors were found during follow-up examination. Six cases were primary, and nine were recurrent (Table 1).
All patients underwent preoperative computed tomography (CT), CT angiography(CTA), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to clarify the relationship between the tumor and important vessels in the abdominal or pelvic cavity. Most patients with recurrence underwent PET examination.
檢測農藥品種為敵敵畏、氧化樂果、甲基對硫磷、乙烯菌核利、聯苯菊酯、氯氰菊酯、氰戊菊酯;檢測基質為辣椒。
Surgery and vascular reconstruction
The incisions varied according to the location, size, and extent of the tumor. A median abdominal incision was usually adopted to facilitate exposure and incision extension,which could extend from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis. A lateral incision was added when necessary. In cases in which the mass encompassed the unilateral iliac artery and vein (Figure 1A and B), one side of the inguinal ligament was cut off, and the femoral artery was dissociated with a thin catheter to control bleeding during mass exposure (Figure 1C). The femoral and common iliac veins were ligated. The common iliac artery was isolated. Heparin was injected at 0.5 mg/kg body weight before vascular occlusion. After circulatory block, the femoral and common iliac arteries were cut off approximately 1 cm from the edge of the tumor, and the tumor was removed "" together with involved blood vessels and organs. Vessel reconstruction was completed between the common iliac artery and femoral artery(Figure 1D). In some cases, the mass encompassed the abdominal aorta and bilateral iliac arteries and adhered to the inferior vena cava (IVC) (Figure 2A and B). The abdominal aorta and left external iliac artery were fully exposed during mass exposure(Figure 2C). The right common iliac artery was further dissociated, and the left internal iliac artery was ligated. Resection was completed along with partial resection of the abdominal aorta and right common iliac artery and whole resection of the left common iliac artery. “Y-type” artificial vascular reconstruction was established among the abdominal aorta, right common iliac artery, and left external iliac artery (Figure 2D).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (v16.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL,United States) and GraphPad Prism software (v5, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA,United States). The mean and range were used for the analysis of variables.Differences between groups were analyzed using Student’s-test for comparing means.values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0)license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: htt p://creativecommons.org/License s/by-nc/4.0/
There were no perioperative deaths or infections of artificial vessels. One patient developed postoperative deep vein thrombosis in one leg after IVC transection during surgery, and no invasive treatment was performed. One patient developed external iliac artery occlusion 3 d after reconstruction. The condition improved after enhanced anticoagulant therapy. All the patients were discharged as scheduled. Pathology confirmed that there were eight cases of liposarcoma (LPS), two cases of leiomyosarcoma (LMS), two cases of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS), and three cases of other types of tumors (solitary fibroma, invasive fibroma, and myxofibrosarcoma) (Table 1).
The differences in intraoperative blood loss and transfusion volume were further analyzed. For patients who underwent unilateral or bilateral iliac artery reconstruction, no significant difference in blood loss was found (= 0.06) (Figure 3A).However, the volume of transfused blood was significantly higher for patients who received bilateral arterial reconstruction than for those who received unilateral arterialreconstruction (< 0.001) (Figure 3B). For patients with recurrence, the volume of blood loss and transfusion volume were significantly improved compared with primary cases (Figure 4A and B).
All 15 patients were followed routinely, and 11 of them remained alive at the last follow-up. The follow-up duration ranged from 4 mo to 6.4 years, with an average of 20.8 mo. Two patients relapsed during the follow-up (1 case of recurrent UPS and 1 case of recurrent LMS). Four patients died, including two patients with UPS, one with primary LMS, and one with recurrent LPS (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Retroperitoneal tumors, especially RPSs, frequently invade major vessels due to their unique anatomical location and growth characteristics[8]. The most commonly involved vessels are iliac vessels, followed by the abdominal aorta, IVC, and renal veins. The most common type of RPS requiring vascular reconstruction is LPS, particularly for multiple recurrent lesions. Retroperitoneal neoplasms involving major blood vessels are not a contraindication for surgical resection. Management of RPS is technically feasible with appropriate planning and requires interdisciplinary cooperation among surgeons in professional MDTs led by sarcoma surgeons,including specialists in general surgery, urology surgery, vascular surgery, and interventional therapy. Multiple imaging modalities, such as CT, CTA, MRI, or 3D imaging, are recommended when necessary to clarify the relationship between the tumor and adjacent vessels. Intraoperative arteriography can not only block the blood flow of the artery to be ligated but also further specify the blood supply of the tumor.Complete surgical resection of RPSs invading vital organs and major vessels requires intraoperative cooperation, especially between vascular and urological surgeons[9].
Single blind


Resection of major involved vessels such as the IVC or abdominal aorta is sometimes necessary for complete oncological clearance[11]. If the abdominal aorta below the level of the renal artery is involved, the tumor can be removed together with the abdominal aorta and iliac artery. Nephrectomy can be performed in the context of normal renal function of the other kidney. However, when the tumor involves the abdominal aorta above the renal artery level, complete resection is often difficult to achieve because of the affected celiac trunk or superior mesenteric artery. For the treatment of invaded veins, partial resection and angioplasty of the renal vein should be adopted as often as possible. If they are invaded, the common iliac vein and internal iliac vein can be resected, which will not cause severe postoperative lower limb edema due to the presence of an adequate collateral vessel network. In the case of iliac vessel involvement, the close proximity of the vein and artery often requires both venous and arterial resection to gain local control. Only three patients in our group underwent IVC partial resection or transection because most tumors were still arterially invasive. The IVC can be partially excised if it has been invaded or ligated directly if the invasion is below the renal vein. The need for IVC reconstruction should be assessed according to preoperative imaging, intraoperative findings, and the extent of surgery[12].


