基于優化MaxEnt模型的疣果匙薺在中國的適生區預測與分析
郭云霞 王亞鋒 付志璽 馬蓿
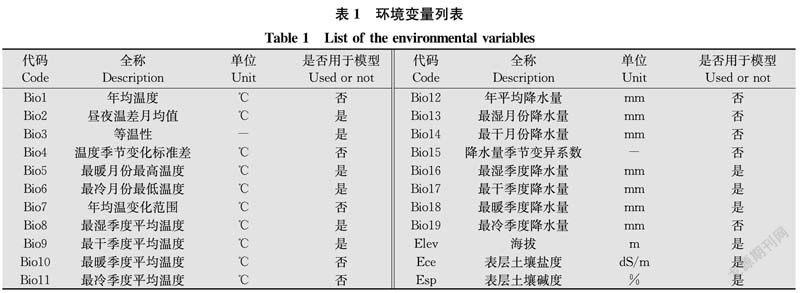
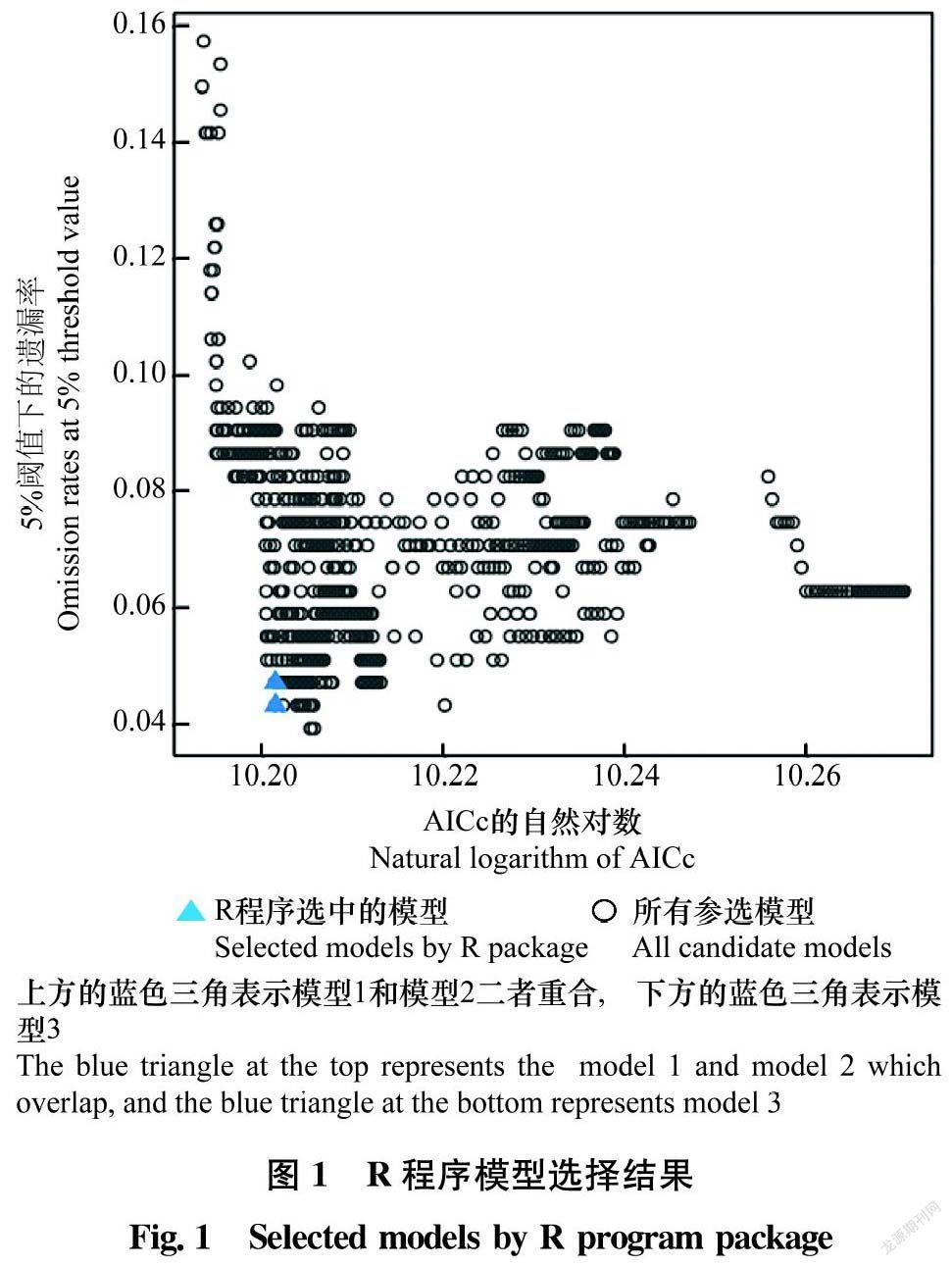
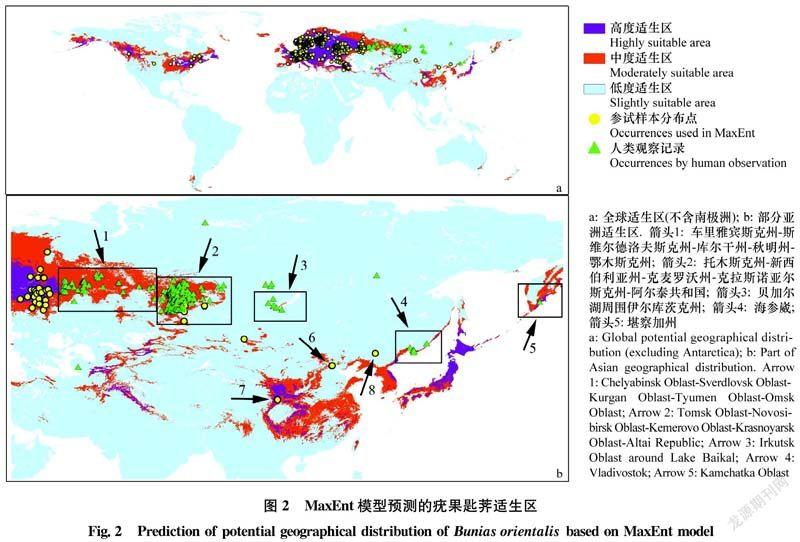
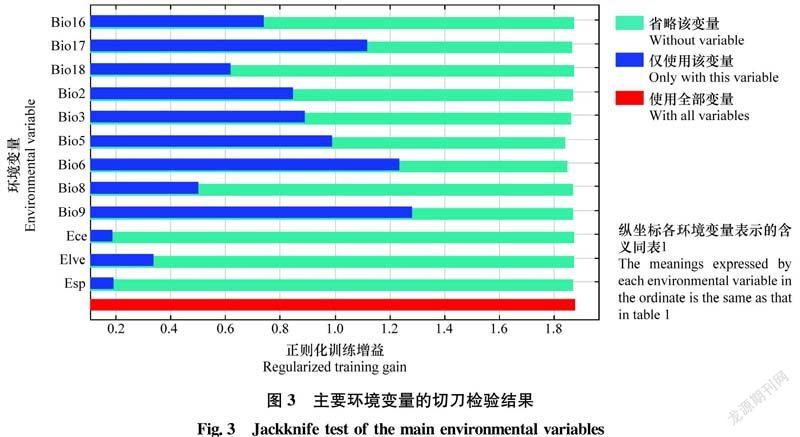
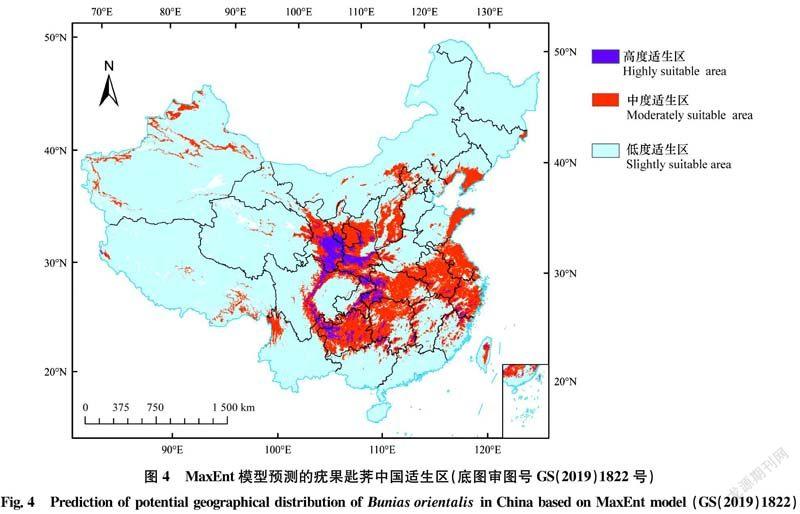
摘要 本文優化了疣果匙薺分布數據篩選方式和MaxEnt軟件參數設置,使用ENMTools剔除了冗余分布數據,調用R程序包Kuenm從1 240個不同參數組合的MaxEnt模型中篩選確定了最優參數。基于分布數據和參數優化的MaxEnt預測結果表明,疣果匙薺在中國的高度適生區和中度適生區分別占陸地總面積的9.4%和60.1%左右,溫度和降水量是影響疣果匙薺分布的主要非生物因素。疣果匙薺在中國的入侵風險主要集中在4個方面,一是隨植物引種傳入擴散,二是國內既有發生區的擴大,三是隨進口糧谷傳入擴散,四是沿邊境地區自然傳入。
關鍵詞 疣果匙薺; MaxEnt; 適生區; 參數優化
中圖分類號: Q948
文獻標識碼: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2021148
