浙貝母灰霉病病原真菌的分子鑒定
李吉二 溫思思 張羽加 金洛稼 趙偉春
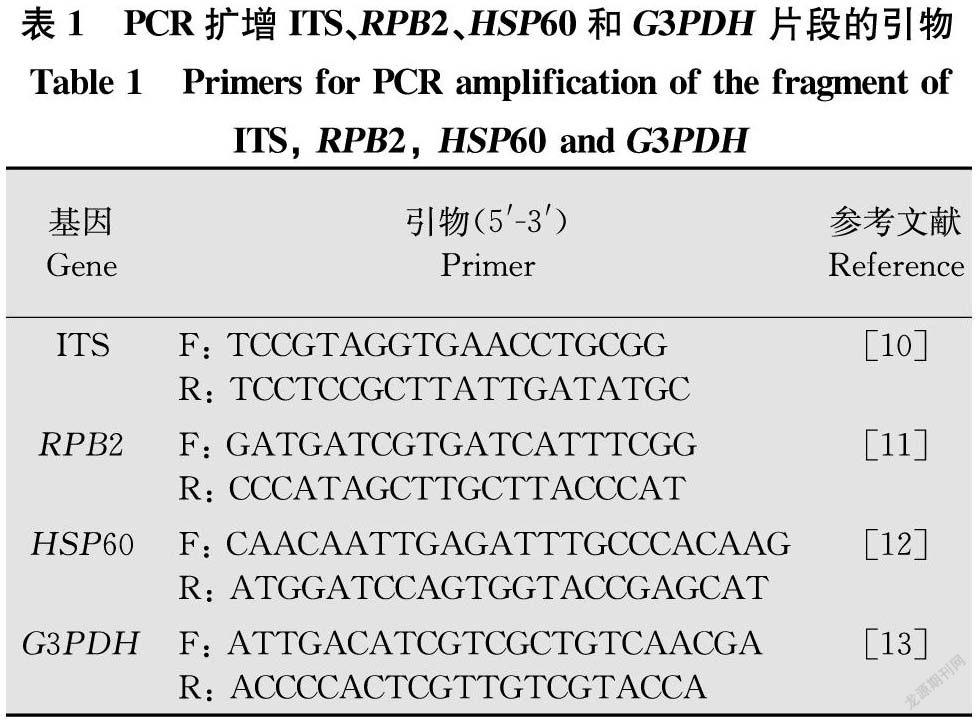
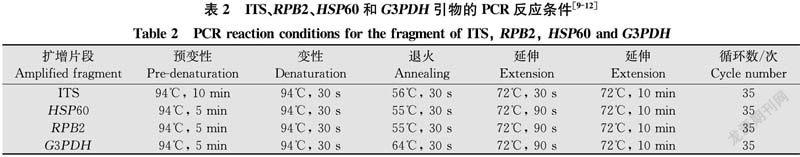

摘要 為了鑒定引起浙貝母Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. 灰霉病的病原真菌,于2015年-2019年收集浙貝母灰霉病樣品,采用常規組織分離法在PDA培養基上分離純化獲得10株葡萄孢屬Botrytis真菌。進一步以內轉錄間隔區(internal transcribed spacer,ITS)、RNA聚合酶亞基Ⅱ(the second largest subunit of the nuclear RNA polymerase enzyme Ⅱ,RPB2)、熱激蛋白60(heat shock protein 60,HSP60)和甘油醛-3-磷酸脫氫酶(glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase,G3PDH)為DNA條形碼,用特異性引物進行PCR擴增并測序,運用CodonCode Aligner拼接序列及BLAST分析,這10個菌株序列相同,為同一菌株,在GenBank中進行同源性比對,用MEGA 10.1構建系統發育樹,確定此菌株與灰葡萄孢Botrytis cinerea相應序列的一致性為100%。盆栽接種法檢測表明此菌株可引起浙貝母灰霉病。據此認為浙貝母灰霉病的病原真菌是灰葡萄孢而非普遍認為的橢圓葡萄孢Botrytis elliptica。
關鍵詞 浙貝母; 灰霉病; 病原真菌; 灰葡萄孢; 分子鑒定
中圖分類號: S435.672
文獻標識碼: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2021091
Abstract In order to identify the pathogenic fungi causing grey mold on Fritillaria thunbergii Miq., the disease samples were collected from 2015 to 2019, conventional tissue isolate method was used to isolate and purify the pathogen from samples on PDA medium and the ten isolates belonging to Botrytis were obtained. The specific sequence of ITS (internal transcribed spacer), RPB2 (the second largest subunit of the nuclear RNA polymerase enzymeⅡ), HSP60 (heat shock protein 60) and G3PDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) were used as DNA barcode. They were amplified by PCR and sequenced, respectively. The sequences were spliced using CodonCode Aligner software and then BLAST analysis was carried out. These ten isolates are same strain with same sequence. The sequences were aligned in GenBank, and the phylogenetic trees were constructed using MEGA 10.1 software. The results showed that this strain shared 100% identity with Botrytis cinerea. The pathogenicity test by in vivo pot inoculation revealed that this strain can cause gray mold disease on F.thunbergii. Therefore, the pathogenic fungus causing mold disease of F.thunbergii is B.cinerea rather than B.elliptica, which was generally believed.
Key words Fritillaria thunbergii; grey mold disease; pathogenic fungus; Botrytis cinerea; molecular identification
浙貝母Fritillaria thunbergii Miq.為百合科Liliaceae貝母屬Fritillaria多年生草本植物,著名的“浙八味”之一。目前在浙江、江西、湖南、江蘇和安徽大面積栽培,是當地農民收入的主要來源[1]。然而,隨著種植面積的不斷擴大,重茬和鱗莖營養繁殖,浙貝母病害發生日益突出,其中以灰霉病危害最重,高發年病株率達82%以上[23],2017年,2018年,2020年浙江省磐安縣浙貝母灰霉病普遍發生,部分田塊全田枯死,藥農普遍稱之為“難治之癥”,每年給種植戶造成10%~30%的損失[12,45]。
浙貝母灰霉病,也稱“早枯”“青塌腐”“眼圈病”。葉、莖、花、果實均能受害,以葉片的癥狀最為明顯,葉片染病,有時病斑上長出灰色霉狀物,殘留在田間的菌核、菌絲體和分子孢子是次年灰霉病發生的主要侵染來源[1, 3, 6]。……