The most common intraoperative complication of resection of RPS involving iliac vessels is hemorrhage. Increased intraoperative bleeding is associated with a poor prognosis[2]. Herein, no statistically significant difference in blood loss was found between the unilateral and bilateral iliac arterial reconstruction groups. The volume of blood transfusion, however, was significantly higher for cases with bilateral arterial reconstruction than for those with unilateral arterial reconstruction. This result was mainly due to accurate preoperative evaluation of tumor arterial blood supply,individualized selection of surgical approach, and effective blood occlusion. Regarding bilateral artery reconstruction cases, patients with larger tumors were more often affected by severe anemia than those with smaller tumors, and occlusion of the abdominal aorta was more likely to cause unstable blood pressure than occlusion of other vessels, so a higher volume of intraoperative blood transfusion was needed.

Combined excision of the organs or structures involved requires a balance between the expected morbidity and the oncologic benefit. It is debatable whether excision should be extended to include uninvolved organs adjacent to the primary tumor.Challenging structures such as the pancreas or the spine, if clinically involved, may also be removed, but this practice increases morbidity and mortality[14]. If the tumor invades the iliac vessel and penetrates into pelvic muscle or even bone, an overly cautious resection may increase the clinical risk and probability of positive microscopic margins. In such circumstances, a second operation after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy is highly recommended[15].
2.試驗日糧。試驗日糧參照美國國家研究委員會(NRC,1994)標準,自配飼料公母豬飼料。日糧配方和營養水平見表1,表2。
Complete or "" compartmental resection of RPS with involvement of blood vessels may offer the only chance for cure for those patients who are eligible for surgery. However, for some highly malignant and recurrent RPSs, such as UPS and LMS, survival remains poor despite vascular reconstruction. In this group, four patients died, including one who suffered recurrence, one with primary UPS, and one with primary LMS (Table 2). Therefore, adjuvant therapies that include radiation and immunotherapy need to be explored to further improve patient survival.
臨別,兩人再次握手告別。伍亦苒的告別詞是這么說的,熱情地歡迎王總下來再來,我覺得王總是值得交往的朋友,因公,我欣賞你的干練果斷,因私,我喜歡你的幽默風趣,待人和善不乏童趣。還有,你骨子里那份淡淡的憂郁氣質,特別讓女人動心吶。
The difficulty of resecting recurrent RPS increases over time, especially for lesions involving major blood vessels and organs. Recurrent RPS is usually more aggressive and less differentiated than primary RPS, which results in a worse prognosis. Welldifferentiated liposarcoma (WDLPS) may undergo subtype transition and become dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS). It was found that 47.8% (11/23) of patients with initial WDLPS experienced pathological progression such that their recurrent tumors were of the DDLPS subtype[13]. Recurrent tumors adhere to blood vessels in a dense manner, and the original anatomical location is usually slightly different.Therefore, recurrent tumors are more likely to bleed during surgery than are primary tumors. Here, we found that the amount of bleeding and the transfusion volume were significantly increased for patients with recurrence.
However, there are some limitations to this retrospective clinical analysis. In largesample studies, arterial reconstruction was found to be accompanied by high postoperative morbidity, such as patency of arteries[16]. Due to the limited sample size, we only reported one patient with artificial vessel occlusion. Given the short mean follow-up time and limited sample size, it was impossible to calculate the overall survival or the local recurrence rate at 3 or 5 years; thus, future studies need to consider these clinical outcomes.
數形結合思想在數學學習與研究中的應用是十分廣泛的,如方程、不等式、函數等領域都經常使用。初中生數學思維不夠成熟,邏輯思維不夠全面,很多數學知識對其來講是生澀的,也是抽象的,而在教學中滲透數學思想,就可以使得生澀、抽象的數學知識變得直觀、具體,很大程度上降低數學知識的難度,所以初中數學教學實踐中運用數形結合思想有助于學生對數學知識的記憶。
CONCLUSION
Resection for RPS involving the iliac artery is safe, effective, and practical in a specialized MDT center that is highly experienced in this complex field of surgery.Despite the recurrence rate of RPS remaining high, resection combined with vascular reconstruction improves the R0 or R1 resection rate and results in encouraging survival for patients who were otherwise considered unresectable. Bleeding control and adequate blood transfusion affect patient recovery and surgical outcomes to a certain extent. Members from general surgery, vascular surgery, anesthesiology, blood transfusion, and intensive care teams should cooperate closely for the treatment of RPS.

The authors thank Ma LJ at the Department of General Surgery, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University for helping with image editing.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Mycoplasma hominis meningitis after operative neurosurgery: A case report and review of literature
- Recurrence of sigmoid colon cancer–derived anal metastasis: A case report and review of literature
- New method to remove tibial intramedullary nail through original suprapatellar incision: A case report
- Metastasis to the thyroid gland from primary breast cancer presenting as diffuse goiter: A case report and review of literature
- Gastric submucosal lesion caused by an embedded fish bone: A case report
- Epibulbar osseous choristoma: Two case reports