Abstract The selection method of distribution data of Bunias orientalis and the parameter setting of MaxEnt software were optimized in this study. The redundant distribution data were eliminated by ENMTools, and the optimal parameters were selected from MaxEnt model with 1 240 different parameter combinations by using the R program package Kuenm. The prediction results with MaxEnt showed that the highly and moderately suitable areas accounted for about 9.4% and 60.1% of the total land area in China, respectively. Temperature and precipitation were the main abiotic factors affecting the distribution of B.orientalis. The invasion risks of B.orientalis in China were mainly concentrated on four aspects: spread accompanying the introduction of plant, expansion of domestic existing areas, spread accompanying the introduction of imported grain, and natural spread along the border areas.
Key words Bunias orientalis; MaxEnt; potential geographical distribution; optimization of parameter setting
疣果匙薺Bunias orientalis L. 是列入我國《進境植物檢疫性有害生物名錄》的入侵性雜草,屬十字花科Brassicaceae,匙薺屬Bunias,起源于高加索南部地區并在過去250多年里迅速擴張,現已遍布中歐和斯堪的那維亞半島[1],歐洲東部和南部以及俄羅斯遠東和西伯利亞地區、亞洲的中亞和西亞、北美洲的美國和加拿大也有分布,我國目前僅在東北、甘肅和北京有零星發現[25]。該物種生態適應性極強,能產生大量種子形成龐大的土壤種子庫,可由小段殘根或刈割殘茬迅速再生,并可能借助化感作用抑制其他植物生長,產生有毒化學物質抵御植食性昆蟲取食,從而迅速形成單一茂密群落,與本土植物爭奪養分、陽光和傳粉昆蟲,對本地生態系統和生物多樣性構成嚴重威脅[68]。此外,疣果匙薺還充當了某些重要植物病毒的天然越冬寄主,促進了植物病毒在田間的保存和流行[9]。……

